- 著者
- Ryo Nakabayashi Noriko Takeda-Kamiya Yutaka Yamada Tetsuya Mori Mai Uzaki Takashi Nirasawa Kiminori Toyooka Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.305-310, 2021-09-25 (Released:2021-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Plants release specialized (secondary) metabolites from their roots to communicate with other organisms, including soil microorganisms. The spatial behavior of such metabolites around these roots can help us understand roles for the communication; however, currently, they are unclear because soil-based studies are complex. Here, we established a multimodal metabolomics approach using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to spatially assign metabolites under laboratory conditions using agar. In a case study using Catharanthus roseus, we showed that 58 nitrogen (N)-containing metabolites are released from the roots into the agar. For the metabolite assignment, we used 15N-labeled and non-labeled LC-MS/MS data, previously reported. Four metabolite ions were identified using authentic standard compounds as derived from monoterpene indole alkaloids (MIAs) such as ajmalicine, catharanthine, serpentine, and yohimbine. An alkaloid network analysis using dot products and spinglass methods characterized five clusters to which the 58 ions belong. The analysis clustered ions from the indolic skeleton-type MIAs to a cluster, suggesting that other communities may represent distinct metabolite groups. For future chemical assignments of the serpentine community, key fragmentation patterns were characterized using the 15N-labeled and non-labeled MS/MS spectra.
- 著者
- Ryo Nakabayashi Noriko Takeda-Kamiya Yutaka Yamada Tetsuya Mori Mai Uzaki Takashi Nirasawa Kiminori Toyooka Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.21.0504a, (Released:2021-06-24)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Plants release specialized (secondary) metabolites from their roots to communicate with other organisms, including soil microorganisms. The spatial behavior of such metabolites around these roots can help us understand roles for the communication; however, currently, they are unclear because soil-based studies are complex. Here, we established a multimodal metabolomics approach using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to spatially assign metabolites under laboratory conditions using agar. In a case study using Catharanthus roseus, we showed that 58 nitrogen (N)-containing metabolites are released from the roots into the agar. For the metabolite assignment, we used 15N-labeled and non-labeled LC-MS/MS data, previously reported. Four metabolite ions were identified using authentic standard compounds as derived from monoterpene indole alkaloids (MIAs) such as ajmalicine, catharanthine, serpentine, and yohimbine. An alkaloid network analysis using dot products and spinglass methods characterized five clusters to which the 58 ions belong. The analysis clustered ions from the indolic skeleton-type MIAs to a cluster, suggesting that other communities may represent distinct metabolite groups. For future chemical assignments of the serpentine community, key fragmentation patterns were characterized using the 15N-labeled and non-labeled MS/MS spectra.
- 著者
- Jichen Wang Hideyuki Suzuki Nanako Nakashima Mariko Kitajima Hiromitsu Takayama Kazuki Saito Mami Yamazaki Naoko Yoshimoto
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.281-289, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 26
Marasmin [S-(methylthiomethyl)-L-cysteine-4-oxide] is a pharmaceutically valuable sulfur-containing compound produced by the traditional medicinal plant, Tulbaghia violacea. Here, we report the identification of an S-oxygenase, TvMAS1, that produces marasmin from its corresponding sulfide, S-(methylthiomethyl)-L-cysteine. The amino acid sequence of TvMAS1 showed high sequence similarity to known flavin-containing S-oxygenating monooxygenases in plants. Recombinant TvMAS1 catalyzed regiospecific S-oxygenation at S4 of S-(methylthiomethyl)-L-cysteine to yield marasmin, with an apparent Km value of 0.55 mM. TvMAS1 mRNA accumulated with S-(methylthiomethyl)-L-cysteine and marasmin in various organs of T. violacea. Our findings suggest that TvMAS1 catalyzes the S-oxygenation reaction during the last step of marasmin biosynthesis in T. violacea.
4 0 0 0 OA Beyond NERICA:
- 著者
- Kazuki SAITO Yoshimichi FUKUTA Seiji YANAGIHARA Kokou AHOUANTON Yoshimi SOKEI
- 出版者
- 日本熱帯農業学会
- 雑誌
- Tropical Agriculture and Development (ISSN:18828450)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.2, pp.51-57, 2014 (Released:2014-09-11)
- 参考文献数
- 29
Four rainfed upland experiments were conducted in Benin to assess yield differences in 65 rice varieties, including the interspecific hybrids: the upland New Rice for Africa (NERICA) varieties developed from crossing Oryza sativa L. and O. glaberrima Steud.. The mean grain yields ranged from 32 to 350 g/m2 across experiments. The genotype × environment (G×E) interaction accounted for 15% of the total sum of squares, with environment and genotype responsible for 74 and 12%, respectively. Upland indica B6144F-MR-6-0-0 performed well in three out of four environments, showing consistently higher yields than other upland NERICA varieties and their parents. Upland indica Aus257 was stable across environments with good adaption to poor soil fertility. None of the upland NERICA varieties showed consistently higher yields than their parents across the four environments. The group of long-duration varieties (e.g. IR 8, IR 24, Taichung Native1) performed well only in most-favorable environments. The high-yielding varieties B6144F-MR-6-0-0 and Aus257 were intermediate in panicle number (160–180 panicles/m2 on average). This was the only common characteristic among the highest yielding varieties. These results suggest that further increases in rice yields in the rainfed uplands of West Africa are most likely to occur through using upland indica varieties as donors.
- 著者
- Ryo Nakabayashi Kei Hashimoto Tetsuya Mori Kiminori Toyooka Hiroshi Sudo Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.311-315, 2021-09-25 (Released:2021-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Spatial metabolomics uses imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) to localize metabolites within tissue section. Here, we performed matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance-IMS (MALDI-FTICR-IMS) to identify the localization of asparaptine A, a naturally occurring inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme, in green spears of asparagus (Asparagus officinalis). Spatial metabolome data were acquired in an untargeted manner. Segmentation analysis using the data characterized tissue-type-dependent and independent distribution patterns in cross-sections of asparagus spears. Moreover, asparaptine A accumulated at high levels in developing lateral shoot tissues. Quantification of asparaptine A in lateral shoots using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) validated the IMS analysis. These results provide valuable information for understanding the function of asparaptine A in asparagus, and identify the lateral shoot as a potential region of interest for multiomics studies to examine gene-to-metabolite associations in the asparaptine A biosynthesis.
3 0 0 0 OA MassBase: A large-scaled depository of mass spectrometry datasets for metabolome analysis
- 著者
- Takeshi Ara Nozomu Sakurai Hideyuki Suzuki Koh Aoki Kazuki Saito Daisuke Shibata
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.1, pp.167-171, 2021-03-25 (Released:2021-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Depository of low-molecular-weight compounds or metabolites detected in various organisms in a non-targeted manner is indispensable for metabolomics research. Due to the diverse chemical compounds, various mass spectrometry (MS) setups with state-of-the-art technologies have been used. Over the past two decades, we have analyzed various biological samples by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, or capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry, and archived the datasets in the depository MassBase (http://webs2.kazusa.or.jp/massbase/). As the format of MS datasets depends on the MS setup used, we converted each raw binary dataset of the mass chromatogram to text file format, and thereafter, information of the chromatograph peak was extracted in the text file from the converted file. In total, the depository comprises 46,493 datasets, of which 38,750 belong to the plant species and 7,743 are authentic or mixed chemicals as well as other sources (microorganisms, animals, and foods), as on August 1, 2020. All files in the depository can be downloaded in bulk from the website. Mass chromatograms of 90 plant species obtained by LC-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance MS or Orbitrap MS, which detect the ionized molecules with high accuracy allowing speculation of chemical compositions, were converted to text files by the software PowerGet, and the chemical annotation of each peak was added. The processed datasets were deposited in the annotation database KomicMarket2 (http://webs2.kazusa.or.jp/km2/). The archives provide fundamental resources for comparative metabolomics and functional genomics, which may result in deeper understanding of living organisms.
- 著者
- Somnuk Bunsupa Kana Komastsu Ryo Nakabayashi Kazuki Saito Mami Yamazaki
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.5, pp.511-518, 2014-12-25 (Released:2015-02-27)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 8 16
Anabasine is an alkaloid found in a small number of Nicotiana species. The components of the anabasine biosynthetic pathway have yet to be identified. Here, we report the reinvestigation of biosynthetic pathways of anabasine and related tobacco alkaloids in genetically engineered cells. Hairy roots of N. tabacum harboring a lysine/ornithine decarboxylase gene from Lupinus angustifolius (La-L/ODC) were fed with labeled [ε-15N]- or [α-15N]-L-lysine. Relative to the unfed control, feeding of labeled 15N-L-lysine greatly enhanced anabasine levels 13.5-fold in La-L/ODC-expressing line compared to 5.3-fold in the control line, suggesting that both LDC activity and substrate supplied are important factors for the efficient production of anabasine. GUS-expressing line showed preferential incorporation of [ε-15N]-L-lysine into anabasine, indicating the main biosynthetic pathway of Δ1-piperideine intermediate in tobacco is asymmetrically processes. In contrast, the expression of La-L/ODC showed the symmetric labeling of 15N atom into anabasine, implying the occurrence of free cadaverine, which is produced by La-L/ODC enzyme, during the biosynthesis of Δ1-piperideine intermediate. No considerable incorporation of 15N into other tobacco alkaloids such as, nicotine, anatabine, and anatalline, was detected. Detailed analysis using ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry indicated that two 15N atoms were incorporated into anabasine in La-L/ODC-expressing lines after feeding [ε-15N]- or [α-15N]-L-lysine. Our results not only provide information insight into the biosynthesis of anabasine but also suggest an alternative route for the production of anabasine by genetic engineering.
- 著者
- Shuhei Yasumoto Satoru Sawai Hyoung Jae Lee Masaharu Mizutani Kazuki Saito Naoyuki Umemoto Toshiya Muranaka
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.2, pp.205-211, 2020-06-25 (Released:2020-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 22
Genome editing using site-specific nucleases, such as transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat–CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR-Cas9), is a powerful technology for crop breeding. For plant genome editing, the genome-editing reagents are usually expressed in plant cells from stably integrated transgenes within the genome. This requires crossing processes to remove foreign nucleotides from the genome to generate null segregants. However, in highly heterozygous plants such as potato, the progeny lines have different agronomic traits from the parent cultivar and do not necessarily become elite lines. Agrobacteria can transfer exogenous genes on T-DNA into plant cells. This has been used both to transform plants stably and to express the genes transiently in plant cells. Here, we infected potato, with Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring TALEN-expression vector targeting sterol side chain reductase 2 (SSR2) gene and regenerated shoots without selection. We obtained regenerated lines with disrupted-SSR2 gene and without transgene of the TALEN gene, revealing that their disruption should be caused by transient gene expression. The strategy using transient gene expression by Agrobacterium that we call Agrobacterial mutagenesis, developed here should accelerate the use of genome-editing technology to modify heterozygous plant genomes.
- 著者
- Tsubasa Shoji Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.1113a, (Released:2023-01-23)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A group of anti-nutritional specialized metabolites called steroidal glycoalkaloids (SGAs) are produced in Solanum species such as tomato, potato, and eggplant. The transcription factor JASMONATE-RESPONSIVE ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 4 (JRE4) regulates many SGA biosynthesis genes in tomato and potato. Here we report that the expression of a cluster of genes encoding nitrate transporter 1/peptide transporter family (NPF) members is downregulated in the jre4-1 loss-of-function tomato mutant, which has a low-SGA phenotype compared to the wild type. NPFs are a large family of plant membrane transporters that transport a wide range of substrates, including specialized metabolites. We found that the JRE4-regulated NPF genes are induced by the defense-related phytohormone jasmonate. Conversely, jasmonate-mediated induction of gene expression was attenuated by ethylene treatment of the leaves. The co-regulation of the NPF genes with SGA biosynthesis genes by JRE4 suggests that NPF transporters are involved in the SGA pathway.
- 著者
- Ryo Nakabayashi Tomoko Nishizawa Tetsuya Mori Hiroshi Sudo Isao Fujii Takashi Asano Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.4, pp.265-267, 2019-12-25 (Released:2019-12-27)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 8
Asparaptine, a conjugate of L-arginine and asparagusic acid, was found in green asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) using ultrahigh-resolution metabolomics for sulfur-containing metabolites (S-metabolites), called S-omics. Asparaptine has been shown to inhibit the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Larger amounts of this S-metabolite are therefore required for further analysis; however, there are limitations that asparagus is a perennial plant and its spears, wherein asparaptine accumulates, can be mainly harvested at the spring to summer season. In order to overcome these, we prepared a callus and suspension cell line from green asparagus. Untargeted metabolome analysis using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was performed in the materials as well as spears and three calluses derived from wild type Asparagus. The analysis demonstrated that the amount of asparaptine in the callus derived from the green asparagus was more than the others per mg dry weight. The suspension cell line treated with methyljasmonate showed the induction of asparaptine, suggesting that the asparaptine production is modifiable under appropriate culture conditions. The described materials can be utilized for the production of asparaptine and in integrated metabolomics to study the biosynthesis of this S-metabolite, which is currently unknown.
2 0 0 0 OA [研究報告] イタリア中部地震における心理社会的支援
- 著者
- 齋藤 和樹 前田 潤 Kazuki Saito Jun Maeda 日本赤十字秋田看護大学看護学部 室蘭工業大学工学研究科ひと文化領域
- 雑誌
- 日本赤十字秋田看護大学・日本赤十字秋田短期大学紀要 = Journal of the Japanese Red Cross Akita College of Nursing and the Japanese Red Cross Junior College of Akita (ISSN:21868263)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.14, pp.29-34, 2010-03-31
2009年4月6日早朝に発生したイタリア中部地震後のイタリア赤十字社(IRCS)およびラクイラ大学で行っている心理社会的支援について、現地視察調査を行った。IRCSでは、国際赤十字赤新月社連盟(IFRC)の心理社会的支援プログラムとは別の独自の心理社会的ケアを行っていた。それらのいくつかは、「ユーモア」に基づいたものであり、「ドクトル・クラウン」という存在もあった。IRCSの心理社会的支援は、災害の生存者に対してのみならず、救援者に対しても行われていた。IFRCには、心理社会的支援のための十分な資器材がそろっていた。ラクイラ大学が行っていたサバイバーの精神的健康に関する調査には、グローバルスタンダードになっているGHQやIES-Rなどが含まれていた。
- 著者
- Zhigang Yang Ryo Nakabayashi Tetsuya Mori Satoshi Takamatsu Susumu Kitanaka Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.7, pp.952-956, 2016-07-01 (Released:2016-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 18
Oryza sativa L. (rice) is an important staple crop across the world. In the previous study, we identified 36 specialized (secondary) metabolites including 28 flavonoids. In the present study, a metabolome analysis using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was conducted on the leaf, bran, and brown and polished rice grains to better understand the distribution of these metabolites. Principal component analysis using the metabolome data clearly characterized the accumulation patterns of the metabolites. Flavonoids, e.g., tricin, tricin 7-O-rutinoside, and tricin 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, were mainly present in the leaf and bran but not in the polished grain. In addition, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activity of the metabolites were assayed in vitro. Tricin 4′-O-(erythro-β-guaiacylglyceryl)ether and isoscoparin 2″-O-(6‴-(E)-feruloyl)-glucopyranoside showed the strongest activity for inhibiting nitric oxide (NO) production and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging, respectively.
- 著者
- Naoyuki Umemoto Shuhei Yasumoto Muneo Yamazaki Kenji Asano Kotaro Akai Hyoung Jae Lee Ryota Akiyama Masaharu Mizutani Yozo Nagira Kazuki Saito Toshiya Muranaka
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.3, pp.211-218, 2023-09-25 (Released:2023-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Genome editing is highly useful for crop improvement. The method of expressing genome-editing enzymes using a transient expression system in Agrobacterium, called agrobacterial mutagenesis, is a shortcut used in genome-editing technology to improve elite varieties of vegetatively propagated crops, including potato. However, with this method, edited individuals cannot be selected. The transient expression of regeneration-promoting genes can result in shoot regeneration from plantlets, while the constitutive expression of most regeneration-promoting genes does not result in normally regenerated shoots. Here, we report that we could obtain genome-edited potatoes by positive selection. These regenerated shoots were obtained via a method that combined a regeneration-promoting gene with the transient expression of a genome-editing enzyme gene. Moreover, we confirmed that the genome-edited potatoes obtained using this method did not contain the sequence of the binary vector used in Agrobacterium. Our data have been submitted to the Japanese regulatory authority, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), and we are in the process of conducting field tests for further research on these potatoes. Our work presents a powerful method for regarding regeneration and acquisition of genome-edited crops through transient expression of regeneration-promoting gene.
- 著者
- Tsubasa Shoji Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.421-425, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 1
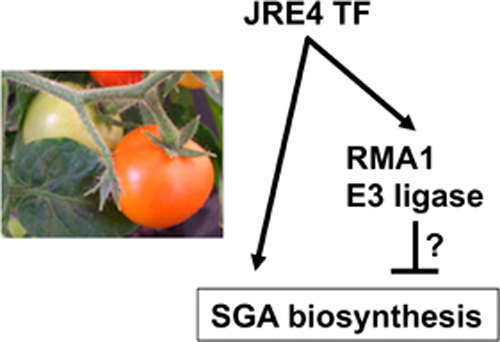
RING membrane-anchor (RMA) E3 ubiquitin ligases are involved in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated protein degradation, which mediates the regulated destruction of ER-resident enzymes in various organisms. We determined that the transcription factor JASMONATE-RESPONSIVE ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 4 (JRE4) co-regulates the expression of the RMA-type ligase gene SlRMA1, but not its homolog SlRMA2, with steroidal glycoalkaloid biosynthesis genes in tomato, perhaps to prevent the overaccumulation of these metabolites.
1 0 0 0 OA MassBase: A large-scaled depository of mass spectrometry datasets for metabolome analysis
- 著者
- Takeshi Ara Nozomu Sakurai Hideyuki Suzuki Koh Aoki Kazuki Saito Daisuke Shibata
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.20.0911a, (Released:2021-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Depository of low-molecular-weight compounds or metabolites detected in various organisms in a non-targeted manner is indispensable for metabolomics research. Due to the diverse chemical compounds, various mass spectrometry (MS) setups with state-of-the-art technologies have been used. Over the past two decades, we have analyzed various biological samples by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, or capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry, and archived the datasets in the depository MassBase (http://webs2.kazusa.or.jp/massbase/). As the format of MS datasets depends on the MS setup used, we converted each raw binary dataset of the mass chromatogram to text file format, and thereafter, information of the chromatograph peak was extracted in the text file from the converted file. In total, the depository comprises 46,493 datasets, of which 38,750 belong to the plant species and 7,743 are authentic or mixed chemicals as well as other sources (microorganisms, animals, and foods), as on August 1, 2020. All files in the depository can be downloaded in bulk from the website. Mass chromatograms of 90 plant species obtained by LC-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance MS or Orbitrap MS, which detect the ionized molecules with high accuracy allowing speculation of chemical compositions, were converted to text files by the software PowerGet, and the chemical annotation of each peak was added. The processed datasets were deposited in the annotation database KomicMarket2 (http://webs2.kazusa.or.jp/km2/). The archives provide fundamental resources for comparative metabolomics and functional genomics, which may result in deeper understanding of living organisms.
- 著者
- Ryo Nakabayashi Tomoko Nishizawa Tetsuya Mori Hiroshi Sudo Isao Fujii Takashi Asano Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Cell and Molecular Biology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19.1002a, (Released:2019-12-18)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 8
Asparaptine, a conjugate of L-arginine and asparagusic acid, was found in green asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) using ultrahigh-resolution metabolomics for sulfur-containing metabolites (S-metabolites), called S-omics. Asparaptine has been shown to inhibit the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Larger amounts of this S-metabolite are therefore required for further analysis; however, there are limitations that asparagus is a perennial plant and its spears, wherein asparaptine accumulates, can be mainly harvested at the spring to summer season. In order to overcome these, we prepared a callus and suspension cell line from green asparagus. Untargeted metabolome analysis using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was performed in the materials as well as spears and three calluses derived from wild type Asparagus. The analysis demonstrated that the amount of asparaptine in the callus derived from the green asparagus was more than the others per mg dry weight. The suspension cell line treated with methyljasmonate showed the induction of asparaptine, suggesting that the asparaptine production is modifiable under appropriate culture conditions. The described materials can be utilized for the production of asparaptine and in integrated metabolomics to study the biosynthesis of this S-metabolite, which is currently unknown.
1 0 0 0 IR 赤十字国際救援派遣要員のストレス要因分析
- 著者
- 齋藤 和樹 前田 潤 丸山 真理子 Kazuki SAITO Jun MAEDA Mariko MARUYAMA 看護学科(臨床心理学) 室蘭工業大学共通講座(災害心理学) 秋田赤十字病院心療センター
- 出版者
- 日本赤十字秋田短期大学紀要編集委員会
- 雑誌
- 日本赤十字秋田短期大学紀要 = Bulletin of the Japanese Red Cross Junior College of Akita (ISSN:13430033)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.10, pp.23-32, 2006-03-15
- 被引用文献数
- 1
日本赤十字社から海外に派遣された救援要員のストレス要因を50人のアンケート結果から分析した。アンケートでは、時系列に沿って「I.海外派遣が決まってから出発するまで」、「II.現地に到着直後」、「III.現地で活動中」、「IV.帰国が決まって帰国するまで」、「V.帰国後仕事に復帰して」の5つの時期に、「1.どのようなストレスを感じたか」、「2.それらにどのように対処したか」、「3.その対処はどの程度有効であったか」、「4.感じているストレスに対して所属する機関や周囲の人にどのように対応してもらいたかったか」を聞いた。各時期にさまざまなストレスがあり、対処法もさまざまであったが、いくつかの時期に共通して見られるストレス要因も見いだせた。それらは「情報不足」、「コミュニケーション・言語の問題」である。これらを解決することは、派遣要員のストレスの軽減になるだろう。また、対処法の効果の10段階評価を見ると、「V.帰国後仕事に復帰して」が他の時期に比して低かった。帰国後の職場での派遣員への理解と配慮の必要性も伺われた。Stress factors of 50 delegates who were sent abroad from the Japanese Red Cross Society were analyzed. A special questionnaire was created to analyze stress factors at 5 situation points throughout the time line, which included" I. Pre-departure", "II. Initial arrival in the field", "III. During the mission", "IV. Mission completion, before returning to Japan.", and "V. After returning to Japan and the workplace." There were 4 questions for each situation included; "1. What kind of stress did you experience?", "2. How did you cope with the stress?", "3. How effective was your coping strategy?", "4. What did you want your workplace to do to assist you in coping?". Various kinds of stress factors in each situation and various coping styles are found. "Lack of information" and "communication and language problems", however, were common stress factors throughout all the situations. Solving these problems is expected to reduce their stress levels. In addition, the mean score of question 3 (coping effectiveness) in Situation V (after returning) showed lower scores than the other situations. The necessity for understanding and care given to the delegates after they come back to Japan was suggested.
- 著者
- Mouritala Sikirou Kazuki Saito Enoch G. Achigan-Dako Khady Nani Dramé Adam Ahanchédé Ramaiah Venuprasad
- 出版者
- 日本作物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Production Science (ISSN:1343943X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.4, pp.423-434, 2015 (Released:2015-09-19)
- 参考文献数
- 89
- 被引用文献数
- 39
In sub-Saharan Africa, the demand for higher rice production continues to grow rapidly. Although there is a huge potential for increasing rice production through expansion of the rice cultivation area in wetlands, iron (Fe) toxicity tends to occur and consequently results in low rice yield. Development and deployment of varieties tolerant to Fe toxicity is one of the practical options to overcome this constraint. Several tolerant varieties have been developed through conventional breeding but progress in breeding has been generally slow mainly due to large genotype × environment interaction and field heterogeneity, which make rice selection ineffective. In addition, there are no valid managed-stress screening protocols which are highly efficient and that can predict rice performance in the diverse target environments of West Africa. Many O. glaberrima accessions have superior tolerance, but only a few of them have been utilized in breeding programs. The known quantitative trait loci (QTLs) related to Fe toxicity, have not been used for marker-assisted selection (MAS), as they gave small effects with a large confidence interval. Accelerating rice breeding efficiency for tolerance to Fe toxicity requires establishment of reliable screening protocols, use of O. glaberrima accessions as donors, identification of large-effect QTLs and MAS using such QTLs. This paper reviews the past and current efforts in West Africa to develop new varieties with superior tolerance to Fe toxicity.
- 著者
- Koichi Futakuchi Moussa Sié Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- 日本作物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Production Science (ISSN:1343943X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, no.3, pp.151-163, 2012 (Released:2012-06-29)
- 参考文献数
- 80
- 被引用文献数
- 23 3
Oryza glaberrima has mostly been used as a source to improve stress resistance of Oryza sativa. Improvement of this species could be an approach to use its adaptability to local environments in Africa such as multiple resistance to several indigenous constraints. The yield of O. glaberrima was inferior to that of O. sativa under favorable growth conditions but not under unfavorable conditions. Moreover, spikelet number before grain shattering was no less in O. glaberrima than in O. sativa at any fertilizer input levels, suggesting that the yield potential of O. glaberrima is as high as that of O. sativa. Inferior yield of O. glaberrima reported in favorable environments could result from grain shattering enhanced by such growth environments where higher incidence of lodging, which is another undesirable character of O. glaberrima, can occur. Regarding characteristics associated to yield generation, O. glaberrima seemed to possess: higher dry matter production and greater leaf area than O. sativa at least until heading; a lower photosynthetic rate per leaf area but a higher rate against the same leaf nitrogen content in a low content range; higher responsiveness of dry matter, leaf area and leaf photosynthesis to increases in nitrogen inputs; lower water-use efficiency on dry matter accumulation and gas exchange bases; faster progress of leaf senescence during maturity; and faster completion of grain filling during maturity than O. sativa.