- 著者
- Linda M. Robles Laura H. Reichenberg James H. Grissom Ⅲ Richard J. Chi Kenneth J. Piller
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.0926a, (Released:2022-12-16)
- 参考文献数
- 49
It is estimated that multiple sclerosis (MS) affects over 2.8 million people worldwide, with a prevalence that is expected to continue growing over time. Unfortunately, there is no cure for this autoimmune disease. For several decades, antigen-specific treatments have been used in animal models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) to demonstrate their potential for suppressing autoimmune responses. Successes with preventing and limiting ongoing MS disease have been documented using a wide variety of myelin proteins, peptides, autoantigen-conjugates, and mimics when administered by various routes. While those successes were not translatable in the clinic, we have learned a great deal about the roadblocks and hurdles that must be addressed if such therapies are to be useful. Reovirus sigma1 protein (pσ1) is an attachment protein that allows the virus to target M cells with high affinity. Previous studies showed that autoantigens tethered to pσ1 delivered potent tolerogenic signals and diminished autoimmunity following therapeutic intervention. In this proof-of-concept study, we expressed a model multi-epitope autoantigen (human myelin basic protein, MBP) fused to pσ1 in soybean seeds. The expression of chimeric MBP-pσ1 was stable over multiple generations and formed the necessary multimeric structures required for binding to target cells. When administered to SJL mice prophylactically as an oral therapeutic, soymilk formulations containing MBP-pσ1 delayed the onset of clinical EAE and significantly reduced developing disease. These results demonstrate the practicality of soybean as a host for producing and formulating immune-modulating therapies to treat autoimmune diseases.
- 著者
- Natsu Takayanagi Mai Mukai Munetaka Sugiyama Misato Ohtani
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.329-333, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 18
During organ regeneration, differentiated cells acquire cell proliferation competence before the re-start of cell division. In Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), CDKA;1, a cyclin-dependent kinase, RID1, a DEAH-box RNA helicase, and SRD2, a small nuclear RNA transcription factor, are implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation competence. Here, we report phytohormonal transcriptional regulation of these cell proliferation competence-associated genes during callus initiation. We can induce the callus initiation from Arabidopsis hypocotyl explants by the culture on the auxin-containing medium. By RT-quantitative PCR analysis, we observed higher mRNA accumulation of CDKA;1, RID1, and SRD2 in culture on the auxin-containing medium than in culture on the auxin-free medium. Promoter-reporter analysis showed that the CDKA;1, RID1, and SRD2 expression was induced in the stele regions containing pericycle cells, where cell division would be resumed to make callus, by the culture in the medium containing auxin and/or cytokinin. However, the expression levels of these genes in cortical and epidermal cells, which would not originate callus cells, were variable by genes and phytohormonal conditions. We also found that the rid1-1 mutation greatly decreased the expression levels of CDKA;1 and SRD2 during callus initiation specifically at 28°C (restrictive temperature), while the srd2-1 mutation did not obviously decrease the expression levels of CDKA;1 and RID1 regardless of temperature conditions but rather even increased them at 22°C (permissive temperature). Together, our results implicated the phytohormonal and differential regulation of cell proliferation competence-associated genes in the multistep regulation of cell proliferation competence.
- 著者
- Takashi Nobusawa Hiroshi Yamatani Makoto Kusaba
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.317-321, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Controlling the flowering time is crucial for propagating plant species and crop production. ALTERED MERISTEM PROGRAM1 (AMP1) in Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a putative carboxypeptidase, and an AMP1 mutant (amp1) was found to cause highly pleiotropic phenotypes including a short plastochron, an enlarged shoot apical meristem, and reduced apical dominance. Although amp1 also shows an early flowering phenotype, its mechanism has not been investigated in detail. The most important floral integrator or florigen gene, FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), has a close relative, TWIN SISTER OF FT (TSF). In this report, we generated a new allele of tsf using a genome-editing technique and produced ft tsf double and amp1 ft tsf triple mutants. The flowering time of amp1 ft tsf was equally as late as ft tsf under long-day conditions. In addition, the expression level of FT in amp1 was 2.4-fold higher than that in wild-type, even five days after germination under long-day conditions. These results suggest that the elevated expression level of FT is responsible for the early flowering phenotype of amp1. Furthermore, expression of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), a negative regulator of FT expression, is severely repressed in amp1, raising the possibility that low expression levels of FLC contributes to upregulation of FT expression and the early flowering phenotype of amp1.
- 著者
- Sho Takeda Taisuke Togawa Kei-ichiro Mishiba Katsuyuki T. Yamato Yuji Iwata Nozomu Koizumi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.303-310, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 2
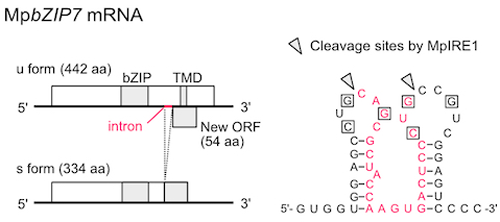
The unfolded protein response (UPR) or the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response is a homeostatic cellular response conserved in eukaryotes to alleviate the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER. In the present study, we characterized the UPR in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha to obtain insights into the conservation and divergence of the UPR in the land plants. We demonstrate that the most conserved UPR transducer in eukaryotes, IRE1, is conserved in M. polymorpha, which harbors a single gene encoding IRE1. We showed that MpIRE1 mediates cytoplasmic splicing of mRNA encoding MpbZIP7, a M. polymorpha homolog of bZIP60 in flowering plants, and upregulation of ER chaperone genes in response to the ER stress inducer tunicamycin. We further showed that MpIRE1 also mediates downregulation of genes encoding secretory and membrane proteins in response to ER stress, indicating the conservation of regulated IRE1-dependent decay of mRNA. Consistent with their roles in the UPR, Mpire1ge and Mpbzip7ge mutants exhibited higher sensitivity to ER stress. Furthermore, an Mpire1ge mutant also exhibited retarded growth even without ER stress inducers, indicating the importance of MpIRE1 for vegetative growth in addition to alleviation of ER stress. The present study provides insights into the evolution of the UPR in land plants.
- 著者
- Edjohn Aaron Macauyag Hiroyuki Kajiura Takao Ohashi Ryo Misaki Kazuhito Fujiyama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.291-301, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 56
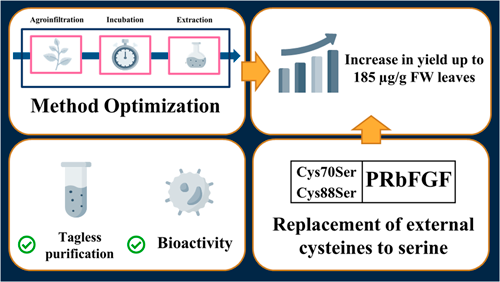
The human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is a protein that plays a pivotal role in cellular processes like cell proliferation and development. As a result, it has become an important component in cell culture systems, with applications in biomedical engineering, cosmetics, and research. Alternative production techniques, such as transient production in plants, are becoming a feasible option as the demand continues to grow. High-level bFGF production was achieved in this study employing an optimized Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression system, which yielded about a 3-fold increase in production over a conventional system. This yield was further doubled at about 185 µg g−1 FW using a mutant protease-resistant version that degraded/aggregated at a three-fold slower rate in leaf crude extracts. To achieve a pure product, a two-step purification technique was applied. The capacity of the pure protease-resistant bFGF (PRbFGF) to stimulate cell proliferation was tested and was found to be comparable to that of E. coli-produced bFGF in HepG2 and CHO-K1 cells. Overall, this study demonstrates a high-level transient production system of functional PRbFGF in N. benthamiana leaves as well as an efficient tag-less purification technique of leaf crude extracts.
- 著者
- Yoshiki Tanahara Kaho Yamanaka Kentaro Kawai Yukiko Ando Takashi Nakatsuka
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.273-280, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
Matthiola incana is an important floricultural plant that blooms from winter to spring, and had been desired to be established a transformation system. This study successfully obtained stable transgenic plants from M. incana. We used Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring a binary vector containing the β-glucuronidase gene (GUS) under the control of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter to evaluate the transformation frequency of M. incana. We observed that cocultivation with the A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 for 5 days effectively enhanced the infection frequency, assessed through a transient GUS expression area in the seedling. Furthermore, the addition of 100 µM acetosyringone was necessary for Agrobacterium infection. However, we could not obtain transgenic plants on a shoot formation medium supplemented with 1 mg l−1 6-benzyladenine (BA). For callus formation from the leaf sections, a medium supplemented with 1–50 µM fipexide (FPX), a novel callus induction chemical, was employed. Then, the callus formation was observed after 2 weeks, and an earlier response was detected than that in the BA medium (4–6 weeks). Results also showed that cultivation in a selection medium supplemented with 12.5 µM FPX obtained hygromycin-resistant calli. Thus, this protocol achieved a 0.7% transformation frequency. Similarly, progenies from one transgenic line were observed on the basis of GUS stains on their leaves, revealing that the transgenes were also inherited stably. Hence, FPX is considered a breakthrough for establishing the transformation protocol of M. incana, and its use is proposed in recalcitrant plants.
- 著者
- Shilian Huang Yanchun Qiao Xinmin Lv Jianguang Li Dongmei Han Dongliang Guo
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.259-272, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 61
Potassium chlorate can promote off-season flowering in longan, but the molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, four-year-old ‘Shixia’ longan trees were injected in the trunk with potassium chlorate, and terminal buds were sampled and analyzed using transcriptomics and bioinformatics tools. To generate a reference longan transcriptome, we obtained 207,734 paired-end reads covering a total of 58,514,149 bp, which we assembled into 114,445 unigenes. Using this resource, we identified 3,265 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that were regulated in longan terminal buds in response to potassium chlorate treatment for 2, 6 or 30 days, including 179 transcription factor genes. By reference to the Arabidopsis literature, we then defined 38 longan genes involved in flowering, from which we constructed the longan flowering pathway. According to RNA-seq data, at least 24 of these genes, which participate in multiple signaling pathways, are involved in potassium chlorate-stimulated floral induction, and the differential regulation in terminal buds of ten floral pathway genes (GI, CO, GID1, GA4, GA5, FLC, AP1, LFY, FT and SOC1) was confirmed by qRT-PCR. These data will contribute to an improved understanding of the functions of key genes involved in longan floral induction by potassium chlorate.
- 著者
- Zhe-Yu Liu Jiao-Jiao Ji Feng Jiang Xing-Rui Tian Jian-Kuan Li Jian-Ping Gao
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.251-257, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Codonopsis pilosula, a traditional Chinese medicinal and edible plant, contains several bioactive components. However, the biosynthetic mechanism is unclear because of the difficulties associated with functional gene analysis. Therefore, it is important to establish an efficient genetic transformation system for gene function analysis. In this study, we established a highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated callus genetic transformation system for C. pilosula using stems as explants. After being pre-cultured for 3 days, the explants were infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 harboring pCAMBIA1381-35S::GUS at an OD600 value of 0.3 for 15 min, followed by co-cultivation on MS induction medium for 1 day and delayed cultivation on medium supplemented with 250 mg l−1 cefotaxime sodium for 12 days. The transformed calli were selected on screening medium supplemented with 250 mg l−1 cefotaxime sodium and 2.0 mg l−1 hygromycin and further confirmed by PCR amplification of the GUS gene and histochemical GUS assay. Based on the optimal protocol, the induction and transformation efficiency of calli reached a maximum of 91.07%. The establishment of a genetic transformation system for C. pilosula calli lays the foundation for the functional analysis of genes related to bioactive components through genetic engineering technology.
- 著者
- Elena Kurzbach Matthias Strieker Ute Wittstock
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.241-250, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 42
Glucosinolates, a group of sulfur-containing specialized metabolites of the Brassicales, have attracted a lot of interest in nutrition, medicine and agriculture due to their positive health effects and their involvement in plant defense. Their biological activities and the extensive knowledge of their biosynthesis have inspired research into development of crops with enhanced glucosinolate contents as well as their biotechnological production in homologous and heterologous systems. Here, we provide proof-of-concept for transgenic suspension cultures of carrot (Daucus carota, Apiacae) as a scalable production platform for plant specialized metabolites using benzylglucosinolate as a model. Two T-DNAs carrying in total six genes of the benzylglucosinolate biosynthesis pathway from Arabidopsis thaliana as well as NPTII and BAR as selectable markers were transferred to carrot cells by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Putative transformants selected based on their kanamycin and BASTA resistances were subjected to HPLC-MS analysis. Of 79 putative transformants, 17 produced benzylglucosinolate. T-DNA-integration was confirmed for the five best producers. Callus from these transformants was used to establish suspension cultures for quantitative analysis. When grown in 60-ml-cultures, the best transformants produced roughly 2.5 nmol (g fw)−1 benzylglucosinolate, together with up to 10 nmol (g fw)−1 desulfobenzylglucosinolate. Only one transformant produced more benzylglucosinolate than desulfobenzylglucosinolate. The concentration of sulfate in the medium was not a major limiting factor. High production seemed to be associated with poor growth and vice versa. Therefore, future research should try to optimize medium and cultivation process and to separate growth and production phase by using an inducible promoter.
- 著者
- Yusuke Shikanai Mayu Asada Takafumi Sato Yusuke Enomoto Mutsumi Yamagami Katsushi Yamaguchi Shuji Shigenobu Takehiro Kamiya Toru Fujiwara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.221-227, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Calcium (Ca) deficiency affects the yields and quality of agricultural products. Susceptibility to Ca deficiency varies among crops and cultivars; however, its genetic basis remains largely unknown. Genes required for low Ca tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana have been identified. In this study, we identified a novel gene required for low Ca tolerance in A. thaliana. We isolated a mutant sensitive to low Ca concentrations and identified Glucan synthase-like (GSL) 8 as a gene responsible for low Ca tolerance. GSL8 is a paralog of the previously identified low Ca tolerance gene GSL10, which encodes β-1,3 glucan(callose) synthase. Under low Ca conditions, the shoot growth of gsl8 mutants were inhibited compared to wild-type plants. A grafting experiment indicated that the shoot, but not root, genotype was important for the shoot growth phenotype. The ectopic accumulation of callose under low Ca conditions was reduced in gsl8 mutants. We further investigated the interaction between GSL8 and GSL10 by testing the gsl8 gsl10 double mutant for sensitivity to low Ca concentrations. The double mutant exhibited a more severe phenotype than the single mutant under 0.3 mM Ca, indicating additive effects of GSL8 and GSL10 with respect to low Ca tolerance. These results establish that GSL genes are required for low Ca tolerance in A. thaliana.
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.1, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 著者
- Reika Hasegawa Tomoki Arakawa Kenjiro Fujita Yuichiro Tanaka Zen Ookawa Shingo Sakamoto Hironori Takasaki Miho Ikeda Ayumi Yamagami Nobutaka Mitsuda Takeshi Nakano Masaru Ohme-Takagi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.209-214, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 51
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Brassinosteroid (BR) is a phytohormone that acts as important regulator of plant growth. To identify novel transcription factors that may be involved in unknown mechanisms of BR signaling, we screened the chimeric repressor expressing plants (CRES-T), in which transcription factors were converted into chimeric repressors by the fusion of SRDX plant-specific repression domain, to identify those that affect the expression of BR inducible genes. Here, we identified a homeobox-leucine zipper type transcription factor, BRASSINOSTEROID-RELATED-HOMEOBOX 3 (BHB3), of which a chimeric repressor expressing plants (BHB3-sx) significantly downregulated the expression of BAS1 and SAUR-AC1 that are BR inducible genes. Interestingly, ectopic expression of BHB3 (BHB3-ox) also repressed the BR inducible genes and shorten hypocotyl that would be similar to a BR-deficient phenotype. Interestingly, both BHB3-sx and BHB3-ox showed pale green phenotype, in which the expression of genes related photosynthesis and chlorophyll contents were significantly decreased. We found that BHB3 contains three motifs similar to the conserved EAR-repression domain, suggesting that BHB3 may act as a transcriptional repressor. These results indicate that BHB3 might play an important role not only to the BR signaling but also the regulation of greenings.
- 著者
- Darunmas Sankhuan Meiqiao Ji Sota Takanashi Yuto Imamura Shoichi Sato Kanyaratt Supaibulwatana Masahiro Otani Masaru Nakano
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.205-208, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
LEAFY (LFY), which encodes a plant-specific transcription factor, plays an important role in the transition from vegetative to reproductive development. Ectopic expression of LFY has been reported to induce dwarfism and early flowering in some model plants. In order to examine the possibility of using LFY for molecular breeding of ornamental plants, we produced and characterized transgenic plants ectopically expressing LFY from Arabidopsis thaliana (AtLFY) in the liliaceous ornamental plant Tricyrtis sp. Nine independent transgenic plants have been obtained, and all of them exhibited dwarf phenotypes compared with the vector control. These transgenic plants could be classified into three types according to the degree of dwarfism: one showed an extreamly dwarf phenotype with smaller leaves (Type I); two showed moderately dwarf phenotypes (Type II); and six showed slightly dwarf phenotypes (Type III). All of Type I, Type II and Type III transgenic plants produced flower buds 1–3 weeks earlier than the vector control. Vector control and Type III transgenic plants produced 1–4 apical flower buds, whereas Type I and Type II transgenic plants produced only a single apical flower bud. Type I and Type II transgenic plants often produced non-fully-opened flowers. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis showed that the AtLFY expression level generally correlated with the degree of dwarfism. These results indicate that morphological alterations observed in the transgenic plants was induced by ectopic expression of AtLFY. Lower levels of ectopic expression of LFY may be valuable for producing dwarf and early flowering ornamental plants.
- 著者
- Reika Hasegawa Kenjiro Fujita Yuichiro Tanaka Hironori Takasaki Miho Ikeda Ayumi Yamagami Nobutaka Mitsuda Takeshi Nakano Masaru Ohme-Takagi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.185-189, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The brassinosteroid (BR) phytohormone is an important regulator of plant growth. To identify novel transcription factors that regulate BR responses, we screened chimeric repressor gene silencing technology (CRES-T) plants, in which transcription factors were converted into chimeric repressors by the fusion of SRDX plant-specific repression domain, with brassinazole (Brz), an inhibitor of BR biosynthesis. We identified that a line that expressed the chimeric repressor for zinc finger homeobox transcription factor, BRASSINOSTEORID-RELATED-HOMEOBOX-2 (BHB2-sx), exhibited Brz-hypersensitive phenotype with shorter hypocotyl under dark, dwarf and round and dark green leaves similar to BR-deficient phenotype. Similar to BHB2-sx plants, bhb2 knockout mutant also exhibited Brz hypersensitive phenotype. In contrast, ectopic expression of BHB2 (BHB2-ox) showed hypocotyl elongation phenotype (BR excessive), showing decrease to Brz sensitivity. The expression of the DWF4 and CPD BR biosynthesis genes was repressed in BHB2-sx plants, whereas it was enhanced in BHB2-ox plants. The BR deficient-like phenotype of BHB2-sx plants was partially restored by treatment with brassinolide (BL), indicating that the BR deficient phenotype of BHB2-sx plant may be due to suppression of BR biosynthesis. Our results indicate that BHB2 is a positive regulator of BR response may be due to the promotion of BR biosynthesis genes.
- 著者
- Yuki Yanagawa Yuma Suenaga Yusuke Iijima Akitoshi Okino Ichiro Mitsuhara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.179-183, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Previously, we developed a method that uses temperature-controlled atmospheric-pressure plasma to induce protein uptake in plant cells. In the present work, we examined the mechanism underlying such uptake of a fluorescent-tagged protein in tobacco leaf cells. Intact leaf tissue was irradiated with N2 plasma generated by a multi-gas plasma jet and then exposed to the test protein (histidine-tagged superfolder green fluorescence protein fused to adenylate cyclase); fluorescence intensity was then monitored over time as an index of protein uptake. Confocal microscopy revealed that protein uptake potential was retained in the leaf tissue for at least 3 h after plasma treatment. Further examination indicated that the introduced protein reached a similar amount to that after overnight incubation at approximately 5 h after irradiation. Inhibitor experiments revealed that protein uptake was significantly suppressed compared with negative controls by pretreatment with sodium azide (inhibitor of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis) or sucrose or brefeldin A (inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis) but not by pretreatment with genistein (inhibitor of caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis) or cytochalasin D (inhibitor of micropinocytosis/phagocytosis), indicating that the N2 plasma treatment induced protein transportation across the plant plasma membrane via clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
- 著者
- Yuko Maki Hiroshi Soejima Tamizi Sugiyama Takeo Sato Junji Yamaguchi Masaaki K. Watahiki
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.173-177, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 3
3-Phenyllactic acid (PLA) is a common secondary product of Lactobacillus sp. and promotes adventitious-root formation in Azuki beans (Vigna angularis). Root promotion activity of PLA is synergistically enhanced by tryptophan (Trp). In this study, stereoisomers of PLA and Trp amide conjugates and their alkyl esters were synthesized to investigate the structure–activity relationships on root-promotion activity. The rooting activity of D-PLA-L-Trp conjugate shows more than 40 times higher than that of the mixture of D-PLA and L-Trp. Modification of PLA-Trp with ethyl ester showed the highest activity at 3,400 times of a mixture of D-PLA and L-Trp. However, L-or D-PLA-D-Trp conjugate and the isopropyl ester of PLA-Trp conjugates, both lost the root promotion activity and implicated that a requirement for steric structure for PLA related root promotion mechanism. Unlike auxin substances, which are commonly used as rooting agents that displayed high activity in low concentrations, PLA-Trp ethyl ester exhibited far less phytotoxicity at high concentration of 1 mM, despite its high rooting activity. Innovation of PLA-Trp ethyl ester may be expected for agricultural aspects with low environmental impact.
- 著者
- Ana Maria Huerta-Olalde Alejandra Hernández-García Rodolfo López-Gómez Sylvia Patricia Fernández-Pavía María Guadalupe Zavala-Páramo Rafael Salgado-Garciglia
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.165-171, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 49
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Blackberry is an economically important crop in Mexico, and its yield is substantially reduced by gray mold, a disease caused by Botrytis cinerea. One of the means to obtain B. cinerea-resistant plants is gamma irradiation. Shoot tips of in vitro-micropropagated blackberry plants (Rubus fruticosus ‘Tupy’) were irradiated with five doses of Cobalt-60 gamma radiation (0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 Gy) and cultured on Murashige and Skoog basal medium containing 1.0 mg l−1 benzylaminopurine and 0.06 mg l−1 indole-3-butyric acid (MSB medium). After 28 days of culture, survival was evaluated to determine mean lethal dose (LD50), and 200 shoots were further irradiated at the determined LD50 (30.8 Gy). After 28 days, the surviving shoots were micropropagated on MSB medium for 60 days. Non-irradiated shoots were screened for the in vitro selection of resistant B. cinerea, exposing them to different concentrations of sterile culture filtrate of B. cinerea (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 g l−1) for 28 days to determine mean lethal concentration (LC50), and the irradiated surviving shoots were further exposed to the determined LC50 (4.6 g l−1). Three surviving lines (rfgum5, rfgum6, and rfgum17) that did not present changes compared with the control shoots were micropropagated to obtain plantlets, which were further subjected to in vitro resistance assays using detached leaves inoculated with B. cinerea (1×103 spores ml−1). Plants of rfgum5 and rfgum6 mutant lines were highly resistant and presented similar growth to control plants. Therefore, this methodology is useful to obtain B. cinerea-resistant blackberry plants.
- 著者
- Akari Harada Nanami Tsuji Nozomi Fujimoto Mia Matsuo Miha Saito Nobuyuki Kanzawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.155-163, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 59
Flowering locus T (FT) is known to promote flowering in response to photoperiodic conditions and has recently been shown to contribute to other phenomenon, such as diurnal stomatal movement. In legumes, FTs are classified into three subtypes, though the role of each subtype is not well defined. It has been reported that when FT of Lotus japonicus (LjFT) is heterologously expressed in Arabidopsis, LjFT functions as a mobile florigen to promote flowering, similar to Arabidopsis FT (AtFT). In this study, we expressed AtFT in L. japonicus using the SUC2 promoter and showed that heterologous expression of AtFT was able to promote flowering in the plant. We also showed that AtFT expression does not affect stomatal closing nor nyctinastic leaf movement. These findings contribute to our understanding of flower development and have potential application to breeding or plant biotechnology.
- 著者
- Aili Ailizati Isura Sumeda Priyadarshana Nagahage Atsuko Miyagi Toshiki Ishikawa Maki Kawai-Yamada Taku Demura Masatoshi Yamaguchi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.147-153, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 1
An Arabidopsis NAC domain transcription factor VND-INTERACTING2 (VNI2) was originally isolated as an interacting protein with another NAC domain transcription factor, VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 (VND7), a master regulator of xylem vessel element differentiation. VNI2 inhibits transcriptional activation activity of VND7 by forming a protein complex. Here, to obtain insights into how VNI2 regulates VND7, we tried to identify the amino acid region of VNI2 required for inhibition of VND7. VNI2 has an amino acid sequence similar to the ETHYLENE-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING FACTOR (ERF)-associated amphiphilic repression (EAR) motif, conserved in transcriptional repressors, at the C-terminus. A transient expression assay showed that the EAR-like motif of VNI2 was not required for inhibition of VND7. The C-terminal deletion series of VNI2 revealed that 10 amino acid residues, highly conserved in the VNI2 orthologs contributed to effective repression of the transcriptional activation activity of VND7. Observation of transgenic plants ectopically expressing VNI2 showed that the identified 10 amino acid sequence strongly affected xylem vessel formation and plant growth. These data indicated that the 10 amino acid sequence of VNI2 has an important role in its transcriptional repression activity and negative regulation of xylem vessel formation.
- 著者
- Katsutoshi Tsuda Toshiya Suzuki Manaki Mimura Ken-Ichi Nonomura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.139-146, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 3
In transgenic experiments, we often face fundamental requirements such as overexpressing a certain gene, developing organelle markers, testing promoter activities, introducing large genomic fragments, and combinations of them. To fulfill these multiple requirements in rice, we developed simple binary vectors with or without maize ubiquitin (UBQ) promoter, Gateway cassette and fluorescent proteins. First, we compared stabilities of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S and maize UBQ promoters for constitutive gene expression in transgenic rice. We show that the 35S promoter was frequently silenced after shoot regeneration, whereas maize UBQ promoter achieved stable expression in various young tissues. Binary vectors with Gateway cassettes under the control of the UBQ promoter allowed us to develop stable organelle markers for nuclei, microtubules and P-bodies in rice. The maize UBQ promoter can be easily replaced with any promoters of interest as exemplified by reporters of mitotic cells and provascular bundles. Finally, by introducing two genomic fluorescent reporters, we showed utilities of the Gateway cassette and two selection markers in large DNA fragment transfer and sequential transformations, respectively. Thus, these binary vectors provide useful choices of transgenic experiments in rice.