- 著者
- 佐藤 哲男 細川 正清 渥美 亮 鈴木 亘 伯水 英夫 永井 栄一
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.5, pp.662-664, 1994-05-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 79 135
We measured the plasma concentrations of 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidine] carbonyloxycamptothecin (CPT-11) and the active metabolite 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38), after treatment with CPT-11 to rats pretreated with bis-p-nitrophenylphosphate (BNPP) which is a specific inhibitor of carboxylesterase, and non-pretreated rats. The plasma level of SN-38 was decreased in the BNPP-pretreated group compared with these of non-pretreated group, indicating that the esterase involved in CPT-11 metabolism is a carboxylesterase. We also characterized the molecular species of carboxylesterase involved in CPT-11 metabolism using enzyme preparations purified from liver microsomes. Thirteen carboxylesterase isozyme activities towards CPT-11 were compared and guinea pig GLP1 was found to have the highest activity, while human HU1 isozyme had relatively lower activity than those of animal species. In studies on the kinetic parameters of the hydrolysis of CPT-11 by the purified carboxylesterase isozymes the highest Vmax value of the isozymes was found in human HU1 and the smallest was seen in rat RL1. The Vmax/Km for RL1 showed the largest value of 21.7 nmol/mg protein/mM.
- 著者
- 藤田 靖之 八重樫 隆 澤田 誠吾 尾山 廣 芳本 忠 鶴 大典
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.5, pp.648-652, 1995-05-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 5 5
A hydrolytic enzyme which catalyzes hydrolysis of the ester-linkage of a series of 17-O-acyl derivatives of 7-ethylcamptothecin-21-(2-dimethylamino) ethylamide [acyl derivatives of 22E] was purified from rat liver and its properties were characterized. It hydrolyzed the ester-linkage of all 22E derivatives tested as well as p-nitrophenyl acetate at pH 8-9 but had no effect on 7-ethyl-10-[4-(piperidino)-1-piperidino] carbonyloxycamptothecin (CPT-11 : irinotecan), unlike CPT-11 converting carboxylesterase, which was previously purified from rat serum [Tsuji T. et al., J. Pharmacobio-Dyn., 14, 341 (1991)]. The enzyme had no effect on either acetyl choline or butyrylcholine. It was inhibited by several organophosphorous compounds such as diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP), bis-(pnitrophenyl) phosphate and paraoxon, but was insensitive to inhibitors specific for choline esterases. These results indicate that this liver esterase is clearly distinct from choline esterase and serum CPT-11 converting enzyme and is able to convert pro-drugs, O-acyl derivatives of 22E, to an antitumor agent.
- 著者
- Nanami Shigetomi Kenta Kamiya Toru Takamori Naoki Yoshimura Sayaka Ozawa Keiichi Hirono Fukiko Ichida Masato Taguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.1, pp.110-115, 2019-01-01 (Released:2019-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The purpose of this study was to determine the serum protein binding of tadalafil in children with protein-losing enteropathy (PLE) and to evaluate the specific binding of the drug to human serum-derived proteins in vitro. Seventeen serum samples from two PLE patients used after biochemical tests were collected, and the unbound fraction of tadalafil was determined by an ultrafiltration method. The serum albumin concentrations observed in patients #1 and #2 were 2.4–4.2 and 2.9–3.5 g/dL, respectively. The ranges of unbound fraction of tadalafil in patients #1 and #2 were 3.9–13 and 5.0–7.0%, respectively. This suggested that serum albumin was at least a binding carrier for tadalafil because the unbound fraction of tadalafil and serum albumin were slightly correlated. The unbound fraction of tadalafil at the total concentration of 300 ng/mL was negatively dependent on the serum albumin concentration (range: 1.0–5.0 g/dL) in vitro. In the presence of albumin, the additive effect of γ-globulin on the unbound fraction of tadalafil was marginal, but the addition of α1-acid glycoprotein to test samples decreased the unbound fraction of the drug. The decrease in the unbound fraction of tadalafil was greater at low albumin levels (2 g/dL). The addition of lipoprotein to test samples also decreased the unbound fraction of tadalafil, suggesting that lipoprotein was also a binding carrier of the drug. These results suggested that the disposition and/or response to tadalafil in PLE patients was altered by the change in protein bindings of the drug.
- 著者
- Kosuke Shimizu Miki Takada Tomohiro Asai Kenji Irimura Kazuhiko Baba Naoto Oku
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.6, pp.783-786, 2002 (Released:2002-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 10 13
To enhance the therapeutic efficacy as well as to reduce the side effect, we attempted to liposomalize 4β-aminoalkyl-4′-O-demethyl-4-desoxypodophyllotoxin (TOP-53), a novel and effective topoisomerase II inhibitor. More than 90% of TOP-53 was efficiently incorporated into the liposomes composed of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and cholesterol by remote-loading method. Anti-tumor activity of liposomal TOP-53 against solid tumor was examined in vivo using colon26 NL-17 carcinoma model mice. Three doses of liposomal TOP-53 (12 mg/kg/dose) showed significant tumor growth suppression (97.5% reduction determined at day 25) and the increase in life span (33%) of tumor-bearing mice. Furthermore, one mouse out of 5 was completely cured after treatment. Since similar efficacy was observed in the free TOP-53 treated group, liposomalization does not contribute much to the enhancement of therapeutic efficacy. However, a slight but measurable damage at the injection site was observed when free TOP-53 was injected, and the damage was diminished by the liposomalization. Taken together, liposomalization reduces the side effect rather than enhancing the therapeutic efficacy when TOP-53 is used.
- 著者
- Naoto Okada Kazuyoshi Kawazoe Kazuhiko Teraoka Toshihide Kujime Masahiro Abe Yasuo Shinohara Kazuo Minakuchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.10, pp.1622-1626, 2013-10-01 (Released:2013-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 27 43
Denosumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, inhibits the activation of osteoclasts. Some clinical trials have shown that denosumab suppresses bone resorption in patients with advanced cancer, but hypocalcemia has been reported as a serious adverse effect after the administration of denosumab. It is difficult to predict hypocalcemia in such cases because the risk factors for denosumab-induced hypocalcemia have not been reported. Accordingly, the aim of the present study was to identify the risk factors for hypocalcemia induced by denosumab. We retrospectively reviewed the records of patients who had received denosumab at Tokushima University Hospital between April 2012 and May 2013. Fifty-three patients were analyzed and eleven patients had hypocalcemia after administration of denosumab. Univariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the patients who had not been administered zoledronic acid before receiving denosumab or had lower creatinine clearance (CCr) appeared to have a higher risk of hypocalcemia (p<0.05). The cut off value of CCr was 50.4 mL/min calculated by receiver-operator characteristics curves. Moreover, multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that non-administration of zoledronic acid (odds ratio 10.43, p<0.05) and CCr less than 50.0 mL/min (odds ratio 5.90, p<0.05) were independent risk factors for denosumab-induced hypocalcemia. These findings provide useful information regarding the monitoring of hypocalcemia in patients receiving denosumab.
- 著者
- Congyun Jin Yoshiaki Yao Atsushi Yonezawa Satoshi Imai Hiroki Yoshimatsu Yuki Otani Tomohiro Omura Shunsaku Nakagawa Takayuki Nakagawa Kazuo Matsubara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.11, pp.1990-1995, 2017-11-01 (Released:2017-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) plays a role in various biochemical oxidation-reduction reactions. Flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and FAD, the biologically active forms, are made from riboflavin. Riboflavin transporters (RFVTs), RFVT1-3/Slc52a1-3, have been identified. However, the roles of human (h)RFVTs in FMN and FAD homeostasis have not yet been fully clarified. In this study, we assessed the contribution of each hRFVT to riboflavin, FMN and FAD uptake and efflux using in vitro studies. The transfection of hRFVTs increased cellular riboflavin concentrations. The uptake of riboflavin by human embryonic kidney cells transfected with hRFVTs was significantly increased, and the efflux was accelerated in a time-dependent manner. However, the uptake and efflux of FMN and FAD hardly changed. These results strongly suggest that riboflavin, rather than FMN or FAD, passes through plasma membranes via hRFVTs. Our findings could suggest that hRFVTs are involved in riboflavin homeostasis in the cells, and that FMN and FAD concentrations are regulated by riboflavin kinase and FAD synthase.
- 著者
- Aurpita Shaha Hiroyuki Mizuguchi Yoshiaki Kitamura Hiromichi Fujino Masami Yabumoto Noriaki Takeda Hiroyuki Fukui
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.9, pp.1440-1447, 2018-09-01 (Released:2018-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 23
The significant correlation between nasal symptom scores and level of histamine H1 receptor (H1R) mRNA in nasal mucosa was observed in patients with pollinosis, suggesting that H1R gene is an allergic disease sensitive gene. We demonstrated that H1R and interleukin (IL)-9 gene are the allergic rhinitis (AR)-sensitive genes and protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ) signaling and nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) signaling are involved in their expressions, respectively. Honey bee products have been used to treat allergic diseases. However, their pathological mechanism remains to be elucidated. In the present study, we investigated the mechanism of the anti-allergic effect of royal jelly (RJ) and Brazilian green propolis (BGPP). Treatment with RJ and BGPP decreased in the number of sneezing on toluene 2,4-diissocyanate (TDI)-stimulated rats. The remarkable suppression of H1R mRNA in nasal mucosa was observed. RJ and BGPP also suppressed the expression of IL-9 gene. RJ and BGPP suppressed phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced Tyr311 phosphorylation of PKCδ in HeLa cells. In RBL-2H3 cells, RJ and BGPP also suppressed NFAT-mediated IL-9 gene expression. These results suggest that RJ and BGPP improve allergic symptoms by suppressing PKCδ and NFAT signaling pathways, two important signal pathways for the AR pathogenesis, and suggest that RJ and BGPP could be good therapeutics against AR.
- 著者
- Jiangang Chen Wenfang Lu Hao Chen Xiaoli Bian Guangde Yang
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b18-00661, (Released:2018-11-30)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 3 10
In this study, a series of salicylic acid derivatives were designed and synthesized as novel non-saccharide α-glucosidase inhibitors. Biological evaluation indicated that when compared to acarbose, compounds T9, T10, and T32 exhibited a higher potency of α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 0.15 ± 0.01 mM, 0.086 ± 0.01 mM and 0.32 ± 0.02 mM, respectively. Evaluation of the inhibition kinetics indicated that T9, T10, T32, and acarbose interacted with α-glucosidase in a mixed non-competitive inhibitory manner. Moreover, T9, T10, and T32 statically quenched the fluorescence of α-glucosidase by formation of an inhibitor-α-glucosidase complex. The docking results showed that hydrogen bonds were generated between the test compounds and α-glucosidase. The antioxidant study revealed that compound T10 exhibited a higher antioxidant activity via scavenging 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl free radical (DPPH), thereby inhibiting lipid peroxidation and the total reduction capacity. In brief, the salicylic acid derivatives identified in this study were promising candidates for development as novel non-saccharide α-glucosidase inhibitors.
- 著者
- Kosuke Baba Reiko Hiramatsu Benjamart Suradej Riho Tanigaki Sayaka Koeda Tomonori Waku Takao Kataoka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.12, pp.1757-1768, 2018-12-01 (Released:2018-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 1 10
The pentacyclic triterpenoid ursolic acid was previously shown to inhibit the intracellular trafficking of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus. In the present study, we further investigated the biological activities of three pentacyclic triterpenoids closely related to ursolic acid on the interleukin 1α-induced expression and intracellular trafficking of ICAM-1. In human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells, asiatic acid, corosolic acid, and maslinic acid interfered with the intracellular transport of ICAM-1 to the cell surface. Endoglycosidase H-sensitive glycans were linked to ICAM-1 in asiatic acid-, corosolic acid-, and maslinic acid-treated cells. Unlike corosolic acid, asiatic acid and maslinic acid increased the amount of the ICAM-1 protein. Moreover, asiatic acid increased the co-localization of ICAM-1 with calnexin (an ER marker), but not GM130 (a cis-Golgi marker). Asiatic acid, corosolic acid, and maslinic acid inhibited yeast α-glucosidase activity, but not Jack bean α-mannosidase activity. These results indicate that asiatic acid, corosolic acid, and maslinic acid interfere with the intracellular transport of ICAM-1 to the cell surface and cause the accumulation of ICAM-1 linked to endoglycosidase H-sensitive glycans.
- 著者
- Takashi Yamauchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.8, pp.1342-1354, 2005 (Released:2005-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 129
- 被引用文献数
- 112 153
Much has been learned about the activity-dependent synaptic modifications that are thought to underlie memory storage, but the mechanism by which these modifications are stored remains unclear. A good candidate for the storage mechanism is Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM kinase II). CaM kinase II is one of the most prominent protein kinases, present in essentially every tissue but most concentrated in brain. Although it has been about a quarter of a century since the finding, CaM kinase II has been of the major interest in the region of brain science. It plays a multifunctional role in many intracellular events, and the expression of the enzyme is carefully regulated in brain regions and during brain development. Neuronal CaM kinase II regulates important neuronal functions, including neurotransmitter synthesis, neurotransmitter release, modulation of ion channel activity, cellular transport, cell morphology and neurite extension, synaptic plasticity, learning and memory, and gene expression. Studies concerning this kinase have provided insight into the molecular basis of nerve functions, especially learning and memory, and indicate one direction for studies in the field of neuroscience. This review presents the molecular structure, properties and functions of CaM kinase II, as a major component of neurons, based mainly developed on findings made in our laboratory.
- 著者
- KITAZATO KENJI TAKEDA SETSUO UNEMI NORIO
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:0386846X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.5, no.10, pp.803-810, 1982
- 被引用文献数
- 9
1, 3, 3, 5, 5-Pentaziridino-1-thia-2, 4, 6-traiza-3, 5-diphosphorine-1-oxide (SOAz), a new antitumor agent, was evaluated for antitumor activity against various mouse- and rattumor systems. The optimal treatment regimens of SOAz (i.p.) gave 262% and 134% increase in life span (ILS) in mice P338 leukemia and L1210 leukemia implanted intraperitoneally, respectively, and 239% ILS in rats with Yoshida sarcoma of which 86% survived for 60 d after intraperitoneal tumor implantation. The compound showed a definite activity against Lewis lung carcinoma implanted intravenously. The compound also exhibited 80-100% inhibition of tumor local growth in all of four experimental tumor systems used in the present study. In contrast to cyclophosphamide, SOAz was active against B16 melanoma and Meth A, and demonstrated high activity against a subline of L1210 leukemia resistant to cyclophosphamide.
- 著者
- Hiroaki KUBO Tasashi OSAWA Kohki TAKASHIMA Masakazu MIZOBE
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, no.5, pp.741-747, 1996-05-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 27 29
To improve the bioavailability of the sparingly water-soluble drug, 1-(3, 4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2, 3-bis(methoxycarbonyl)-4-hydroxy-6, 7, 8-trimethoxynaphthalene (TA-7552), the usefulness of the co-grinding method with D-mannitol was investigated. The co-grinding was performed at various weight ratios of TA-7552 and D-mannitol using a ball mill. The particle size was markedly reduced with increasing amount of D-mannitol. A mixture ratio greater than or equal to 1 : 3 of the drug and D-mannitol produced submicron-sized particles. In dogs, bioavailability increased with increasing amount of D-mannitol. The 1 : 9 coground mixture gave complete absorption, as did a lecithin solution of the drug. Even co-ground powders with lower amounts of D-mannitol provided relatively high bioavailability in comparison with ground drug powder alone of a similar particle size. Further, pharamacological examination using rats indicated that the inhibition of cholesterol absorption was intestified with the reduction of particle size. These findings suggest that the co-grinding method with D-mannitol is useful for enhancing the bioavailability and pharmacological effectiveness of this sparingly water-soluble drug.
- 著者
- Ki-Bae Hong Sung Hee Han Yooheon Park Hyung Joo Suh Hyeon-Son Choi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.8, pp.1269-1276, 2018-08-01 (Released:2018-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 7
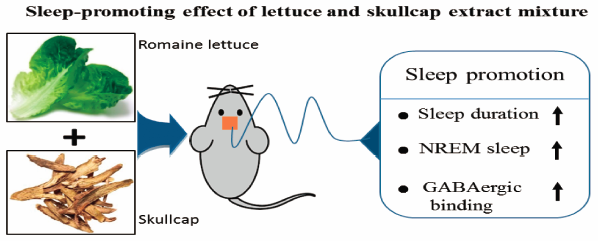
The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of romaine lettuce leaves extract (RE), skullcap root extract (SE) and their mixture on sleep behaviors in vertebrate models. HPLC analysis showed that RE contains lactucopicrin (0.02±0.01 mg/g extract), chlorogenic acid (4.05±0.03 mg/g extract), caffeic acid (2.38±0.03 mg/g extract), and chicoric acid (7.02±0.32 mg/g extract) as main phenolic compounds, while SE includes baicalin (99.4±0.5 mg/g extract), baicalein (8.28±0.21 mg/g extract), and wogonin (3.09±0.32 mg/g extract). The mixture of RE (100 mg/g extract) and SE (40 mg/g extract) increased total sleep time by 50.9% compared with the control in pentobarbital-induced sleep model. In electroencephalography (EEG) analysis, RE/SE mixture significantly increased Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM), in which delta wave was enhanced by around 40% compared with normal control, leading to the increase of sleep time. In caffeine-induced wake model, RE/SE mixture greatly decreased (53%) caffeine-induced wake time, showing a similar level to normal control. In addition, caffeine-induced decreased of NREM and delta wave effectively increased with RE/SE mixture; NREM and delta wave increased by 85% and 108%, respectively. Furthermore, RE/SE mixture was shown to bind to a gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA)-benzodiazepine (BZD) receptor stronger than RE or SE single extract. Taken together, RE/SE mixture effectively improved sleep behavior with the increase of NREM via GABAA-BZD receptor binding. RE/SE mixture can be used as an herbal agent for sleep disorders.
1 0 0 0 OA Lipid Bilayers Manipulated through Monolayer Technologies for Studies of Channel-Membrane Interplay
- 著者
- Shigetoshi Oiki Masayuki Iwamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.3, pp.303-311, 2018-03-01 (Released:2018-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 82
- 被引用文献数
- 12
Fluidity and mosaicity are two critical features of biomembranes, by which membrane proteins function through chemical and physical interactions within a bilayer. To understand this complex and dynamic system, artificial lipid bilayer membranes have served as unprecedented tools for experimental examination, in which some aspects of biomembrane features have been extracted, and to which various methodologies have been applied. Among the lipid bilayers involving liposomes, planar lipid bilayers and nanodiscs, recent developments of lipid bilayer methods and the results of our channel studies are reviewed herein. Principles and techniques of bilayer formation are summarized, which have been extended to the current techniques, where a bilayer is formed from lipid-coated water-in-oil droplets (water-in-oil bilayer). In our newly developed method, termed the contact bubble bilayer (CBB) method, a water bubble is blown from a pipette into a bulk oil phase, and monolayer-lined bubbles are docked to form a bilayer through manipulation by pipette. An asymmetric bilayer can be readily formed, and changes in composition in one leaflet were possible. Taking advantage of the topological configuration of the CBB, such that the membrane’s hydrophobic interior is contiguous with the surrounding bulk organic phase, oil-dissolved substances such as cholesterol were delivered directly to the bilayer interior to perfuse around the membrane-embedded channels (membrane perfusion), and current recordings in the single-channel allowed detection of immediate changes in the channels’ response to cholesterol. Chemical and mechanical manipulation in each monolayer (monolayer technology) allows the examination of dynamic channel-membrane interplay.
- 著者
- Jun Ho Kim Jin Hyup Lee Young Jun Kim
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b15-00585, (Released:2015-11-06)
- 参考文献数
- 14
This article has been retracted by the Editorial Committee of The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan because it contains scientific misconduct. Although the data published in this article were generated in part by the first author, the authors violated authorship and sponsorship protocol.
- 著者
- Kazuaki Matsumoto Akari Shigemi Kazuro Ikawa Naoko Kanazawa Yuko Fujisaki Norifumi Morikawa Yasuo Takeda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.2, pp.235-238, 2015-02-01 (Released:2015-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 5 22
Ganciclovir is a nucleoside guanosine analogue that exhibits therapeutic activity against human cytomegalovirus infection, and is primarily excreted via glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. The adverse effects induced by ganciclovir therapy are generally of a hematological nature and include thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Low marrow cellularity and elevated serum creatinine have been identified as risk factors for ganciclovir-induced neutropenia. However, the risk factors for thrombocytopenia have yet to be determined. Therefore, this study investigated patients administered ganciclovir to determine the risk factors for thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Thrombocytopenia occurred in 41 of these patients (30.6%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified three independent risk factors for thrombocytopenia: cancer chemotherapy (odds ratio (OR)=3.1), creatinine clearance (<20 mL/min) (OR=12.8), and the ganciclovir dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) (OR=15.1). Leukopenia occurred in 36 patients (28.6%), and white blood cell count (<6000 cells/mm3) (OR=3.7) and the ganciclovir dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) (OR=7.8) were identified as risk factors. These results demonstrated that several factors influenced the occurrence of ganciclovir-induced thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, and suggest that special attention should be paid to patients receiving cancer chemotherapy with a low creatinine clearance (<20 mL/min) and high dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) in order to avoid ganciclovir-induced thrombocytopenia.
- 著者
- Shuichi Fujimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.10, pp.1923-1929, 2007-10-01 (Released:2007-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 12 22
TAS-103, 6-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno-[2,1-c]quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride, is a dual topoisomerases I and II inhibitor. Antitumor activities of TAS-103 against fresh surgical specimens resected from 525 patients (32 types of tumors) were examined by flow cytometric (FCM) analysis of DNA integrity of tumor cells, and compared with those of five other investigational new drugs and 31 clinically available anticancer agents. Concentrations of clinically available anticancer agents were set at one-tenth of the peak plasma concentration (PPC) of the clinically recommended doses. On the other hand, since PPCs of investigational new drugs in humans were frequently unknown, these were estimated by a method that determines the theoretically achievable concentration in body fluid (TAC method). Correlations between TAC and PPC were examined for 16 clinically available anticancer agents, and it was found that TAC at 7n (the modified Fibonacci's dose-escalation scheme) of 14 drugs corresponded well with each one-tenth of PPC. By defining a 30% or more reduction in the integrated diploid peak as effective and a 60% or more reduction as definitely effective, TAS-103 at 5 μg/ml (7n) showed significantly higher effective rates and definitely effective rates than those of all other investigational new drugs, as well as almost all clinically available anticancer agents, against various malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer, brain tumor and renal cancer. These results strongly suggest that TAS-103 will be expected to show excellent antitumor activities against a wide range of human tumors.
- 著者
- Kosuke Shimizu Miki Takada Tomohiro Asai Koichi Kuromi Kazuhiko Baba Naoto Oku
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.10, pp.1385-1387, 2002 (Released:2002-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 6 8
A novel anti-tumor agent, 6-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno[2,1-c]quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride (TAS-103), effectively inhibits both topoisomerase I and II activities. To enhance anti-tumor efficacy and to reduce the side effects of the agent, liposomalization of TAS-103 was performed. TAS-103 was effectively entrapped in liposomes by a remote-loading method, and was stable at 4 °C and in the presence of 50% serum. To evaluate the anti-tumor efficacy of liposomal TAS-103, the growth inhibition against Lewis lung carcinoma cells in vitro and the therapeutic efficacy against solid tumor-bearing mice in vivo were examined. Liposomal TAS-103 showed strong cytotoxic effect against Lewis lung carcinoma cells in a dose dependent manner and effectively suppressed solid tumor growth accompanying longer survival time of tumor-bearing mice in comparison with the mice treated with free TAS-103. These results suggest that liposomal TAS-103 is useful for cancer therapy.
- 著者
- Jin Sun Lee Myung Sun Lee Won Keun Oh Ji Young Sul
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.8, pp.1427-1432, 2009-08-01 (Released:2009-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 26 53
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) is highly expressed in breast carcinomas to support their continuous growth and proliferation, but has low expression level in normal tissues. Considerable interest has been developed in searching for novel FASN inhibitors as a therapeutic target for breast cancer. In present study, amentoflavone was isolated from Selaginella tamariscina, a traditional oriental medicine that has been used to treat cancer for many years, and was found to significantly inhibit the in vitro enzymatic activity of FASN at concentrations above 50 μM. Amentoflavone was also found to decrease fatty acid synthesis by the reduction of [3H]acetyl-CoA incorporation into lipids in FASN-overexpressed SK-BR-3 human breast cancer cells. Furthermore, this study showed that amentoflavone, at a concentration greater than 75 μM, increased the cleavage-activity of caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), and administration of pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK completely rescued the SK-BR-3 cells from PARP cleavages. The sequential internucleosomal DNA fragmentation in SK-BR-3 cells was observed at a concentration of 100 μM. A decrease in breast cancer cell growth was observed in SK-BR-3 cells at 12 and 24 h post treatment with 100 μM of amentoflavone, followed by a dramatic suppression after 48 h. The inhibition of cancer-growth by amentoflavone was dose-dependent, showing a slight reduction at 50 μM and significant reduction at concentrations of 75 and 100 μM. FASN-nonexpressed NIH-3T3 normal cell growth was not decreased by amentoflavone-treatment, both in time- and dose-dependent manners. These data provide evidence that amentoflavone isolated from S. tamariscina induced breast cancer apoptosis through blockade of fatty acid synthesis.
- 著者
- Zhihua Yue Jinhai Shi Haona Li Huiyi Li
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.2, pp.158-162, 2018-02-01 (Released:2018-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 11
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are likely to be used concomitantly with acyclovir or valacyclovir in clinical practice, but the study on the safety of such combinations was seldom reported. The objective of the study was to investigate reports of acute kidney injury (AKI) events associated with the concomitant use of oral acyclovir or valacyclovir with an NSAID by using the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS) database between January 2004 and June 2012. The frequency of AKI events in patients while simultaneously taking either acyclovir or valacyclovir and an NSAID was compared using the Chi-square test. The effect of concomitant use of acyclovir or valacyclovir and individual NSAIDs on AKI was analyzed by the reporting odds ratio (ROR). The results showed that AKI was reported as the adverse event in 8.6% of the 10923 patients taking valacyclovir compared with 8.7% of the 2556 patients taking acyclovir (p=NS). However, AKI was significantly more frequently reported in patients simultaneously taking valacyclovir and an NSAID (19.4%) than in patients simultaneously taking acyclovir and an NSAID (10.5%) (p<0.01). The results also suggested that increased risk of AKI was likely associated with the concomitant use of valacyclovir and some NSAIDs such as loxoprofen, diclofenac, etodolac, ketorolac, piroxicam or lornoxicam. The case series from the AERS indicated that compared with acyclovir, valacyclovir is more likely to be affected by NSAIDs, and the concomitant use of valacyclovir with some NSAIDs might be associated with increased risk of AKI. The drug interactions with this specific combination of medications are worth exploring further.