- 著者
- Setsuo Kinoshita Tadahaya Mizuno Megumi Hori Michiaki Kohno Hiroyuki Kusuhara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.12, pp.2069-2075, 2019-12-01 (Released:2019-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Proteome profiling based on two-dimensional (2D)-DIGE might be a useful tool for investigating drug-like compounds and the mode of action of drugs. However, obtaining data for profiling requires high labor costs, and it is difficult to control the reproducibility of spot positions because 2D-DIGE usually requires large-size glass plates and spot alignments are greatly affected by the quality of DryStrips and polyacrylamide gels (PAGs). Therefore, we have developed a novel platform by employing small size DryStrips and PAGs, and an image analysis strategy based on dual correction of spot alignment and volume. Our system can automatically detect a large number of consistent spots through all images. Cytosol fractions of HeLa cells treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or bortezomib were analyzed, 1697 consistent spots were detected, and 775 of them were significantly changed with the treatment. Deviations between different days and lot sets of DryStrips and PAGs were investigated by calculating the correlation coefficients. The mean values of the correlation between days and lot sets were 0.96 and 0.94, respectively. Clustering analysis of all the treatment data clearly separated the DMSO or bortezomib treated groups beyond day deviations. Thus, we have succeeded in developing an easy-to-handle 2D-DIGE system that can be a novel proteome profiling platform.
- 著者
- Kentaro Ayada Masahiro Tsuchiya Hiroyuki Yoneda Kouji Yamaguchi Hiroyuki Kumamoto Keiichi Sasaki Takeshi Tadano Makoto Watanabe Yasuo Endo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.8, pp.1326-1330, 2017-08-01 (Released:2017-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Recent studies suggest that histamine—a regulator of the microcirculation—may play important roles in exercise. We have shown that the histamine-forming enzyme histidine decarboxylase (HDC) is induced in skeletal muscles by prolonged muscular work (PMW). However, histological analysis of such HDC induction is lacking due to appropriate anti-HDC antibodies being unavailable. We also showed that the inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α can induce HDC, and that PMW increases both IL-1α and IL-1β in skeletal muscles. Here, we examined the effects (a) of PMW on the histological evidence of HDC induction and (b) of IL-1β and TNF-α on HDC activity in skeletal muscles. By immunostaining using a recently introduced commercial polyclonal anti-HDC antibody, we found that cells in the endomysium and around blood vessels, and also some muscle fibers themselves, became HDC-positive after PMW. After PMW, TNF-α, but not IL-1α or IL-1β, was detected in the blood serum. The minimum intravenous dose of IL-1β that would induce HDC activity was about 1/10 that of TNF-α, while in combination they synergistically augmented HDC activity. These results suggest that PMW induces HDC in skeletal muscles, including cells in the endomysium and around blood vessels, and also some muscle fibers themselves, and that IL-1β and TNF-α may cooperatively mediate this induction.
- 著者
- Hironori Tsuchiya Maki Mizogami Takahiro Ueno Kenji Shigemi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.6, pp.988-992, 2012-06-01 (Released:2012-06-02)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 5 11
The cardiotoxic effects of local anesthetics increase in cardiac ischemia which is characterized by the tissue pH lowering to 6.5 or less. Apart from the cardiac channel blockade, the membrane interaction has been referred to as another mode of their cardiotoxic action. By using biomimetic membranes, we verified the hypothesis that bupivacaine and lidocaine may increasingly interact with cardiac mitochondrial membranes under ischemia-like acidic conditions. Biomimetic membranes were prepared with different phospholipids and cholesterol to be unilamellar vesicles suspended in buffers of pH 7.4, 6.9, 6.4 or 5.9. Bupivacaine and lidocaine were reacted with the membrane preparations at cardiotoxically relevant concentrations and their membrane interactivities were determined by measuring fluorescence polarization. Both drugs interacted with 100 mol% 1,2-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, peripheral nerve cell-mimetic and cardiomyocyte-mimetic membranes to increase membrane fluidity, although lowering the reaction pH from 7.4 to 5.9 decreased their membrane-fluidizing effects. In cardiomyocyte mitochondria-mimetic membranes containing 20 mol% cardiolipin, however, bupivacaine and lidocaine reversely increased their membrane interactivities at pH 5.9–6.4 compared with pH 7.4. Such increases were greater in anionic phospholipid membranes which consisted of substantial amounts of cardiolipin and phosphatidylserine. Positively charged bupivacaine and lidocaine would form ion-pairs with the negatively charged head-groups of anionic phospholipids under acidic conditions, thereby increasing the induced membrane fluidization. The mitochondrial membrane interactions depending on pH lowering may be, at least in part, responsible for local anesthetic cardiotoxicity enhanced in acidosis associated with cardiac ischemia.
1 0 0 0 OA Risk Factors for Severe Hyponatremia Related to Cisplatin: A Retrospective Case-Control Study
- 著者
- Shiro Hatakeyama Toshihiro Shida Hiroaki Yamaguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.11, pp.1891-1897, 2019-11-01 (Released:2019-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Onset of severe hyponatremia following cisplatin (CDDP) administration has been previously reported. However, the risk factors associated with hyponatremia still remain unclear. We conducted a retrospective, single-center, case-control study to identify independent risk factors of severe hyponatremia in patients with various types of cancers. Adult patients who received intravenous CDDP administration between January 2012 and December 2017 met the inclusion criteria. The investigators recorded patients’ demographics and clinical information retrospectively, and assessed the lowest serum sodium level within 21 d of the first CDDP administration. Risk factors for grade ≥3 hyponatremia were examined via a logistic regression analysis. Among a total of 472 patients, fifty patients (10.6%) developed grade ≥3 hyponatremia. Univariate analysis revealed that age (≥65 years), presence of small cell lung or esophageal cancer, and lower sodium concentrations in the serum (<138 mEq/L) were significantly associated with grade 3 and 4 hyponatremia. Additionally, multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the presence of small cell lung cancer (adjusted odds ratio, 3.26; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.07–10.00) and lower sodium concentrations in the serum (<138 mEq/L) (adjusted odds ratio, 6.18; 95%CI, 3.21–11.90) were independent risk factors of grade 3 and 4 hyponatremia. Thus, serum sodium concentrations in patients with these risk factors should be closely monitored after CDDP administration.
- 著者
- Ken Konaka Takumi Sakurada Tatsuhiko Saito Sachiko Mori Masaki Imanishi Soji Kakiuchi Shuji Fushitani Keisuke Ishizawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.11, pp.1839-1845, 2019-11-01 (Released:2019-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Uridine 5′-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), a metabolic enzyme of irinotecan active metabolite, has two genetic polymorphisms (UGT1A1*6 and UGT1A1*28). In UGT1A1 homozygous or heterozygous patients, metabolism is delayed and the risk of developing adverse effects is increased, and therefore, dose reduction of irinotecan is considered. However, the specific dose reduction rate of irinotecan for heterozygous patients is uncertain. We studied the necessity of irinotecan dose reduction and its optimal dose in UGT1A1 heterozygous patients with lung cancer. Patients with lung cancer treated with irinotecan in the Tokushima University Hospital or Tokushima Municipal Hospital were included in this study. The dose of irinotecan was evaluated based on the relative dose intensity (RDI). The time to treatment failure (TTF) was defined as the period until treatment change, death, or progressive disease based on response evaluation criteria of solid tumors. We targeted 31 patients treated with irinotecan: 12 wild types (WT), 14 heterozygotes, and 1 complex heterozygote and 4 homozygotes. There was no significant difference in the TTF, but the mean RDI during the entire treatment period was significantly different in the wild type (79%), heterozygous (62%), and complex heterozygous and homozygous groups (46%). In addition, the proportion of patients who completed treatment without dose reduction in the WT group tended to be higher than that in the other groups. For lung cancer patients with UGT1A1 heterozygote types who start irinotecan therapy, reducing the initial dose by approximately 20% might be a safer chemotherapy without decreasing the therapeutic effect.
- 著者
- Mari Hara Nakano Chihiro Udagawa Arata Shimo Yasuyuki Kojima Reiko Yoshie Hisamitsu Zaha Norie Abe Tokiwa Motonari Mikiko Unesoko Kenji Tamura Tatsunori Shimoi Masayuki Yoshida Teruhiko Yoshida Hiromi Sakamoto Ken Kato Taisei Mushiroda Koichiro Tsugawa Hitoshi Zembutsu
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00527, (Released:2019-10-09)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 14
Trastuzumab has been administered to patients with HER2-positive cancer, however, the cardiotoxicity is identified as one of the life-threatening toxicities. Clinically useful biomarker for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity has been expected to be developed. To identify a novel genetic marker(s) determining the risk of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity, we performed a first genome-wide association study (GWAS) in Japanese population. We enrolled 481 patients who had been treated with trastuzumab and carried out a GWAS using 11 cases (with cardiotoxicity) and 257 controls (without cardiotoxicity). Top 100 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which revealed the smallest P values in GWAS (P = 7.60 x 10-7 - 2.01 x 10-4) were further examined using replication samples consisted of 14 cases and 199 controls. The combined analysis of the GWAS and replication study indicated possible association of five loci with trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity (rs9316695 on chromosome 13q14.3, rs28415722 on chromosome 15q26.3, rs7406710 on chromosome 17q25.3, rs11932853 on chromosome 4q25, and rs8032978 on chromosome 15q26.3, Pcombined = 6.00 x 10-6, 8.88 x 10-5, 1.07 x 10-4, 1.42 x 10-4, 1.60 x 10-4, respectively). Furthermore, we developed a risk prediction model for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity using the five marker SNPs. The incidence of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with risk score ≥ 5 was significantly higher (42.5%) compared to that in patients with score ≤ 4 (1.8%) (P = 7.82 x 10-15, odds ratio = 40.0). These findings suggest the potential to improve the ability of physicians to avoid the trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity for patients with HER2-positive cancer.
1 0 0 0 OA Therapeutic Application of Stem Cell Technology toward the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
- 著者
- Kaneyasu Nishimura Jun Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.171-175, 2013-02-01 (Released:2013-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 27 37
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is one of the candidate diseases for cell transplantation therapy, since successful clinical experiments have accumulated using human fetal tissue grafting for PD patients. Although some grafted PD patients have shown drastic improvements, several issues still remain with regard to using human fetal tissue. This review highlights the recent advances in stem cell technology toward clinical applications using human pluripotent stem cells. In particular, pluripotent stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), are the focus as a source of cell transplantation therapy that can be used instead of human fetal tissues. Additionally, efficient methods for stem cell maintenance and differentiation have been developed and improved toward the clinical transition. These advances in the basic technologies have helped accelerate the realization of regenerative medicine. We also review the current topics regarding disease modeling and drug screening using iPSC technology. Finally, we also describe the future prospects of these stem cell research fields toward clinical application.
1 0 0 0 OA Antibody Fragments for On-Site Testing of Cannabinoids Generated via in Vitro Affinity Maturation
- 著者
- Izumi Morita Hiroyuki Oyama Mayumi Yasuo Kazuhisa Matsuda Kengo Katagi Aya Ito Hiroka Tatsuda Hiroyuki Tanaka Satoshi Morimoto Norihiro Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.174-181, 2017-02-01 (Released:2017-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 10 17
Law enforcement against illicit use of cannabis and related substances requires rapid, feasible, and reliable tools for on-site testing of cannabinoids. Notably, methods based on cannabinoid-specific antibodies enable efficient screening of multiple specimens. Antibody engineering may accelerate development of modern and robust testing systems. Here, we used in vitro affinity maturation to generate a single-chain Fv fragment (scFv) that recognizes with high affinity the psychoactive cannabinoid, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). A mouse monoclonal antibody against THC, Ab-THC#33, with Ka 6.2×107 M−1 (as Fab fragment) was established by the hybridoma technique. Then, a “wild-type” scFv (wt-scFv) with Ka, 1.1×107 M−1 was prepared by bacterial expression of a fusion gene combining the VH and VL genes for Ab-THC#33. Subsequently, random point mutations in VH and VL were generated separately, and the resulting products were assembled into mutant scFv genes, which were then phage-displayed. Repeated panning identified a mutant scFv (scFv#m1-36) with 10-fold enhanced affinity (Ka 1.1×108 M−1) for THC, in which only a single conservative substitution (Ser50Thr) was present at the N-terminus of the VH-complementarity-determining region 2 (CDR2) sequence. In competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the mutant scFv generated dose–response curves with midpoint 0.27 ng/assay THC, which was 3-fold lower than that of wt-scFv. Even higher reactivity with a major THC metabolite, 11-nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, indicated that the mutant scFv will be useful for testing not only THC in confiscated materials, but also the metabolite in urine. Indeed, the antibody fragment is potentially suitable for use in advanced on-site testing platforms for cannabinoids.
- 著者
- Shunsuke Nakamori Jun Takahashi Sumiko Hyuga Jinwei Yang Hiroaki Takemoto Takuro Maruyama Naohiro Oshima Nahoko Uchiyama Yoshiaki Amakura Masashi Hyuga Takashi Hakamatsuka Yukihiro Goda Hiroshi Odaguchi Toshihiko Hanawa Yoshinori Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.9, pp.1538-1544, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 12
The analgesic effect of Ephedra Herb (EH) is believed to be derived from the anti-inflammatory action of pseudoephedrine (Pse). We recently reported that ephedrine alkaloids–free EH extract (EFE) attenuates formalin-induced pain to the same level as that achieved by EH extract (EHE), which suggests that the analgesic effect of EH may not be due to ephedrine alkaloids (EAs). To examine the contribution of EAs to the analgesic effect of EH, mice were injected with formalin to induce a biphasic pain reaction (first phase, 0–5 min; second phase, 10–45 min) at various time points after oral administration of the following test drugs: ephedrine (Eph), Pse, “authentic” EHE from Tsumura & Co. (EHE-Ts), EFE, and EHE that was used as the source of EFE (EHE-To). Biphasic pain was suppressed at 30 min after administration of Eph, EHE-Ts, and EHE-To. At 6 h after administration of EFE, EHE-To, and Pse—and at 4 to 6 h after administration of EHE-Ts—only second-phase pain was suppressed; however, the effect of Pse at 6 h was not significant. These results suggested that EHE has a biphasic analgesic effect against biphasic formalin-induced pain: in the first phase of analgesia (30 min after administration), biphasic pain is suppressed by Eph; in the second phase of analgesia (4–6 h after administration), second-phase pain is alleviated by constituents other than EAs, although Pse may partially contribute to the relief of second-phase pain.
- 著者
- Xiaoying Yu Xindi Zhang Hua Jin Zhiwei Wu Chunlu Yan Zhijun Liu Xinghua Xu Shuangfang Liu Feifei Zhu
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.9, pp.1482-1490, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 23
Zhengganxifeng decoction (ZGXFD) is a traditional Chinese medicinal formula, from “Medical Zhong parameter West recorded” by Xichun Zhang, which has been applied to the treatment of clinical essential hypertension. Besides its effect in blood pressure reduction, ZGXFD is also known to be a radical therapy with little or no side effects. Compared with western medicines, Chinese medicinal formulas have the advantage of simultaneously attacking multiple targets. However, such a property brings trouble to the pharmacological studies of Chinese medicines. This study investigated the composition of gut microbiota in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) treated with ZGXFD. ZGXFD was shown to cause similar effects in the treatment group as benazepril: both were able to reduce in SHR the microbial diversity, Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio and coccus to bacillus (C/B) ratio. Meanwhile, ZGXFD can maintain the integrity of intestinal mechanistic barrier and elevate the percentage of bacteria producing short chain fatty acids (SCFA). By investigating renin–angiotensin system (RAS) system, we found that ZGXFD can decrease the expression of angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) in lungs, which in turn causes a increase in AngI produces angiotensin1–7 (Ang1–7) and decrease in AngII. ZGXFD regulate blood pressure in SHR via RAS.
- 著者
- Keita Hirai Toshihiro Shirai Yuya Suzuki Tatsuki Shimomura Kunihiko Itoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00385, (Released:2019-09-03)
- 参考文献数
- 39
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Vitamin D has an immune-modulating effect, related to the pathophysiology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, few studies have focused on the difference between patients with asthma and COPD in the association of circulating vitamin D levels with clinical outcomes. We sought to investigate the associations of circulating vitamin D levels with health-related quality of life (HR-QOL), severity, and exacerbations. Subjects included 152 asthma patients and 50 COPD patients. We measured plasma concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [25(OH)D3]. HR-QOL was assessed using the EuroQoL 5-Dimension (EQ-5D) and the 12-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-12) scales. Exacerbations were recorded during a one-year follow-up. Associations between plasma 25 (OH)D3 concentrations and outcome variables were evaluated using linear regression. Plasma concentrations of 25(OH)D3 were positively associated with the EQ-5D index value and the SF-12 physical component score in patients with asthma; however, such associations were not observed in patients with COPD. A significant association between severity and plasma concentrations of 25(OH)D3 was found only in patients with COPD. The hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) of plasma 25(OH)D3 concentrations (per 1 ng/mL decrease) for time to first exacerbation was 1.38 (1.10–1.75; p = 0.006) and 0.95 (0.87–1.03; p = 0.179) in patients with COPD and asthma, respectively. Lower concentrations of plasma 25(OH)D3 contributed to lower HR-QOL in patients with asthma, and were associated with severity and risk of future exacerbations in patients with COPD.
- 著者
- Keita Hirai Toshihiro Shirai Yuuka Rachi Sekiko Uehara Megumi Ueda Eiji Nakatani Kunihiko Itoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00476, (Released:2019-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Genetic variations in glucocorticoid-induced transcript 1 (GLCCI1) have been associated with the response to corticosteroid treatment. However, the associations of GLCCI1 polymorphisms or gene expression with the prognosis of asthma and pathophysiological factors related to steroid insensitivity remain unclear. We sought to investigate the associations of GLCCI1, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2), and histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) mRNA expression levels and the GLCCI1 rs37973 polymorphism with asthma severity and future exacerbation in patients with asthma. Subjects included 25 patients with severe asthma and 127 patients with nonsevere asthma. mRNA expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were measured and evaluated as predictors of severe asthma using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The hazard ratios of the mRNA expression levels for time to first exacerbation in the 1-year follow-up period were calculated. GLCCI1, Nrf2, and HDAC2 mRNA expression levels were significantly lower in patients with severe asthma than in patients with nonsevere asthma and could predict severe asthma with an area under the ROC curve of 0.68, 0.71, and 0.65, respectively. In contrast, no relationship was found between the GLCCI1 rs37973 polymorphism and severe asthma. The hazard ratios for asthma exacerbation in patients with low GLCCI1, Nrf2, and HDAC2 mRNA expression levels were 3.24 (95% confidence interval, 1.42–7.40), 3.13 (1.37–7.16), and 2.98 (1.22–7.25), respectively. Patients with severe asthma could be distinguished by lower GLCCI1, Nrf2, and HDAC2 mRNA levels in peripheral blood cells, and all of these gene signatures could predict future asthma exacerbations.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Ishida Michiro Iizuka Yanglan Ou Shunpei Morisawa Ayumu Hirata Yusuke Yagi Kohei Jobu Yasuyo Morita Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.7, pp.1128-1133, 2019-07-01 (Released:2019-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 7
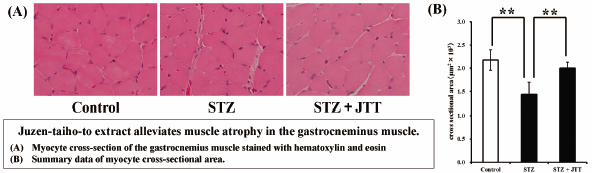
In diabetic patients, skeletal muscle atrophy occurs due to increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Skeletal muscle atrophy reduces the QOL of patients and worsens life prognosis. Therefore, development of preventive therapy for muscle atrophy in hyperglycemic state is eagerly awaited. Juzentaihoto is a medicinal herb that has a function to supplement physical strength, and it is expected to prevent muscle atrophy. To determine the preventive effect of juzentaihoto on muscle atrophy in hyperglycemic state, streptozotocin (STZ) was administered to induce diabetes in mice and the preventive effect of juzentaihoto was evaluated. Mice that received juzentaihoto extract (JTT) showed that the decrease in muscle fiber cross-sectional area in the gastrocnemius muscle was reversed. Additionally, the expression level of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), an inflammatory cytokine, in serum decreased, and that of ubiquitin ligase (atrogin-1, muscle RING-finger protein-1) mRNA in skeletal muscle decreased. An anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 showed increased levels in the serum and increased levels in spleen cell culture supernatant collected from mice that received JTT. JTT had no effect on the blood glucose level. These results suggest that prophylactic administration of JTT to STZ-induced diabetic mice affects immune cells such as in spleen, causing an anti-inflammatory effect and inhibiting excessive activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, to reverse muscle atrophy.
- 著者
- Shinji Oshima Kazuhiko Senoo Akio Negishi Hayato Akimoto Kousuke Ohara Naoko Inoue Shigeru Ohshima Nobuaki Kutsuma Kazuhiko Juni Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.313-322, 2016-03-01 (Released:2016-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 2 6
Article 25-2 of the Japanese Pharmacists’ Act was revised in June 2014, establishing the position of pharmacists as “advisors on the use of pharmaceuticals.” Prior to the Act’s revision, we investigated the perceptions of patients and pharmacists about pharmacists’ roles using a social science methodology. We also examined current opinions and necessary factors for the future growth and development of pharmacists. This questionnaire survey was conducted using an internet method. Patients and pharmacists answered 12 questions. Responses from 529 patients and 338 pharmacists were analyzed. For all items, pharmacists’ awareness of their roles exceeded patients’ awareness of the roles. In this study, the difference between pharmacist and patient awareness was larger than in similar research conducted in the United States. The greatest difference was observed in three items: “Understanding the effects of the drugs the patients are taking” (rate of high ratings: pharmacists 80.2%, patients 37.8%), “Understanding the health changes caused by the drugs dispensed to the patients” (pharmacists 80.2%, patients 28.4%), and “Consciously protecting patients from the adverse effects of drugs” (pharmacists 82.8%, patients 42.2%), indicating role discrepancy. Partition analysis indicated the three factors for a pharmacist to be regarded as a drug therapy or medication specialist: “The patient regards the pharmacist as his/her family or regular pharmacist,” “The pharmacist is making it easy for a patient to talk with him/her” and “The pharmacist is aware of a patient’s use of products other than prescribed drugs, such as over the counter (OTC) medications or health foods and nutritional supplements.” Future efforts are necessary to resolve role discrepancy and implement ongoing monitoring.
- 著者
- Insaf Bahrini Rikinari Hanayama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.6, pp.977-981, 2019-06-01 (Released:2019-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection leads to chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma in 50–80% of the cases. Interferons (IFNs) and the nucleoside analog ribavirin form the basis of the treatment of this infection but are not considered sufficiently effective and cause several side effects. In this study, we developed a novel viral-specific drug delivery method. Enveloped viruses, including HCV, expose an anionic phospholipid, phosphatidylserine (PS), on their surface to mediate their binding and entry into cells for infection. To target such exposed PS on HCV, we developed a chimeric recombinant protein containing human IFN and mouse lactadherin (also known as milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8), which binds with high affinity to PS. The IFN–lactadherin fusion protein showed a high binding affinity toward PS and HCV and consequently blocked viral replication in the infected cells more efficiently than conventional IFN. Overall, these data suggest that conjugation with lactadherin facilitates the delivery of any protein drug to PS-exposing enveloped viruses.
- 著者
- 坂田 眞砂代 河合 透 大隈 邦夫 伊原 博隆 平山 忠一
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, no.11, pp.1065-1068, 1993-11-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 11 12
We describe a method for the removal of endotoxins from various crude antigen solutions originating from gram-negative bacteria using aminated poly(γ-methyl L-glutamate) (PMLG) spherical particles. The aminated PMLG adsorbents showed high affinity for various purified endotoxins at an ionic strength of μ=0.1. The endotoxin-adsorbing capacity of the adsorbent increased with increase in the amino-group content of the adsorbent. The adsorbent (3.2 meq/g amino-group content) showed the highest affinity for endotoxin at ionic strengths ranging from μ=0.025-0.8. The adsorption of Bordetella pertussis antigen to the adsorbent decreased with increasing amino-group content of the adsorbent at an ionic strength of μ=0.2. The adsorption of B. bronchiseptica protein to the adsorbent increased with increasing amino-group content of the adsorbent, but decreased with increasing ionic strength. The adsorbent (3.2 meq/g of amino-group content) selectively reduced endotoxin in crude antigen solutions originating from gram-negative bacteria, B. pertussis, B. bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida, even at a high ionic strength (μ=0.2-0.4) without affecting the recovery of the protective antigens.
- 著者
- Qiaomei Dai Meiqiao Wang Yaozhang Li Ji Li
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00083, (Released:2019-04-23)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 11
To study the role of asarinin on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and its treatment mechanism on dendritic cells (DCs) and T cells. Before the onset of arthritis, asarinin were given orally to CIA mouse. Macroscopic scoring and micrometer caliper measurement were used to assess arthritis. The occurrence of cartilage destruction and bone erosion were assessed by histology of knee. Sandwich ELISA and PCR were used to assess the level of cytokines in hindpaw and arthritic joint. The CD11c MicroBeads were employed to isolate CD11c+ cells from the spleen. Quantitative PCR was used to determine DCs surface molecules of spleen. Macroscopic score and the frequency of arthritis were inhibited by asarinin. Swelling of hindpaws, inflammatory cell infiltration in the synovium, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion were delayed with asarinin. Asarinin treatment suppressed the expression of Th1 cytokines and increased the levels of Th2 cytokines (IL-10), TGF-β and Foxp3 in the synovium and hindpaw, however T-bet mRNA levels in synovium decreased. Lower expression of TLR9 and NF-kB were found in DCs after asarinin treatment. There was no difference in the expression of ICAM-1, OX40-L, and 4-1BBL in spleen DCs between the asarinin group and model control group. Asarinin can treat CIA. TLR9/NF-κB pathway may be involved in the asarinin treatment of CIA by skewing the balance of Th1/Th2/Treg to a Th2 type.
- 著者
- Masahiko Imai Hiromasa Yokoe Masayoshi Tsubuki Noriko Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b18-01002, (Released:2019-04-12)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 16
Cancer is the leading cause of death and there is a particularly pressing need to develop effective treatments for breast and prostate cancer. In the current study, we show the inhibitory effects of cinnamic acid derivatives, including caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE, 1), on the growth of breast and prostate cancer cells. Among the compounds examined, 3,4,5-trihydroxycinnamic acid decyl ester (6) showed the most potent inhibition of cancer cell growth by the induction of apoptosis. Compound 6 could be a new anti-cancer agent for use against breast and prostate cancer.
- 著者
- Weibin Du Chiharu Fukano Mari Yonemoto Tomokazu Matsuoka Keisuke Masuyama Katsuyo Ohashi-Doi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.4, pp.601-606, 2019-04-01 (Released:2019-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy (SCIT) with non-standardized house dust (HD) extracts has been used in Japan since 1963 for house dust mite (HDM)-allergic patients. Since the potencies of HD extracts are unknown, the allergenic potency of HD extracts was examined by comparing with a standardized HDM allergen extracts. The major allergen content of HDM in the extracts was measured using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The immunoglobulin E (IgE) inhibitory activities of the extracts were measured by a competitive ELISA. The extract concentrations giving 50% inhibition of IgE binding (log10 IC50) were determined from dose–response curves and defined as inhibitory activities. A linear regression line was constructed from the log10 IC50 values of the standardized HDM extract to interpolate the relative potency of the HD extract with strength of 1 : 10 w/v (HD 1 : 10). The amounts of major allergens (Der f 1, Der p 1 and Der 2) were 116.3 µg/mL in the HDM allergen extract (100000 Japanese Allergy Units [JAU]/mL) and 0.77 µg/mL in the HD 1 : 10. The inhibitory activity (log10 IC50 values) of HD 1 : 10 was 2.389 ± 0.078, indicating the allergenic potency was between 200 and 2000 JAU/mL. Based on regression analysis (R2 >0.99), the allergenic potency of HD 1 : 10 was estimated to be 842 ± 128 JAU/mL. The present study determined the major allergen content of HD extract, which contributes to its allergenic potency. The allergenic potency of HD 1 : 10 was ca. 100-fold less than that of HDM allergen extract.
- 著者
- Kazunari Iwao Rushiana Tokie Kawai Masako Oda Hiroshi Saitoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.9, pp.1566-1571, 2017-09-01 (Released:2017-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The objective of this study was to evaluate the interactions between various drugs and aojiru (green juice), a popular health food in Japan, using a simple centrifugation method. The mixture of drug solution and aojiru suspension was gently shaken and centrifuged. The drug concentration in the supernatant fluid was then determined by HPLC. The concentration of rhodamine 123 (Rho-123), a model compound, in the supernatant fluid significantly decreased after mixing with aojiru, indicating extensive binding of Rho-123 to the insoluble components of aojiru. When administered into rat small intestinal loops together with aojiru, the plasma Rho-123 concentrations became much smaller than those when administered alone. This result strongly suggested that a strong interaction observed in vitro was well reflected in modulated absorption. Among seven drugs tested, chlorpromazine and imipramine exerted binding properties to aojiru similar to or greater than Rho-123. As a small part of both Rho-123 and imipramine was released when the aojiru precipitate was resuspended, their binding to aojiru was considered to be tight. The binding of diltiazem, fexofenadine, glibenclamide, metformin, and norfloxacin to aojiru was much weaker or almost negligible compared with that of chlorpromazine and imipramine. The present results suggest that aojiru can decrease the intestinal absorption of some clinically relevant drugs through tight binding in the small intestine and that the present centrifugation method is useful for predicting in vivo interactions between drugs and aojiru.