- 著者
- Masatomo Miura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.5, pp.645-654, 2015-05-01 (Released:2015-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 77
- 被引用文献数
- 48 122
Imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib are tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that have become first-line treatments for Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). According to European LeukemiaNet recommendations, the clinical response of CML patients receiving TKI therapy should be evaluated after 3, 6, and 12 months. For patients not achieving a satisfactory response within 3 months, the mean plasma concentration for the three months of TKI administration must be considered. In TKI therapy for CML patients, therapeutic drug monitoring is a new strategy for dosage optimization to obtain a faster and more effective clinical response. The imatinib plasma trough concentration (C0) should be set above 1000 ng/mL to obtain a response and below 3000 ng/mL to avoid serious adverse events such as neutropenia. For patients with a UGT1A1*6/*6, *6/*28, or *28/*28 genotype initially administered 300–400 mg/d, a target nilotinib C0 of 500 ng/mL is recommended to prevent elevation of bilirubin levels, whereas for patients with the UGT1A1*1 allele initially administered 600 mg/d, a target nilotinib C0 of 800 ng/mL is recommended. For dasatinib, it is recommended that a higher Cmax or C2 (above 50 ng/mL) to obtain a clinical response and a lower C0 (less than 2.5 ng/mL) to avoid pleural effusion be maintained by once daily administration of dasatinib. Although at present clinicians consider the next pharmacotherapy from clinical responses (efficacy/toxicity) obtained by a fixed dosage of TKI, the TKI dosage should be adjusted based on target plasma concentrations to maximize the efficacy and to minimize the incidence of adverse events.
- 著者
- Shiho Nagata Tetsuro Marunouchi Kouichi Tanonaka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b18-00785, (Released:2019-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 16
Protein quality control (PQC) in the heart plays an important role to maintain cellular protein homeostasis. Impairment of PQC may cause the development of heart failure. It is well known that histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an essential enzyme for regulating the cellular PQC response. In this study, we aimed at examining the association between HDAC6 and the chaperone system and the effects of HDAC6 inhibition in the development of heart failure following myocardial infarction (MI). MI was induced by coronary artery ligation. Coronary artery-ligated and sham-operated rats were divided into groups that were orally administered suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) or vehicle from the 2nd to 8th week after the operation. The cardiac function and protein expression levels in the viable left ventricle were analyzed by echocardiography, western blotting, and immunohistochemistry at the 2nd and 8th weeks after the operation. The deacetylase activity of HDAC6 was markedly elevated during the development of heart failure after MI. In the failing heart, a decrease in heat-shock protein (HSP) contents and an accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins were observed, indicating PQC dysfunction. Inhibition of HDAC6 activity by SAHA treatment enhanced the translocation of heat-shock transcription factor 1 to the nucleus and induced the expression of HSP, resulting in maintenance of cellular protein homeostasis. The cardiac pump function after MI was also improved by SAHA administration. Our findings suggest that inhibition of HDAC6 activity is a novel approach for the treatment of heart failure following MI.
2 0 0 0 OA Attenuation of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor-Stimulated Signaling via S-Nitrosylation
- 著者
- Kengo Nakahara Kana Fujikawa Hideki Hiraoka Ikuko Miyazaki Masato Asanuma Akihiro Ito Nobumasa Takasugi Takashi Uehara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.6, pp.1044-1047, 2019-06-01 (Released:2019-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 12
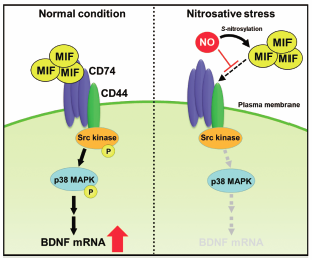
Nitric oxide (NO) is a key signaling molecule that has various effects via S-nitrosylation, a reversible post-translational modification that affects the enzymatic activity, localization, and metabolism of target proteins. As chronic nitrosative stress correlates with neurodegeneration, the targets have received focused attention. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) plays a pivotal role in the induction of gene expression to control inflammatory responses. MIF acts as a ligand for CD74 receptor and activates the Src-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade. MIF also elevates the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which contributes to the viability of neurons. Here, we show that MIF is S-nitrosylated by a physiological NO donor. Interestingly, the induction of S-nitrosylation resulted in a loss of MIF activity following stimulation of the Src and p38 MAPK signaling pathways and the induction of BDNF expression. Our results shed light on the pathogenic mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- 著者
- Yukio Suga Mayako Uchida Shinya Suzuki Hideki Sugawara Kazuhiro Torigoe Akihiko Futamura Yoshihiro Uesawa Takayuki Nakagawa Hisamitsu Takase
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.5, pp.801-806, 2019-05-01 (Released:2019-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 10
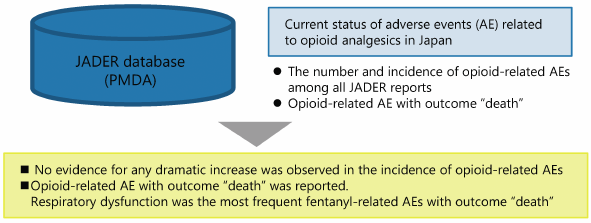
Opioid analgesics have greatly contributed to the advancement of pain management. However, although opioids have been appropriately used in Japan, they rarely induce serious adverse events, such as respiratory depression. The present study aimed to investigate the temporal changes in the occurrence of opioid-related adverse events and deaths between 2004 and 2017 in Japan using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database. We analyzed the following points using data extracted from JADER website: 1) temporal changes in the number and proportion of opioid-related adverse event reports; 2) temporal changes in the number of morphine-, oxycodone-, and fentanyl-related adverse event reports per annual consumption; and 3) cases in which the reported outcome following opioid-related adverse events was death. Our results showed no dramatic changes in the overall incidence of opioid-related adverse events, despite the temporal changes in the annual consumption and shared component of each opioid during the survey period. However, the number and rate of fentanyl-related adverse events and their outcome “death” increased since 2010, being the highest among all adverse event including those related to morphine and oxycodone. Outcome “death” by fentanyl-related adverse events was caused mainly due to respiratory depression. These findings suggest that, although opioid-related adverse events can be controlled through proper monitoring and management by medical personnel in Japan, extra caution should be continuously paid for the rare but serious fentanyl-induced adverse events.
- 著者
- Yuko Yamakage Hitomi Tsuiji Takao Kohno Himari Ogino Takashi Saito Takaomi C. Saido Mitsuharu Hattori
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.3, pp.354-356, 2019-03-01 (Released:2019-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 8
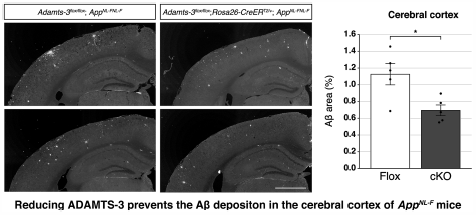
Reelin is a secreted protein that antagonizes the deposition and toxicity of amyloid β peptide (Aβ). Therefore, augmentation of Reelin activity may ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We have recently reported that a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 3 (ADAMTS-3) cleaves and inactivates Reelin in the mouse brain. In the present study, we investigated the effect of reducing ADAMTS-3 on deposition of Aβ by crossbreeding drug-inducible ADAMTS-3 conditional knock-out (cKO) mice with “next-generation” AD model mice. We found that reducing ADAMTS-3 inhibited deposition of Aβ significantly in AppNL-F mice, which produce human wild-type Aβ. On the other hand, reducing ADAMTS-3 had no effect in AppNL-G-F mice, which produce the Arctic mutant Aβ (E22G) that forms protofibrils more efficiently than does wild-type Aβ. Thus, the findings suggest that the administration of an inhibitor against ADAMTS-3 will prevent the progression of AD pathology caused by deposition of wild-type Aβ.
- 著者
- Keiko MORITO Toshiharu HIROSE Junei KINJO Tomoki HIRAKAWA Masafumi OKAWA Toshihiro NOHARA Sumito OGAWA Satoshi INOUE Masami MURAMATSU Yukito MASAMUNE
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.4, pp.351-356, 2001 (Released:2002-04-26)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 391 473
The human estrogen receptor (hER) exists as two subtypes, hER α and hER β, that differ in the C-terminal ligand-binding domain and in the N-terminal transactivation domain. In this study, we investigated the estrogenic activities of soy isoflavones after digestion with enteric bacteria in competition binding assays with hER α or hER β protein, and in a gene expression assay using a yeast system. The estrogenic activities of these isoflavones were also investigated by the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Isoflavone glycoside binds weakly to both receptors and estrogen receptor-dependent transcriptional expression is poor. The aglycones bind more strongly to hER β than to hER α. The binding affinities of genistein, dihydrogenistein and equol are comparable to the binding affinity of 17 β-estradiol. Equol induces transcription most strongly with hER α and hER β. The concentration required for maximal gene expression is much higher than expected from the binding affinities of the compounds, and the maximal activity induced by these compounds is about half the activity of 17 β-estradiol. Although genistin binds more weakly to the receptors and induces transcription less than does genistein, it stimulates the growth of MCF-7 cells more strongly than does genistein.
- 著者
- Yasushi Hori Manami Fujisawa Kenji Shimada Akira Oda Shinichiro Katsuyama Keiji Wada
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.4, pp.486-491, 2004 (Released:2004-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 11 32
We have established a new method of HPLC analysis for the rapid separation from human serum and the quantification of 4-O-methylpyridoxine (MPN), which is contained in Ginkgo biloba seeds, and which, when consumed in large amounts, causes vomiting and convulsions. As a result of using IPCC-MS3 (GL Science, Tokyo, Japan), an ion-pair reagent, in the mobile phase, we succeeded in separating MPN in the deproteinized serum sample which was introduced directly onto the reverse-phase HPLC column. For the calibration curve of MPN standard solution, prepared with fluorescence detection at an excitation wavelength of 290 nm and an emission wavelength of 400 nm, a good linear relationship was obtained within the HPLC injection range of 10 ng—10 pg (in terms of the injected sample concentration, range: 1.0 μg/ml—1 ng/ml), allowing the detection of minute amounts, with the limit of detection (concentration of injected sample: 500 pg/ml) being 5 pg. In addition, when MPN solution was added to human reference serum to give a concentration of 0.002 μg/ml, the mean recovery rate was 92.5%, with RSD=7.09% (n=5). The time required for one analysis using this method is approximately 30 min, and thus it offers the advantages of greater speed and superior analytical sensitivity over the conventional methods, which require solid-phase extraction. We employed our new method to determine both the serum levels of MPN in 5 patients with Ginkgo biloba seed poisoning and the levels of free-form MPN in such seeds obtained in 8 regions of Japan.
- 著者
- Tomohito Tsukamoto Eiko Sakai Shunsuke Iizuka Marcos Taracena-Gándara Fuminori Sakurai Hiroyuki Mizuguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.7, pp.1089-1095, 2018-07-01 (Released:2018-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 16
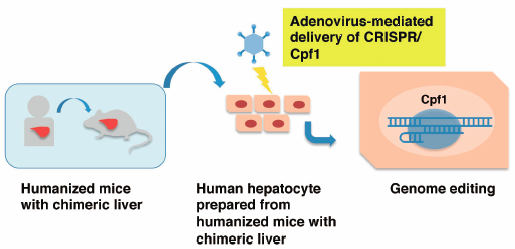
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein (Cas) 9 system is now widely used as a genome editing tool. CRISPR-associated endonuclease in Prevotella and Francisella 1 (Cpf1) is a recently discovered Cas endonuclease that is designable and highly specific with efficiencies comparable to those of Cas9. Here we generated the adenovirus (Ad) vector carrying an Acidaminococcus sp. Cpf1 (AsCpf1) expression cassette (Ad-AsCpf1) for the first time. Ad-AsCpf1 was applied to primary human hepatocytes prepared from humanized mice with chimeric liver in combination with the Ad vector expressing the guide RNA (gRNA) directed to the Adeno-associated virus integration site 1 (AAVS1) region. The mutation rates were estimated by T7 endonuclease I assay around 12% of insertion/deletion (indel). Furthermore, the transduced human hepatocytes were viable (ca. 60%) at two weeks post transduction. These observations suggest that the Ad vector-mediated delivery of the CRISPR/AsCpf1 system provides a useful tool for genome manipulation of human hepatocytes.
- 著者
- Mitsuyoshi Okita Yuki Yayoshi Kousuke Ohara Akio Negishi Hayato Akimoto Naoko Inoue Sachihiko Numajiri Shigeru Ohshima Seiichi Honma Shinji Oshima Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.10, pp.1730-1738, 2017-10-01 (Released:2017-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 3
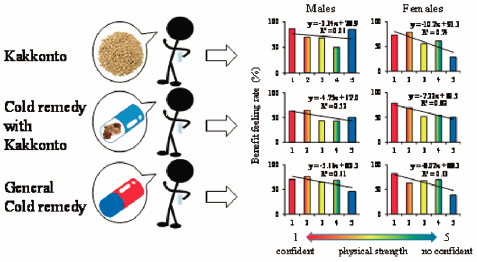
Kakkonto (KK), a traditional Japanese Kampo formulation for cold and flu, is generally sold as an OTC pharmaceuticals used for self-medication. Kampo formulations should be used according to the Sho-symptoms of Kampo medicine. These symptoms refer to the subjective symptoms themselves. Although with OTC pharmaceuticals, this is often not the case. We surveyed the relationship of agreement of Sho with the benefit feeling rate (BFR) of patients who took KK (n=555), cold remedies with KK (CK, n=315), and general cold remedies (GC, n=539) using internet research. BFR of a faster recovery was greater in participants who took the medication early and who had confidence in their physical strength in all treatment groups. BFR was significantly higher in the GC group than in the KK group for patients with headache, runny nose, blocked nose, sneezing, and cough. BFR was also significantly higher in the GC group than in the CK group for headache (males) and cough (females). BFR was the highest in the KK group for stiff shoulders. All cold remedies were more effective when taken early, and the larger the number of Sho that a patient had, the greater the BFR increased. Therefore, a cold remedy is expected to be most effective when there are many cold symptoms and when it is taken at an early stage of the common cold.
- 著者
- Mahitab Elsayed Daisuke Kobayashi Toshio Kubota Naoya Matsunaga Ryusei Murata Yuko Yoshizawa Natsuki Watanabe Tohru Matsuura Yuya Tsurudome Takashi Ogino Shigehiro Ohdo Takao Shimazoe
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.8, pp.1238-1246, 2016-08-01 (Released:2016-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 64
- 被引用文献数
- 2 22
Bisphosphonates and statins are known to have antitumor activities against different types of cancer cell lines. In the present study, we investigated the antiproliferative effects of the combination of zoledronic acid (ZOL), a bisphophosphonate, and fluvastatin (FLU), a statin, in vitro on two types of human pancreatic cancer cell lines, Mia PaCa-2 and Suit-2. The pancreatic cancer cell lines were treated with ZOL and FLU both individually and in combination to evaluate their antiproliferative effects using WST-8 cell proliferation assay. In this study, we demonstrated a potent synergistic antiproliferative effect of both drugs when used in combination in both cell lines. Moreover, we studied the molecular mechanism behind this synergistic effect, which was inhibited by the addition of the mevalonate pathway products, farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Furthermore, we aimed to determine the effect of ZOL and FLU combination on RhoA and Ras guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP)-proteins. The combination induced a marked accumulation in RhoA and unprenylated Ras. GGPP and FPP reversed the increase in the amount of both proteins. These results indicated that the combination treatment impaired RhoA and Ras signaling pathway by the inhibition of geranylgeranylation and/or farnesylation. This study provides a potentially effective approach for the treatment of pancreatic cancer using a combination treatment of ZOL and FLU.
- 著者
- Naofumi Seira Naoki Yanagisawa Akiko Suganami Takuya Honda Makiko Wasai John W. Regan Keijo Fukushima Naoto Yamaguchi Yutaka Tamura Takayoshi Arai Toshihiko Murayama Hiromichi Fujino
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.10, pp.1806-1812, 2017-10-01 (Released:2017-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3
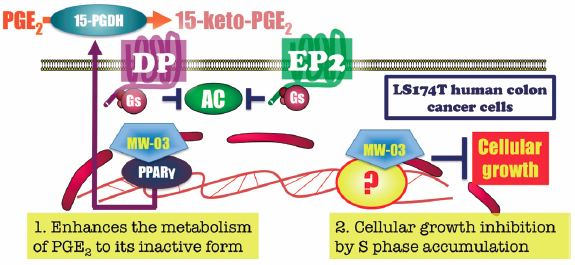
Increases in the expression of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) are widely known to be involved in aberrant growth in the early stage of colon cancer development. We herein demonstrated that the novel indole compound MW-03 reduced PGE2-induced cAMP formation by catalization to an inactive metabolite by inducing 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase through the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ. MW-03 also inhibited colon cancer cell growth by arresting the cell cycle at the S phase. Although the target of MW-03 for cell cycle inhibition has not yet been identified, these dual anti-cancer effects of MW-03 itself and/or its leading compound(s) on colon cancer cells may reduce colon cancer development and, thus, have potential as a novel treatment for the early stage of this disease.
- 著者
- Hiroki Sasaki Yoichi Sunagawa Kenji Takahashi Atsushi Imaizumi Hiroyuki Fukuda Tadashi Hashimoto Hiromichi Wada Yasufumi Katanasaka Hideaki Kakeya Masatoshi Fujita Koji Hasegawa Tatsuya Morimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.5, pp.660-665, 2011-05-01 (Released:2011-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 68 334
Curcumin is a polyphenol that is commonly used for its perceived health benefits. However, the absorption efficacy of curcumin is too low to exhibit beneficial effects. We have successfully developed a highly absorptive curcumin dispersed with colloidal nano-particles, and named it THERACURMIN. The absorption efficacy of THERACURMIN was investigated and compared with that of curcumin powder. The area under the blood concentration–time curve (AUC) after the oral administration of THERACURMIN was found to be more than 40-fold higher than that of curcumin powder in rats. Then, healthy human volunteers were administered orally 30 mg of THERACURMIN or curcumin powder. The AUC of THERACURMIN was 27-fold higher than that of curcumin powder. In addition, THERACURMIN exhibited an inhibitory action against alcohol intoxication after drinking in humans, as evidenced by the reduced acetaldehyde concentration of the blood. These findings demonstrate that THERACURMIN shows a much higher bioavailability than currently available preparations. Thus, THERACURMIN may be useful to exert clinical benefits in humans at a lower dosage.
- 著者
- Takeo Yasu Kenji Momo Shunsuke Kobayashi Seiichirou Kuroda Arinobu Tojo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b17-00806, (Released:2017-12-06)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 16
Ponatinib, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor marketed in 2016, is a key drug used for treating chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This study aimed to develop a simple method for determining plasma ponatinib concentration. The analysis required extraction of a 400-μL sample of plasma and precipitation of proteins using an Oasis HLB cartridge. Ponatinib and bosutinib, which is used as an internal standard, were separated by HPLC using a mobile phase of acetonitrile: 0.037 mol/L KH2PO4 (pH 4.5) (39:61, v/v) on a Capcell Pack C18 MG II (250 mm × 4.6 mm) monitored at 250 nm, with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. This assay method was then used for determining plasma ponatinib concentration in a 42-year-old man treated with ponatinib at 15 mg/day. The calibration curve was found to be linear for the plasma concentration range of 5–250 ng/mL with a regression coefficient (r2) of 0.9999. The coefficients of intra-day and inter-day validation under these concentrations were 2.1–6.0% and 4.5–8.0%, respectively. The assay accuracy was -1.5–9.0%, and the recovery was greater than 86%. The plasma concentration of the patient at 2.5 and 3 h after 15 mg ponatinib administration was 43.6 ng/mL and 49.3 ng/mL, respectively. This method of HPLC equipped with UV detection for determining plasma ponatinib concentration has several advantages, such as simplicity and applicability to routine therapeutic drug monitoring at hospital laboratories.
2 0 0 0 OA Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori Motility by (+)-Syringaresinol from Unripe Japanese Apricot
- 著者
- Mitsuo Miyazawa Hirotoshi Utsunomiya Ken-ichi Inada Tomoki Yamada Yoshiharu Okuno Harunari Tanaka Masae Tatematsu
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.1, pp.172-173, 2006 (Released:2006-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 24 56
A methanol extract from unripe Japanese apricot showed inhibitory activity of Helicobacter pylori motility. Inhibitory compound 1 was isolated and identified as (+)-syringaresinol (1) by spectoroscopic means. (+)-Syringaresinol (1) inhibited >90% of the H. pylori motility at a concentration of 500 μg/ml and the IC50 value was 50 μg/ml.
2 0 0 0 OA SELEX-Based Screening of Exosome-Tropic RNA
- 著者
- Takuma Yamashita Haruka Shinotsuka Yuki Takahashi Kana Kato Makiya Nishikawa Yoshinobu Takakura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.12, pp.2140-2145, 2017-12-01 (Released:2017-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 9
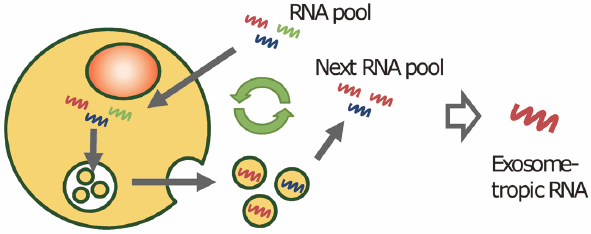
Cell-derived nanosized vesicles or exosomes are expected to become delivery carriers for functional RNAs, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA). A method to efficiently load functional RNAs into exosomes is required for the development of exosome-based delivery carriers of functional RNAs. However, there is no method to find exosome-tropic exogenous RNA sequences. In this study, we used a systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) method to screen exosome-tropic RNAs that can be used to load functional RNAs into exosomes by conjugation. Pooled single stranded 80-base RNAs, each of which contains a randomized 40-base sequence, were transfected into B16-BL6 murine melanoma cells and exosomes were collected from the cells. RNAs extracted from the exosomes were subjected to next round of SELEX. Cloning and sequencing of RNAs in SELEX-screened RNA pools showed that 29 of 56 clones had a typical RNA sequence. The sequence found by SELEX was enriched in exosomes after transfection to B16-BL6 cells. The results show that the SELEX-based method can be used for screening of exosome-tropic RNAs.
- 著者
- Osamu Nakajima Tomoko Nishimaki-Mogami Kazunari Kondo
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.11, pp.1876-1880, 2016-11-01 (Released:2016-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Genome editing has undergone rapid development during the last three years. It is anticipated that genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for food purposes will be widely produced using the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat/Cas9 (CRISPR)/Cas9 system in the near future. However, the Cas9 gene may then enter the genomes of GMOs for food if the breeding process is not strictly managed, which could lead to the Cas9 protein or associated peptides being produced within these organisms. A variety of peptides could theoretically be produced from the Cas9 gene by using open reading frames different from that of Cas9 in the GMOs. In this study, Cas9 and the peptides potentially encoded by Cas9 genes were studied regarding their immunogenicity, in terms of the digestibility of Cas9 and the homology of the peptides to food allergens. First, the digestibility and thermal stability of Cas9 were studied. Digestibility was tested with natural or heat-denatured Cas9 in simulated gastric fluid in vitro. The two types of Cas9 were digested rapidly. Cas9 was also gradually degraded during heat treatment. Second, the peptides potentially encoded by Cas9 genes were examined for their homology to food allergens. Specifically, an 8-mer exact match search and a sliding 80-mer window search were performed using allergen databases. One of the peptides was found to have homology with a food allergen.
- 著者
- Yugo Chisaki Shoki Aoji Yoshitaka Yano
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.6, pp.824-829, 2017-06-01 (Released:2017-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 17
In general, the risk of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) is higher in elderly patients than in younger patients. In this study, we performed a comprehensive assessment of the risks of possible drug–ADR combinations in elderly patients using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database of the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA, Japan) using the reporting odds ratio (ROR) as an index. Data recorded from April 2004 to September 2015 in the JADER database were downloaded from the PMDA website. The patients were classified into younger (≤69 years old) and elderly (≥70 years old) groups. The ROR and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated for all combinations of drugs and ADRs for which there were three or more reports in the database, focusing particularly on the combinations where more than 100 cases had been reported in elderly and younger patients. The most frequently reported drug–ADR combination was methotrexate with interstitial lung disease (646 cases). The combination with the highest ROR was methotrexate with lymphoproliferative disorder (ROR: 484.6, 95% CI: 334.1–702.9). In total, 27 drug–ADR combinations were found to have high risk in elderly patients. In conclusion, the findings of this comprehensive assessment of drug–ADR combinations using the JADER database will be valuable for updating the ADR risks for elderly patients in clinical setting.
- 著者
- Keiko Unno Hiroshi Yamada Kazuaki Iguchi Hitoshi Ishida Yasunori Iwao Akio Morita Yoriyuki Nakamura
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.6, pp.902-909, 2017-06-01 (Released:2017-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 19
Theanine, an amino acid in tea, has significant anti-stress effects on animals and humans. However, the effect of theanine was blocked by caffeine and gallate-type catechins, which are the main components in tea. We examined the anti-stress effect of green tea with lowered caffeine, low-caffeine green tea, on humans. The study design was a single-blind group comparison and participants (n=20) were randomly assigned to low-caffeine or placebo tea groups. These teas (≥500 mL/d), which were eluted with room temperature water, were taken from 1 week prior to pharmacy practice and continued for 10 d in the practice period. The participants ingested theanine (ca. 15 mg/d) in low-caffeine green tea. To assess the anxiety of participants, the state-trait anxiety inventory test was used before pharmacy practice. The subjective stress of students was significantly lower in the low-caffeine-group than in the placebo-group during pharmacy practice. The level of salivary α-amylase activity, a stress marker, increased significantly after daily pharmacy practice in the placebo-group but not in the low-caffeine-group. These results suggested that the ingestion of low-caffeine green tea suppressed the excessive stress response of students. This study was registered at the University Hospital Medical Information Network (ID No. UMIN14942).
- 著者
- Ji-hoon Kim Chung-Oui Hong Yun-chang Koo Hee-Don Choi Kwang-Won Lee
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.2, pp.260-264, 2012-02-01 (Released:2012-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 8 37
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have been reported to exhibit a variety of biological effects including anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activities. The extent of an in vitro glycation reaction mixture of collagen and glycolaldehyde was assayed to investigate the inhibition of glycolaldehye-derived advanced glycation end products (glycol-AGEs) formation with GNPs in collagen, which is a major protein component of the human dermis. GNP-treated collagen showed significantly less glycation (56.3±4.2%) than an untreated glycation control. Moreover, GNP-treated glycation in a collagen lattice model significantly decreased the AGEs distribution in the model system. Taken together, these results suggest that GNPs have the potential for use in the prevention of glycation-induced skin aging.
- 著者
- Naho Maruyama Shigeru Tansho-Nagakawa Chizuru Miyazaki Kazuyuki Shimomura Yasuo Ono Shigeru Abe
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.161-168, 2017-02-01 (Released:2017-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 14
Hydrosol prepared from the flowers of Rosa damascena (rose water) has been traditionally used for various health-related issues, including skin troubles such as erythema, itchiness, swelling. For the care of these skin troubles caused by microbial infection, both antimicrobial and antiinflammatory effects are required. Here, we investigated the effects of rose water on the growth of Candida albicans and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which cause skin infections, and on the function of neutrophils, which play a major role in the regulation of inflammatory reactions. To assess its modulatory effects on neutrophils, the effects of rose water against neutrophil adhesion response were evaluated. Rose water inhibited mycelial growth of C. albicans at a concentration of ca. 2.2%, and reduced viability of MRSA within 1 h. Rose water suppressed neutrophil activation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLP) at 5–15%. It also reduced the LPS- and TNF-α-induced cell surface expression of the adhesion-related molecule, cluster of differentiation (CD) 11b, but did not affect the migratory capacity of neutrophils with or without chemoattractant. These results suggest that rose water may reduce the pathogenicity of microbes, and attenuate neutrophil stimulation, which is involved in inflammatory responses. These findings suggest that rose water has a potential effect to inhibit skin inflammation caused by microbes.