- 著者
- Kimiko Tomioka Midori Shima Keigo Saeki
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, pp.18, 2022 (Released:2022-05-03)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background: Community health activities by public health nurses (PHNs) are known to improve lifestyle habits of local residents, and may encourage the practice of infectious disease prevention behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. We investigated the association between prefecture-level COVID-19 incidence rate and the number of PHNs per population in Japan, by the COVID-19 variant type.Methods: Our data were based on government surveys where prefectural-level data are accessible to the public. The outcome variable was the COVID-19 incidence rate (i.e., the cumulative number of COVID-19 cases per 100,000 population for each variant type in 47 prefectures). The explanatory variable was the number of PHNs per 100,000 population by prefecture. Covariates included socioeconomic factors, regional characteristics, healthcare resources, and health behaviors. The generalized estimating equations of the multivariable Poisson regression models were used to estimate adjusted incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for the COVID-19 cases. We performed stratified analyses by variant type (i.e., wild type, alpha variant, and delta variant).Results: A total of 1,705,224 confirmed COVID-19 cases (1351.6 per 100,000 population) in Japan were reported as of September 30, 2021. The number of PHNs per 100,000 population in Japan was 41.9. Multivariable Poisson regression models showed that a lower number of PHNs per population was associated with higher IRR of COVID-19. Among all COVID-19 cases, compared to the highest quintile group of the number of PHNs per population, the adjusted IRR of the lowest quintile group was consistently significant in the models adjusting for socioeconomic factors (IRR: 3.76, 95% CI: 2.55–5.54), regional characteristics (1.73, 1.28–2.34), healthcare resources (3.88, 2.45–6.16), and health behaviors (2.17, 1.39–3.37). These significant associations were unaffected by the variant type of COVID-19.Conclusion: We found that the COVID-19 incidence rate was higher in prefectures with fewer PHNs per population, regardless of the COVID-19 variant type. By increasing the number of PHNs, it may be possible to contain the spread of COVID-19 in Japan and provide an effective human resource to combat emerging infectious diseases in the future.
- 著者
- Mina Hayama-Terada Yuri Aochi Satoyo Ikehara Takashi Kimura Kazumasa Yamagishi Takuyo Sato Hiroyasu Iso
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.12, 2023 (Released:2023-02-03)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Background: Few prospective studies have investigated the association between paternal occupational exposures and risk of infant congenital heart defects (CHDs). We investigated the associations between paternal occupational exposures, frequency of use, and concurrent or sequential exposure to a mixture of compounds and the risk of infant CHDs.Methods: Our study examined 28,866 participants in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) associated with paternal occupational exposures during the 3 months until pregnancy was noticed after adjustment for potential confounding factors of the infant CHDs. CHD diagnosis was ascertained from medical record.Results: In total, 175 were diagnosed with infant CHDs. The number of fathers who were exposed to the following substances at least once a month were: 11,533 for photo copying machine/laser printer, 10,326 for permanent marker, 8,226 for soluble paint/inkjet printer, 6,188 for kerosene/petroleum/benzene/gasoline, 4,173 for organic solvents, 3,433 for chlorine bleach/germicide, 2,962 for engine oil, 2,931 for insecticide, 2,460 for medical sterilizing disinfectant, 1,786 for welding fumes, 1,614 for dyestuffs, 1,247 for any products containing lead-like solder, 986 for herbicide, 919 for radiation/radioactive substances/isotopes, 837 for lead-free solder, 341 for microbes, 319 for formalin/formaldehyde, 301 for agricultural chemical not listed above or unidentified, 196 for general anesthetic for surgery at hospital, 171 for anti-cancer drug, 147 for chromium/arsenic/cadmium, 88 for mercury and 833 for other chemical substances. Paternal occupational exposure regularly to photo copying machine or laser printer and soluble paint/inkjet printer were associated with higher risks of infant CHDs: the adjusted ORs (95%CIs) were 1.38 (1.00–1.91) and 1.60 (1.08–2.37), respectively. The higher risks were also observed for occasional exposure to engine oil, any products containing lead-like solder lead-free solder, and microbes; the adjusted ORs (95%CIs) were 1.68 (1.02–2.77), 2.03 (1.06–3.88), 3.45 (1.85–6.43), and 4.51, (1.63–12.49), respectively.Conclusions: Periconceptional paternal occupational exposure was associated with a higher risk of infant CHDs. Further studies using biomarkers of the association between paternal occupational exposure and infant CHDs are warranted.
- 著者
- Daisuke Hori Tsukasa Takahashi Yudai Kaneda Akihiko Ozaki Takahiro Tabuchi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.10, 2023 (Released:2023-02-02)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Background: Before the COVID-19 vaccine became available, many Japanese people were undecided about whether or not to receive them. Their decisions were keys to achieving herd immunity. The impact of the type of information source on the COVID-19 vaccine uptake decision-making process remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the association between information source usage on COVID-19 and subsequent vaccine uptake status among those who have yet to decide whether to receive vaccines from non-prioritized people for vaccination.Methods: Prospective cohort online self-administered surveys were conducted in February 2021 (T1), before the start of the mass vaccination program, and September–October 2021 (T2), when the vaccines were available to all citizens. The survey’s target population was registered monitors of an Internet research company. Participants who answered “I want to get vaccinated after waiting to see how it goes.” at T1 were eligible for analysis. The outcome variable was the COVID-19 vaccine uptake status in T2, and the predictors were 20 types of information sources, categorized based on people (family members, etc.), institutions (governments, etc.), or media (TV news, etc.). Adjusted odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals were estimated using logistic regression adjusted for possible confounders.Results: The 5,139 respondents, mean age and standard deviation was 42.8 ± 12.5, 55.7% female, were eligible for analysis. 85.7% completed vaccination (including reserved/intended people) in T2. In the multivariate logistic analysis, odds ratios (95% confidence interval) for vaccine uptake were 1.49 (1.18–1.89) for workplaces/schools, 1.81 (1.33–2.47) for LINE, 0.69 (0.55–0.86) for Internet news and 0.62 (0.48–0.82) for video sharing sites.Conclusions: The type of information source usage played an important role in the decision to vaccinate against COVID-19. Although caution is needed in interpreting the results, obtaining information from workplaces/schools and LINE was influential in promoting immunization.
27 0 0 0 OA Early prenatal exposure to air pollutants and congenital heart disease: a nested case-control study
- 著者
- Zhao Ma Weiqin Li Jicui Yang Yijuan Qiao Xue Cao Han Ge Yue Wang Hongyan Liu Naijun Tang Xueli Yang Junhong Leng
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.4, 2023 (Released:2023-01-13)
- 参考文献数
- 56
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background: Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most common congenital malformations in humans. Inconsistent results emerged in the existed studies on associations between air pollution and congenital heart disease. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the association of gestational exposure to air pollutants with congenital heart disease, and to explore the critical exposure windows for congenital heart disease.Methods: The nested case-control study collected birth records and the following health data in Tianjin Women and Children’s Health Center, China. All of the cases of congenital heart disease from 2013 to 2015 were selected matching five healthy controls for each case. Inverse distance weighting was used to estimate individual exposure based on daily air pollution data. Furthermore, the conditional logistic regression with distributed lag non-linear model was performed to identify the association between gestational exposure to air pollution and congenital heart disease.Results: A total of 8,748 mother-infant pairs were entered into the analysis, of which 1,458 infants suffered from congenital heart disease. For each 10 µg/m3 increase of gestational exposure to PM2.5, the ORs (95% confidence interval, 95%CI) ranged from 1.008 (1.001–1.016) to 1.013 (1.001–1.024) during the 1st–2nd gestation weeks. Similar weak but increased risks of congenital heart disease were associated with O3 exposure during the 1st week and SO2 exposure during 6th–7th weeks in the first trimester, while no significant findings for other air pollutants.Conclusions: This study highlighted that gestational exposure to PM2.5, O3, and SO2 had lag effects on congenital heart disease. Our results support potential benefits for pregnancy women to the mitigation of air pollution exposure in the early stage, especially when a critical exposure time window of air pollutants may precede heart development.
- 著者
- Kazue Ishitsuka Mayumi Tsuji Megumi Yamamoto Rie Tanaka Reiko Suga Mami Kuwamura Toshihide Sakuragi Masayuki Shimono Koichi Kusuhara the Japan Environment and Children’s Study Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.47, 2023 (Released:2023-08-30)
- 参考文献数
- 50
Background: Fish are a rich source of essential nutrients that protect against preterm birth. However, as fish can absorb environmental pollutants, their consumption can also increase the risk of preterm birth. This study aimed to assess whether maternal fish consumption during pregnancy is associated with preterm birth in a nationwide large Japanese cohort that consumed relatively high amounts and many types of fish.Methods: This study included 81,428 mother-child pairs enrolled in a nationwide prospective Japanese birth cohort study. Fish consumption was assessed using a validated food frequency questionnaire. Multivariate logistic regression was used to investigate the association of total consumption of fish, fatty fish and lean fish, fish paste, and seafood and clams with preterm birth, adjusted for potential confounders.Results: There was no association between overall fish consumption and preterm births. However, the highest quintile of fish paste consumption was significantly associated with an increased risk of preterm birth (odds ratio [OR]: 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI: 1.04, 1.17]). The consumption of baked fish paste at least three times per week was significantly associated with preterm birth (OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.03, 1.40). Consumption of other types of fish, except fish paste, was not significantly associated with preterm birth risk.Conclusions: Fish paste consumption may increase the risk of preterm birth. Further studies are required to confirm this association.
- 著者
- Ahmed Arafa Yoshihiro Kokubo Keiko Shimamoto Rena Kashima Emi Watanabe Yukie Sakai Jiaqi Li Masayuki Teramoto Haytham A. Sheerah Kengo Kusano
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, pp.10, 2022 (Released:2022-03-04)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Background: A protective role for physical activity against the development of atrial fibrillation (AF) has been suggested. Stair climbing is a readily available form of physical activity that many people practice. Herein, we investigated the association between stair climbing and the risk of AF in a Japanese population.Methods: In this prospective cohort study, we used data of 6,575 people registered in the Suita Study, aged 30–84 years, and had no history of AF. The frequency of stair climbing was assessed by a baseline questionnaire, while AF was diagnosed during the follow-up using a 12-lead ECG, health records, check-ups, and death certificates. We used the Cox regression to calculate the hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals of AF incidence for climbing stairs in 20–39%, 40–59%, and ≥60% compared with <20% of the time.Results: Within 91,389 person-years of follow-up, 295 participants developed AF. The incidence of AF was distributed across the stair climbing groups <20%, 20–39%, 40–59%, and ≥60% as follows: 3.57, 3.27, 3.46, and 2.63/1,000 person-years, respectively. Stair climbing ≥60% of the time was associated with a reduced risk of AF after adjustment for age and sex 0.69 (0.49, 0.96). Further adjustment for lifestyle and medical history did not affect the results 0.69 (0.49, 0.98).Conclusion: Frequent stair climbing could protect from AF. From a preventive point of view, stair climbing could be a simple way to reduce AF risk at the population level.
- 著者
- TAKANO Kadzumi
- 出版者
- 日本衛生学会
- 雑誌
- Environmental health and preventive medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.1, pp.28-32, 1996-04
On April 26th 1986, an accidental explosion occurred at Chernobyl nuclear power station #4, located in the Ukraine, in the former Soviet Union. From May 1991, in order to prevent internal exposure to cesium-137 (^<137>Cs) in the inhabitants of the Chechersk district of the Gomel region in the Republic of Belarus, which was an area highly contaminated by the Chernobyl accident, the author continuously measured internal ^<137>Cs accumulations within inhabitants of the district with a whole-body counter, and the levels of ^<137>Cs in milk, beef, pork, mushrooms, potatoes and flour with a GM-semiconductor detector. Then the author analyzed the relationships between the inhabitants′ daily habits and their measured cesium levels. The author measured ^<137>Cs accumulation within 528 inhabitants and in agricultural produce in the Chechersk disrict. There was no correlation between the internal ^<137>Cs levels within inhabitants and the surface contamination by ^<137>Cs within the residential area. However, a comparison of internal exposure levels by age and sex revealed a significant variation between adult males and both male and female children, and between adult males and females (p<0.001). Food supplied in school was the cause of lower levels in children because it was strictly controlled by the local health authority. The difference between adult males and adult females was thought to be due to the difference in the length of working time in the fields, or in the amount of food from pastures, lakes and forests. Some of the measurement values of agricultural produce with the GM-semiconductor detector exceeded the provisional standards of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, where milk, beef, pork and mushrooms had been measured while potatoes and flour had not. Results for milk (r=0.829), beef (r=0.916), pork (R=0.896) and mushrooms (r=0.670) all showed a strong correlation with the concentration of ^<137>Cs on the surface for fields and pastures, while those for potatoes and flour showed no correlation. According to this survey, the internal levels of ^<137>Cs of inhabitants living within the contaminated areas were not related to the concentration of ^<137>Cs in the residential areas, but to the foodstuffs they consumed. Thehefore, by avoiding contaminated foodstuffs, the inhabitants could reduce internal exposure and their risk.
- 著者
- Sani Rachman Soleman Zhaoqing Lyu Takuya Okada Mariko Harada Sassa Yukiko Fujii Manal A.M. Mahmoud Daniel K Ebner Kouji H. Harada
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.1, 2023 (Released:2023-01-07)
- 参考文献数
- 75
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background: Healthcare workers (HCWs) employed personal protective equipment (PPE) during the COVID-19 pandemic, crucial to protecting themselves from infection. To highlight the efficacy of PPE in preventing environmental infection among HCWs, a systematic review was conducted in line with PRISMA guidance.Methods: A search of the PubMed and Web of Science databases was conducted from January 2019 to April 2021 using pre-defined search terms. Articles were screened by three researchers. The approved papers were read in full and included in this review if relevance was mutually agreed upon. Data were extracted by study design and types of PPEs.Results: 47 of 108 identified studies met the inclusion criteria, with seven reviews and meta-analyses, seven cohort, nine case-control, fifteen cross-sectional studies, four before and after, four case series, and one modeling studies. Wearing PPE offered COVID-19 protection in HCWs but required adequate training. Wearing surgical masks provided improved protection over cloth masks, while the benefit of powered air-purifying respirators is less clear, as are individual gowns, gloves, and/or face shields.Conclusions: Wearing PPE, especially facial masks, is necessary among HCWs, while training in proper use of PPE is also important to prevent COVID-19 infection.
- 著者
- Yoshimitsu Shimomura Tomotaka Sobue Ling Zha Tetsuhisa Kitamura Motoki Iwasaki Manami Inoue Taiki Yamaji Shoichiro Tsugane Norie Sawada
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.19, 2023 (Released:2023-03-07)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: The association between meat, fish, or fatty acid intake and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) has been investigated in a few studies, and the results were inconsistent. In addition, most studies are mainly based on the United States and European countries, in which the dietary patterns differ from that in Asia. Therefore, the risk of AML/MDS from meat, fish, or fatty acid intake in Asia requires further exploration. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between AML/MDS incidence and meat, fish, or fatty acid intake using the Japan Public Health Center–based prospective study.Methods: The present study included 93,366 participants who were eligible for analysis and followed up from the 5-year survey date until December 2012. We estimated the impact of their intake on AML/MDS incidence using a Cox proportional hazards model.Results: The study participants were followed up for 1,345,002 person-years. During the follow-up period, we identified 67 AML and 49 MDS cases. An increased intake of processed red meat was significantly associated with the incidence of AML/MDS, with a hazard ratio of 1.63 (95% confidence interval, 1.03–2.57) for the highest versus lowest tertile and a Ptrend of 0.04. Meanwhile, the intake of other foods and fatty acids was not associated with AML/MDS.Conclusion: In this Japanese population, processed red meat was associated with an increased incidence of AML/MDS.
- 著者
- Kyung-Duk Min Sun-Young Kim Sung-il Cho
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.48, 2023 (Released:2023-08-31)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: The effect of ambient PM2.5 on the incidence of tuberculosis (TB) has been investigated in epidemiological studies. However, they did not separately study new and relapsed TB infection and focused on relatively short-term effects of PM2.5. In this regard, we examined the associations of long-term PM2.5 exposures with both new and relapsed TB incidences in South Korea, where the disease burden of TB is greatest among high-income countries.Methods: An area-level ecological study of 250 districts was conducted from 2015 to 2019. Age- and sex-standardized TB incidence ratios for each district and year were used as outcome variables, and their associations with PM2.5 concentrations for one to five-year average were examined. Negative binomial regression models incorporating spatiotemporal autocorrelation were employed using integrated nested Laplace approximations. Stratified analyses were conducted by type of TB (total, new, and relapsed cases).Results: Districts with higher PM2.5 concentrations tended to have significantly higher TB recurrence rate. The relative risks per 10 µg/m3 PM2.5 increase were 1.218 (95% credible interval 1.051–1.411), 1.260 (1.039–1.527) and 1.473 (1.015–2.137) using the two, three and five-year average PM2.5 exposures, respectively.Conclusions: The results imply that interventions for reducing air pollution might help prevent TB recurrence.
- 著者
- Takafumi Abe Jun Kitayuguchi Noritoshi Fukushima Masamitsu Kamada Shinpei Okada Kenji Ueta Chiaki Tanaka Yoshiteru Mutoh
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, pp.26, 2022 (Released:2022-06-18)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 15
Background: Physical inactivity during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic may have hindered the development of fundamental movement skills in preschoolers. This serial cross-sectional study compared fundamental movement skills by age group before and during the COVID-19 pandemic (2019–2020), among Japanese preschoolers aged 3–5 years.Methods: Of the 22 preschools within Unnan City, Shimane Prefecture, Japan, 21 (95.5%) and 17 (77.3%) participated in the 2019 and 2020 surveys, respectively. We analyzed 608 and 517 preschoolers in both surveys. Fundamental movement skills were objectively assessed with a 25 m run, standing long jump, and softball throw, based on the Japanese physical activity guidelines for preschoolers. Mann–Whitney U tests were used to compare the fundamental movement skills data between periods.Results: For the 25 m run, participants aged 5 years were faster before than during the pandemic (p = 0.018), while participants aged 3 and 4 years showed no significant differences. Participants aged 3–5 years showed no significant differences before and during the pandemic for the standing long jump (p ≥ 0.072). For the softball throw, all grades scored higher before than during the pandemic (p < 0.001).Conclusions: These findings suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic impeded the development of fundamental motor skills, especially for object control skills. This highlights the need for interventions aimed at developing fundamental motor skills in preschoolers during and after the pandemic.
- 著者
- Qing Li
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, pp.43, 2022 (Released:2022-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 63
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Humans have enjoyed forest environments for ages because of the quiet atmosphere, beautiful scenery, mild climate, pleasant aromas, and fresh, clean air. In Japan, since 2004, serial studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of forest environments (Forest bathing/Shinrin-yoku) on human health. My research team has established a new medical science called Forest Medicine. The Forest Medicine is a new interdisciplinary science, belonging to the categories of alternative medicine, environmental medicine and preventive medicine, which studies the effects of forest environments (Forest bathing/Shinrin-yoku) on human health. It has been reported that Forest bathing/Shinrin-yoku has the following beneficial effects on human health:1 Shinrin-yoku increases human natural killer (NK) activity, the number of NK cells, and the intracellular levels of anti-cancer proteins, suggesting a preventive effect on cancers. 2 Shinrin-yoku reduces blood pressure and heart rate showing preventive effect on hypertension and heart diseases. 3 Shinrin-yoku reduces stress hormones, such as urinary adrenaline and noradrenaline and salivary/serum cortisol contributing to stress management. 4 Shinrin-yoku increases the activity of parasympathetic nerves and reduces the activity of sympathetic nerves to stabilize the balance of autonomic nervous system. 5 Shinrin-yoku improve sleep. 6 Shinrin-yoku increases the levels of serum adiponectin and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. 7 In the Profile of Mood States (POMS) test, Shinrin-yoku reduces the scores for anxiety, depression, anger, fatigue, and confusion, and increases the score for vigor, showing preventive effects on depression. 8 Shinrin-yoku may apply to rehabilitation medicine 9 Shinrin-yoku in city parks also has benefits on human health. 10 Shinrin-yoku may have preventive effect on COVID-19 by boosting immune function and by reducing mental stress.Taken together, these findings suggest that Shinrin-yoku may have potential preventive effects on non-communicable diseases.
- 著者
- Ahmed Arafa Rena Kashima Yoshihiro Kokubo Masayuki Teramoto Yukie Sakai Saya Nosaka Haruna Kawachi Keiko Shimamoto Chisa Matsumoto Qi Gao Chisato Izumi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.26, 2023 (Released:2023-05-03)
- 参考文献数
- 63
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: Alcohol consumption is a modifiable lifestyle, but its role in heart failure (HF) development is controversial. Herein, we investigated the prospective association between alcohol consumption and HF risk.Methods: A total of 2,712 participants (1,149 men and 1,563 women) from the Suita Study were followed up every two years. Cox regression was applied to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) of HF risk for heavy drinking (≥46 g/day in men or ≥23 g/day in women) and never drinking compared to light drinking (<23 g/day in men or <11.5 g/day in women). Then, we combined the results of the Suita Study with those from other eligible prospective cohort studies in a meta-analysis using the random-effects model.Results: In the Suita Study, within a median follow-up period of 8 years, 319 HF cases (162 in men and 157 in women) were detected. In men, but not women, never and heavy drinking carried a higher risk of HF than light drinking: HRs (95% CIs) = 1.65 (1.00, 2.73) and 2.14 (1.26, 3.66), respectively. Alike, the meta-analysis showed a higher risk of HF among heavy drinkers: HR (95% CI) = 1.37 (1.15, 1.62) and abstainers: HR (95% CI) = 1.18 (1.02, 1.37).Conclusion: We indicated a J-shaped association between alcohol consumption and HF risk among Japanese men. The results of the meta-analysis came in line with the Suita Study. Heavy-drinking men should be targeted for lifestyle modification interventions.
5 0 0 0 OA Risk of Transmission of Airborne Infection during Train Commute Based on Mathematical Model
- 著者
- Hiroyuki FURUYA
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, no.2, pp.78-83, 2007 (Released:2007-04-24)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Objective: In metropolitan areas in Japan, train commute is very popular that trains are over-crowded with passengers during rush hour. The purpose of this study is to quantify public health risk related to the inhalation of airborne infectious agents in public vehicles during transportation based on a mathematical model. Methods: The reproduction number for the influenza infection in a train (RA) was estimated using a model based on the Wells-Riley model. To estimate the influence of environmental parameters, the duration of exposure and the number of passengers were varied. If an infected person will not use a mask and all susceptible people will wear a mask, a reduction in the risk of transmission could be expected. Results: The estimated probability distribution of RA had a median of 2.22, and the distribution was fitted to a log-normal distribution with a geometric mean of 2.22 and a geometric standard deviation of 1.53, under the condition that there are 150 passengers, and that 13 ventilation cycles per hour, as required by law, are made. If the exposure time is less than 30 min, the risk may be low. The exposure time can increase the risk linearly. The number of passengers also increases the risk. However, RA is fairly insensitive to the number of passengers. Surgical masks are somewhat effective, whereas High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) masks are quite effective. Doubling the rate of ventilation reduces RA to almost 1. Conclusions: Because it is not feasible for all passengers to wear a HEPA mask, and improvement in the ventilation seems to be an effective and feasible means of preventing influenza infection in public trains.
- 著者
- Kimiko Tomioka Kenji Uno Masahiro Yamada
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.7, 2023 (Released:2023-01-21)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 5
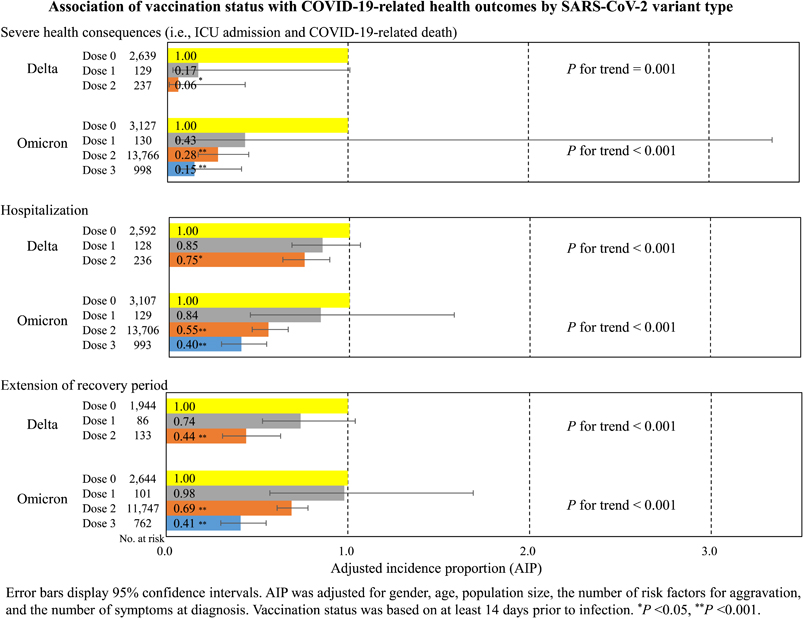
Background: Many previous studies have reported COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness, but there are few studies in Japan. This community-based, retrospective observational study investigated the association between vaccination status and COVID-19-related health outcomes in COVID-19 patients by SARS-CoV-2 variant type.Methods: The study participants were 24,314 COVID-19 patients aged 12 or older whose diagnoses were reported to the Nara Prefecture Chuwa Public Health Center from April 2021 to March 2022, during periods when the alpha, delta, and omicron variants of COVID-19 were predominant. The outcome variables were severe health consequences (SHC) (i.e., ICU admission and COVID-19-related death), hospitalization, and extension of recovery period. The explanatory variable was vaccination status at least 14 days prior to infection. Covariates included gender, age, population size, the number of risk factors for aggravation, and the number of symptoms at diagnosis. The generalized estimating equations of the multivariable Poisson regression models were used to estimate the adjusted incidence proportion (AIP) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for each health outcome. We performed stratified analyses by SARS-CoV-2 variant type, but the association between vaccination status and COVID-19-related health outcomes was stratified only for the delta and omicron variants due to the small number of vaccinated patients during the alpha variant.Results: Of the 24,314 participants, 255 (1.0%) had SHC; of the 24,059 participants without SHC, 2,102 (8.7%) were hospitalized; and of the 19,603 participants without SHC, hospitalization, and missing data on recovery period, 2,960 (15.1%) had extension of recovery period. Multivariable Poisson regression models showed that regardless of SARS-CoV-2 variant type or health outcome, those who received two or more vaccine doses had significantly lower risk of health outcomes than those who did not receive the vaccine, and there was a dose-response relationship in which the AIP for health outcomes decreased with an increased number of vaccinations.Conclusion: A higher number of vaccinations were associated with lower risk of COVID-19-related health outcomes, not only in the delta variant but also in the omicron variant. Our findings suggest that increasing the number of COVID-19 vaccine doses can prevent severe disease and lead to early recovery of patients not requiring hospitalization.
- 著者
- Ai Hori Takahiro Tabuchi Naoki Kunugita
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.5, 2023 (Released:2023-01-18)
- 参考文献数
- 25
Background: Heated tobacco product (HTP) use has increased substantially between 2016 and 2017 in Japan. This study aims to clarify how HTP use (IQOS, Ploom, and glo) spread across the different combustible cigarette smoking statuses during 2015–16 and 2017–18 in Japan.Methods: We compared the two periods of (i) 2015 to 2016 (N = 5,366) and (ii) 2017 to 2018 (N = 3,422) from a longitudinal study randomly sampling members from the Japan “Society and New Tobacco” Internet Survey (JASTIS). Multivariable logistic regression models for current HTP use in the previous 30 days by combustible cigarette smoking status in the previous year were used adjusting for socio-demographic factors.Results: HTP use increased by 10 times in the 2017–18 cohort compared with the 2015–16 cohort according to the adjusted odds ratio (95% confidence interval) for current HTP use as 10.2 (7.03–14.8). According to smoking status, significantly higher adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of current HTP use for the after period were observed: 2.60 (1.37–4.94) for never smokers, 7.82 (3.64–16.8) for former smokers, 21.1 (5.73–77.9) for current smokers with intention to quit, and 17.0 (9.58–30.3) for current smokers without intention to quit.Conclusion: During 2015 to 2018 in Japan, HTP use dramatically increased in all subgroups except for never smokers.
- 著者
- Jiayu He Yuanyuan Liu Ai Zhang Qianfeng Liu Xueli Yang Naixiu Sun Baoqun Yao Fengchao Liang Xiaochang Yan Yang Liu Hongjun Mao Xi Chen Nai-jun Tang Hua Yan
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.3, 2023 (Released:2023-01-11)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background: Weather conditions are a possible contributing factor to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of irreversible loss of vision. The present study evaluated the joint effects of meteorological factors and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on AMD.Methods: Data was extracted from a national cross-sectional survey conducted across 10 provinces in rural China. A total of 36,081 participants aged 40 and older were recruited. AMD was diagnosed clinically by slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy, fundus photography, and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT). Meteorological data were calculated by European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) reanalysis and were matched to participants’ home addresses by latitude and longitude. Participants’ individual PM2.5 exposure concentrations were calculated by a satellite-based model at a 1-km resolution level. Multivariable-adjusted logistic regression models paired with interaction analysis were performed to investigate the joint effects of meteorological factors and PM2.5 on AMD.Results: The prevalence of AMD in the study population was 2.6% (95% CI 2.42–2.76%). The average annual PM2.5 level during the study period was 63.1 ± 15.3 µg/m3. A significant positive association was detected between AMD and PM2.5 level, temperature (T), and relative humidity (RH), in both the independent and the combined effect models. For PM2.5, compared with the lowest quartile, the odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) across increasing quartiles were 0.828 (0.674,1.018), 1.105 (0.799,1.528), and 2.602 (1.516,4.468). Positive associations were observed between AMD and temperature, with ORs (95% CI) of 1.625 (1.059,2.494), 1.619 (1.026,2.553), and 3.276 (1.841,5.830), across increasing quartiles. In the interaction analysis, the estimated relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI) and the attributable proportion (AP) for combined atmospheric pressure and PM2.5 was 0.864 (0.586,1.141) and 1.180 (0.768,1.592), respectively, indicating a synergistic effect between PM2.5 and atmospheric pressure.Conclusions: This study is among the first to characterize the coordinated effects of meteorological factors and PM2.5 on AMD. The findings warrant further investigation to elucidate the relationship between ambient environment and AMD.
- 著者
- Masayuki Shima Narumi Tokuda Hideki Hasunuma Yoshiko Kobayashi Hiroyuki Tanaka Hideaki Sawai Hiroaki Shibahara Yasuhiro Takeshima Munetaka Hirose the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS) Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Hygiene
- 雑誌
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, pp.37, 2022 (Released:2022-09-28)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background: Epidural analgesia relives pain during labor. However, the long-term effects on neurodevelopment in children remain unclear. We explored associations between exposure to epidural analgesia during labor and childhood neurodevelopment during the first 3 years of life, in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS), a large-scale birth cohort study.Methods: Pregnant women were recruited between January 2011 and March 2014, and 100,304 live births of singleton children born at full-term by vaginal delivery, and without congenital diseases were analyzed. Data on mothers and children were collected using a self-administered questionnaires and medical record transcripts. The children’s neurodevelopment was repeatedly assessed for five domains (communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem solving, and personal-social), using the Ages and Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition, at six time points from age 6 to 36 months. After adjusting for potential confounders, the associations between exposure to epidural analgesia during labor and children’s neurodevelopment at each time point were assessed.Results: Of the 42,172 children with valid data at all six time points, 938 (2.4%) were born to mothers who received epidural analgesia during labor. Maternal exposure to epidural analgesia was associated with neurodevelopmental delays during the first 3 years after birth. Delay risks in gross and fine motor domains were the greatest at 18 months (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 1.40 [1.06, 1.84] and 1.54 [1.17, 2.03], respectively), subsequently decreasing. Delay risks in communication and problem-solving domains were significantly high at 6 and 24 months, and remained significant at 36 months (aOR [95% CI]: 1.40 [1.04, 1.90] and 1.28 [1.01, 1.61], respectively). Exposure to epidural analgesia was also associated with the incidence of problem solving and personal-social delays from 18 to 24 months old. Neurodevelopmental delay risks, except for communication, were dominant in children born to mothers aged ≥30 years at delivery.Conclusions: This study showed that maternal exposure to epidural analgesia during labor was associated with neurodevelopmental delays in children during the first 3 years after birth.
3 0 0 0 OA Analysis of Bacterial Flora in Dohyo Soil
- 著者
- OSAFUNE Tetsuaki MITSUBOSHI Masahiro ITO Takashi AOKI Shigeji EHARA Tomoko HASHIGUCHI Hiroshi MINAMI Kazufumi
- 出版者
- 日本衛生学会
- 雑誌
- Environmental health and preventive medicine (ISSN:1342078X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, no.1, pp.11-16, 2007-01
- 参考文献数
- 11
Objectives: Sumo wrestling is one of the most popular sports in Japan. Injuries are not uncommon as this is a vigorous contact sport. Sumo wrestlers have little in the way of protective clothing; their main garb is the mawashi, making them prone to exposure to any microorganisms in the dohyo. The bacterial flora of the dohyo has received little attention. If the constituent flora is identified, then appropriate treatment or prevention of any bacterial lesions or infections incurred by the wrestlers is possible. Methods: The Vitek AMS system used in this study was developed by McDonnell Douglas Corporation. In this system, the physiological and biochemical properties of Gram-positive and -negative bacilli, Gram-positive and -negative cocci, and fungi isolated from clinical materials and environments are examined using test cards specifically for each microorganism group, and the results are automatically read by a computer and encoded. Obtained codes are compared with a built-in database, and bacterial species of test strains are identified. Results: In this study, using the automatic identification kit VITEK or ATB, we describe the aerobic bacterial flora found in the dohyo over the four seasons of the year. We also investigated the effect of salt on the bacterial flora as sumo wrestlers toss salt on the dohyo before each match. We show the relationship between salinity changes and variations in the flora observed upon the addition of salt. Without salt, at the beginning of a match, Gram-negative bacteria predominate. When salt is added, there is a transient decrease in the incidence of flora followed by an increase in the incidence Grampositive cocci. Conclusions: Sixteen bacterial genera were identified using the bacterial identification systems in dohyo soil samples during the year. The number of identified bacterial species was 32. Even in the presence of salt, there is a measurable amount of bacterial flora in dohyo soil; salt does not act as an antibacterial agent.
- 著者
- Koizumi Akio Harada Kouji H Niisoe Tamon Adachi Ayumu Fujii Yukiko Hitomi Toshiaki Kobayashi Hatasu Wada Yasuhiko Watanabe Takao Ishikawa Hirohiko
- 出版者
- Springer
- 雑誌
- Environmental health and preventive medicine (ISSN:13474715)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2011-11-10
- 被引用文献数
- 59
福島県成人住民の放射性セシウムへの経口、吸入曝露の先行評価を実施. 京都大学プレスリリース. 2011-11-14.