1 0 0 0 OA 慢性関節リウマチにおける局所極低温療法と積極的運動療法の効果
- 著者
- 石原 義恕 藤田 朝雄 小林 邦雄 大土井 淑郎 斎藤 幾久次郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3-4, pp.119-130, 1983 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 10
In order to compare the result of local cryo-therapy on rheumatoid arthritis against the conventional local heat application a comparative clinical study was performed.Twenty rheumatoid patients with bilateral knee joint involvement were selected cryo-therapy was given for five minutes with cryogenic air generator (Nihonsanso-L-10) at-100°C on below in eleven patients, whereas local heat was applied with hot packs for 15 minutes at 70-80°C in nine patients.All the patient underwent a daily active exercise schedule after the local treatment, these treatment were given for three months continuously and the result were evaluated. For the evaluation, twelve items were selected including, range of motion, muscle strength, walking capacity, roentgengram and etc.The patients were evaluated before the treatment, 1.5 months after the treatment and at the end of the treatment.The result: both groups showed some improvement in general, but there was no significant difference between them, muscle stiffness and joint pain seemed to be slightly between after the cryo-therapy compared to the local heat application, however post-treatment x-ray showed some progression of joint destruction in the former. The result suggest that local cryo-therapy has a certain place in rheumatoid treatment although not significantly better than the conventional local heat application, if it is applied under due care.
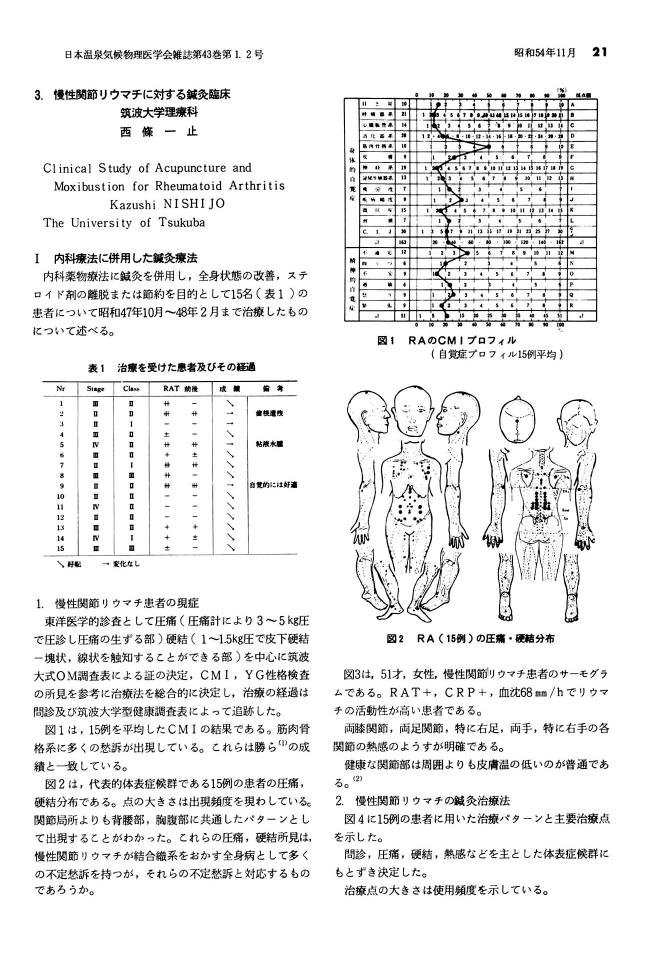
1 0 0 0 OA 慢性関節リウマチに対する鍼灸臨床
- 著者
- 西條 一止
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.1-2, pp.21-28,39, 1979 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 6
1 0 0 0 OA 「水中運動療法の歴史的概観」
- 著者
- 清水 富弘
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.72, no.4, pp.274-275, 2009 (Released:2013-05-21)
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉の分析法
- 著者
- 滝沢 英夫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.1, pp.13-14, 2010 (Released:2013-09-05)
1 0 0 0 OA 整膚の効果—脳波による検討—
- 著者
- 原田 克彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.73, no.4, pp.241-247, 2010 (Released:2013-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 15
Introduction Seifu, devised in 1992 by Xu, is a therapeutic technique of “pulling the skin”. Its effects on the blood pressure, edema, and pain were previously reported in part 1. In this report, Electroencephalography (EEG) changes between before and after Seifu were evaluated.Subjects and Methods The electroencephalograph was performed using an FM-717 biofeedback system (FUTEK, Yokohama, Japan). EEG was recorded for 1 minute each before and after Seifu, and changes in brain waves were analyzed. The subjects were 7 males and 39 females with a mean age of 74.7±16.2 years who underwent Seifu for 5 minutes or longer (5-30 mins, mean : 13.8±6.3 mins) a total of 131 times. EEG was also recorded for 1 minutes each before and after Seifu by 2 Seifu therapists.Results The percentages of β-dominant (p<0.05) and θ-dominant (p<0.001) periods significantly decreased, and the percentages of α2-distribution (p<0.01) and α3-distribution (p<0.05) periods significantly increased. With one therapist, β waves decreased, after both the first and second Seifu treatments. With the other therapist, α1 and α2 waves increased, but θ waves decreased, after both the first and second Seifu treatments.Discussion The results indicate that sleepiness was resolved, tension was mitigated, and the level of relaxation rose, after Seifu. In other words, Seifu brought about a feeling of calm wakefulness. This suggests an increase in serotonin secretion after Seifu. Serotonin generated from tryptophan is a neurotransmitter with an antidepressant effect and causes composure and a sense of stability. An increase in serotonin secretion is reported to induce calm wakefulness and α2-dominant EEG traces. Therefore, the results of our study suggest that Seifu treatment of a sufficient duration stimulates serotonin secretion. Seifu is performed by “simple and constant rhythmic movements”. The technique of Seifu closely resembles that of grooming. Such simple and constant rhythmic movements are considered to stimulate serotonin secretion, and grooming reportedly increases serotonin secretion in both the groomer and groomed. Therefore, the health of not only the Seifu recipient but also Seifu therapist is considered to be promoted by increased serotonin secretion.Conclusion The changes in EEG traces after Seifu of a sufficient duration suggested increased serotonin secretion. Seifu is considered to promote the health of not only the recipient but also the therapist by increasing serotonin secretion.
1 0 0 0 OA 世界における鍼灸への期待と「日本鍼灸の特質と技術革新」
- 著者
- 西條 一止
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.1, pp.28-28, 2007 (Released:2010-04-30)
1 0 0 0 OA 半身浴による生理変化
- 著者
- 山崎 律子 本多 泰揮 原田 潮 鈴木 裕二 大塚 吉則
- 出版者
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.3, pp.165-171, 2007-05
Purpose: Half-body bathing is popular among young women as well as elderly people. As a matter of fact, it is reported that half-body bathing has a smaller burden than whole-body bathing from the point of physical influence. To clarify the relation between bathing habitude and health maintenance, that is, as an approach to general understanding the physiological effects by repeating bathing stimuli, the physiological changes by continuing half-body bathing were studied. Methods: Half-body bathing was repeated for 4 weeks in healthy female subjects (N=10, age:30.1±4.8, height:160.4±6.1cm, weight:55.6±7.0kg, body mass index:20.9±1.6kg/m2, mean±SD). Bathing was performed for 30 minutes and 3times a week, with a level of epigastrium without immersing arms. Changes of blood flow and energy expenditure were measured during bathing at 0W and 4W. Results and Discussion: By continuing bathing, blood flow increased more rapidly and higher during bathing, in addition, resting energy expenditure increased by 200 kcal/day with a significant difference. From these findings, it is assumed that repeated half-body bathing enhances the increase of blood flow through repeating thermal stimuli, which leads to elevated basal metabolism.
- 著者
- 海崎 彩
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.2, pp.127-142, 2014-02-28 (Released:2014-06-26)
- 参考文献数
- 33
背景・目的 : 夏季暑熱環境下では食物摂取が減少し、体格や競技力に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。そこで、夏季の食物摂取の減少について調査し、体格に及ぼす影響を調べるとともにエネルギー代謝や甲状腺ホルモンとの関連について検討した。方法 : 高校硬式野球部に所属する男子生徒を対象として、春季~冬季にわたり栄養調査、身体計測、生活時間調査(AC : activity record)を3回行った。さらに、安静時エネルギー代謝量(REE : resting energy expenditure)、甲状腺ホルモンを測定し、エネルギー(E)摂取との関連を調べた。栄養調査からE摂取量を計算し、ACから総エネルギー消費量(TEE : total enregy expenditure)を算出し、エネルギー(E)バランスを決定した。またREEは呼気ガス分析により測定し、甲状腺ホルモンはT3、FT3、FT4を定量した。結果 : 夏季のE摂取の減少は、約70%の選手で起こったので、E摂取が減少した群をLA、減少しなかった群をHAとした。TEEは両群ともに夏季に増加したので、E摂取が減少したLAではEバランスは有意に低下し負に傾いた(約-690kcal/day)。彼らの体重および上腕周囲長はそれぞれ春季よりも有意に減少し(p<0.05)、その減少率は約2~4%であった。食事のエネルギー構成比率は、LAでは高炭水化物食、HAでは高脂肪食の傾向であった。また、E摂取が減少すると、マクロ栄養素もミクロ栄養素も減少した。REEは、夏季に有意に減少し、E摂取の減少と関連することが示唆された。一方、T3、FT3は、夏季には変化はなかったが、冬季に有意に上昇しREEとの関連が見られた。結論 : 夏季環境下におけるE摂取の減少は、体重および上腕周囲長の減少を引き起こし、体格に影響を与えた。E摂取の減少は、REEの低下と関連することが示唆された。
1 0 0 0 OA 皮膚疾患
- 著者
- 久保田 一雄
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.1, pp.18-19, 1999 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉医学は医学に成り得るか?
- 著者
- 久保田 一雄
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.3, pp.153-154, 2008 (Released:2010-04-30)
1 0 0 0 西郷隆盛:そして大久保利通と島津斉彬
- 著者
- 原口 泉
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.1, pp.9-10, 2004
1 0 0 0 OA 1.保険診療機関における鍼灸治療の現状と将来へ
- 著者
- 瀬尾 憲正
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.73, no.1, pp.32-32, 2009 (Released:2013-09-05)
1 0 0 0 IR 芒硝・食塩配合浴用剤の効果
- 著者
- 渡邊 智 藤原 敏雄 川崎 義巳 大塚 吉則
- 出版者
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.4, pp.235-239, 1997-08-01
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 2
We investigated the effects of bathing with bath preparation (sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, 30g/200l) on the thermal preservability in healthy volunteers. We also investigated these effects on the antioxidative defense system in patients with vibration syndrome (VS). In these investigations, we measured the activities of erythrocyte superoxide dismutase (SOD). After immersion at 41℃ for 5 min, forearm skin temperature, photoplethysmograph, and transepidermal water loss increased significantly as compared with those after bathing in a plain water. After bathing for 4 weeks at around 40℃ for 10min, activities of erythrocyte SOD increased significantly. These data indicate that bathing with the bath preparation has a stronger effect on thermal preservability in healthy volunteers and activation of the antioxidative defense system in patients with vibration syndrome due to a significant increase in activities of erythrocyte SOD.
1 0 0 0 空気中のマイナスイオンが脳波に与える影響
- 著者
- 渡部 一郎 真野 行生 野呂 浩史
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.3, pp.121-126, 1998-05
- 被引用文献数
- 3
High levels of negative ions have been detected in the air in forests, at spas, near waterfalls, and so forth, and there have been reported that they have a favorable effect on human beings' feeling of comfort and their feeling of fatigue. In this study we prepared an experimental room in which it was possible to maintain temperature constant at 25°C and constant humidity, and turn the supply of negative ions on and off, and in addition to assessing comfort level and fatigue level subjectively, we assessed them by means of the -wave component of the EEG, which indicates the degree of relaxation, and by auditory evoked potential P300, which reflects attentiveness and degree of fatigue.<br>Methods: The subjects were 15 healthy physicians and nurses. The experiment was conducted in a room maintained at a constant temperature of 25°C and a constant humidity of 50% during a 2-hour period on different days without informing the subjects of whether the air was loaded with negative ions or not. Constant temperature and humidity were maintained, and the level of negative ions was adjusted by using a shinki genertor (Geochto Ltd.). The parameters measured were determined with a flicker test and P300 (auditory evoked) test, and the α-wave ratio was calculated from the 60-minute closed-eye resting EEG.<br>Results: A higher percentage of subjects reported subjective comfort when the air was loaded with neagtive ions (6/15, 40%) than when it was not (4/15, 27%).<br>Significant difference was not observed in the P300 tests, but the α<sub>2</sub> (10-13Hz) ratio of the EEG and flicker test tended to be higher with negative ion-air than without nagative ion-air.
- 著者
- 白倉 卓夫 田村 耕成
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.2, pp.121-126, 1995-02
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Effect of carbon dioxide bath on cardiovascular functions and peripheral circulation were studied using a new system of carbon dioxide bath. The subjects consisted of 13 males and 17 females, ranging from 50 to 84 years old, 67.4±8.3 in average, having the complaints resulting mainly from arteriosclerosis such as coldness on extremities or exertional pains of lower extremities. Each subject took a bath in plain water (PW) on the first experimental day and then a bath in carbon dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>) at the same time on the second experimental day. Both baths were done for 10min. at 39°C of water temperature. The results obtained were as follows.<br>1) Mean blood pressure (MBP) was elevating during bath and lowered below prebath level immediately after bath in both PW and CO<sub>2</sub> groups. However, MBP in CO<sub>2</sub> group was lower significantly (p<0.05) than in PW group 20 and 30min after bath.<br>2) Both body and skin temperatures were similarly elevated at all points to be measured directly after bath, and then lowerd gradually thereafter. There was no significance in changes between both groups.<br>4) An increase in cutaneous blood flow was observed at the same grade in both groups during and after bath, though no showing significant difference between both groups.<br>5) PO<sub>2</sub> in venous blood increased after bath, while PCO<sub>2</sub> decreased. However, no significant difference in these changes was observed between both groups.<br>6) Tendency to increase in CV R-R was observed during and after bath, though no significant difference was showed between both groups.<br>7) Relating to the feeling to bath, all subjects had the feeling of "warmness" at the beginning of bath and also of comfortableness during and after bath in both PW and CO<sub>2</sub> groups. However, there was no difference in the intensity of these feelings between both groups.<br>8) No side reaction due to an inhalation of carbon dioxide during bath was observed in all subjects.<br>From these results, it is expected that a new carbon dioxide bath results in benefit for patients with disturbance of peripheral circulation.
1 0 0 0 温熱とヒートショックプロテイン(HSP)とその意義
- 著者
- 伊藤 要子
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 = THE JOURNAL OF JAPANESE ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICAL MEDICINE, BALNEOLOGY AND CLIMATOLOGY (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.1, pp.23-24, 2007-11-01