1 0 0 0 OA うたせ湯が筋負荷後の筋血流量、筋硬度、皮膚血流量および鼓膜温に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 美和 千尋 横山 登 河原 ゆう子 出口 晃 田中 紀行 島崎 博也 鈴村 恵理 川村 陽一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.3, pp.178-185, 2011 (Released:2012-12-07)
- 参考文献数
- 10
この研究はうたせ湯が筋収縮後のヒトの肩の筋血流量、筋硬度および体温に及ぼす影響を明らかにすることを目的に行なった。若年男性8人(平均20.4歳)を対象とし、レーザー組織血液酸素モニターにより僧帽筋の中部繊維の血流量を、筋硬度計により筋硬度を測定した。他に、レーザードップラーにより皮膚血流量を、サーミスターにより鼓膜温も測定した。測定は安静10分間と筋負荷後の40℃うたせ湯、肩たたき器によるマッサージ、40℃ホットパックと何もしない自然回復を5分間、その後30分間安静を行なった。安静時の室内は室温27℃、湿度42%RHを維持した。その結果、うたせ湯は有意な筋硬度の減少および皮膚血流量の増加、筋血流量の増加傾向を示した。マッサージでは有意な筋硬度の減少、皮膚血流量の増加が認められた。ホットパックでは有意な筋硬度の減少がみられた。鼓膜温は安静時を除いて有意な変化は認められなかった。これらの結果により、うたせ湯は筋と皮膚の血流量増加を伴って、筋硬度を減少させるものであり、肩こりの緩和に効果のある方法の一つであるといえる。
1 0 0 0 OA 1-4.全身入浴またはシャワー浴の継続がその後の入浴によるHSP70に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 伊藤 要子 石澤 太市 綱川 光男 谷野 伸吾
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.1, pp.30-31, 2014-11-28 (Released:2015-01-15)
- 参考文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 塩原温泉ヘルスツーリズム
- 著者
- 大塚 美昭 大塚 好一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.1, pp.15-16, 2010 (Released:2013-09-05)
1 0 0 0 OA 42℃入浴における体温と最高動脈血流速度の変化
- 著者
- 島崎 博也 水野 圭祐 水谷 真康 中村 毅 前田 一範 出口 晃 川村 直人 鈴村 恵理 美和 千尋 森 康則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.2, pp.63-69, 2018-08-31 (Released:2018-09-26)
- 参考文献数
- 15
【背景と目的】温泉の効果の一つに温熱作用がある.この効果は体温を上昇させ,体温調節機能が作動し,血流量の増大を引き起こす.今回,これらの変化が,浴槽の大きさ,温泉の泉質によるものかを検討した. 【方法】成人健常男性10名(平均年齢25.2歳)を対象として10分間42℃の入浴を実施した.実施は,大浴槽(約1700L:アルカリ性単純温泉)と家庭浴槽(約300L:温水,0.1%人工塩化物泉)を用いた.測定項目は,深部体温「深部温モニターコアテンプ CM-210」と最高動脈血流速度「超音波血流計スマートドップ45」とし,それぞれの値を入浴中10分目,後安静10分目,20分目,30分目で比較し,さらに各条件で前安静値からの変化を求めた. 【結果】入浴10分目で深部体温と最高動脈血流速度の上昇値は,大浴槽の温泉が家庭浴槽での値に比べ,有意な高値を示した.また,大浴槽の温泉の深部体温は入浴3分目から有意に上昇した.後安静での深部体温は,大浴槽の温泉は15分間,家庭浴槽の人工塩化物泉は16分間,温水は13分間有意な上昇が維持された. 【考察】温泉大浴槽の方が家庭浴槽に比べて,深部体温上昇,最高動脈血流速度が大きかったのは,大浴槽では豊富な湯量により湯温の下降を妨げ,家庭用浴槽での深部体温上昇が継続されたのは,人工塩化物泉が体温上昇を維持させたと考える.
1 0 0 0 OA 生薬浴用剤 (川〓・陳皮) の効果に関する検討
- 著者
- 堀切 豊 日吉 俊紀 川平 和美 田中 信行 渡邊 智 藤原 敏雄 川崎 義巳
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.95-100, 1998 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 15
Phthalides and ligustilide in Senkyu extract and limonene and fravonoids in Chimpi extract have been reported to have strong vasodilation effects.In the present study the circulatory effects of Senkyu and Chimpi extract (crude drug extract) were studied as bath agent in 40.0°C bath water (Senkyu ext. 224mg and Chimpi ext. 272mg/2001). Thirteen healthy men (36.2±5.8 years old) took a bath at 40.0°C for 10 min with and without (only with flavor and dye) crude drug extract and the circulatory effects were followed for 30 min after bathing.Heart rate and cardiac output were increased equally by 10 min bathing either with or without crude drug extract. Although systolic blood pressure was slightly increased during bathing, diastolic blood pressure and total peripheral resistance were significantly decreased during and after bathing with and without crude drug extract. Forehead skin blood flow and sublingual temperature were significantly increased during bathing, and remained at higher level for 10-30 min after bathing with crude drug extract. Venous blood pO2 and pH were significantly increased and pCO2 was decreased equally with and without crude drug extract. Plasma NE was significantly increased by bathing with crude drug extract.Bath agent with Senkyu and Chimpi extract are considered favorable as bath agent to keep high skin blood flow and sublingual temperature probably due to its vasodilating effects.
1 0 0 0 OA 刻み生薬浴用剤浴の効果
- 著者
- 渡邊 智 今西 宣行 藤原 敏雄 川崎 義巳 大塚 吉則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.3, pp.135-140, 1998 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 1
In this study, we investigated the effect of bathing with cut crude drugs on thermal preservability, water holding capacity, and smoothness of the feel. After immersion with cut crude drugs of 5min at 41°C, the forearm skin core temperature was significantly higher than after plain water bathing. Water sorption-desorption tests on the skin in vivo with cut crude drug extract for the functional assessment of the stratum corneum revealed that the GARENIAE FRUCTUS extract, all of cut crude drugs extract, and FOENICULI FRUCTUS extract are significantly superior to plain water bathing in water holding capacity.Furthermore, an evaluation using a skin model revealed that cut crude drugs have effects significantly superior to that of plain water bathing in increasing the smoothness of the feel. The above results clarified that bathing with cut crude drugs has a stronger effect on thermal preservability and that their extract increases water holding capacity and smoothness of the feel.
1 0 0 0 アフガニスタンで命の水を求めて
- 著者
- 中村 哲
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 = THE JOURNAL OF JAPANESE ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICAL MEDICINE, BALNEOLOGY AND CLIMATOLOGY (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.1, 2007-11-01
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉入浴の鼻閉に対する効果 —鼻腔通気度検査による検討—
- 著者
- 鈴村 恵理 出口 晃 島崎 博也 前田 一範 浜口 均 川村 直人 川村 憲市 川村 陽一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.75, no.2, pp.87-94, 2012-02-29 (Released:2013-10-18)
- 参考文献数
- 7
背景:鼻閉はわずらわしい症状である。今回、鼻腔通気度計を利用して温泉入浴(41°Cから42°C)の鼻閉に対する効果を調べた。方法:10人の健常成人ボランティア(男性 10名、平均年齢 27.8±4.4才)に 10分間の温泉入浴をさせた。鼻腔通気度計(HI-801)を利用し、入浴前と後に鼻腔抵抗値を測定した。鼻腔通気度検査方法はアクティブ・アンテリオール法で行った。両側鼻腔抵抗は、左右片側抵抗値よりオームの法則の計算式(1/T=1/R+1/L、T:両側抵抗、R:右側抵抗、L;左側抵抗)に従って算出する。評価には ΔP100Pa 点の抵抗値を適用した。結果:左右別に測定した鼻腔抵抗値は、入浴前鼻腔抵抗値が0.75 Pa/cm3/s以上の群にて有意に入浴後低下した(吸気 P=0.0117、呼気 P=0.0277;Wilcoxon T-test)。入浴前鼻腔抵抗値が 0.75 未満の群では有意な変化は認められなかった。 入浴後両側鼻腔抵抗値は、入浴前鼻腔抵抗値が 0.5Pa/cm3/s以上の群で有意に低下を認めた(P=0.0115;Wilcoxon T-test)。結果:鼻閉は温泉入浴後改善することが示された。温泉入浴により鼻閉症状は改善すると考えられる。
1 0 0 0 OA PT1-4 Balneotherapy research in France: the AFRETH (French Association for Balneotherapy Research)
- 著者
- Christian François ROQUES Claude Eugene BOUVIER
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.5, pp.386-387, 2014-08-29 (Released:2015-01-15)
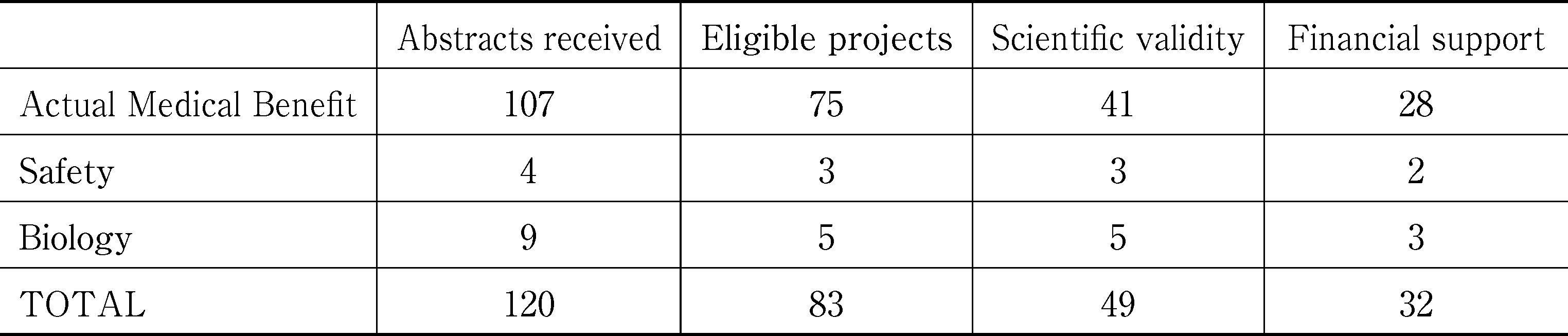
In France, several public and or private scientific investigation bodies are involved in medical balneological scientific investigation (academic or university-linked institutes in Paris, Nancy, Bordeaux, Grenoble, Clermont-Ferrand; private structures in Paris, Aix les Bains, Saujon). However, these last 10 years, the important development in medical balneology investigation could be related to the French Association for Balneotherapy Research (AFRETH). The Afreth has been created in 2004 by the French Union of SPA Contractors, the Union of the mayors of spa resorts and the French branch of the FEMTEC. The AFRETH provides every year a budget of 1 M€ for scientific investigation in balneology. The founders’ representatives, who constitute the association’s administrative committee, take the decision of supporting financially the scientifically validated projects. The scientific validity is pronounced by the scientific committee (12 independent and acknowledged doctors and scientists) on the basis of external independent experts’ advices (methodological, clinical and biological sciences from French academic institutions). 10 calls for projects have been launched and fully implemented. They concerned mainly the actual medical benefit (cf. Table below). A global budget of 11 M€ has been engaged. Regarding the medical benefit have been implemented and published: STOP-TAG (treatment of generalised anxiety, 237 patients); Thermarthrose (knee osteo-arthritis, 462 patients); Maathermes (obesity and overweight, 257 patients); Pacthe (treated breast cancer patients, 250 patients) Thermes & veines (chronic venous insufficiency, 425 patients). These different randomised controlled trials have demonstrated significant results in favour of balneotherapy. Publication is in progress for Rotatherm (a RCT concerning shoulder cuff tendinitis, 186 patients). Are in progress a RCT on COPD (BPCeaux), a RCT on subacute lumbar pain (ITILO). Pilot investigations have been implemented concerning the metabolic syndrome, Alzheimer’s disease and other ageing problems, psychotropic drugs withdrawal, therapeutic education of patients with chronic venous insufficiency. So scientific investigation has to come with usual balneotherapy but also with the development of new trends which have to be scientifically assessed from their initiation.From our experience, we have to emphasize the difficulties related to the patients’ enrolment and the need of new methodological designs, alternative to usual RCT to investigate such a complex therapeutic intervention.
1 0 0 0 OA 二酸化炭素浴における14CO2の経皮吸収
- 著者
- 萬 秀憲 砂川 隆 古元 嘉昭
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.4, pp.207-214, 1992 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 14
人工二酸化炭素浴剤浴での二酸化炭素の経皮吸収に関してウサギを用いて検討した。標識化合物として NaH14CO3 を用い, コハク酸溶液との混合により製造した人工二酸化炭素泉浴 (40℃) をウサギ腹部に適用した。適用時の二酸化炭素濃度は約50ppmであった。適用後, 経時的 (0, 5, 10, 15, 20分後) に血液及び呼気中の二酸化炭素を採取した。また, 適用20分後の主要組織中濃度も測定した。被験液適用5分後の血液及び呼気中にすでに放射能が検出され, 時間経過とともに漸次増加し, 適用20分後の血中濃度は22.0ng/g, 呼気中の二酸化炭素量は9.39μgに達した。適用20分後の主要組織中にも放射能が検出され, 適用20分後までの経皮吸収量は24.49μg, その吸収速度は244.9μg/m2/min (142.9μ1/m2/min) であった。温湯に溶解した二酸化炭素はウサギ皮膚より速やかに吸収され, ついで速やかに呼気中へ排泄されることがわかった。
1 0 0 0 OA 台湾の温泉事情と温泉研究
- 著者
- 大塚 吉則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.72, no.2, pp.105-106, 2009 (Released:2013-03-14)
1 0 0 0 OA 長期マイナスイオン暴露がヒトの生理機能・免疫機能に与える影響
- 著者
- 渡部 一郎 眞野 行生
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.3, pp.123-128, 2001 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 被引用文献数
- 2
A large number of negative air ions have been detected in forests, at spas, and near waterfalls. The air ion had been reported to improve the feelings of comfort, feelings of fatigue and occupational efficiency. Almost all the studies were reported by the short-term exposure of the air ions (2-5 hours) on human. We analyzed the physiological effects and laboratory findings of the long-term exposure of negative air ion (ca. 5000/cc, 5 hours/day, 3 weeks) in double-blind methods.For this study, we made the negative air ion producing machines, in which the steam was combined with electric discharge by high-voltage electrodes. The machines could constantly produce high amount of negative ions (ca. 5, 000 counts/cc). We set these machines in the rest rooms of ten volunteer and programmed to spout negative air ions when they were sleeping at midnight (AM1:00-6:00) for 3 weeks. After 3 weeks exposure of negative air ions or sham condition, we checked the physical and mental tests and sampled the blood.In the exposure of negative air ions, some of the depressive scales and subjective feelings (scores from Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales (AIMS2)) were better than in those in the sham condition, and the local perspiration of palm, which reflected sympathetic nerve function, also decreased by mental and physical stress in the exposure ions more than in the sham condition. This showed that the negative air ion decreased the stress of the sympathetic nerve function. In laboratory findings, there were no significant differences between the clinical data with ions and without ions, and it was shown that ion was harmless in the range of 5, 000 counts/cc 5 hours/day. The percentage of natural killer (NK) cells with the exposure of the ions was lower than without ions. This also indicated the air ion decreased the stress of human.It was shown that the negative air ion might improve human activities and remove the stress. The mechanism of the negative air ions for human is not clear, so that further studies will be needed.
- 著者
- Shinichi ICHIKAWA
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.1, pp.4, 2019-02-28 (Released:2019-04-03)
1 0 0 0 OA サウナ浴の心・循環動態に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 鄭 忠和
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.1, pp.34-37, 1993 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA Special Topics from Japan Thrombotic and Hematostatic Reactions to Bathing in Very Hot Hot-Spring
- 著者
- Hitoshi KURABAYASHI
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.3, pp.177-186, 2015-05-13 (Released:2015-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 23
Very hot hot-spring is loved by the Japanese, although it might cause thrombotic events. It causes addiction to hyperthermia possibly because of an increase in the production of morphine-like substance. Increases in platelet activation, adhesion molecules on the platelet surface, platelet-derived microparticles, and blood viscosity as well as decreases in fibrinolytic capacity and blood pressure were observed after bathing in very hot hot-spring. Bathing in very hot hot-spring is not recommended for the elderly in view of age-related changes in endothelial function, fibrinolytic capacity, dehydration, and dysregulation of blood pressure. Instead, hydrotherapy or bathing in hot-spring in temperatures under 42°C is beneficial with little risk regarding hemostasis and thrombosis.
1 0 0 0 OA 入浴中急死への取り組み
- 著者
- 堀 進悟 鈴木 昌 伊香賀 俊治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.1, pp.14-16, 2013-11-29 (Released:2014-03-14)
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉湖ブルーラグーン体験報告
- 著者
- 石井 敦子 石井 正三 石井 匡
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.2, pp.117-122, 2011 (Released:2013-10-18)
- 参考文献数
- 12
The experience of the thermal spa lake "Blue Lagoon" in Iceland was reported. The plenty of geothermal seawater was supplied from the Svartsengi geothermal power plant to the Blue Lagoon. It was utilized not only as the spa for the public but also for the treatment of psoriasis at the annex clinic. The well-organized project supplying electric power to the community and hot water for the heating system of the public and home use was supposed to be the advanced model to answer to the increasing demand for carbon offset with ecological purposes.
1 0 0 0 総合病院整形外科外来通院患者における温泉意識行動調査について
- 著者
- 矢田部 佳久
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.2, pp.112-116, 2011-01-01
- 参考文献数
- 3
 The effects of hot springs have been described in many studies. However, few studies have reported the use of hot springs by patients. This study aimed to elucidate the use of hot springs by ambulatory orthopaedic patients. We prepared paper questionnaires on the use of hot springs by patients; these questionnaires were administered to ambulatory orthopaedic patients in our general hospital. The questions were as follows: (Q1) Is (Are) there any hot spring(s) near your residence? (Q2) Do you think hot springs are effective for improving your health? (Q3) Have you ever visited a hot spring in the past 1 year? If yes, what was the reason for visiting the hot spring? (Q4) If you did not visit any hot spring, what was the reason for not going? When you are unable to visit hot springs, do you use any alternative methods? (Q5) Do you want hot springs near your residence? The results were as follows: (Q1) Yes, 33 (61%); No, 20 (37%); and No answer, 1 (2%) (Q2) Yes, 15 (28%); Yes (a little), 29 (54%); Neutral, 7 (13%); and No, 3 (6%) (Q3) 1-2 times per year, 18 (33%); 3-4 times per year, 6 (11%); More than 5 times per year, 13 (24%); and No, 17 (31%) (Q4) Bear, 13 (24 %); Alternative, 23 (43%); Use spa, 8 (15%); and Others, 10 (19%) (Q5) Yes, 30 (56%); Yes (a little), 14 (26%); Neutral, 7 (13%); No, 1 (2%); and No answer, 2 (4%). The results of this study suggest that ambulatory orthopaedic patients have a good opinion about the effects of hot springs. Further, these patients visited hot springs. Orthopaedic surgeons must be well informed about the therapeutic use of hot springs.
1 0 0 0 OA 炭酸泉浴における一般反応
- 著者
- W. Schmidt-Kessen 森永 寛 花王 石鹸
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.4, pp.193-203, 1985 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 56
Die Wirkungen des CO2-Bades beruhen auf der freien Diffusion des gelösten Gases und dessen teilweiser Hydration in der Haut. Die Empfindlichkeit cutaner nervöser Rezeptoren wird verändert, die Kaltafferenz gehemmt. Das cutane Pooling verändert die Reaktion auf den hydrostatischen Druck im Bade. Die vermehrte Hautdurchblutung verbessert die Bedingungen des konvektiven Wärmetransportes durch die Haut bei allen Badetemperaturen. Die verschiedenen Effekte sind vielfach therapeutisch nutzbar.
1 0 0 0 OA 女子学生のレイノー現象発作と冬期の気象
- 著者
- 井奈波 良一 岩田 弘敏
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.4, pp.189-194, 1990 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 9
To clarify the relationship between the occurrence of the attacks of Raynaud's phenomenon and weather, maximum, minimum and mean air temperatures in winter were surveyed on the days in which the attacks of Raynaud's phenomenon occurred in 4 female students with Raynaud's phenomenon in the fingers. The results obtained were as follows:1) In general, the percentages of the days when the attacks of Raynaud's phenomenon occurred was the highest from the end of November to December, compared to the January and February results.2) Minimum and mean air temperatures on the days excluding holidays when the attacks of Raynaud's phenomenon occurred were significantly lower than those on the days when the attacks did not occur for the subject who went to school from her own home; this result was not noticeble for the others who lived at the dormitory. In all subjects there were no differences in the maximum air temperatures between the days when the attacks of Raynaud's phenomenon occurred and the days when the attack did not occur.