- 著者
- Rei INOUE Kana HARADA Sayaka WAKAYAMA Masatoshi OOGA Teruhiko WAKAYAMA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2020-059, (Released:2020-06-06)
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Mouse oocytes are generally collected after euthanasia. However, if oocytes were collected without euthanasia, then mice could be used to collect oocytes again after recovery. This condition is especially useful for mice that are genotypically rare. In this study, we examined the reusability of mice after collecting oocytes via a surgical operation. When oocytes were collected using medetomidine/midazolam/butorphanol combination anesthesia and examined for the quality of oocytes after in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), they could develop to full term at the same rate as controls. When oocytes were collected from those mice a second time, the average number of oocytes was reduced by nearly 1/3. However, the blastocyst and offspring rates of those oocytes after IVF or ICSI were the same as those of the control regardless of the recovery day period. Although GV oocytes can be collected from all reused mice, the final number of offspring did not increase. Interestingly, when oocytes were collected from the front position of the ampulla, 76% of the oviducts possessed oocytes after reuse, and the average number of oocytes significantly increased to a level comparable to that of the control. Finally, we examined whether reused mice can be used as recipient females, and then healthy offspring were obtained similarly as the control recipients. In conclusion, we provide a new method to collect a sufficient number of oocytes from reused mice without concern.
- 著者
- Ho-Geun JEGAL Hyo-Jin PARK Jin-Woo KIM Seul-Gi YANG Min-Ji KIM Deog-Bon KOO
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2020-013, (Released:2020-04-22)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Ruthenium red (RR) inhibits calcium (Ca2+) entry from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, and is involved in maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis in mammalian cells. Ca2+ homeostasis is very important for further embryonic development of fertilized oocytes. However, the effect of RR on mitochondria-Ca2+ (mito-Ca2+) levels during in vitro fertilization (IVF) on subsequent blastocyst developmental capacity in porcine is unclear. The present study explored the regulation of mito-Ca2+ levels using RR and/or histamine in fertilized oocytes and their influence on blastocyst developmental capacity in pigs. Red fluorescence intensity by the mito-Ca2+ detection dye Rhod-2 was significantly increased (P < 0.05) in zygotes 6 h after IVF compared to mature oocytes. Based on these results, we investigated the changes in mito-Ca2+ by RR (10 and 20 μM) in presumptive zygotes using Rhod-2 staining and mito-Ca2+ uptake 1 (MICU1) protein levels as an indicator of mito-Ca2+ uptake using western blot analysis. As expected, RR-treated zygotes displayed decreased protein levels of MICU1 and Rhod-2 red fluorescence intensity compared to non-treated zygotes 6 h after IVF. Blastocyst development rate of 20 μM RR-treated zygotes was significantly increased 6 h after IVF (P < 0.05) due to improved mitochondrial functions. Conversely, the blastocyst development rate was significantly decreased in histamine (mito-Ca2+ inhibitor, 100 nM) treated zygotes (P < 0.05). The collective results demonstrate that RR improves blastocyst development in porcine embryos by regulating mito-Ca2+ and MICU1 expression following IVF.
- 著者
- Jinsha LIU Keiji MOCHIDA Ayumi HASEGAWA Kimiko INOUE Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.2, pp.117-127, 2018 (Released:2018-04-13)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 5
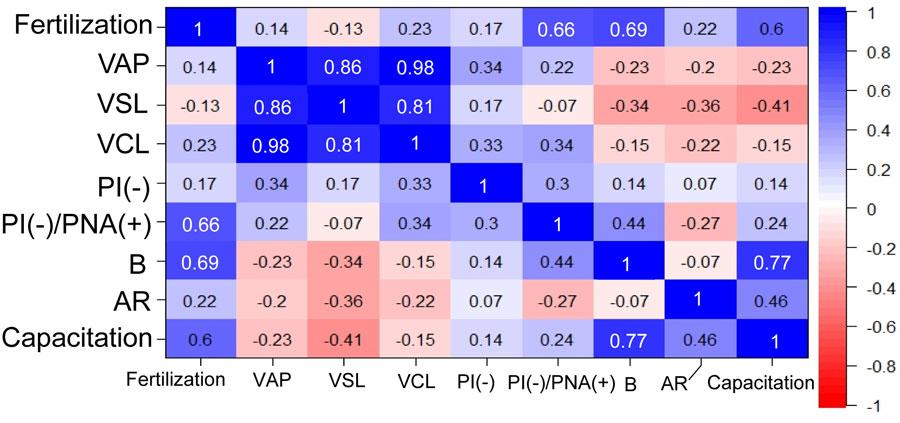
Although it is known that the susceptibility of mouse spermatozoa to freezing-thawing varies greatly with genetic background, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In this study, to map genetic regions responsible for the susceptibility of spermatozoa to freezing-thawing, we performed in vitro fertilization using spermatozoa from recombinant inbred mice derived from the C57BL/6J and DBA/2J strains, whose spermatozoa showed distinct fertilization abilities after freezing. Genome-wide interval mapping identified two suggestive quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with fertilization on chromosomes 1 and 11. The strongest QTL on chromosome 11 included 70 genes at 59.237260–61.324742 Mb and another QTL on chromosome 1 included 43 genes at 153.969506–158.217850 Mb. These regions included at least 15 genes involved with testicular expression and possibly with capacitation or sperm motility. Specifically, the Abl2 gene on chromosome 1, which may affect subcellular actin distribution, had polymorphisms between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J that caused at least three amino acid substitutions. A correlation analysis using recombinant inbred strains revealed that the fertilization rate was strongly correlated with the capacitation rate of frozen-thawed spermatozoa after preincubation. This result is consistent with the fact that C57BL/6J frozen-thawed spermatozoa recover their fertilization capacity following treatment with methyl-β-cyclodextrin to enhance sperm capacitation. Thus, our data provide important clues to the molecular mechanisms underlying cryodamage to mouse spermatozoa.
- 著者
- Longquan REN Mohamed S. MEDAN Mariko OZU Chunmei LI Gen WATANABE Kazuyoshi TAYA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.0601130020, (Released:2006-01-16)
- 被引用文献数
- 20 29
The effect of induced cryptorchidism on testicular function and sperm motility was investigated. Bilateral cryptorchidism was created surgically in adult male rats (treated group), and sham-operated rats were used as a control group. Five rats from each group were sacrificed on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 after surgery. The percentage of motile spermatozoa began to decrease 1 day after the operation, followed by an abrupt decline 3 and 5 days later in cryptorchid rats. Furthermore, there were significant decreases in the other sperm motility parameters 5 days after inducement of cryptorchidism. In cryptorchid rats, plasma concentrations of LH, FSH, testosterone, and inhibin B were significantly lower than in the control group 1 day after the operation. Thereafter, plasma concentrations of LH, FSH, and testosterone gradually increased in the cryptorchid rats. On the other hand, plasma concentrations of inhibin B showed a further decline from day 3 after the operation onward. Concentrations of immunoreactive (ir)-inhibin, but not testosterone, in testicular interstitial fluid were remarkably increased until 3 days after surgery in the cryptorchid rats, and declined thereafter. Testicular response to human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) for testosterone release was decreased in the cryptorchid rats compared with the control rats, indicating that heat stress to testes resulted in a reduction of the activity of Leydig cells and Sertoli cells. These results clearly indicate that heat stress to the testes resulted in a significant reduction of sperm activity within 3 days, and this was followed by changes in testicular endocrine function.
1 0 0 0 OA わが国における脊椎動物行動学研究の歴史と展望
- 著者
- 木村 武二
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.6, pp.j121-j125, 1995 (Released:2010-10-20)
世界的にみた行動学の発展の歴史と対照してみると,わが国における行動学の発展はかなり特殊な経緯をたどって来たし,研究対照やアプローチに関しても未だに偏りが見られる.これらについて概観するとともに,特に脊椎動物を対象とした行動研究の現状と将来の展望について私見を述べた.
- 著者
- Kanako MOROHAKU
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, no.4, pp.281-287, 2019 (Released:2019-08-09)
- 参考文献数
- 63
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Eggs are female germ cells that are required for producing offspring through sexual reproduction. In mammals, eggs are produced in the ovary and ovulated into the oviduct. It is well known that over 99% of eggs are degenerated without ovulation, so that many studies have attempted in vitro folliculogenesis to produce many eggs in different species for a few decades. Although many methods have been developed, a success of in vitro egg production with the resultant live birth of offspring has been limited, especially in livestock animals. More recently, we have succeeded in producing live pups derived from in vitro/ex vivo egg production in mice. This review aims to introduce our recent findings with a brief history of in vitro/ex vivo culture systems for follicles and ovaries.
1 0 0 0 OA 発光オワンクラゲ由来の新規マーカーGFPとトランスジェニックマウスへの応用
- 著者
- 岡部 勝 伊川 正人 山田 秀一 中西 友子 馬場 忠
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.6, pp.j19-j25, 1997 (Released:2010-10-20)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
オワンクラゲ類のもつ蛍光蛋白質は総称してGreen Fluorescent Proteinと呼ばれている.Aequorea victorea(和名:発光オワンクラゲ)のGFPは分子量27 Kdaの蛋白質で,アミノ酸残基65番目のserinと67番目のglycinのペプチド結合部位が脱水縮合を起こした後に酸化されて発色団を形成し蛍光蛋白質となる.この構造変化は酸素以外に特別な因子を必要とせず,蛍光は細胞を観察するだけでよい.外来遺伝子としてGFP遺伝子を導入すると,蛍光をもつ培養細胞,植物,線虫,ハエ,魚,マウスなどが得られる.現在では人工的に作製された,緑,青,黄色など種々の波長の蛍光を出す多くの変異体があり,今後,実験動物の分野で新しいマーカーとして使用される例が増えるものと予想される.本稿では我々の作製したトランジェニックマウスを中心にGFPの応用例を述べる.
- 著者
- Islam M. SAADELDIN Ayman Abdel-Aziz SWELUM Mona ELSAFADI Amer MAHMOOD Syed Hilal YAQOOB Musaad ALFAYEZ Abdullah N. ALOWAIMER
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2018-073, (Released:2019-02-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 15
All-trans retinoic acid (RA) is a metabolite of vitamin A and has pleiotropic actions on many different biological processes, including cell growth and differentiation, and is involved in different aspects of fertility and developmental biology. In the current study, we investigated the effects of RA on camel (Camelus dromedarius) cumulus-oocyte complex in vitro maturation (IVM). IVM medium was supplemented with 0, 10, 20, and 40 µM RA. Application of 20 µM RA significantly reduced the proportion of degenerated oocytes and significantly improved oocyte meiosis and first polar body extrusion compared to the control and other experimental groups. Retinoic acid significantly reduced the mRNA transcript levels of apoptosis-related genes, including BAX and P53, and reduced the BAX/BCL2 ratio. In addition, RA significantly reduced the expression of the Transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) pathway-related transcripts associated with the actin cytoskeleton, ACTA2 and TAGLN; however, RA increased TGFβ expression in cumulus cells. The small molecule SB-431542 inhibits the TGFβ pathway by inhibiting the activity of activin receptor-like kinases (ALK-4, ALK-5, and ALK-7); however, combined supplementation with RA during IVM compensated for the inhibitory effect of SB-431542 on cumulus expansion, oocyte meiosis I, and first polar body extrusion in activated oocytes. The current study shows the beneficial effects of RA on camel oocyte IVM and provides a model to study the multifunctional mechanisms involved in cumulus expansion and oocyte meiosis, particularly those involved in the TGFβ pathway.
1 0 0 0 OA The necessity of ZSCAN4 for preimplantation development and gene expression of bovine embryos
- 著者
- Kazuki TAKAHASHI Pablo J. ROSS Ken SAWAI
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2019-039, (Released:2019-04-25)
- 被引用文献数
- 9
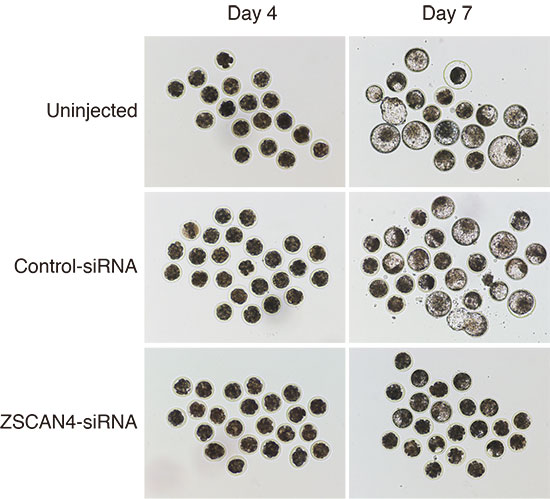
Zinc finger and SCAN domain containing 4 (Zscan4) is a gene that is specifically expressed during zygotic genome activation (ZGA) in mouse preimplantation embryos, and a reduction of Zscan4 transcripts leads to developmental failure. In mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs), Zscan4 is expressed transiently in as little as 1–5% of the cell population. Zscan4 has also been shown to enhance the efficiency of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and their quality. Although ZSCAN4 plays important roles in murine embryos and stem cells, its expression and role in bovine embryos is unknown. This study examines ZSCAN4 transcripts in bovine embryos at various developmental stages and attempts to elucidate the functions of ZSCAN4 during bovine preimplantation development. ZSCAN4 transcripts were found to be upregulated at the 8- and 16-cell stages. We next attempted ZSCAN4 downregulation in bovine early embryos by RNA interference and evaluated developmental competency and transcripts levels of genes involved in ZGA and iPSCs generation. Although the bovine embryos injected with ZSCAN4-siRNA could develop to the 8-cell stage, very few were developing beyond the 16-cell stage. PIWIL2 expression was reduced in ZSCAN4 downregulated embryos. It is possible that ZSCAN4 downregulated embryos fail to regulate gene expression during ZGA. Our results indicate that ZSCAN4 is an important factor for the preimplantation development of bovine embryos.
1 0 0 0 OA 応用動物科学と行動学
- 著者
- 森 裕司
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.6, pp.j155-j157, 1995 (Released:2010-10-20)
動物行動学とは,動物の示す様々な行動の多様性と統一性を明らかにし動物の行動原理を解きあかそうとする学問領域であり,行動の発現機構や,行動の機能すなわち動物が生存し繁殖していく上でその行動が持つ意味,あるいは行動の発達や進化などについて実に様々な視点から研究が展開されている.本稿では,動物行動学の成り立ちとその発展の経緯について概説し,畜産学や獣医学といった応用動物科学分野における動物行動学の現状と今後の課題について考察する.
- 著者
- Adeleh ZABIHI Hamed Karami SHABANKAREH Hadi HAJARIAN Saheb FOROUTANIFAR
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2018-102, (Released:2019-01-18)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This article released online on January 18, 2019 as advance publication was withdrawn from consideration for publication in The Journal of Reproduction and Development at author’s request.
- 著者
- Blanca ALGARRA Verónica MAILLO Manuel AVILÉS Alfonso GUTIÉRREZ-ADÁN Dimitrios RIZOS María JIMÉNEZ-MOVILLA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.5, pp.433-443, 2018 (Released:2018-10-12)
- 参考文献数
- 64
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Previously, our group demonstrated that recombinant porcine oviductin (pOVGP1) binds to the zona pellucida (ZP) of in vitro-matured (IVM) porcine oocytes with a positive effect on in vitro fertilization (IVF). The fact that pOVGP1 was detected inside IVM oocytes suggested that this protein had a biological role during embryo development. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of pOVGP1 on bovine in vitro embryo development. We applied 10 or 50 µg/ml of pOVGP1 during IVF, embryonic in vitro culture (IVC), or both, to evaluate cleavage and embryo development. Blastocyst quality was assessed by analyzing the expression of important developmental genes and the survival rates after vitrification/warming. pOVGP1 was detected in the ZP, perivitelline space, and plasma membrane of blastocysts. No significant differences (P > 0.05) were found in cleavage or blastocyst yield when 10 or 50 µg/ml of pOVGP1 was used during IVF or IVC. However, when 50 µg/ml pOVGP1 was used during IVF + IVC, the number of blastocysts obtained was half that obtained with the control and 10 µg/ml pOVGP1 groups. The survival rates after vitrification/warming of expanded blastocysts cultured with pOVGP1 showed no significant differences between groups (P > 0.05). The use of pOVGP1 during IVF, IVC, or both, increased the relative abundance of mRNA of DSC2, ATF4, AQP3, and DNMT3A, the marker-genes of embryo quality. In conclusion, the use of pOVGP1 during bovine embryo in vitro culture does not affect embryo developmental rates but produces embryos of better quality in terms of the relative abundance of specific genes.
- 著者
- Fuminori TANIHARA Maki HIRATA Nhien Thi NGUYEN Quynh Anh LE Takayuki HIRANO Takeshige OTOI
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2018-116, (Released:2019-02-05)
- 被引用文献数
- 32
Cytoplasmic microinjection (CI) of the CRISPR/Cas9 system enabled the induction of site-specific mutations in porcine zygotes and resulting pigs. However, mosaicism is a serious problem for genetically modified pigs. In the present study, we investigated suitable timing and concentration of CRISPR/Cas9 components for introduction into oocytes/zygotes by CI, to reduce mosaicism in the resulting blastocysts. First, we introduced 20 ng/μl of Cas9 protein and guide RNA (gRNA), targeting the α-1,3-galactosyltransferase (GalT) gene in oocytes before in vitro fertilization (IVF), in zygotes after IVF, or in oocytes/zygotes before and after IVF, twice. CI treatment had no detrimental effects on blastocyst formation rates. The highest value of the rate of mutant blastocysts was observed in zygotes injected after IVF. Next, we injected Cas9 protein and gRNA into zygotes after IVF at a concentration of 20 ng/μl each (20 ng/μl group) or 100 ng/μl each (100 ng/μl group). The ratio of the number of blastocysts that carried mutations to the total number of blastocysts examined in the 100 ng/μl group was significantly higher (P < 0.05) than that in the 20 ng/μl group. Although no blastocysts from the 20 ng/μl group carried a biallelic mutation, 16.7% of blastocysts from the 100 ng/μl group carried a biallelic mutation. In conclusion, increasing the concentration of Cas9 protein and gRNA is effective in generating biallelic mutant blastocysts. To reduce mosaicism, however, further optimization of the timing of CI, and the concentration of CRISPR/Cas9 components, is needed.
- 著者
- Yoshihisa UENOYAMA Naoko INOUE Kei-ichiro MAEDA Hiroko TSUKAMURA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2018-110, (Released:2018-10-08)
- 被引用文献数
- 32
Kisspeptin, identified as a natural ligand of GPR54 in 2001, is now considered as a master regulator of puberty and subsequent reproductive functions in mammals. Our previous studies using Kiss1 knockout (KO) rats clearly demonstrated the indispensable role of kisspeptin in gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)/gonadotropin secretion. In addition, behavioral analyses of Kiss1 KO rats revealed an organizational effect of kisspeptin on neural circuits controlling sexual behaviors. Our studies using transgenic mice carrying a region-specific Kiss1 enhancer-driven reporter gene provided a clue as to the mechanism by which estrogen regulates Kiss1 expression in hypothalamic kisspeptin neurons. Analyses of Kiss1 expression and gonadotropin secretion during the pubertal transition shed light on the mechanism triggering GnRH/gonadotropin secretion at the onset of puberty in rats. Here, we summarize data obtained from the aforementioned studies and revisit the physiological roles of kisspeptin in the mechanism underlying reproductive functions in mammals.
- 著者
- KADOKAWA Hiroya
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.1, pp.121-125, 2007
- 被引用文献数
- 11
Stress due to summer heat has adverse effects on reproduction in Holstein dairy cattle. Summer suppression of reproduction of Holsteins can pose an important economic problem, even in Hokkaido prefecture located in the northern region of Japan. Hokkaido is one of the most important dairy farming areas of Japan. This study is an attempt to clarify the seasonal differences in the parameters of luteinizing hormone (LH) response to exogenous gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) in Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan. A total of 12 prepubertal heifers received an injection with GnRH analogue intramuscularly in either May (n=4, May group), July (n=4, July group), or November (n=4, November group), and serial blood samples were collected to analyze the parameters of the LH response curve after GnRH injection. The parameters were as follows: the basal LH concentration, peak LH concentration, duration from the time of GnRH injection to the time of the peak LH concentration, and area under the LH response curve (AUC). There were no significant differences in the basal and peak LH concentrations or the AUC among the three groups. The July group reached the LH peak significantly (P<0.05) faster than the May group, but there was no significant difference with the November group. Therefore, the results of the present study do not demonstrate an effect of summer heat on the LH response to the exogenous GnRH in Holstein heifers.<br>
- 著者
- Blanca ALGARRA Verónica MAILLO Manuel AVILÉS Alfonso GUTIÉRREZ-ADÁN Dimitrios RIZOS Maria JIMENEZ-MOVILLA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2018-058, (Released:2018-08-06)
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Previously, our group demonstrated that recombinant porcine oviductin (pOVGP1) binds to the zona pellucida (ZP) of in vitro-matured (IVM) porcine oocytes with a positive effect on in vitro fertilization (IVF). The fact that pOVGP1 was detected inside IVM oocytes suggested that this protein had a biological role during embryo development. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of pOVGP1 on bovine in vitro embryo development. We applied 10 or 50 µg/ml of pOVGP1 during IVF, embryonic in vitro culture (IVC), or both, to evaluate cleavage and embryo development. Blastocyst quality was assessed by analyzing the expression of important developmental genes and the survival rates after vitrification/warming. pOVGP1 was detected in the ZP, perivitelline space, and plasma membrane of blastocysts. No significant differences (P > 0.05) were found in cleavage or blastocyst yield when 10 or 50 µg/ml of pOVGP1 was used during IVF or IVC. However, when 50 µg/ml pOVGP1 was used during IVF + IVC, the number of blastocysts obtained was half that obtained with the control and 10 µg/ml pOVGP1 groups. The survival rates after vitrification/warming of expanded blastocysts cultured with pOVGP1 showed no significant differences between groups (P > 0.05). The use of pOVGP1 during IVF, IVC, or both, increased the relative abundance of mRNA of DSC2, ATF4, AQP3, and DNMT3A, the marker-genes of embryo quality. In conclusion, the use of pOVGP1 during bovine embryo in vitro culture does not affect embryo developmental rates but produces embryos of better quality in terms of the relative abundance of specific genes.
- 著者
- 富永 敬一郎
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Animal Reproduction
- 雑誌
- The Journal of reproduction and development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.1, pp.29-38, 2004-02-01
- 参考文献数
- 56
- 被引用文献数
- 3 20
胚に対するグリセリンの浸透圧ショックを緩和するために希釈時に用いられるスクロースの細胞毒性を緩和することを目的として、ストロー内でスクロースによるグリセリン希釈を行った後、さらに、胚に影響しない濃度まで培養液で希釈するストロー内2段階希釈直接移植法を開発した。野外での体内回収胚移植で、この方法はエチレングリコールを用いたダイレクト法と同等の受胎率であった。16細胞期胚の緩慢凍結法において、最適耐凍剤を選定するとともに、リノール酸アルブミンの培養液への添加や、遠心処理で細胞内脂肪を局在化させることによる胚細胞外への除去を試みた。その結果、エチレングリコール区がプロパンディオール区やDMSO区より胚盤胞への発生率が高く、LAA添加は無添加に比べて凍結融解後の胚盤胞への発生率を向上させた。また、2細胞期で遠心処理した16細胞期胚では脂肪大部分除去区の凍結融解後の胚盤胞への発生率は無遠心凍結区より高く、無遠心新鮮区の胚盤胞の細胞数と差はみられなかった。次に、体外受精後2細胞期から胚盤胞期までの胚について、ゲル・ローディング・チップ(GL-ip)を用いた超急速ガラス化法を検討した結果、すべての発育日齢で50%を越える高い胚盤胞への発生率が得られ、発生率及び胚盤胞の細胞数、細胞構成において、それぞれの日齢の新鮮胚対照区と差はみられなかった。また、体外受精7日目胚盤胞のGL-ipガラス化法は緩慢凍結法より生存率が高かった。体内回収胚の発生速度の速い胚盤胞や形態の良好な高品質胚に雄が多いが、この関係は交配種雄牛毎に異なることを明らかにした。また、個体毎に区別した体外受精由来胚では、胚の発生速度あるいは胚盤胞生産率と性別とに関係がみられないことや、切断2分離胚後、雄胚が高品質胚へ早く形態回復することを明らかにした。性判別した体内回収胚にGL‐ipガラス化法を応用した結果、対照の新鮮胚移植と変わらない受胎率が得られた。体外受精由来3、4日目胚から1-2割球をサンプリングし、サンプルをPEP‐PCR、DNA産物を精製し、性判別PCRに供した。同時に、サンプリング胚を7日目まで培養し、発生した胚盤胞をGL-ipガラス化した。その結果、性別が高率に判定でき、ガラス化した胚盤胞は新鮮胚と変わらない高い生存率が得られ、しかも、ガラス化胚が子牛への発生能を持つことを明らかにした。
- 著者
- ISOLA Michela COSSU Margherita DE LISA Antonello ISOLA Raffaella MASSA Denise CASTI Alberto SOLINAS Paola LANTINI M. Serenella
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.1, pp.94-97, 2010
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Oxytocin is a cyclic nonapeptide whose best known effects are stimulation of uterine smooth muscle cells during labor and of milk ejection during lactation. Circulating oxytocin originates from the hypothalamus, but its production has also been documented in peripheral tissues. Furthermore, seminal plasma also contains oxytocin, but its functional role is still unknown, although its secretion is generally ascribed to the prostate. In this study, we investigated the possibility that seminal oxytocin is also secreted by other exocrine glands of the human male genital tract. Intramural (Littrè's) glands isolated from bioptic specimens of normal urethrae were processed for immunogold localization of oxytocin. Immunostaining was detected in principal cells, with gold particles specifically found on secretory granules. Basal and endocrine cells were unstained. The present findings suggest that urethral glands not only produce the mucinous layer that protects and lubricates the urethral wall, but also are potential sources of other seminal components, such as oxytocin, which probably play still unclear roles in reproductive physiology.<br>
- 著者
- Jinsha LIU Keiji MOCHIDA Ayumi HASEGAWA Kimiko INOUE Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2017-148, (Released:2017-12-21)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Although it is known that the susceptibility of mouse spermatozoa to freezing–thawing varies greatly with genetic background, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In this study, to map genetic regions responsible for the susceptibility of spermatozoa to freezing–thawing, we performed in vitro fertilization using spermatozoa from recombinant inbred mice derived from the C57BL/6J and DBA/2J strains, whose spermatozoa showed distinct fertilization abilities after freezing. Genome-wide interval mapping identified two suggestive quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with fertilization on chromosomes 1 and 11. The strongest QTL on chromosome 11 included 70 genes at 59.237260–61.324742 Mb and another QTL on chromosome 1 included 43 genes at 153.969506–158.217850 Mb. These regions included at least 15 genes involved with testicular expression and possibly with capacitation or sperm motility. Specifically, the Abl2 gene on chromosome 1, which may affect subcellular actin distribution, had polymorphisms between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J that caused at least three amino acid substitutions. A correlation analysis using recombinant inbred strains revealed that the fertilization rate was strongly correlated with the capacitation rate of frozen-thawed spermatozoa after preincubation. This result is consistent with the fact that C57BL/6J frozen–thawed spermatozoa recover their fertilization capacity following treatment with methyl-β-cyclodextrin to enhance sperm capacitation. Thus, our data provide important clues to the molecular mechanisms underlying cryodamage to mouse spermatozoa.
1 0 0 0 牛胚移植技術の普及(1992年度斉藤賞受賞講演論文)
- 著者
- 清家 昇
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.6, pp.j121-j127, 1992
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
牛胚移植技術の普及を目指し,多くの酪農家と共に種々のETに取り組んだ.非過排卵処置牛からの採卵は供卵牛にホルモン剤を投与しない為、比較的容易に酪農家に受け入れられ,ET技術を理解して頂く上で有効であった.また,高泌乳牛群を用いたETは農家のET技術への偏見を払拭し,ET技術の素晴らしさを再認識して頂く上で効果的であった.特に,2頭のET牛は乳量日本記録を更新し,多くの酪農家の注目を浴びると共に,優良牛を用いてのET普及に大きく拍車をかけた.更に,優良未経産牛群を用いたETは,供卵牛を所有しない一般酪農家のET取り組み方法として有効であると共に,改良の世代間隔を短縮出来る効果的な手段であった.胚の切断2分離技術は,人為的な1卵性双子の作出により,高価な胚を効率的に移植し,回収胚からより多くの産子を獲得できた.またETS子牛の正常性も明らかとなった.