- 著者
- Keisuke Arikawa
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.58-74, 2018 (Released:2018-02-27)
- 参考文献数
- 50
- 被引用文献数
- 2
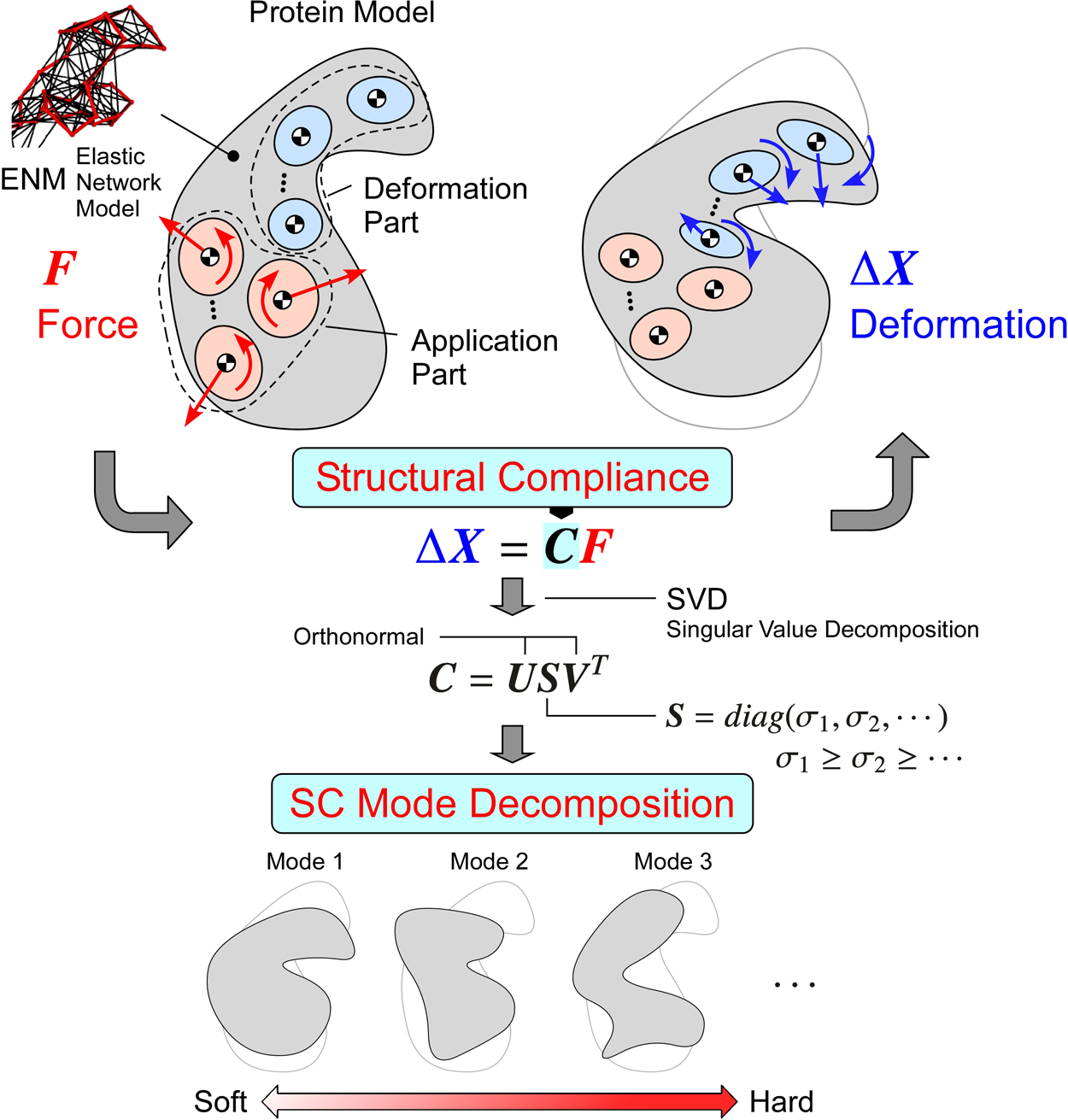
We propose methods for directly analyzing structural compliance (SC) properties of elastic network models of proteins, and we also propose methods for extracting information about motion properties from the SC properties. The analysis of SC properties involves describing the relationships between the applied forces and the deformations. When decomposing the motion according to the magnitude of SC (SC mode decomposition), we can obtain information about the motion properties under the assumption that the lower SC mode motions or the softer motions occur easily. For practical applications, the methods are formulated in a general form. The parts where forces are applied and those where deformations are evaluated are separated from each other for enabling the analyses of allosteric interactions between the specified parts. The parts are specified not only by the points but also by the groups of points (the groups are treated as flexible bodies). In addition, we propose methods for quantitatively evaluating the properties based on the screw theory and the considerations of the algebraic structures of the basic equations expressing the SC properties. These methods enable quantitative discussions about the relationships between the SC mode motions and the motions estimated from two different conformations; they also help identify the key parts that play important roles for the motions by comparing the SC properties with those of partially constrained models. As application examples, lactoferrin and ATCase are analyzed. The results show that we can understand their motion properties through their lower SC mode motions or the softer motions.
- 著者
- Shuya Ishii Madoka Suzuki Shin’ichi Ishiwata Masataka Kawai
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, pp.28-40, 2019 (Released:2019-02-02)
- 参考文献数
- 77
- 被引用文献数
- 6
The majority of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is caused by mutations in sarcomere proteins. We examined tropomyosin (Tpm)’s HCM mutants in humans, V95A and D175N, with in vitro motility assay using optical tweezers to evaluate the effects of the Tpm mutations on the actomyosin interaction at the single molecular level. Thin filaments were reconstituted using these Tpm mutants, and their sliding velocity and force were measured at varying Ca2+ concentrations. Our results indicate that the sliding velocity at pCa ≥8.0 was significantly increased in mutants, which is expected to cause a diastolic problem. The velocity that can be activated by Ca2+ decreased significantly in mutants causing a systolic problem. With sliding force, Ca2+ activatable force decreased in V95A and increased in D175N, which may cause a systolic problem. Our results further demonstrate that the duty ratio determined at the steady state of force generation in saturating [Ca2+] decreased in V95A and increased in D175N. The Ca2+ sensitivity and cooperativity were not significantly affected by the mutations. These results suggest that the two mutants modulate molecular processes of the actomyosin interaction differently, but to result in the same pathology known as HCM.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Terashima Katsumi Imada
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.173-178, 2018 (Released:2018-08-22)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Type III secretion system (T3SS) is a protein translocator complex family including pathogenic injectisome or bacterial flagellum. The inejectisomal T3SS serves to deliver virulence proteins into host cell and the flagellar T3SS constructs the flagellar axial structure. Although earlier studies have provided many findings on the molecular mechanism of the Type III protein export, they were not sufficient to reveal energy transduction mechanism due to difficulties in controlling measurement conditions in vivo. Recently, we developed an in vitro flagellar Type III protein transport assay system using inverted membrane vesicles (IMVs), and analyzed protein export by using the in vitro method. We reproduced protein export of the flagellar T3SS, hook assembly and substrate specificity switch in IMV to a similar extent to what is seen in living cell. Furthermore, we demonstrated that ATP-hydrolysis energy can drive protein transport even in the absence of proton-motive force (PMF). In this mini-review, we will summarize our new in vitro Type III transport assay method and our findings on the molecular mechanism of Type III protein export.
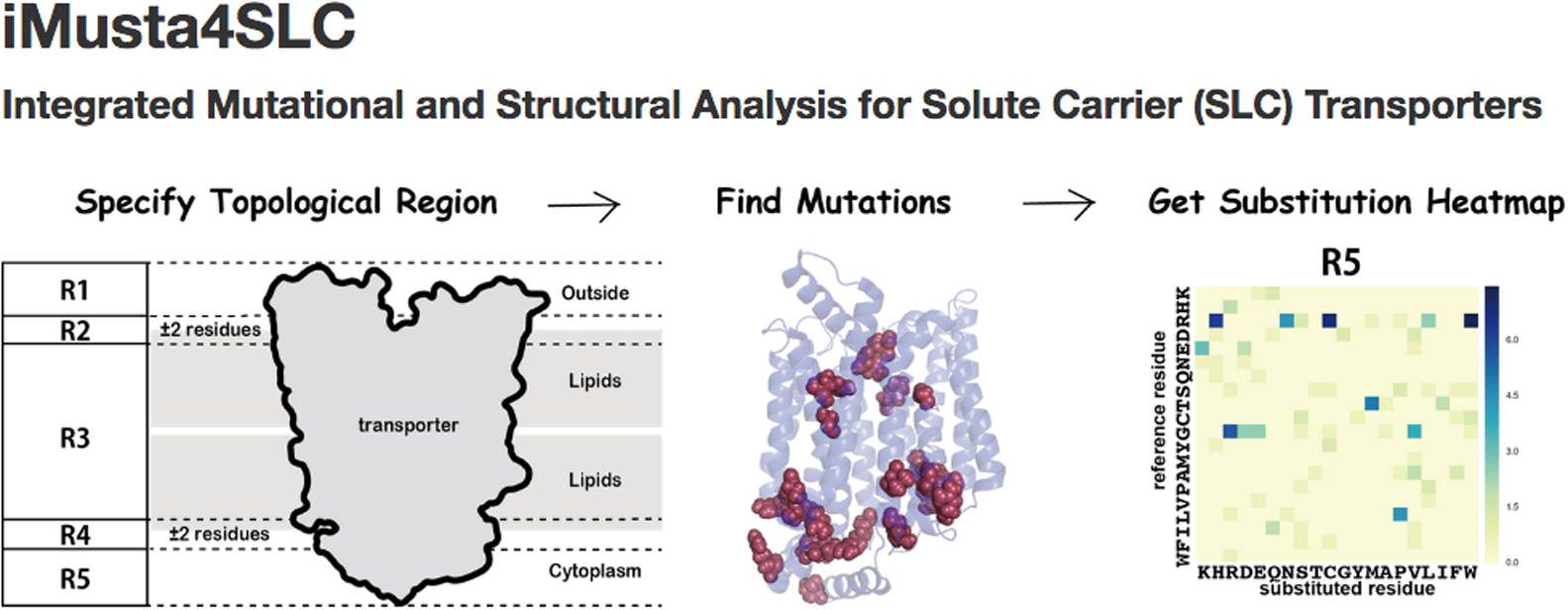
1 0 0 0 OA iMusta4SLC: Database for the structural property and variations of solute carrier transporters
- 著者
- Akiko Higuchi Naoki Nonaka Kei Yura
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.94-103, 2018 (Released:2018-04-27)
- 参考文献数
- 50
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Membrane transporter proteins play important roles in transport of nutrients into the cell, in transport of waste out of the cell, in maintenance of homeostasis, and in signal transduction. Solute carrier (SLC) transporter is the superfamily, which has the largest number of genes (>400 in humans) in membrane transporter and consists of 52 families. SLC transporters carry a wide variety of substrates such as amino acids, peptides, saccharides, ions, neurotransmitters, lipids, hormones and related materials. Despite the apparent importance for the substrate transport, the information of sequence variation and three-dimensional structures have not been integrated to the level of providing new knowledge on the relationship to, for instance, diseases. We, therefore, built a new database named iMusta4SLC, which is available at http://cib.cf.ocha.ac.jp/slc/, that connected the data of structural properties and of pathogenic mutations on human SLC transporters. iMusta4SLC helps to investigate the structural features of pathogenic mutations on SLC transporters. With this database, we found that the mutations at the conserved arginine were frequently involved in diseases, and were located at a border between the membrane and the cytoplasm. Especially in SLC families 2 and 22, the conserved residues formed a large cluster at the border. In SLC2A1, one third of the reported pathogenic missense mutations were found in this conserved cluster.
- 著者
- Kazunori D. Yamada Hafumi Nishi Junichi Nakata Kengo Kinoshita
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, pp.157-163, 2016 (Released:2016-07-14)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Functional sites on proteins play an important role in various molecular interactions and reactions between proteins and other molecules. Thus, mutations in functional sites can severely affect the overall phenotype. Progress of genome sequencing projects has yielded a wealth of information on single nucleotide variants (SNVs), especially those with less than 1% minor allele frequency (rare variants). To understand the functional influence of genetic variants at a protein level, we investigated the relationship between SNVs and protein functional sites in terms of minor allele frequency and the structural position of variants. As a result, we observed that SNVs were less abundant at ligand binding sites, which is consistent with a previous study on SNVs and protein interaction sites. Additionally, we found that non-rare variants tended to be located slightly apart from enzyme active sites. Examination of non-rare variants revealed that most of the mutations resulted in moderate changes of the physico-chemical properties of amino acids, suggesting the existence of functional constraints. In conclusion, this study shows that the mapping of genetic variants on protein structures could be a powerful approach to evaluate the functional impact of rare genetic variations.
- 著者
- Saeko Yanaka Takamasa Ueno Kouhei Tsumoto Kenji Sugase
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.11, pp.103-106, 2015 (Released:2015-04-18)
- 参考文献数
- 7
Structural fluctuation on microsecond to millisecond time scales has been reported to play an important role in proteins that undergo significant structural change during their expression of function. In these proteins, the structural change was obvious in the crystal structures. However, protein motions in solution could contribute to the function of proteins, even if no significant structural difference is observed in crystal structure of different states while they function. In this review, we introduce our recent report on the stabilization mechanism of human leukocyte antigen, and the possibility of fluctuation contributing to several biophysical properties of proteins.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Iwamoto
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.7, pp.21-28, 2011 (Released:2011-02-17)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 36
Insects, the largest group of animals on the earth, owe their prosperity to their ability of flight and small body sizes. The ability of flight provided means for rapid translocation. The small body size allowed access to unutilized niches. By acquiring both features, however, insects faced a new problem: They were forced to beat their wings at enormous frequencies. Insects have overcome this problem by inventing asynchronous flight muscle, a highly specialized form of striated muscle capable of oscillating at >1,000 Hz. This article reviews the structure, mechanism, and molecular evolution of this unique invention of nature.