1 0 0 0 OA Second harmonic generation polarization microscopy as a tool for protein structure analysis
- 著者
- Junichi Kaneshiro Yasushi Okada Tomohiro Shima Mika Tsujii Katsumi Imada Taro Ichimura Tomonobu M. Watanabe
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, pp.147-157, 2019 (Released:2019-09-20)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 2 6
Cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography have been the major tools of protein structure analysis for decades and will certainly continue to be essential in the future. Moreover, nuclear magnetic resonance or Förster resonance energy transfer can measure structural dynamics. Here, we propose to add optical second-harmonic generation (SHG), which is a nonlinear optical scattering process sensitive to molecular structures in illuminated materials, to the tool-kit of structural analysis methodologies. SHG can be expected to probe the structural changes of proteins in the physiological condition, and thus link protein structure and biological function. We demonstrate that a conformational change as well as its dynamics in protein macromolecular assemblies can be detected by means of SHG polarization measurement. To prove the capability of SHG polarization measurement with regard to protein structure analysis, we developed an SHG polarization microscope to analyze microtubules in solution. The difference in conformation between microtubules with different binding molecules was successfully observed as polarization dependence of SHG intensity. We also succeeded in capturing the temporal variation of structure in a photo-switchable protein crystal in both activation and inactivation processes. These results illustrate the potential of this method for protein structure analysis in physiological solutions at room temperature without any labeling.
1 0 0 0 OA Announcement of BPPB paper awards 2021
- 著者
- Haruki Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.035, (Released:2021-12-02)
- 著者
- Kumiko Hayashi Shinsuke Niwa
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.241-243, 2021 (Released:2021-10-20)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 2
- 著者
- Haruki Nakamura Masahide Kikkawa Takeshi Murata
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.030, (Released:2021-10-23)
- 著者
- Akihiko Ishijima Yasushi Okada
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.029, (Released:2021-10-21)
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Noji
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.024, (Released:2021-10-05)
- 著者
- Daisuke Kuroda Kouhei Tsumoto
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.022, (Released:2021-08-21)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Masashi Unno Yuu Hirose Masaki Mishima Takashi Kikukawa Tomotsumi Fujisawa Tatsuya Iwata Jun Tamogami
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.127-130, 2021 (Released:2021-06-18)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 2
1 0 0 0 OA myPresto/omegagene 2020: a molecular dynamics simulation engine for virtual-system coupled sampling
- 著者
- Kota Kasahara Hiroki Terazawa Hayato Itaya Satoshi Goto Haruki Nakamura Takuya Takahashi Junichi Higo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.BSJ-2020013, (Released:2020-10-15)
- 被引用文献数
- 9
- 著者
- Masako Koyama Yoshiyuki Matsuura
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, pp.145-150, 2012 (Released:2012-11-30)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1 4
CRM1 (also known as exportin 1 or Xpo1) is the most versatile nuclear export receptor (exportin) that carries a broad range of proteins and ribonucleoproteins from the nucleus to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore complex. The majority of the export substrates of CRM1 contain a short peptide sequence, so-called leucine-rich nuclear export signal (NES), which typically harbor four or five characteristically spaced hydrophobic residues. The transport directionality is determined by the small GTPase Ran and Ran-binding proteins that control the binding and dissociation of cargo. Here we review recent structural studies that advanced understanding of how NES is specifically recognized by CRM1 in the nucleus, and how NES is rapidly dissociated from CRM1 in the cytoplasm.
- 著者
- Ryota Kojima Takashi Yoshidome
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.011, (Released:2021-04-16)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
1 0 0 0 OA Earthworm individualities when facing a conflict between turn alternation and aversive learning
- 著者
- Tadashi Nakashima Hajime Mushiake Kazuhiro Sakamoto
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.159-164, 2018 (Released:2018-07-31)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 2 5
An individual’s personality develops through a combination of experiences and parental inheritance. When faced with a conflict, will an individual take an innate behavior or a learned one? In such situations, individuality will manifest itself. Here, we focused on turn alternation behavior, which is a habitual tendency to turn in the direction opposite the preceding turn, in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) and examined how this behavior is affected by an aversive stimulus. Of 10 earthworms, 3 were affected by the stimulus. Turn alternation deteriorated in two worms, one of which showed anti-turn alternation behavior, whereas the remaining worm showed an enhanced tendency toward turn alternation. Earthworms have a relatively simple nervous system. This study opens the door to investigate the neuronal basis for individuality that emerges between nature and nurture.
- 著者
- Junko Kamiguri Noriko Tsuchiya Ruri Hidema Zenji Yatabe Masahiko Shoji Chihiro Hashimoto Robert Bernard Pansu Hideharu Ushiki
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, pp.11-19, 2012 (Released:2012-01-17)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
The contraction process of living Vorticella sp. in polymer solutions with various viscosities has been investigated by image processing using a high-speed video camera. The viscosity of the external fluid ranges from 1 to 5 mPa·s for different polymer additives such as hydroxypropyl cellulose, polyethylene oxide, and Ficoll. The temporal change in the contraction length of Vorticella sp. in various macromolecular solutions is fitted well by a stretched exponential function based on the nucleation and growth model. The maximum speed of the contractile process monotonically decreases with an increase in the external viscosity, in accordance with power law behavior. The index values approximate to 0.5 and this suggests that the viscous energy dissipated by the contraction of Vorticella sp. is constant in a macromolecular environment.
- 著者
- Junko Kamiguri Noriko Tsuchiya Ruri Hidema Masatoshi Tachibana Zenji Yatabe Masahiko Shoji Chihiro Hashimoto Robert Bernard Pansu Hideharu Ushiki
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, pp.1-9, 2012 (Released:2012-01-17)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
The contraction process of living Vorticella sp. has been investigated by image processing using a high-speed video camera. In order to express the temporal change in the stalk length resulting from the contraction, a damped spring model and a nucleation and growth model are applied. A double exponential is deduced from a conventional damped spring model, while a stretched exponential is newly proposed from a nucleation and growth model. The stretched exponential function is more suitable for the curve fitting and suggests a more particular contraction mechanism in which the contraction of the stalk begins near the cell body and spreads downwards along the stalk. The index value of the stretched exponential is evaluated in the range from 1 to 2 in accordance with the model in which the contraction undergoes through nucleation and growth in a one-dimensional space.
1 0 0 0 OA Light-induced difference FTIR spectroscopy of primate blue-sensitive visual pigment at 163 K
- 著者
- Shunpei Hanai Kota Katayama Hiroo Imai Hideki Kandori
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.005, (Released:2021-02-13)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
1 0 0 0 OA Biphasic spatiotemporal regulation of GRB2 dynamics by p52SHC for transient RAS activation
- 著者
- Ryo Yoshizawa Nobuhisa Umeki Akihiro Yamamoto Masayuki Murata Yasushi Sako
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.1-12, 2021 (Released:2021-02-05)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 7
RTK-RAS-MAPK systems are major signaling pathways for cell fate decisions. Among the several RTK species, it is known that the transient activation of ERK (MAPK) stimulates cell proliferation, whereas its sustained activation induces cell differentiation. In both instances however, RAS activation is transient, suggesting that the strict temporal regulation of its activity is critical in normal cells. RAS on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane is activated by SOS through the recruitment of GRB2/SOS complex to the RTKs that are phosphorylated after stimulation with growth factors. The adaptor protein GRB2 recognizes phospho-RTKs both directly and indirectly via another adaptor protein, SHC. We here studied the regulation of GRB2 recruitment under the SHC pathway using single-molecule imaging and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy in living cells. We stimulated MCF7 cells with a differentiation factor, heregulin, and observed the translocation, complex formation, and phosphorylation of cell signaling molecules including GRB2 and SHC. Our results suggest a biphasic regulation of the GRB2/SOS-RAS pathway by SHC: At the early stage (<10 min) of stimulation, SHC increased the amplitude of RAS activity by increasing the association sites for the GRB2/SOS complex on the plasma membrane. At the later stage however, SHC suppressed RAS activation and sequestered GRB2 molecules from the membrane through the complex formation in the cytoplasm. The latter mechanism functions additively to other mechanisms of negative feedback regulation of RAS from MEK and/or ERK to complete the transient activation dynamics of RAS.
- 著者
- Yujiro Nagasaka Shoko Hososhima Naoko Kubo Takashi Nagata Hideki Kandori Keiichi Inoue Hiromu Yawo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, pp.59-70, 2020 (Released:2020-07-22)
- 参考文献数
- 51
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Microbial rhodopsin is a large family of membrane proteins having seven transmembrane helices (TM1-7) with an all-trans retinal (ATR) chromophore that is covalently bound to Lys in the TM7. The Trp residue in the middle of TM3, which is homologous to W86 of bacteriorhodopsin (BR), is highly conserved among microbial rhodopsins with various light-driven functions. However, the significance of this Trp for the ion transport function of microbial rhodopsins has long remained unknown. Here, we replaced the W163 (BR W86 counterpart) of a channelrhodopsin (ChR), C1C2/ChRWR, which is a chimera between ChR1 and 2, with a smaller aromatic residue, Phe to verify its role in the ion transport. Under whole-cell patch clamp recordings from the ND7/23 cells that were transfected with the DNA plasmid coding human codon optimized C1C2/ChRWR (hWR) or its W163F mutant (hWR-W163F), the photocurrents were evoked by a pulsatile light at 475 nm. The ion-transporting activity of hWR was strongly altered by the W163F mutation in 3 points: (1) the H+ leak at positive membrane potential (Vm) and its light-adaptation, (2) the attenuation of cation channel activity and (3) the manifestation of outward H+ pump activity. All of these results strongly suggest that W163 has a role in stabilizing the structure involved in the gating-on and -off of the cation channel, the role of “gate keeper”. We can attribute the attenuation of cation channel activity to the incomplete gating-on and the H+ leak to the incomplete gating-off.
- 著者
- Masaki Sasai George Chikenji Tomoki P. Terada
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, pp.281-293, 2016 (Released:2016-11-18)
- 参考文献数
- 73
- 被引用文献数
- 3 5
A simple statistical mechanical model proposed by Wako and Saitô has explained the aspects of protein folding surprisingly well. This model was systematically applied to multiple proteins by Muñoz and Eaton and has since been referred to as the Wako-Saitô-Muñoz-Eaton (WSME) model. The success of the WSME model in explaining the folding of many proteins has verified the hypothesis that the folding is dominated by native interactions, which makes the energy landscape globally biased toward native conformation. Using the WSME and other related models, Saitô emphasized the importance of the hierarchical pathway in protein folding; folding starts with the creation of contiguous segments having a native-like configuration and proceeds as growth and coalescence of these segments. The Φ-values calculated for barnase with the WSME model suggested that segments contributing to the folding nucleus are similar to the structural modules defined by the pattern of native atomic contacts. The WSME model was extended to explain folding of multi-domain proteins having a complex topology, which opened the way to comprehensively understanding the folding process of multi-domain proteins. The WSME model was also extended to describe allosteric transitions, indicating that the allosteric structural movement does not occur as a deterministic sequential change between two conformations but as a stochastic diffusive motion over the dynamically changing energy landscape. Statistical mechanical viewpoint on folding, as highlighted by the WSME model, has been renovated in the context of modern methods and ideas, and will continue to provide insights on equilibrium and dynamical features of proteins.
- 著者
- Ji-Chen Ho Chih-Hung Lee
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.11, pp.17-24, 2015 (Released:2015-02-13)
- 参考文献数
- 70
- 被引用文献数
- 12 36
TRP channels are expressed in various cells in skin. As an organ system to border the host and environment, many nonneuronal cells, including epidermal keratinocytes and melanocytes, express several TRP channels functionally distinct from sensory processing. TRPV1 and TRPV3 in keratinocytes of the epidermis and hair apparatus inhibit proliferation, induce terminal differentiation, induce apoptosis, and promote inflammation. Activation of TRPV4, 6, and TRPA1 promotes regeneration of the severed skin barriers. TRPA1 also enhances responses in contact hypersensitivity. TRPCs in keratinocytes regulate epidermal differentiation. In human diseases with pertubered epidermal differentiation, the expression of TRPCs are altered. TRPMs, which contribute to melanin production in melanocytes, serve as significant prognosis markers in patients with metastatic melanoma. In summary, not only act in sensory processing, TRP channels also contribute to epidermal differentiation, proliferation, barrier integration, skin regeneration, and immune responses. In diseases with aberrant TRP channels, TRP channels might be good therapeutic targets.
- 著者
- Sumita Das Tomoki P. Terada Masaki Sasai
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.136-150, 2018 (Released:2018-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 9
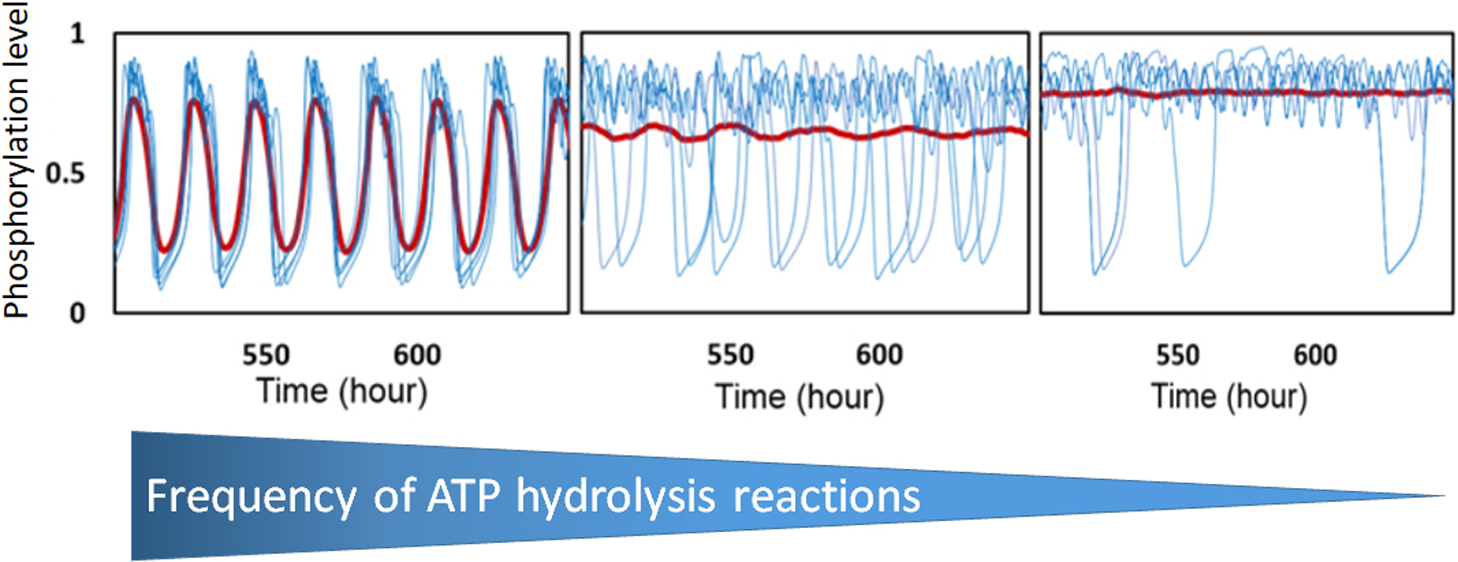
When three cyanobacterial proteins, KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC, are incubated with ATP in vitro, the phosphorylation level of KaiC hexamers shows stable oscillation with approximately 24 h period. In order to understand this KaiABC clockwork, we need to analyze both the macroscopic synchronization of a large number of KaiC hexamers and the microscopic reactions and structural changes in individual KaiC molecules. In the present paper, we explain two coarse-grained theoretical models, the many-molecule (MM) model and the single-molecule (SM) model, to bridge the gap between macroscopic and microscopic understandings. In the simulation results with these models, ATP hydrolysis in the CI domain of KaiC hexamers drives oscillation of individual KaiC hexamers and the ATP hydrolysis is necessary for synchronizing oscillations of a large number of KaiC hexamers. Sensitive temperature dependence of the lifetime of the ADP bound state in the CI domain makes the oscillation period temperature insensitive. ATPase activity is correlated to the frequency of phosphorylation oscillation in the single molecule of KaiC hexamer, which should be the origin of the observed ensemble-level correlation between the ATPase activity and the frequency of phosphorylation oscillation. Thus, the simulation results with the MM and SM models suggest that ATP hydrolysis stochastically occurring in each CI domain of individual KaiC hexamers is a key process for oscillatory behaviors of the ensemble of many KaiC hexamers.