- 著者
- Minoru Kurisu Masayuki Imai
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e210002, (Released:2023-12-19)
How do the living systems emerge from non-living molecular assemblies? What physical and chemical principles supported the process? To address these questions, a promising strategy is to artificially reconstruct living cells in a bottom-up way. Recently, the authors developed the “synthetic minimal cell” system showing recursive growth and division cycles, where the concepts of information molecules, metabolic pathways, and cell reproduction were artificially and concisely redesigned with the vesicle-based system. We intentionally avoided using the sophisticated molecular machinery of the biological cells and tried to redesign the cells in the simplest forms. This review focuses on the similarities and differences between the biological cells and our synthetic minimal cell concerning each concept of cells. Such comparisons between natural and artificial cells will provide insights on how the molecules should be assembled to create living systems to the wide readers in the field of synthetic biology, artificial cells, and protocells research. This review article is an extended version of the Japanese article “Growth and division of vesicles coupled with information molecules,” published in SEIBUTSU-BUTSURI vol. 61, p. 378-381 (2021).
- 著者
- Ken H. Nagai
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.51-57, 2018 (Released:2018-02-09)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4 5
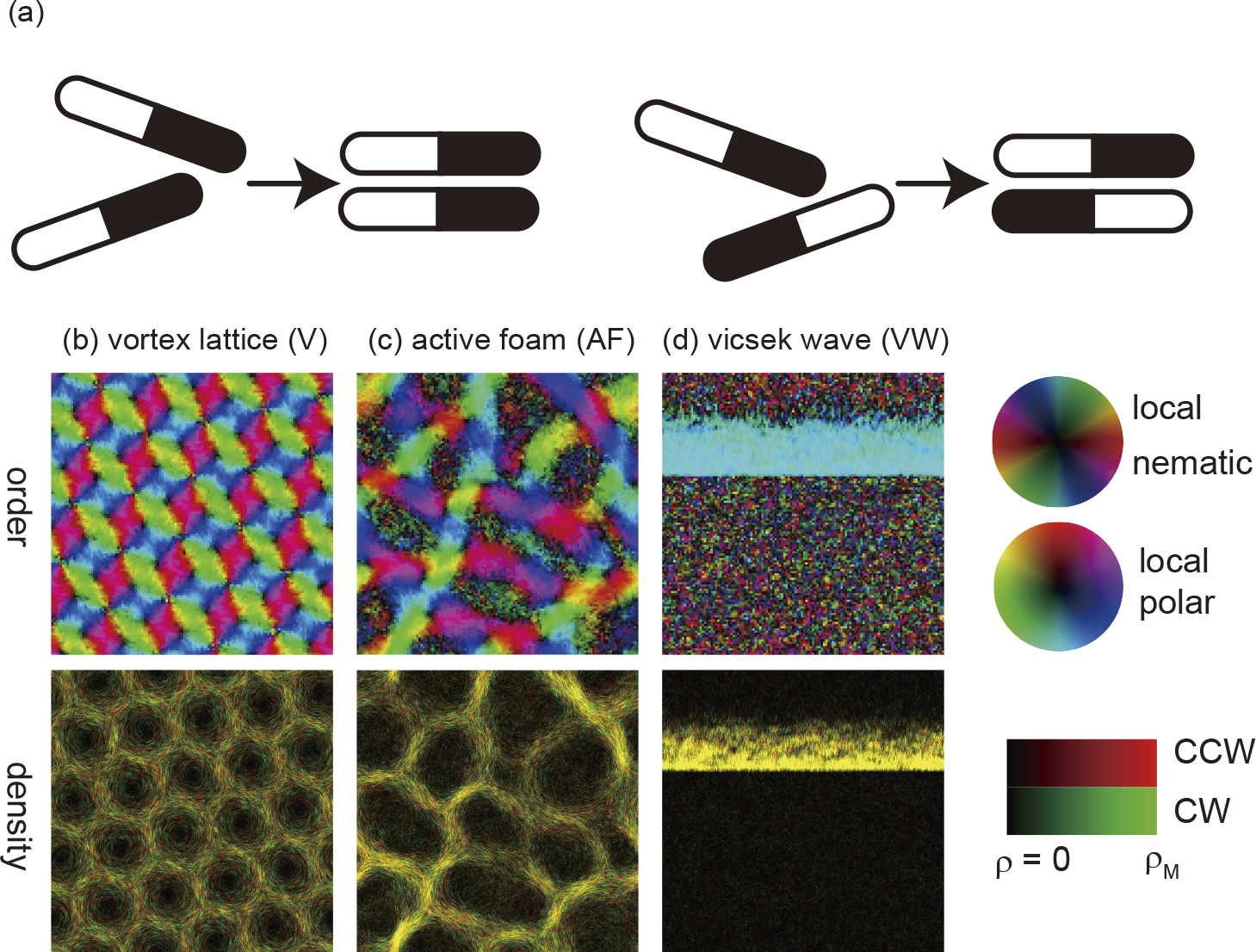
Self-propelled rods, which propel by themselves in the direction from the tail to the head and align nematically through collision, have been well-investigated theoretically. Various phenomena including true long-range ordered phase with the Giant number fluctuations, and the collective motion composed of many vorices were predicted using the minimal mathematical models of self-propelled rods. Using filamentous bacteria and running microtubules, we found that the predicted phenomena by the minimal models occur in the real world. This strongly indicates that there exists the unified description of self-propelled rods independent of the details of the systems. The theoretically predicted phenomena and the experimental results concerning the phenomena are reviewed.
- 著者
- Yuhei Tachi Satoru G. Itoh Hisashi Okumura
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.e190010, 2022 (Released:2022-04-20)
- 参考文献数
- 145
- 被引用文献数
- 3
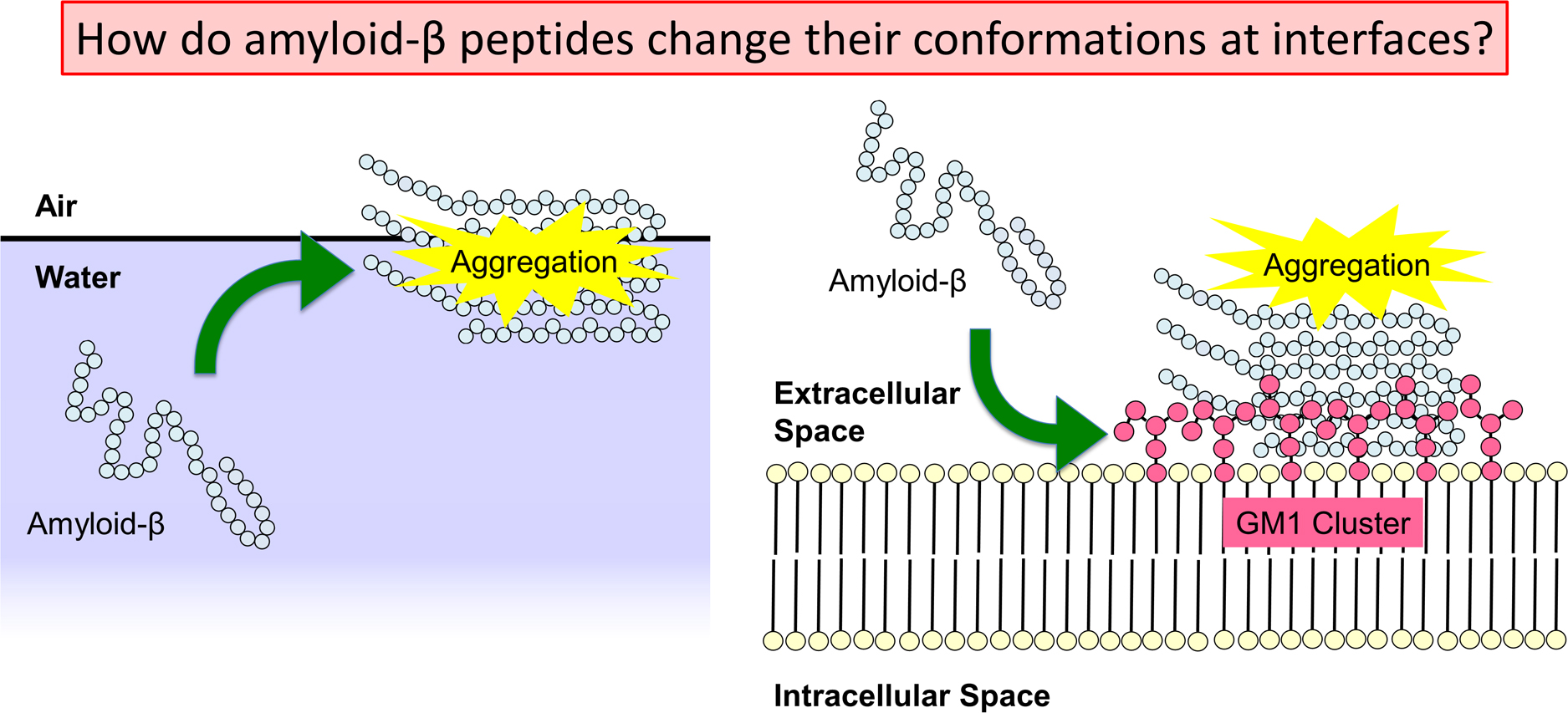
Alzheimer’s disease is thought to be caused by the aggregation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides. Their aggregation is accelerated at hydrophilic/hydrophobic interfaces such as the air–water interface and the surface of monosialotetrahexosylganglioside (GM1) clusters on neuronal cell membranes. In this review, we present recent studies of full-length Aβ (Aβ40) peptides and Aβ(16–22) fragments in such heterogeneous environments by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. These peptides have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino-acid residues and tend to exist at the hydrophilic/hydrophobic interface. Therefore, the peptide concentration increases at the interface, which is one of the factors that promote aggregation. Furthermore, it was found that Aβ40 forms an α-helix structure and then a β-hairpin structure at the interface. The β-hairpin promotes the formation of oligomers with intermolecular β-sheets. It means that not only the high concentration of Aβ40 at the interface but also the structure of Aβ40 itself promotes aggregation. In addition, MD simulations of Aβ40 on recently-developed GM1-glycan clusters showed that the HHQ (13–15) segment of Aβ40 is important for the recognition of GM1-glycan clusters. It was also elucidated that Aβ40 forms a helix structure in the C-terminal region on the GM1-glycan cluster. This result suggests that the helix formation, which is the first step in the conformational changes toward pathological aggregation, is initiated at the GM1-glycan moieties rather than at the lipid-ceramide moieties. These studies will enhance the physicochemical understanding of the structural changes of Aβ at the heterogeneous interfaces and the mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Ebata Satoru Kidoaki
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.e190036, 2022 (Released:2022-10-05)
- 参考文献数
- 101
In living tissues where cells migrate, the spatial distribution of mechanical properties, especially matrix stiffness, is generally heterogeneous, with cell scales ranging from 10 to 1000 μm. Since cell migration in the body plays a critical role in morphogenesis, wound healing, and cancer metastasis, it is essential to understand the migratory dynamics on the matrix with cell-scale stiffness heterogeneity. In general, cell migration is driven by the extension and contraction of the cell body owing to the force from actin polymerization and myosin motors in the actomyosin cytoskeleton. When a cell is placed on a matrix with a simple stiffness gradient, directional migration called durotaxis emerges because of the asymmetric extension and contraction of the pseudopodia, which is accompanied by the asymmetric distribution of focal adhesions. Similarly, to determine cell migration on a matrix with cell-scale stiffness heterogeneity, the interaction between cell-scale stiffness heterogeneity and cellular responses, such as the dynamics of the cell-matrix adhesion site, intracellular prestress, and cell shape, should play a key role. In this review, we summarize systematic studies on the dynamics of cell migration, shaping, and traction force on a matrix with cell-scale stiffness heterogeneity using micro-elastically patterned hydrogels. We also outline the cell migration model based on cell-shaping dynamics that explains the general durotaxis induced by cell-scale stiffness heterogeneity. This review article is an extended version of the Japanese article, Dynamics of Cell Shaping and Migration on the Matrix with Cell-scale Stiffness-heterogeneity, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 61, p. 152–156 (2021).
- 著者
- Tetsushi Komoto Masashi Fujii Akinori Awazu
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.e190018, 2022 (Released:2022-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 1
X chromosome inactivation center (Xic) pairing occurs during the differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells from female mouse embryos, and is related to X chromosome inactivation, the circadian clock, intra-nucleus architecture, and metabolism. However, the mechanisms underlying the identification and approach of X chromosome pairs in the crowded nucleus are unclear. To elucidate the driving force of Xic pairing, we developed a coarse-grained molecular dynamics model of intranuclear chromosomes in ES cells and in cells 2 days after the onset of differentiation (2-day cells) by considering intrachromosomal epigenetic-structural feature-dependent mechanics. The analysis of the experimental data showed that X-chromosomes exhibit the rearrangement of their distributions of open/closed chromatin regions on their surfaces during cell differentiation. By simulating models where the excluded volume effects of closed chromatin regions are stronger than those of open chromatin regions, such rearrangement of open/closed chromatin regions on X-chromosome surfaces promoted the mutual approach of the Xic pair. These findings suggested that local intrachromosomal epigenetic features may contribute to the regulation of cell species-dependent differences in intranuclear architecture.
- 著者
- Marie Kurihara Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, pp.121-129, 2015 (Released:2015-12-11)
- 参考文献数
- 71
- 被引用文献数
- 34 35
One of the major topics in biophysics and physicobiology is to understand and utilize biological functions using various advanced techniques. Taking advantage of the photoreactivity of the seven-transmembrane rhodopsin protein family has been actively investigated by a variety of methods. Rhodopsins serve as models for membrane-embedded proteins, for photoactive proteins and as a fundamental tool for optogenetics, a new technology to control biological activity with light. In this review, we summarize progress of microbial rhodopsin research from the viewpoint of distribution, diversity and potential.
- 著者
- Shingo Wakao Noriko Saitoh Akinori Awazu
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.2, pp.e200020, 2023 (Released:2023-05-23)
- 参考文献数
- 33
Nuclear speckles are nuclear bodies consisting of populations of small and irregularly shaped droplet-like molecular condensates that contain various splicing factors. Recent experiments have revealed the following structural features of nuclear speckles: (I) Each molecular condensate contains SON and SRRM2 proteins, and MALAT1 non-coding RNA surrounds these condensates; (II) During normal interphase of the cell cycle in multicellular organisms, these condensates are broadly distributed throughout the nucleus. In contrast, when cell transcription is suppressed, the condensates fuse and form strongly condensed spherical droplets; (III) SON is dispersed spatially in MALAT1 knocked-down cells and MALAT1 is dispersed in SON knocked-down cells because of the collapse of the nuclear speckles. However, the detailed interactions among the molecules that are mechanistically responsible for the structural variation remain unknown. In this study, a coarse-grained molecular dynamics model of the nuclear speckle was developed by considering the dynamics of SON, SRRM2, MALAT1, and pre-mRNA as representative components of the condensates. The simulations reproduced the structural changes, which were used to predict the interaction network among the representative components of the condensates.
- 著者
- Tony Z. Jia Kuhan Chandru
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e200012, (Released:2023-02-22)
While it is often believed that the origins of life required participation of early biomolecules, it has been recently proposed that “non-biomolecules”, which would have been just as, if not more, abundant on early Earth, could have played a part. In particular, recent research has highlighted the various ways by which polyesters, which do not participate in modern biology, could have played a major role during the origins of life. Polyesters could have been synthesized readily on early Earth through simple dehydration reactions at mild temperatures involving abundant “non-biological” alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) monomers. This dehydration synthesis process results in a polyester gel, which upon further rehydration, can assemble into membraneless droplets proposed to be protocell models. These proposed protocells can provide functions to a primitive chemical system, such as analyte segregation or protection, which could have further led to chemical evolution from prebiotic chemistry to nascent biochemistry. Here, to further shed light into the importance of “non-biomolecular” polyesters at the origins of life and to highlight future directions of study, we review recent studies which focus on primitive synthesis of polyesters from AHAs and assembly of these polyesters into membraneless droplets. Specifically, most of the recent progress in this field in the last five years has been led by laboratories in Japan, and these will be especially highlighted. This article is based on an invited presentation at the 60th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society of Japan held in September, 2022 as an 18th Early Career Awardee.
3 0 0 0 OA Molecular mechanisms of amyloid-β peptide fibril and oligomer formation: NMR-based challenges
- 著者
- Hidekazu Hiroaki
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e200007, (Released:2023-02-03)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
To completely treat and ultimately prevent dementia, it is essential to elucidate its pathogenic mechanisms in detail. There are two major hypotheses for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s dementia: the β-amyloid (Aβ) hypothesis and the tau hypothesis. The modified amyloid hypothesis, which proposes that toxic oligomers rather than amyloid fibrils are the essential cause, has recently emerged. Aβ peptides [Aβ(1–40) and Aβ(1–42)] form highly insoluble aggregates in vivo and in vitro. These Aβ aggregates contain many polymorphisms, whereas Aβ peptides are intrinsically disordered in physiological aqueous solutions without any compact conformers. Over the last three decades, solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) has greatly contributed to elucidating the structure of each polymorph, while solution NMR has revealed the dynamic nature of the transient conformations of the monomer. Moreover, several methods to investigate the aggregation process based on the observation of magnetization saturation transfer have also been developed. The complementary use of NMR methods with cryo-electron microscopy, which has rapidly matured, is expected to clarify the relationship between the amyloid and molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s dementia in the near future. This review article is an extended version of the Japanese article, Insights into the Mechanisms of Oligomerization/Fibrilization of Amyloid β Peptide from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 62, p.39-42 (2022).
- 著者
- Jonathan R. Church Jógvan Magnus Haugaard Olsen Igor Schapiro
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e201007, (Released:2023-01-24)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Multiscale simulations have been established as a powerful tool to calculate and predict excitation energies in complex systems such as photoreceptor proteins. In these simulations the chromophore is typically treated using quantum mechanical (QM) methods while the protein and surrounding environment are described by a classical molecular mechanics (MM) force field. The electrostatic interactions between these regions are often treated using electrostatic embedding where the point charges in the MM region polarize the QM region. A more sophisticated treatment accounts also for the polarization of the MM region. In this work, the effect of such a polarizable embedding on excitation energies was benchmarked and compared to electrostatic embedding. This was done for two different proteins, the lipid membrane-embedded jumping spider rhodopsin and the soluble cyanobacteriochrome Slr1393g3. It was found that the polarizable embedding scheme produces absorption maxima closer to experimental values. The polarizable embedding scheme was also benchmarked against expanded QM regions and found to be in qualitative agreement. Treating individual residues as polarizable recovered between 50% and 71% of the QM improvement in the excitation energies, depending on the system. A detailed analysis of each amino acid residue in the chromophore binding pocket revealed that aromatic residues result in the largest change in excitation energy compared to the electrostatic embedding. Furthermore, the computational efficiency of polarizable embedding allowed it to go beyond the binding pocket and describe a larger portion of the environment, further improving the results.
- 著者
- Mikio Kataoka
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e201006, (Released:2023-01-19)
It marked half a century since the discovery of bacteriorhodopsin two years ago. On this occasion, I have revisited historically important diffraction studies of this membrane protein, based on my recollections. X-ray diffraction and electron diffraction, and electron microscopy, described the low-resolution structure of bacteriorhodopsin within the purple membrane. Neutron diffraction was effective to assign the helical regions in the primary structure with 7 rods revealed by low-resolution structure as well as to describe the retinal position. Substantial conformational changes upon light illumination were clarified by the structures of various photointermediates. Early trials of time-resolved studies were also introduced. Models for the mechanism of light-driven proton pump based on the low-resolution structural studies are also described. Significantly, they are not far from the today’s understanding. I believe that the spirit of the early research scientists in this field and the essence of their studies, which constitute the foundations of the field, still actively fertilizes current membrane protein research.
- 著者
- Tohru Minamino Miki Kinoshita Yusuke V. Morimoto Keiichi Namba
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e190046, (Released:2022-11-19)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
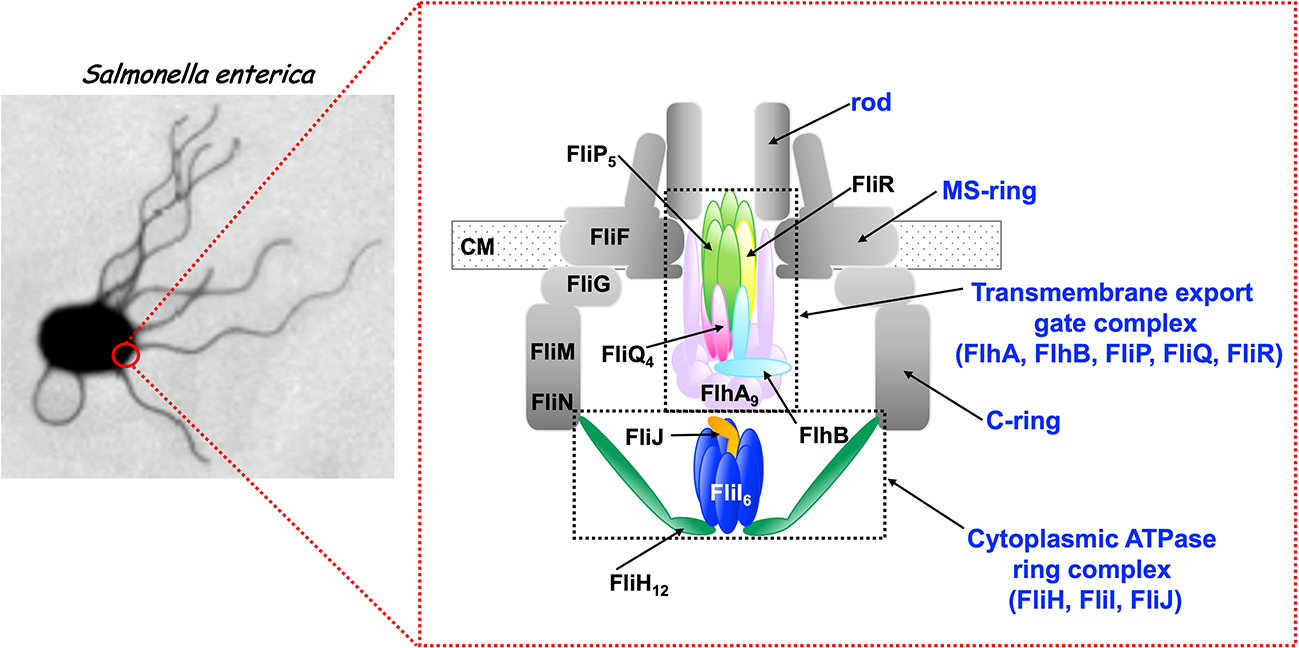
Bacteria employ the flagellar type III secretion system (fT3SS) to construct flagellum, which acts as a supramolecular motility machine. The fT3SS of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is composed of a transmembrane export gate complex and a cytoplasmic ATPase ring complex. The transmembrane export gate complex is fueled by proton motive force across the cytoplasmic membrane and is divided into four distinct functional parts: a dual-fuel export engine; a polypeptide channel; a membrane voltage sensor; and a docking platform. ATP hydrolysis by the cytoplasmic ATPase complex converts the export gate complex into a highly efficient proton (H+)/ protein antiporter that couples inward-directed H+ flow with outward-directed protein export. When the ATPase ring complex does not work well in a given environment, the export gate complex will remain inactive. However, when the electric potential difference, which is defined as membrane voltage, rises above a certain threshold value, the export gate complex becomes an active H+/protein antiporter to a considerable degree, suggesting that the export gate complex has a voltage-gated activation mechanism. Furthermore, the export gate complex also has a sodium ion (Na+) channel to couple Na+ influx with flagellar protein export. In this article, we review our current understanding of the activation mechanism of the dual-fuel protein export engine of the fT3SS. This review article is an extended version of a Japanese article, Membrane voltage-dependent activation of the transmembrane export gate complex in the bacterial flagellar type III secretion system, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 62, p165–169 (2022).
- 著者
- Kazuho Yoshida Takahiro Yamashita Kengo Sasaki Keiichi Inoue Yoshinori Shichida Hideki Kandori
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.14, pp.183-190, 2017 (Released:2017-12-19)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 4
We previously showed that the chimeric proteins of microbial rhodopsins, such as light-driven proton pump bacteriorhodopsin (BR) and Gloeobacter rhodopsin (GR) that contain cytoplasmic loops of bovine rhodopsin, are able to activate Gt protein upon light absorption. These facts suggest similar protein structural changes in both the light-driven proton pump and animal rhodopsin. Here we report two trials to engineer chimeric rhodopsins, one for the inserted loop, and another for the microbial rhodopsin template. For the former, we successfully activated Gs protein by light through the incorporation of the cytoplasmic loop of β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR). For the latter, we did not observe any G-protein activation for the light-driven sodium pump from Indibacter alkaliphilus (IndiR2) or a light-driven chloride pump halorhodopsin from Natronomonas pharaonis (NpHR), whereas the light-driven proton pump GR showed light-dependent G-protein activation. This fact suggests that a helix opening motion is common to G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) and GR, but not to IndiR2 and NpHR. Light-induced difference FTIR spectroscopy revealed similar structural changes between WT and the third loop chimera for each light-driven pump. A helical structural perturbation, which was largest for GR, was further enhanced in the chimera. We conclude that similar structural dynamics that occur on the cytoplasmic side of GPCR are needed to design chimeric microbial rhodopsins.
- 著者
- Hiroaki Hata Duy Phuoc Tran Mohamed Marzouk Sobeh Akio Kitao
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.037, (Released:2021-12-04)
- 被引用文献数
- 22
3 0 0 0 OA Beyond multi-disciplinary and cross-scale analyses of the cyanobacterial circadian clock system
- 著者
- Shuji Akiyama Hironari Kamikubo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.031, (Released:2021-10-23)
- 著者
- Tony Z. Jia Yutetsu Kuruma
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.032, (Released:2021-11-18)
- 著者
- Izuru Kawamura Hayato Seki Seiya Tajima Yoshiteru Makino Arisu Shigeta Takashi Okitsu Akimori Wada Akira Naito Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.019, (Released:2021-07-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
3 0 0 0 OA DNA nanotechnology provides an avenue for the construction of programmable dynamic molecular systems
- 著者
- Yusuke Sato Yuki Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.116-126, 2021 (Released:2021-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 80
- 被引用文献数
- 2
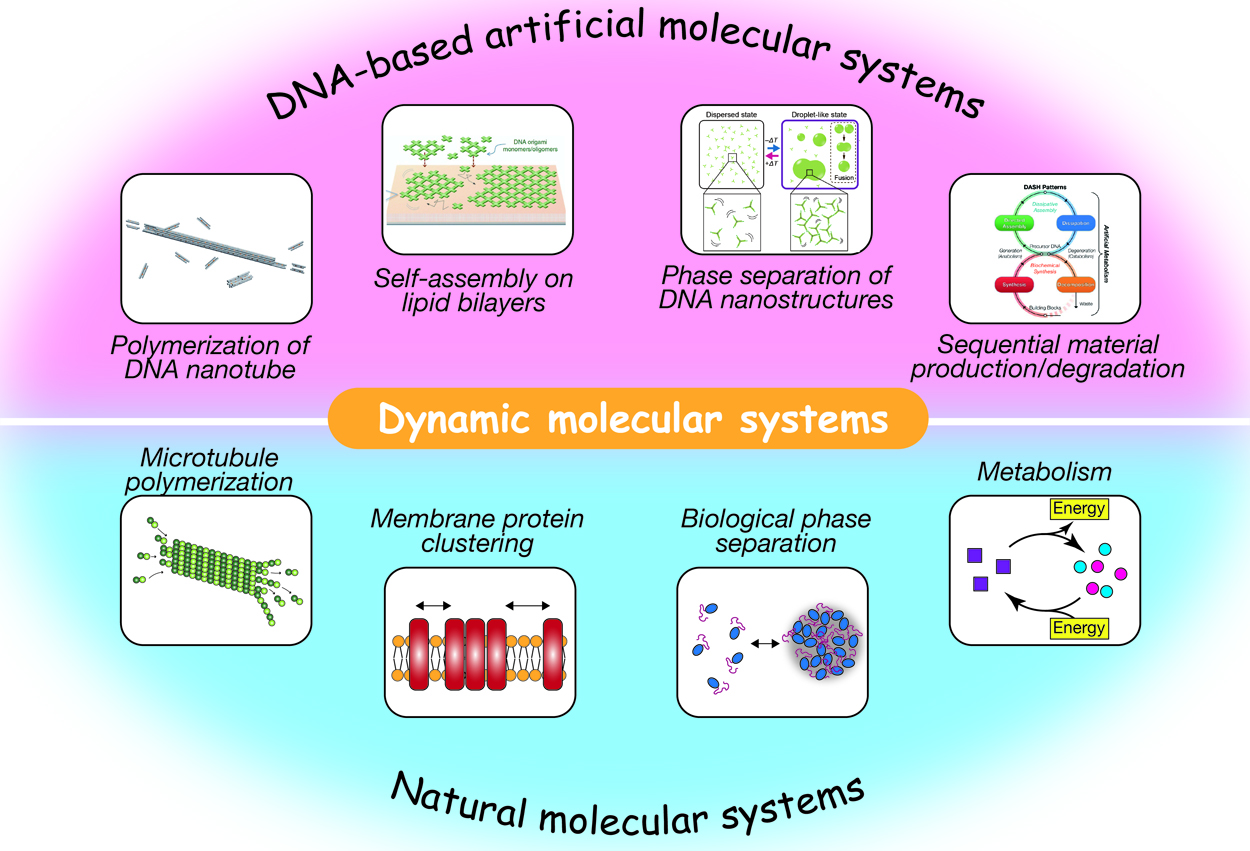
Self-assembled supramolecular structures in living cells and their dynamics underlie various cellular events, such as endocytosis, cell migration, intracellular transport, cell metabolism, and gene expression. Spatiotemporally regulated association/dissociation and generation/degradation of assembly components is one of the remarkable features of biological systems. The significant advancement in DNA nanotechnology over the last few decades has enabled the construction of various-shaped nanostructures via programmed self-assembly of sequence-designed oligonucleotides. These nanostructures can further be assembled into micrometer-sized structures, including ordered lattices, tubular structures, macromolecular droplets, and hydrogels. In addition to being a structural material, DNA is adopted to construct artificial molecular circuits capable of activating/inactivating or producing/decomposing target DNA molecules based on strand displacement or enzymatic reactions. In this review, we provide an overview of recent studies on artificially designed DNA-based self-assembled systems that exhibit dynamic features, such as association/dissociation of components, phase separation, stimulus responsivity, and DNA circuit-regulated structural formation. These biomacromolecule-based, bottom-up approaches for the construction of artificial molecular systems will not only throw light on bio-inspired nano/micro engineering, but also enable us to gain insights into how autonomy and adaptability of living systems can be realized.
- 著者
- Akihiko Nakamura Kei-ichi Okazaki Tadaomi Furuta Minoru Sakurai Jun Ando Ryota Iino
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.BSJ-2020004, (Released:2020-06-09)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
- 著者
- Jean-François Gibrat
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, pp.444-451, 2019 (Released:2019-11-29)
- 参考文献数
- 13
This paper presents a preliminary work consisting of two contributions. The first one is the design of a very efficient algorithm based on an “Overlap-Layout-Consensus” (OLC) graph to assemble the long reads provided by 3rd generation technologies. The second concerns the analysis of this graph using algebraic topology concepts to determine, in advance, whether the assembly of the genome will be straightforward, i.e., whether it will lead to a pseudo-Hamiltonian path or cycle, or whether the results will need to be scrutinized. In the latter case, it will be necessary to look for “loops” in the OLC assembly graph caused by unresolved repeated genomic regions, and then try to untie the “knots” created by these regions.