- 著者
- Masaatsu MIYAUCHI Chizuko HIRAI Hideaki NAKAJIMA
- 出版者
- Center for Academic Publications Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology (ISSN:03014800)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.4, pp.257-263, 2013 (Released:2013-09-24)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 33 39
Although the importance of solar radiation for vitamin D3 synthesis in the human body is well known, the solar exposure time required to prevent vitamin D deficiency has not been determined in Japan. This study attempted to identify the time of solar exposure required for vitamin D3 synthesis in the body by season, time of day, and geographic location (Sapporo, Tsukuba, and Naha) using both numerical simulations and observations. According to the numerical simulation for Tsukuba at noon in July under a cloudless sky, 3.5 min of solar exposure are required to produce 5.5 μg vitamin D3 per 600 cm2 skin corresponding to the area of a face and the back of a pair of hands without ingestion from foods. In contrast, it took 76.4 min to produce the same quantity of vitamin D3 at Sapporo in December, at noon under a cloudless sky. The necessary exposure time varied considerably with the time of the day. For Tsukuba at noon in December, 22.4 min were required, but 106.0 min were required at 09:00 and 271.3 min were required at 15:00 for the same meteorological conditions. Naha receives high levels of ultraviolet radiation allowing vitamin D3 synthesis almost throughout the year.
- 著者
- Masashi Uehara Shota Ikegami Takashi Takizawa Hiroki Oba Noriaki Yokogawa Takeshi Sasagawa Kei Ando Hiroaki Nakashima Naoki Segi Toru Funayama Fumihiko Eto Akihiro Yamaji Kota Watanabe Satoshi Nori Kazuki Takeda Takeo Furuya Sumihisa Orita Hideaki Nakajima Tomohiro Yamada Tomohiko Hasegawa Yoshinori Terashima Ryosuke Hirota Hidenori Suzuki Yasuaki Imajo Hitoshi Tonomura Munehiro Sakata Ko Hashimoto Yoshito Onoda Kenichi Kawaguchi Yohei Haruta Nobuyuki Suzuki Kenji Kato Hiroshi Uei Hirokatsu Sawada Kazuo Nakanishi Kosuke Misaki Hidetomi Terai Koji Tamai Eiki Shirasawa Gen Inoue Kenichiro Kakutani Yuji Kakiuchi Katsuhito Kiyasu Hiroyuki Tominaga Hiroto Tokumoto Yoichi Iizuka Eiji Takasawa Koji Akeda Norihiko Takegami Haruki Funao Yasushi Oshima Takashi Kaito Daisuke Sakai Toshitaka Yoshii Tetsuro Ohba Bungo Otsuki Shoji Seki Masashi Miyazaki Masayuki Ishihara Seiji Okada Yasuchika Aoki Katsumi Harimaya Hideki Murakami Ken Ishii Seiji Ohtori Shiro Imagama Satoshi Kato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-0183, (Released:2021-12-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: In elderly patients with cervical spinal cord injury, comorbidities such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are common, with frequent administration of antiplatelet/anticoagulant (APAC) drugs. Such patients may bleed easily or unexpectedly during surgery despite prior withdrawal of APAC medication. Few reports have examined the precise relationship between intraoperative blood loss and history of APAC use regarding surgery for cervical spine injury in the elderly.The presentmulticenter database survey aimed to answer the question of whether the use of APAC drugs affected the amount of intraoperative blood loss in elderly patients with cervical spinal cord trauma.Methods: The case histories of 1512 patients with cervical spine injury at 33 institutes were retrospectively reviewed. After excluding cases without spinal surgery or known blood loss volume, 797 patients were enrolled. Blood volume loss was the outcome of interest. We calculated propensity scores using the inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) method. As an alternative sensitivity analysis, linear mixed model analyses were conducted as well.Results: Of the 776 patients (mean age: 75.1 ± 6.4 years) eligible for IPTW calculation, 157 (20.2%) were taking APAC medications before the injury. After weighting, mean estimated blood loss was 204 mL for non-APAC patients and 215 mL for APAC patients. APAC use in elderly patients was not significantly associated with surgical blood loss according to the IPTW method with propensity scoring or linear mixed model analyses. Thus, it appeared possible to perform surgery expecting comparable blood loss in APAC and non-APAC cases.Conclusions: This multicenter study revealed no significant increase in surgical blood loss in elderly patients with cervical trauma taking APAC drugs. Surgeons may be able to prioritize patient background, complications, and preexisting conditions over APAC use before injury when examining the surgical indications for cervical spine trauma in the elderly.
- 著者
- Koji Tamai Hidetomi Terai Akinobu Suzuki Hiroaki Nakamura Masaomi Yamashita Yawara Eguchi Shiro Imagama Kei Ando Kazuyoshi Kobayashi Morio Matsumoto Ken Ishii Tomohiro Hikata Shoji Seki Masaaki Aramomi Tetsuhiro Ishikawa Atsushi Kimura Hirokazu Inoue Gen Inoue Masayuki Miyagi Wataru Saito Kei Yamada Michio Hongo Kenji Endo Hidekazu Suzuki Atsushi Nakano Kazuyuki Watanabe Junichi Ohya Hirotaka Chikuda Yasuchika Aoki Masayuki Shimizu Toshimasa Futatsugi Keijiro Mukaiyama Masaichi Hasegawa Katsuhito Kiyasu Haku Iizuka Kotaro Nishida Kenichiro Kakutani Hideaki Nakajima Hideki Murakami Satoru Demura Satoshi Kato Katsuhito Yoshioka Takashi Namikawa Kei Watanabe Kazuyoshi Nakanishi Yukihiro Nakagawa Mitsunori Yoshimoto Hiroyasu Fujiwara Norihiro Nishida Masataka Sakane Masashi Yamazaki Takashi Kaito Takeo Furuya Sumihisa Orita Seiji Ohtori
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.4, pp.179-184, 2017-10-20 (Released:2017-11-27)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
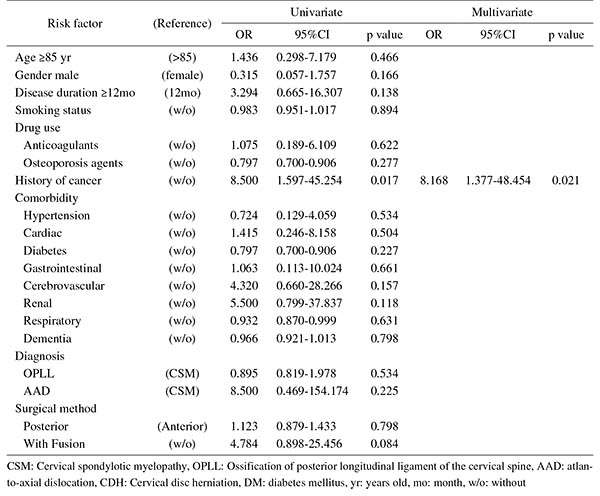
Introduction: With an aging population, the proportion of patients aged ≥80 years requiring cervical surgery is increasing. Surgeons are concerned with the high incidence of complications in this population, because "age" itself has been reported as a strong risk factor for complications. However, it is still unknown which factors represent higher risk among these elderly patients. Therefore, this study was conducted to identify the risk factors related to surgical complications specific to elderly patients by analyzing the registry data of patients aged ≥80 years who underwent cervical surgery.Methods: We retrospectively studied multicenter collected registry data using multivariate analysis. Sixty-six patients aged ≥80 years who underwent cervical surgery and were followed up for more than one year were included in this study. Preoperative patient demographic data, including comorbidities and postoperative complications, were collected from multicenter registry data. Complications were considered as major if they required invasive intervention, caused prolonged morbidity, or resulted in prolongation of hospital stay. Logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the risk factors for complications. A p-value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.Results: The total number of patients with complications was 21 (31.8%), with seven major (10.6%) and 14 minor (21.2%) complications. Multivariate logistic regression analysis, after adjusting for age, revealed two significant risk factors: preoperative cerebrovascular disorders (OR, 6.337; p=0.043) for overall complications and cancer history (OR, 8.168; p=0.021) for major complications. Age, presence of diabetes mellitus, and diagnosis were not significant predictive factors for complications in this study.Conclusions: Preoperative cerebrovascular disorders and cancer history were risk factors for complications after cervical surgery in patients over 80 years old. Surgeons should pay attention to these specific risk factors before performing cervical surgery in elderly patients.
- 著者
- Yuka Noda Kazuhiro Imura Hideaki Nakajima Tadashi Okoshi Jin Nakazawa
- 雑誌
- 研究報告モバイルコンピューティングとパーベイシブシステム(MBL) (ISSN:21888817)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2020-MBL-96, no.30, pp.1-8, 2020-09-22
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of people suffering from bone related health issues. This can be attributed to our sedentary lifestyle, which allows us to go for days without getting adequate sunlight. Exposure to sunlight, or UV radiation is often associated with negative images of skin cancer and sun buns; however, adequate UV exposure is important in creating vitamin D, which plays a key role in maintaining the levels of calcium in our bodies. While many studies point out the benefits of exposure to sunlight, existing researches dealing with behavior change tries to promote sun protection behaviors or tries to prevent people from exposing themselves to UV radiation. This poses an alternate threat of bone related health issues towards those who are not getting enough sunlight. In order to motivate people to continue to get adequate sunlight exposure, we will create an application that provides interventions geared toward one's personality, as well as using context aware notifications to allow for behavior change. This system will employ the use of the OCEAN Model to determine the personality types of the users and will attempt to persuade the user to change their behavior with UIs that are designed specifically for those personality types.
- 著者
- Yuka Noda Kazuhiro Imura Hideaki Nakajima Tadashi Okoshi Jin Nakazawa
- 雑誌
- 研究報告ユビキタスコンピューティングシステム(UBI) (ISSN:21888698)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2020-UBI-67, no.30, pp.1-8, 2020-09-22
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of people suffering from bone related health issues. This can be attributed to our sedentary lifestyle, which allows us to go for days without getting adequate sunlight. Exposure to sunlight, or UV radiation is often associated with negative images of skin cancer and sun buns; however, adequate UV exposure is important in creating vitamin D, which plays a key role in maintaining the levels of calcium in our bodies. While many studies point out the benefits of exposure to sunlight, existing researches dealing with behavior change tries to promote sun protection behaviors or tries to prevent people from exposing themselves to UV radiation. This poses an alternate threat of bone related health issues towards those who are not getting enough sunlight. In order to motivate people to continue to get adequate sunlight exposure, we will create an application that provides interventions geared toward one's personality, as well as using context aware notifications to allow for behavior change. This system will employ the use of the OCEAN Model to determine the personality types of the users and will attempt to persuade the user to change their behavior with UIs that are designed specifically for those personality types.
1 0 0 0 OA Role of Transcription Factors in Differentiation and Reprogramming of Hematopoietic Cells
- 著者
- Hideaki Nakajima
- 出版者
- The Keio Journal of Medicine
- 雑誌
- The Keio Journal of Medicine (ISSN:00229717)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.2, pp.47-55, 2011 (Released:2011-07-03)
- 参考文献数
- 62
- 被引用文献数
- 21 30
Differentiation of hematopoietic cells is a sequential process of cell fate decision originating from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), allowing multi- or oligopotent progenitors to commit to certain lineages. HSCs are cells that are able to self-renew and repopulate the marrow for the long term. They first differentiate into multipotent progenitors (MPPs), which give rise to common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs) and common myeloid progenitors (CMPs). CMPs then differentiate into granulocyte monocyte progenitors (GMPs) and megakaryocyte erythroid progenitors (MEPs), which are the precursors of granulocytes/monocytes and erythrocytes/megakaryocytes, respectively. Lineage specification at differentiation branch points is dictated by the activation of lineage-specific transcription factors such as C/EBPα, PU.1, and GATA-1. The role of these transcription factors is generally instructive, and the expression of a single factor can often determine cell fate. Differentiation was long regarded as an irreversible process, and it was believed that somatic cells would not change their fate once they were differentiated. This paradigm was first challenged by the finding that ectopic cytokine signals could change the fate of differentiation, probably through modulating internal transcription networks. Subsequently, we and others showed that virtually all progenitors, including CLPs, CMPs, GMPs, and MEPs, still retain differentiation plasticity, and they can be converted into lineages other than their own by ectopic activation of only a single lineage-specific transcription factor. These findings established a novel paradigm for cellular differentiation and opened up an avenue for artificially manipulating cell fate for clinical use .