33 0 0 0 OA Light-driven Proton Pumps as a Potential Regulator for Carbon Fixation in Marine Diatoms
- 著者
- Susumu Yoshizawa Tomonori Azuma Keiichi Kojima Keisuke Inomura Masumi Hasegawa Yosuke Nishimura Masuzu Kikuchi Gabrielle Armin Yuya Tsukamoto Hideaki Miyashita Kentaro Ifuku Takashi Yamano Adrian Marchetti Hideya Fukuzawa Yuki Sudo Ryoma Kamikawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Microbial Ecology / Japanese Society of Soil Microbiology / Taiwan Society of Microbial Ecology / Japanese Society of Plant Microbe Interactions / Japanese Society for Extremophiles
- 雑誌
- Microbes and Environments (ISSN:13426311)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.2, pp.ME23015, 2023 (Released:2023-06-20)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Diatoms are a major phytoplankton group responsible for approximately 20% of carbon fixation on Earth. They perform photosynthesis using light-harvesting chlorophylls located in plastids, an organelle obtained through eukaryote-eukaryote endosymbiosis. Microbial rhodopsin, a photoreceptor distinct from chlorophyll-based photosystems, was recently identified in some diatoms. However, the physiological function of diatom rhodopsin remains unclear. Heterologous expression techniques were herein used to investigate the protein function and subcellular localization of diatom rhodopsin. We demonstrated that diatom rhodopsin acts as a light-driven proton pump and localizes primarily to the outermost membrane of four membrane-bound complex plastids. Using model simulations, we also examined the effects of pH changes inside the plastid due to rhodopsin-mediated proton transport on photosynthesis. The results obtained suggested the involvement of rhodopsin-mediated local pH changes in a photosynthetic CO2-concentrating mechanism in rhodopsin-possessing diatoms.
- 著者
- Yu Nakajima Takashi Tsukamoto Yohei Kumagai Yoshitoshi Ogura Tetsuya Hayashi Jaeho Song Takashi Kikukawa Makoto Demura Kazuhiro Kogure Yuki Sudo Susumu Yoshizawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Microbial Ecology · The Japanese Society of Soil Microbiology
- 雑誌
- Microbes and Environments (ISSN:13426311)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.1, pp.89-97, 2018 (Released:2018-03-29)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Light-driven ion-pumping rhodopsins are widely distributed among bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes in the euphotic zone of the aquatic environment. H+-pumping rhodopsin (proteorhodopsin: PR), Na+-pumping rhodopsin (NaR), and Cl−-pumping rhodopsin (ClR) have been found in marine bacteria, which suggests that these genes evolved independently in the ocean. Putative microbial rhodopsin genes were identified in the genome sequences of marine Cytophagia. In the present study, one of these genes was heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli cells and the rhodopsin protein named Rubricoccus marinus halorhodopsin (RmHR) was identified as a light-driven inward Cl− pump. Spectroscopic assays showed that the estimated dissociation constant (Kd,int.) of this rhodopsin was similar to that of haloarchaeal halorhodopsin (HR), while the Cl−-transporting photoreaction mechanism of this rhodopsin was similar to that of HR, but different to that of the already-known marine bacterial ClR. This amino acid sequence similarity also suggested that this rhodopsin is similar to haloarchaeal HR and cyanobacterial HRs (e.g., SyHR and MrHR). Additionally, a phylogenetic analysis revealed that retinal biosynthesis pathway genes (blh and crtY) belong to a phylogenetic lineage of haloarchaea, indicating that these marine Cytophagia acquired rhodopsin-related genes from haloarchaea by lateral gene transfer. Based on these results, we concluded that inward Cl−-pumping rhodopsin is present in genera of the class Cytophagia and may have the same evolutionary origins as haloarchaeal HR.
18 0 0 0 OA Bacterium Lacking a Known Gene for Retinal Biosynthesis Constructs Functional Rhodopsins
- 著者
- Yu Nakajima Keiichi Kojima Yuichiro Kashiyama Satoko Doi Ryosuke Nakai Yuki Sudo Kazuhiro Kogure Susumu Yoshizawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Microbial Ecology / Japanese Society of Soil Microbiology / Taiwan Society of Microbial Ecology / Japanese Society of Plant Microbe Interactions / Japanese Society for Extremophiles
- 雑誌
- Microbes and Environments (ISSN:13426311)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.4, pp.ME20085, 2020 (Released:2020-12-05)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 15
Microbial rhodopsins, comprising a protein moiety (rhodopsin apoprotein) bound to the light-absorbing chromophore retinal, function as ion pumps, ion channels, or light sensors. However, recent genomic and metagenomic surveys showed that some rhodopsin-possessing prokaryotes lack the known genes for retinal biosynthesis. Since rhodopsin apoproteins cannot absorb light energy, rhodopsins produced by prokaryotic strains lacking genes for retinal biosynthesis are hypothesized to be non-functional in cells. In the present study, we investigated whether Aurantimicrobium minutum KNCT, which is widely distributed in terrestrial environments and lacks any previously identified retinal biosynthesis genes, possesses functional rhodopsin. We initially measured ion transport activity in cultured cells. A light-induced pH change in a cell suspension of rhodopsin-possessing bacteria was detected in the absence of exogenous retinal. Furthermore, spectroscopic analyses of the cell lysate and HPLC-MS/MS analyses revealed that this strain contained an endogenous retinal. These results confirmed that A. minutum KNCT possesses functional rhodopsin and, hence, produces retinal via an unknown biosynthetic pathway. These results suggest that rhodopsin-possessing prokaryotes lacking known retinal biosynthesis genes also have functional rhodopsins.
- 著者
- Yu Nakajima Takashi Tsukamoto Yohei Kumagai Yoshitoshi Ogura Tetsuya Hayashi Jaeho Song Takashi Kikukawa Makoto Demura Kazuhiro Kogure Yuki Sudo Susumu Yoshizawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Microbial Ecology · The Japanese Society of Soil Microbiology
- 雑誌
- Microbes and Environments (ISSN:13426311)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ME17197, (Released:2018-03-16)
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Light-driven ion-pumping rhodopsins are widely distributed among bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes in the euphotic zone of the aquatic environment. H+-pumping rhodopsin (proteorhodopsin: PR), Na+-pumping rhodopsin (NaR), and Cl–-pumping rhodopsin (ClR) have been found in marine bacteria, which suggests that these genes evolved independently in the ocean. Putative microbial rhodopsin genes were identified in the genome sequences of marine Cytophagia. In the present study, one of these genes was heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli cells and the rhodopsin protein named Rubricoccus marinus halorhodopsin (RmHR) was identified as a light-driven inward Cl– pump. Spectroscopic assays showed that the estimated dissociation constant (Kd,int.) of this rhodopsin was similar to that of haloarchaeal halorhodopsin (HR), while the Cl–-transporting photoreaction mechanism of this rhodopsin was similar to that of HR, but different to that of the already-known marine bacterial ClR. This amino acid sequence similarity also suggested that this rhodopsin is similar to haloarchaeal HR and cyanobacterial HRs (e.g., SyHR and MrHR). Additionally, a phylogenetic analysis revealed that retinal biosynthesis pathway genes (blh and crtY) belong to a phylogenetic lineage of haloarchaea, indicating that these marine Cytophagia acquired rhodopsin-related genes from haloarchaea by lateral gene transfer. Based on these results, we concluded that inward Cl–-pumping rhodopsin is present in genera of the class Cytophagia and may have the same evolutionary origins as haloarchaeal HR.
11 0 0 0 OA Microbial Rhodopsins as Multi-functional Photoreactive Membrane Proteins for Optogenetics
- 著者
- Shin Nakao Keiichi Kojima Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1357-1363, 2021-10-01 (Released:2021-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 51
- 被引用文献数
- 10
In life science research, methods to control biological activities with stimuli such as light, heat, pressure and chemicals have been widely utilized to understand their molecular mechanisms. The knowledge obtained by those methods has built a basis for the development of medicinal products. Among those various stimuli, light has the advantage of a high spatiotemporal resolution that allows for the precise control of biological activities. Photoactive membrane protein rhodopsins from microorganisms (called microbial rhodopsins) absorb visible light and that light absorption triggers the trans–cis photoisomerization of the chromophore retinal, leading to various functions such as ion pumps, ion channels, transcriptional regulators and enzymes. In addition to their biological significance, microbial rhodopsins are widely utilized as fundamental molecular tools for optogenetics, a method to control biological activities by light. In this review, we briefly introduce the molecular basis of representative rhodopsin molecules and their applications for optogenetics. Based on those examples, we discuss the high potential of rhodopsin-based optogenetics tools for basic and clinical research in pharmaceutical sciences.
- 著者
- Marie Kurihara Vera Thiel Hirona Takahashi Keiichi Kojima David M. Ward Donald A. Bryant Makoto Sakai Susumu Yoshizawa Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.2, pp.154-164, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 1
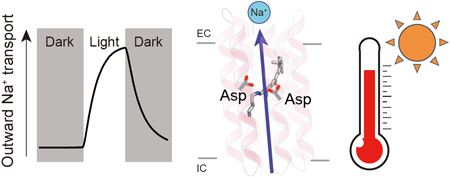
Rhodopsins are transmembrane proteins with retinal chromophores that are involved in photo-energy conversion and photo-signal transduction in diverse organisms. In this study, we newly identified and characterized a rhodopsin from a thermophilic bacterium, Bellilinea sp. Recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing the rhodopsin showed light-induced alkalization of the medium only in the presence of sodium ions (Na+), and the alkalization signal was enhanced by addition of a protonophore, indicating an outward Na+ pump function across the cellular membrane. Thus, we named the protein Bellilinea Na+-pumping rhodopsin, BeNaR. Of note, its Na+-pumping activity is significantly greater than that of the known Na+-pumping rhodopsin, KR2. We further characterized its photochemical properties as follows: (i) Visible spectroscopy and HPLC revealed that BeNaR has an absorption maximum at 524 nm with predominantly (>96%) the all-trans retinal conformer. (ii) Time-dependent thermal denaturation experiments revealed that BeNaR showed high thermal stability. (iii) The time-resolved flash-photolysis in the nanosecond to millisecond time domains revealed the presence of four kinetically distinctive photointermediates, K, L, M and O. (iv) Mutational analysis revealed that Asp101, which acts as a counterion, and Asp230 around the retinal were essential for the Na+-pumping activity. From the results, we propose a model for the outward Na+-pumping mechanism of BeNaR. The efficient Na+-pumping activity of BeNaR and its high stability make it a useful model both for ion transporters and optogenetics tools.
- 著者
- Keiichi Kojima Hiroshi C. Watanabe Satoko Doi Natsuki Miyoshi Misaki Kato Hiroshi Ishikita Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.179-188, 2018 (Released:2018-09-07)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 7 9
Anion channelrhodopsin-2 (ACR2), a light-gated channel recently identified from the cryptophyte alga Guillardia theta, exhibits anion channel activity with exclusive selectivity. In addition to its novel function, ACR2 has become a focus of interest as a powerful tool for optogenetics. Here we combined experimental and computational approaches to investigate the roles of conserved carboxylates on the anion transport activity of ACR2 in Escherichia coli membrane. First, we replaced six conserved carboxylates with a neutral residue (i.e. E9Q, E56Q, E64Q, E159Q, E219Q and D230N), and measured anion transport activity using E. coli expression system. E159Q and D230N exhibited significantly lower anion transport activity compared with wild-type ACR2 (1/12~1/3.4), which suggests that E159 and D230 play important roles in the anion transport. Second, to explain its molecular aspects, we constructed a homology model of ACR2 based on the crystal structure of a cation channelrhodopsin (ChR). The model structure showed a cavity formed by four transmembrane helices (TM1, TM2, TM3 and TM7) similar to ChRs, as a putative anion conducting pathway. Although E159 is not located in the putative pathway, the model structure showed hydrogen bonds between E159 and R129 with a water molecule. D230 is located in the pathway near the protonated Schiff base (PSB) of the chromophore retinal, which suggests that there is an interaction between D230 and the PSB. Thus, we demonstrated the functional importance and the hypothetical roles of two conserved carboxylates, E159 and D230, in the anion transport activity of ACR2 in E. coli membrane.
- 著者
- Izuru Kawamura Hayato Seki Seiya Tajima Yoshiteru Makino Arisu Shigeta Takashi Okitsu Akimori Wada Akira Naito Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.177-185, 2021 (Released:2021-08-07)
- 参考文献数
- 53
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Middle rhodopsin (MR) found from the archaeon Haloquadratum walsbyi is evolutionarily located between two different types of rhodopsins, bacteriorhodopsin (BR) and sensory rhodopsin II (SRII). Some isomers of the chromophore retinal and the photochemical reaction of MR are markedly different from those of BR and SRII. In this study, to obtain the structural information regarding its active center (i.e., retinal), we subjected MR embedded in lipid bilayers to solid-state magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The analysis of the isotropic 13C chemical shifts of the retinal chromophore revealed the presence of three types of retinal configurations of dark-adapted MR: (13-trans, 15-anti (all-trans)), (13-cis, 15-syn), and 11-cis isomers. The higher field resonance of the 20-C methyl carbon in the all-trans retinal suggested that Trp182 in MR has an orientation that is different from that in other microbial rhodopsins, owing to the changes in steric hindrance associated with the 20-C methyl group in retinal. 13Cζ signals of Tyr185 in MR for all-trans and 13-cis, 15-syn isomers were discretely observed, representing the difference in the hydrogen bond strength of Tyr185. Further, 15N NMR analysis of the protonated Schiff base corresponding to the all-trans and 13-cis, 15-syn isomers in MR showed a strong electrostatic interaction with the counter ion. Therefore, the resulting structural information exhibited the property of stable retinal conformations of dark-adapted MR.
- 著者
- Marie Kurihara Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, pp.121-129, 2015 (Released:2015-12-11)
- 参考文献数
- 71
- 被引用文献数
- 34 35
One of the major topics in biophysics and physicobiology is to understand and utilize biological functions using various advanced techniques. Taking advantage of the photoreactivity of the seven-transmembrane rhodopsin protein family has been actively investigated by a variety of methods. Rhodopsins serve as models for membrane-embedded proteins, for photoactive proteins and as a fundamental tool for optogenetics, a new technology to control biological activity with light. In this review, we summarize progress of microbial rhodopsin research from the viewpoint of distribution, diversity and potential.
- 著者
- Izuru Kawamura Hayato Seki Seiya Tajima Yoshiteru Makino Arisu Shigeta Takashi Okitsu Akimori Wada Akira Naito Yuki Sudo
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.bppb-v18.019, (Released:2021-07-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
- 著者
- Yuki Sudo Rikou Tanaka Toshitatsu Kobayashi Naoki Kamo Toshiyuki Kohno Chojiro Kojima
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.7, pp.51-58, 2011 (Released:2011-06-18)
- 参考文献数
- 34
An approach of cell-free synthesis is presented for the functional expression of transmembrane proteins without the need of refolding. The transmembrane region of the pharaonis halobacterial transducer protein, pHtrII, was translated with various large soluble tags added (thioredoxin, glutathione S-transferase, green fluorescent protein and maltose binding protein). In this system, all fusion pHtrII were translated in a soluble fraction, presumably, forming giant micelle-like structures. The detergent n-dodecyl-β-D-maltoside was added for enhancing the solubilization of the hydrophobic region of pHtrII. The activity of the expressed pHtrII, having various tags, was checked using a pull-down assay, using the fact that pHtrII forms a signaling complex with pharaonis phoborhodopsin (ppR) in the membrane, as also in the presence of a detergent. All tagged pHtrII showed a binding activity with ppR. Interestingly, the binding activity with ppR was positively correlated with the molecular weight of the soluble tags. Thus, larger soluble tags lead to higher binding activities. We could show, that our approach is beneficial for the preparation of active membrane proteins, and is also potentially applicable for larger membrane proteins, such as 7-transmembrane proteins.
- 著者
- Yuki Sudo Hiroyuki Terashima Rei Abe-Yoshizumi Seiji Kojima Michio Homma
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.5, pp.45-52, 2009 (Released:2009-06-12)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 18 22
Flagellar motor proteins, MotA/B and PomA/B, are essential for the motility of Escherichia coli and Vibrio alginolyticus, respectively. Those complexes work as a H+ and a Na+ channel, respectively and play important roles in torque generation as the stators of the flagellar motors. Although Asp32 of MotB and Asp24 of PomB are believed to function as ion binding site(s), the ion flux pathway from the periplasm to the cytoplasm is still unclear. Conserved residues, Ala39 of MotB and Cys31 of PomB, are located on the same sides as Asp32 of MotB and Asp24 of PomB, respectively, in a helical wheel diagram. In this study, a series of mutations were introduced into the Ala39 residue of MotB and the Cys31 residue of PomB. The motility of mutant cells were markedly decreased as the volume of the side chain increased. The loss of function due to the MotB(A39V) and PomB(L28A/C31A) mutations was suppressed by mutations of MotA(M206S) and PomA(L183F), respectively, and the increase in the volume caused by the MotB(A39V) mutation was close to the decrease in the volume caused by the MotA(M206S) mutation. These results demonstrate that Ala39 of MotB and Cys31 of PomB form part of the ion flux pathway and pore with Met206 of MotA and Leu183 of PomA in the MotA/B and PomA/B stator units, respectively.
- 著者
- Rei Abe Yoshizumi Shiori Kobayashi Mizuki Gohara Kokoro Hayashi Chojiro Kojima Seiji Kojima Yuki Sudo Yasuo Asami Michio Homma
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, pp.21-29, 2013 (Released:2013-02-05)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
Flagellar motors embedded in bacterial membranes are molecular machines powered by specific ion flows. Each motor is composed of a stator and a rotor and the interactions of those components are believed to generate the torque. Na+ influx through the PomA/PomB stator complex of Vibrio alginolyticus is coupled to torque generation and is speculated to trigger structural changes in the cytoplasmic domain of PomA that interacts with a rotor protein in the C-ring, FliG, to drive the rotation. In this study, we tried to overproduce the cytoplasmic loop of PomA (PomA-Loop), but it was insoluble. Thus, we made a fusion protein with a small soluble tag (GB1) which allowed us to express and characterize the recombinant protein. The structure of the PomA-Loop seems to be very elongated or has a loose tertiary structure. When the PomA-Loop protein was produced in E. coli, a slight dominant effect was observed on motility. We conclude that the cytoplasmic loop alone retains a certain function.