- 著者
- 西塚 泰美
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.3, pp.150-151, 1978
- 著者
- 西塚 泰美
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.2, pp.76-77, 1985
- 著者
- 山本 格
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.7, pp.383-395, 2003-07-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 1
In 1989, we have developed a novel vitamin C derivative, 2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid (AA-2G), which is highly stable to heat and oxidative stress. This stable form of ascorbate, of which hydroxy moiety at the C-2 position is regiospecifically substituted with glucose, was enzymatically synthesizes with mammalian intestinal and rice seed α-glucosidase, and cyclodextrin glucanotans-ferase from Bachillus stearothermophylus. In 1999, we have also reported a series of 6-acylated forms of AA-2G, 6-Acyl-AA-2Gs, of which hydroxy moiety at the C-6 position of AA-2G is substituted with fatty acids having a different length of carbon chains. Exposure both of AA-2G and 6-Acyl-AA-2G to the mammalian biomembrance results in the formation of active vitamin C by α-glucosidase and/or esterase. AA-2G has been admitted as a medicinal additive for whitening and is widely used in domestic and foreign countries for years. Our of the various acylated derivatives, 6-O-dodecanoyl-2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid is considered to be the most expected candidate in application for medicinal use, for examples, preservation solution for the grafts, whitening ingredient, food additives and medicines, because it is the most prominent one in terms of the stability, effectiveness and skin permeability. The two types of ascorbate derivatives are very useful vitamin C source, especially in the tissue culture experiments and contribute the finding of unknown physiological action, and to the clarification of the mode of action of ascorbate. It has been found that vitamin C stimulates the cytokine generation and enhances the cytokine-induced biological activity in immune and neurological responses, although ascorbate alone is without effect. These findings suggest that AA-2G and 6-Acyl-AA-2G not only may serve as useful agents for the medicinal and cosmetic use, but also contributes to shed some light on a new aspect of the biological activity of ascorbate.
- 著者
- 中村 重信
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.11, pp.621-628, 2013-11-25 (Released:2017-08-10)
In 1882-3, many Japanese sailors suffered from beriberi and some died in warships. Japanese government started a committee to prevent beriberi. A parallel controlled trial for beriberi was carried out in 1884 by Kanehiro Takagi who had studied at St Thomas Hospital in London and noticed a remarkable difference in the frequency of beriberi between Japan and London. He determined the ratio of nitrogen to carbon content of food taken by the crew of warship Rhujo which sailed from Japan to Hawaii via Chile and resulted in a miserable occurrence of beriberi. Carbon content in the food was higher during the voyage from Chile to Hawaii than that from Hawaii to Japan, the latter of which brought about beriberi much less frequently. These data prompted Dr. Takagi a trial voyage under similar conditions except partially replacing polished rice with meat in crew's diet. Dr. Takagi postulated the Emperor on importance of diet during the trial voyage. Warship Tsukuba set out on the trial voyage in February, 1884 and arrived at Hawaii without any beriberi patient. The success in preventing beriberi led to taking food without polished rice in Japanese navy, while Japanese army and professors in Tokyo Imperial University neglected these data due to an erroneous assumption that beriberi might be infectious. A mistaken trust in polished rice had prevailed in Japan until 1923 when vitamin B_1 deficiency derived from polished rice was revealed as a cause of beriberi. Thereafter, the incidence of beriberi has decreased dramatically.
- 著者
- 松田 誠
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.2, pp.128, 2012-02-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 著者
- 秋山 伸隆
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.85, no.4, pp.198-199, 2011
- 著者
- 古和 久典
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.93, no.4, pp.176-177, 2019-04-25 (Released:2020-04-30)
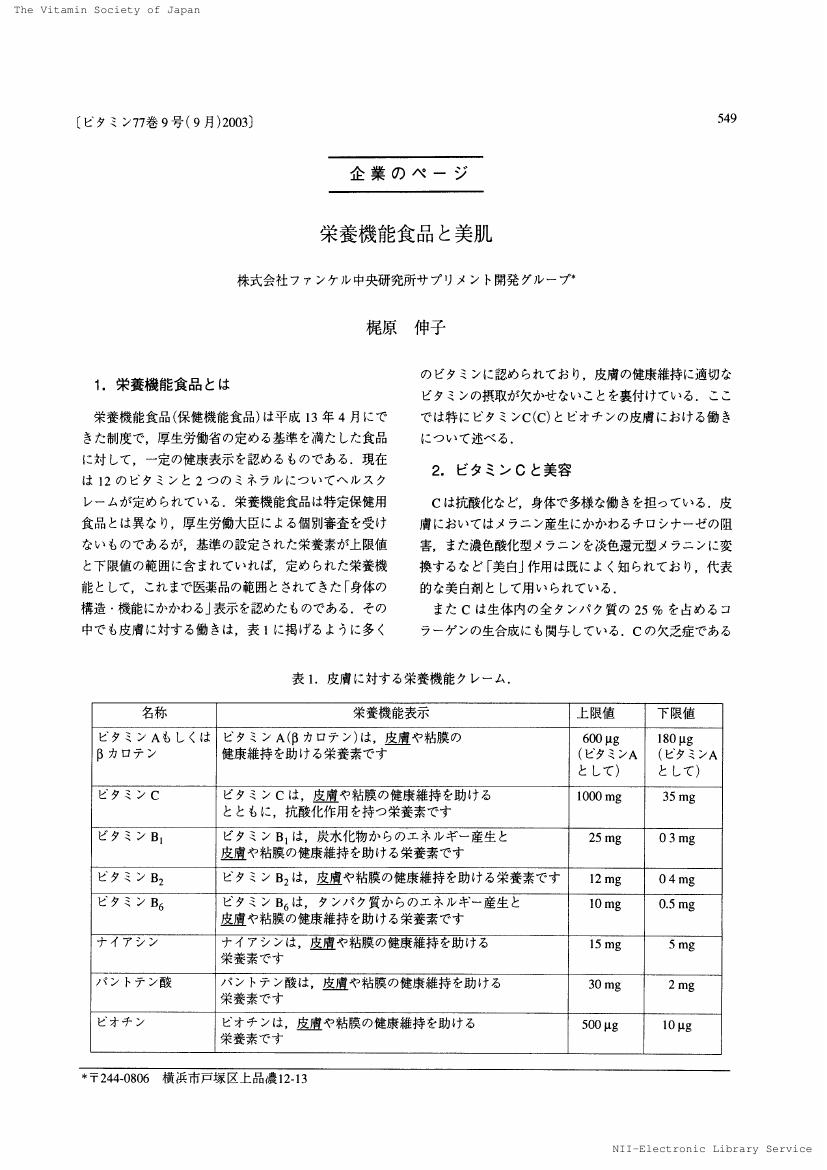
1 0 0 0 OA 栄養機能食品と美肌
- 著者
- 梶原 伸子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.9, pp.549-551, 2003-09-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 6
1 0 0 0 OA 中国製干しカキおよびオイスターソースのビタミンB12含有量の測定と同定
- 著者
- Fei Teng
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.90, no.7, pp.341, 2016 (Released:2017-12-26)
緒言 ビタミンB12
1 0 0 0 OA 壊血病は過去の病気ではない
- 著者
- 佐藤 安訓 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.11, pp.609-611, 2008-11-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 2
1 0 0 0 OA 第69回大会一般演題要旨(ポスター発表)
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.91, no.4, pp.293-310, 2017-04-25 (Released:2019-11-25)
- 著者
- 稲垣 長典
- 出版者
- 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.51, no.8, 1977-08-25
1 0 0 0 OA ビタミンCに与えたポーリングのインパクト(随想のページ)
- 著者
- 村田 晃
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.3, pp.81-82, 2007-03-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 著者
- 沼田 周助
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.8, pp.413-418, 2014
Previous meta-analyses of studies on the association between blood homocysteine concentration and schizophrenia suggest that elevated blood homocysteine concentration is a risk factor for schizophrenia. However, observational studies on this association have potential problems such as confounding and reverse causation. Mendelian randomization analysis is a method to analyze instrumental variables using genetic variants and can be used for assessing causal relationships. Therefore, we used this Mendelian randomization analysis to investigate the association between blood homocysteine concentration and schizophrenia. As a result, we demonstrated that increased blood homocysteine concentration might be associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia in the Japanese population. This result will offer important insight into the pathophysiology and treatments of schizophrenia.
- 著者
- 岡村 正人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.11, pp.555-557, 2000-11-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA ビタミンC輸送体SVCT1の遺伝子欠損は腎臓でのビタミンC再吸収を低下させる
- 著者
- 岸本 祐樹 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.10, pp.490-492, 2010-10-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 著者
- 柴田 克己
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.91, no.4, pp.241, 2017 (Released:2018-05-01)
1 0 0 0 OA レスベラトロールの非抗酸化作用について
- 著者
- 福井 浩二
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.90, no.5-6, pp.286-289, 2016 (Released:2017-12-26)
1 0 0 0 OA 離乳後1 週間のビオチンは膵島および膵β細胞を増殖させる
- 著者
- 塩沢 浩太 白川 仁 駒井 三千夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.93, no.2, pp.58-60, 2019-02-25 (Released:2020-02-29)
- 著者
- 橋詰 直孝
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.8, pp.401-406, 1986-08-25 (Released:2018-03-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 1