1 0 0 0 OA 異分野融合に想う
- 著者
- 加藤 晃一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.5, pp.233, 2018 (Released:2018-09-29)
- 著者
- Nagata Takashi Koyanagi Mitsumasa Tsukamoto Hisao Isono Kunio Arikawa Kentaro Terakita Akihisa
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.2, 2010
1 0 0 0 OA RNAシークエンシング
- 著者
- 城口 克之
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.6, pp.290-294, 2013 (Released:2013-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
The term “RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq)” often means the sequencing of cDNA generated from RNA as well as the direct sequencing of RNA. RNA-Seq has become well known as next generation sequencers emerge, particularly because their high throughput nature of data collection makes RNA-Seq a powerful tool for genome-wide gene expression analysis. In this review, I introduce, mainly from a technical point of view, a basic scheme of RNA sequencing, its development, and its application in several interesting studies.
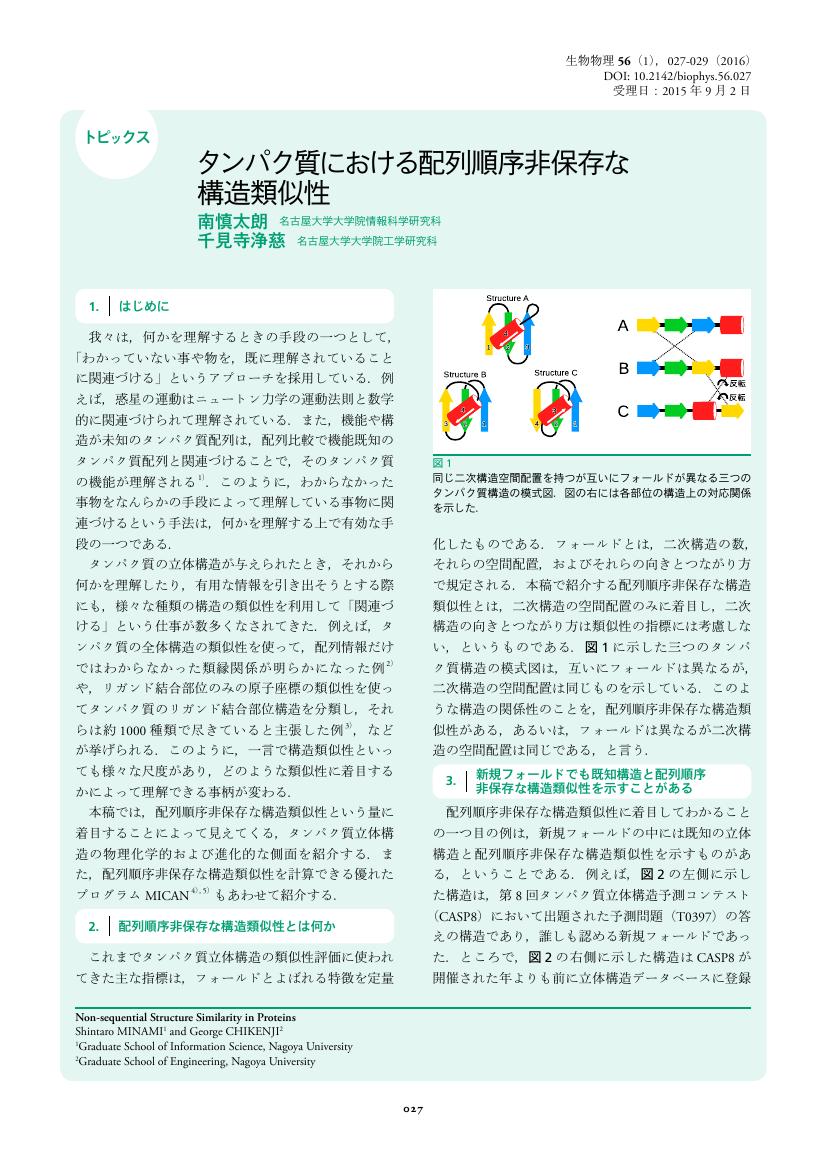
1 0 0 0 OA タンパク質における配列順序非保存な構造類似性
- 著者
- 南 慎太朗 千見寺 浄慈
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.1, pp.027-029, 2016 (Released:2016-01-27)
- 参考文献数
- 8
1 0 0 0 OA 海外だより
- 著者
- 矢澤 真幸
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.4, pp.224-225, 2017 (Released:2017-07-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 記憶と核酸
- 著者
- 永田 豊
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.5, no.5, pp.256-272, 1965-09-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 43
1 0 0 0 OA 高速AFMによるタンパク質集合体のダイナミクスの観察
- 著者
- 中山 隆宏 紺野 宏記 山田 正仁 小野 賢二郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.2, pp.086-088, 2018 (Released:2018-03-31)
- 参考文献数
- 9
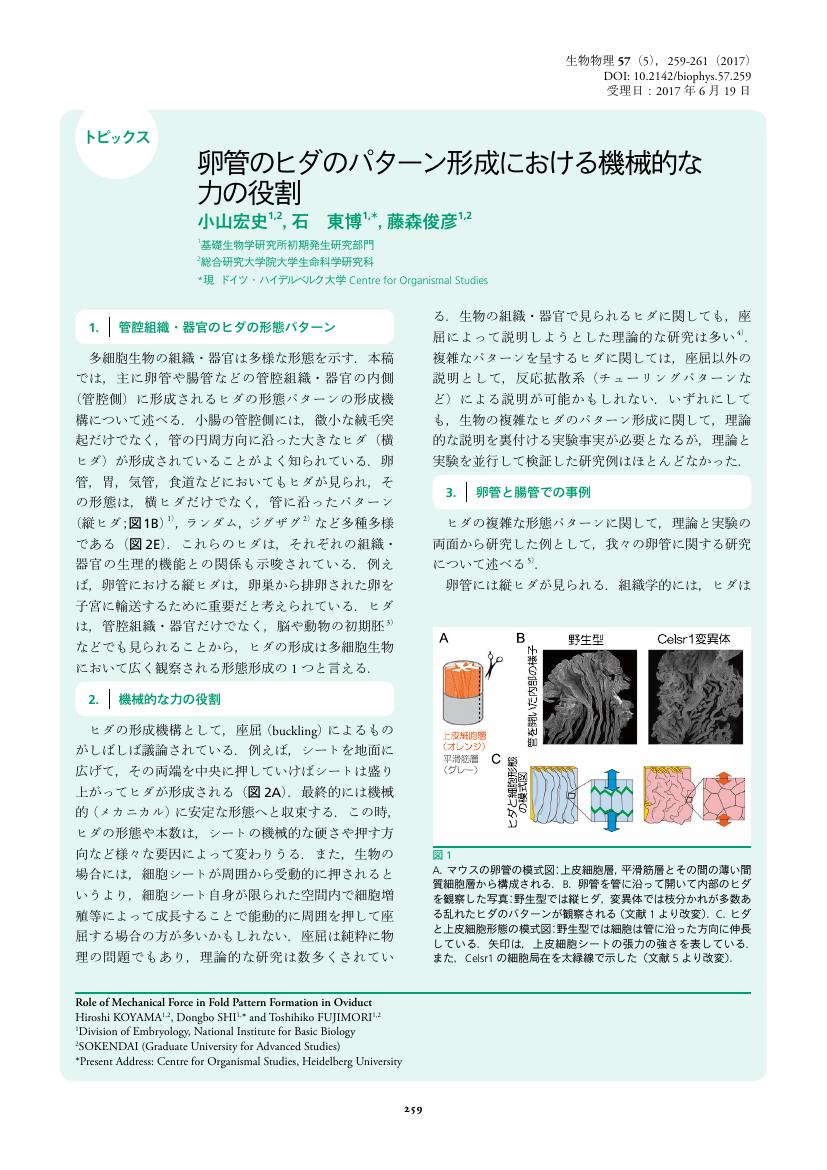
1 0 0 0 OA 卵管のヒダのパターン形成における機械的な力の役割
- 著者
- 小山 宏史 石 東博 藤森 俊彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.5, pp.259-261, 2017 (Released:2017-09-26)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA ミオシンホスファターゼ阻害タンパク質 CPI-17の構造と機能
- 著者
- 大木 進野 江藤 真澄 松澤 史子 甲斐荘 正恒
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.2, pp.72-77, 2005 (Released:2005-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 17
Cell motility, including smooth muscle contraction and cell migration, is regulated by reversible phosphorylation of myosin. Recent studies have shown that myosin phosphatase (MP), along with kinases, contributes dynamically to the regulation of myosin-II phosphorylation. An MP specific inhibitor named CPI-17, which is expressed in smooth muscle and neuronal cells, mediates receptor signaling leading to myosin-II phosphorylation. In this review, we discuss structure/function relationships of CPI-17 stemming from our recent NMR studies and computer modeling results. The combination of biophysical approaches with biochemical techniques has revealed the inhibitory mechanism of CPI-17.
1 0 0 0 OA タンパク質の低温変性
- 著者
- 田村 厚夫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.1, pp.40-43, 1995-01-25 (Released:2009-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 27
It has been known that proteins can be denatured not only by increasing the temperature but also by decreasing it. The latter phenomenon, which is normally called "cold denaturation", shows common features of protein unfolding as well as characteristics that are specific to each protein.
- 著者
- Iwama Kazuya Imaki Takahito Yagi Masahiro Hiraoka Wakako
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, 2012
1 0 0 0 OA 電子スピン共鳴で探るモータータンパク質のダイナミクス
- 著者
- 荒田 敏昭
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.4, pp.172-177, 2012 (Released:2012-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 22
A motor protein moves on a large scale at molecular level. We have used site-directed spin-labeling electron spin resonance (ESR) to detect molecular orientation, residual side-chain mobility and inter-residual distances. Especially, the distances of 8-80 Å can be measured by continuous-wave and recently developed pulse ESR. We applied these techniques to the studies on conformational dynamics of motor proteins, myosin and kinesin, and muscular switch proteins troponin-tropomyosin. In these systems, the flexible elements undergo thermal motion and fluctuate on large scale between distinct structural states during activity.
1 0 0 0 OA 周波数変調原子間力顕微鏡による抗体分子の高分解能観察
- 著者
- 小林 圭 山田 啓文
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.4, pp.234-237, 2016 (Released:2016-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 著者
- 田中 実 友永 健士 木下 政人 若松 佑子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.2, pp.93-96, 2003 (Released:2003-03-25)
1 0 0 0 OA 1L1100 ラット尿中フェロモンの性質 : 性経験に伴う変化とその作用
- 著者
- 富岡 麻由美 辻川 健一 山口 尊史 稲村 耕平 柏柳 誠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.supplement, pp.S91, 2000-08-05 (Released:2017-05-01)
1 0 0 0 OA 3P032 グリセロールが非天然状態にあるタンパク質に与える影響を残基毎に調べる : リゾチーム0SS変異体と2SS変異体の相違(蛋白質 C) 物性 : 安定性、折れたたみなど)
- 著者
- 山崎 向太 木村 雅也 野田 康夫 橘 秀樹 瀬川 新一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.supplement, pp.S197, 2004-11-10 (Released:2017-05-01)
1 0 0 0 OA ダイヤモンドを用いた光検出磁気共鳴顕微鏡:新しいin vivoイメージング技術
- 著者
- 五十嵐 龍治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.4, pp.212-215, 2017 (Released:2017-07-28)
- 参考文献数
- 8
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA キネシンの運動解析から見えてきた熱ラチェットメカニズム
- 著者
- 西山 雅祥 樋口 秀男
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.2, pp.75-80, 2004 (Released:2004-03-23)
Kinesin is an ATP-driven molecular motor that moves processively along a microtubule in a stepwise manner. The steps occur not only in the forward direction, but also in the backward. Here, we have studied the bidirectional stepping mechanism of kinesin motors. The stepping mechanism of the forward and backward movements was well characterized by Feynman's thermal ratchet model. The driving force of the stepwise movement is essentially Brownian motion, but it is biased in the forward direction by utilizing the free energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP.
1 0 0 0 OA 生物とオートマトンの進化
- 著者
- 田村 博 黒川 隆夫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, no.4, pp.175-180, 1968-07-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 13
1 0 0 0 OA 生物物理学における振動分光法の未来
- 著者
- 古谷 祐詞
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.4, pp.162-163, 2010 (Released:2010-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 9