- 著者
- 中村 重信
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.11, pp.621-628, 2013-11-25 (Released:2017-08-10)
In 1882-3, many Japanese sailors suffered from beriberi and some died in warships. Japanese government started a committee to prevent beriberi. A parallel controlled trial for beriberi was carried out in 1884 by Kanehiro Takagi who had studied at St Thomas Hospital in London and noticed a remarkable difference in the frequency of beriberi between Japan and London. He determined the ratio of nitrogen to carbon content of food taken by the crew of warship Rhujo which sailed from Japan to Hawaii via Chile and resulted in a miserable occurrence of beriberi. Carbon content in the food was higher during the voyage from Chile to Hawaii than that from Hawaii to Japan, the latter of which brought about beriberi much less frequently. These data prompted Dr. Takagi a trial voyage under similar conditions except partially replacing polished rice with meat in crew's diet. Dr. Takagi postulated the Emperor on importance of diet during the trial voyage. Warship Tsukuba set out on the trial voyage in February, 1884 and arrived at Hawaii without any beriberi patient. The success in preventing beriberi led to taking food without polished rice in Japanese navy, while Japanese army and professors in Tokyo Imperial University neglected these data due to an erroneous assumption that beriberi might be infectious. A mistaken trust in polished rice had prevailed in Japan until 1923 when vitamin B_1 deficiency derived from polished rice was revealed as a cause of beriberi. Thereafter, the incidence of beriberi has decreased dramatically.
- 著者
- 松田 誠
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.2, pp.128, 2012-02-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 著者
- 秋山 伸隆
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.85, no.4, pp.198-199, 2011
- 著者
- 古和 久典
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.93, no.4, pp.176-177, 2019-04-25 (Released:2020-04-30)
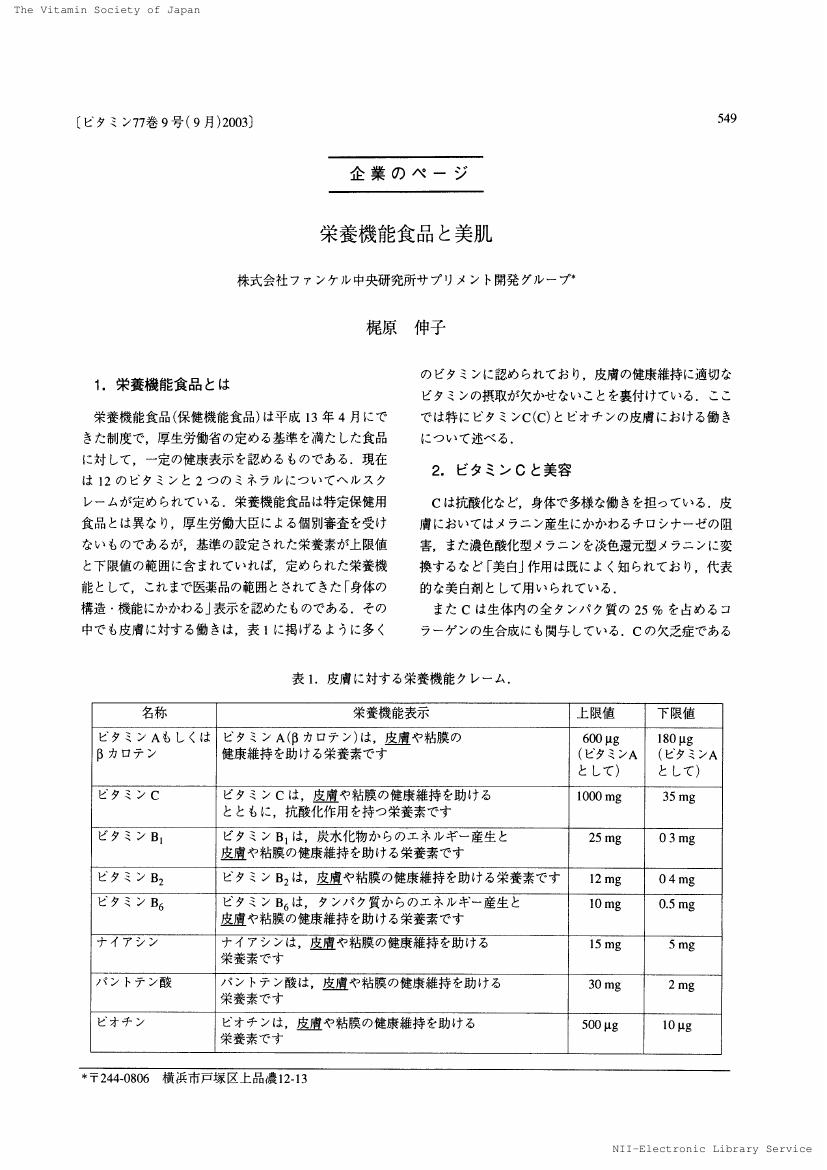
1 0 0 0 OA 栄養機能食品と美肌
- 著者
- 梶原 伸子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.9, pp.549-551, 2003-09-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 6
1 0 0 0 OA 中国製干しカキおよびオイスターソースのビタミンB12含有量の測定と同定
- 著者
- Fei Teng
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.90, no.7, pp.341, 2016 (Released:2017-12-26)
緒言 ビタミンB12
1 0 0 0 OA 壊血病は過去の病気ではない
- 著者
- 佐藤 安訓 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.11, pp.609-611, 2008-11-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 2
1 0 0 0 OA 第69回大会一般演題要旨(ポスター発表)
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.91, no.4, pp.293-310, 2017-04-25 (Released:2019-11-25)
1 0 0 0 OA ビタミンCに与えたポーリングのインパクト(随想のページ)
- 著者
- 村田 晃
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.3, pp.81-82, 2007-03-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 著者
- 沼田 周助
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.8, pp.413-418, 2014
Previous meta-analyses of studies on the association between blood homocysteine concentration and schizophrenia suggest that elevated blood homocysteine concentration is a risk factor for schizophrenia. However, observational studies on this association have potential problems such as confounding and reverse causation. Mendelian randomization analysis is a method to analyze instrumental variables using genetic variants and can be used for assessing causal relationships. Therefore, we used this Mendelian randomization analysis to investigate the association between blood homocysteine concentration and schizophrenia. As a result, we demonstrated that increased blood homocysteine concentration might be associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia in the Japanese population. This result will offer important insight into the pathophysiology and treatments of schizophrenia.
- 著者
- 岡村 正人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.11, pp.555-557, 2000-11-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA ビタミンC輸送体SVCT1の遺伝子欠損は腎臓でのビタミンC再吸収を低下させる
- 著者
- 岸本 祐樹 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.10, pp.490-492, 2010-10-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 著者
- 柴田 克己
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.91, no.4, pp.241, 2017 (Released:2018-05-01)
1 0 0 0 OA レスベラトロールの非抗酸化作用について
- 著者
- 福井 浩二
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.90, no.5-6, pp.286-289, 2016 (Released:2017-12-26)
1 0 0 0 OA 離乳後1 週間のビオチンは膵島および膵β細胞を増殖させる
- 著者
- 塩沢 浩太 白川 仁 駒井 三千夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.93, no.2, pp.58-60, 2019-02-25 (Released:2020-02-29)
- 著者
- 橋詰 直孝
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.8, pp.401-406, 1986-08-25 (Released:2018-03-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 男性避妊とビタミンA
- 著者
- 目崎 喜弘
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.5-6, pp.292-293, 2014-06-25 (Released:2017-08-10)
- 著者
- 飯島 健志 馬場 修 河田 哲典 上野 順士 田所 忠弘 前川 昭男
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.10, pp.497-502, 1989-10-25 (Released:2018-03-16)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
DNPH法,DP法及びHPLC法を用いて20種類の食品中の総AsA含量を測定し,測定法による値の相違について検討した.その結果,トマトジュース,ジャガイモ,アルファルファモヤシ,ダイズモヤシ及び調製粉乳では,いずれの測定法によってもほぼ一致した値が得られた.しかしブラックマッペモヤシではHPLC法,紅茶及びシイタケではDP法が,それぞれ他の測定法に比べ高値を示したので,DNPH-HPLC法を用いてさらに検討した.その結果,ブラックマッペモヤシではDP法,DNPH法とほぼ同値となったが,紅茶ではDNPH法よりも低値を示し,シイタケでは検出されなかった.これより紅茶及びシイタケのAsA測定法については,さらに検討の余地があることが判った.
1 0 0 0 OA ビオチン合成酵素の立体構造
- 著者
- 近藤 寛樹
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.12, pp.624-625, 2004-12-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 3
ビオチン合成の最後の段階, デスチオビオチン(DTB)への硫黄の導入, の最大の謎は活性化されていないメチル基とメチレン基にどのような仕組みで硫黄が挿入されるかという点である. この反応がbioオペロン中のbioB遺伝子の産物BioB, つまりビオチン合成酵素(モノマー分子量3.8万の二量体のタンパク質)によって触媒されること, また反応にフラボドキシン, フラボドキシン還元酵素, NADPH, S-アデノシルメチオニン(AdoMet), システイン, ジチオスレイトールが必要とされることなどがわかっていた. ビオチン合成酵素はAdoMetから還元的に生成する5'-デオキシアデノシルラジカルを利用する一群の酵素のスーパーファミリーに属し, これらには保存されたcys-X-X-X-Cys-X-X-Cys(いわゆるシステインボックス, Xは任意のアミノ酸)の配列が存在して鉄硫黄クラスターの結合部位となっている. 最近AdoMetとDTBが結合した形の大腸菌ビオチン合成酵素の立体構造が3.4Aの分解能で解かれた.
1 0 0 0 OA 1. ビタミンE補充は糖尿病網膜症の改善に役立つか?
- 著者
- 太田 好次
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.75, no.12, pp.575-576, 2001-12-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 9