2 0 0 0 OA 1.ビタミンC大量投与による頭痛の治療 : ビタミンC研究委員会第42回会議研究発表要旨
- 著者
- 川野 正七
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.5-6, pp.181-182, 1980-06-25 (Released:2018-03-07)
2 0 0 0 OA ビタミンE の新しい機能と安全性
- 著者
- 阿部 皓一 松尾 俊輝 青木 由典
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.90, no.5-6, pp.290-292, 2016 (Released:2017-12-26)
2 0 0 0 OA 敗血症に対するビタミンC療法の有効性
- 著者
- 谷津 智史 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.92, no.7, pp.322-324, 2018 (Released:2019-07-31)
2 0 0 0 OA 眼内圧上昇の眼組織ビタミンB_1含有量に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 浅山 亮二 浜田 幸子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.3, pp.237-240, 1967-09-25 (Released:2018-02-10)
The intra-ocular pressure of the rabbits was maintained for one hour at 150,140,130,110,90,70,and 56mmHg with a leveling manometer and the concentration of total thiamine, free thiamine and thiamine phosphate in the retina and the optic nerve was measured. The concentration of total thiamine and its phosphate in the retina decreased with the elevation of the intra-ocular pressure over 90mmHg. When the intra-ocular pressure persisted at 150mmHg for 2.5 hours, contents of thiamine phosphate in the retina decreased further than when the elevation persisted for one hour. When the duration of the elevation of the intra-ocular pressure at 150mmHg was limited to one hour, the decrease of the total thiamine and its phosphate in the retina proved to be reversible by the normalizing of the intra-ocular pressure. But when the elevation of the intra-ocular pressure at 150mmHg persisted for 2.5 hours, decreased contents of the total thiamine and its phosphate were not reversed even when the intra-ocular pressure returned to normal. The intra-ocular pressure was maintained at 30,56,and 150mmHg with a manometer. One hour after an intravenous injection of thiamine propyldisulfide 10mg per kg, the concentration of total thiamine, free thiamine and thiamine phosphate in the ocular tissues was measured. The concentration of all types of thiamine in the retina and the choroid almost decreased when the intra-ocular pressure became higher than 56mmHg, as compared with the concentration in these tissues of normal intra-ocular pressure one hour after an intravenous injection of thiamine propyldisulfide 10mg per kg, and these decreases became greater with the elevation of the intra-ocular pressure.
2 0 0 0 OA 1-III-5 亜鉛はマクロファージの形質分化制御を介して腸管炎症を抑制する(一般演題要旨,ビタミン・バイオファクター研究のさらなる魅力~大和まほろぱからの発信~,第67回大会講演要旨)
- 著者
- 東村 泰希 内藤 裕二 高木 智久 水島 かつら 吉川 敏一
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.89, no.4, pp.225, 2015-04-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
2 0 0 0 高度好熱菌由来ホモセリン脱水素酵素の結晶学的研究
- 著者
- 赤井 翔太 生城 浩子 澤井 大樹 林 秀行 神谷 信夫 宮原 郁子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.7, pp.358-365, 2014
Homoserine dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde to L-homoserine. Homoserine dehydrogenase is required for the biosynthesis of the three essential amino acids, i.e. lysine, methionine, and isoleucine, from aspartic acid. This enzyme attracts attention also as a promising antifungal drug target. We have determined the crystal structures of homoserine dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus HB8 in both substrate-free form and homoserine-binding form by X-ray diffraction. Crystallization conditions were surveyed at 293 K by using a hanging-drop vapor-diffusion method. The substrate-free form was solved to 1.4 Å resolution and the homoserine-binding form was solved to 2.0 Å resolution. The homoserine dehydrogenase was a dimer with each subunit composed of three distinct domains, nucleotide-binding, dimerization, and substrate-binding domain. In the homoserine-binding forms, the amino group of homoserine made a hydrogen bond to the side chain carboxylate of Glu180. This hydrogen bond induced the conformation change of Thr165-Pro183 loop, which made the loop close to the active site. The substrate homoserine was rigidly recognized by several amino acid residues in the enzyme active site, indicating that Lys99 or Lys195 would be an essential catalytic residue to facilitate hydride transfer.
- 著者
- 福岡 正喜 中西 由香 Bernhard Krautler 虎谷 哲夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.4, pp.244, 2003-04-25 (Released:2017-12-26)
2 0 0 0 OA トリプトファン-ナイアシン転換率におよぼすビタミンとミネラルの影響
- 著者
- 柴田 克已
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.11, pp.519-529, 1997-11-25 (Released:2018-04-07)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Niacin is biosynthesized from tryptophan and its ability is enough to sustain the demand of niacin animal or human body. Therefore, niacin itself does not need to take. Vitamin B groups and minerals are required in the conversion of niacin from tryptophan. Thus, we investigated the effects of feeding with a thiamin-free, riboflavin-free, pyridoxine-free, or mineral-deficient diet on the conversion ratio of tryptophan to niacin in rats. In the thiamin-free experiment, the ratio was higher in the thiamin-free group than in the control. In riboflavin-deficient rats, the conversion ratio was not affected. In the pyridoxine-free experiment, the ratio was lower in the pyridoxine-free group than in the control. In the mineral-deficient experiment, the sum of the urinary excretion of nicotinamide and its metabolites was lower in a deficient group than in the control. Accordingly, deficiencies of pyridoxine and/or minerals directly caused niacin deficiency, but thiamin- and riboflavin-deficiencies did not.
- 著者
- 佐藤 安訓 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.12, pp.660, 2008-12-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
2 0 0 0 OA 赤ワインに含まれるポリフェノール・レスベラトロールに関する最近の話題
- 著者
- 井上 裕康
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.12, pp.621-623, 2004-12-25 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 13
レスベラトロールは赤ワインに含まれる抗酸化作用を持つフィトアレキシン(抗菌性物質)である. レスベラトロールは中等度のワイン消費が心血管病, 脳卒中, 痴呆の危険度と負の相関を示す, いわゆる「フレンチパラドックス」に関与する物質と考えられてきた. 我々は最近, レスベラトロールが核内受容体PPAR(peroxisome proliferators activated receptor)αとPPARγを選択的に活性化すること, さらにPPARα活性化が脳保護効果をもたらすことを見いだした. これらの知見は「フレンチパラドックス」を説明する新しい作用機構を提供すると考えている. 一方で, レスベラトロールは寿命延長効果を持つカロリー制限模倣物質であること, オレイルエタノールアミドがPPARαの新しい内因性リガンドであり, その活性化によって食欲をコントロールすることが報告されている. そこでこれらの知見を含めて, 今後の展望とともに紹介したい.
- 著者
- 妹尾 春樹 畑 隆一郎
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.9, pp.501-513, 1994-09-25 (Released:2018-03-30)
Stellate cells (vitamin A-storing cells, lipocytes, fat-storing cells, Ito cells) exist in the perisinusoidal space of the hepatic lobule, and store 80% of retinoids in the whole body as retinyl palmitate in lipid droplets in the cytoplasm. Under physiological conditions, these cells play key roles in the control of retinoid homeostasis ; they express specific receptors for retinol-binding protein (RBP), a binding protein specific for retinol, on their cell surface, and take up the complex of retinol and RBP by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Whereas, under pathological conditions such as liver cirrhosis, these cells lose retinoids, and synthesize a large amount of extracellular matrix (ECM) components including collagen, proteoglycan and adhesive glycoproteins. Morphology of these cells also changes from the star-shaped stellate cells to that of fibroblasts or myofibroblasts. ECM components regulate the morphology, proliferation, and functions of the stellate cells. L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate, a long-acting vitamin C derivative, further modulates this cellular regulation by ECM components.
2 0 0 0 OA 小児科診療において経験する二次性低カルニチン血症
- 著者
- 野崎 章仁
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.89, no.12, pp.573-578, 2015-12-25 (Released:2017-08-10)
- 著者
- 森重 福美 木本 英治 角田 隆巳 田中 英彦 桂 義元 川崎 宏
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.5-6, pp.182, 1980-06-25 (Released:2018-03-07)
1 0 0 0 OA ビタミンD受容体の遺伝子多型と疾患(<特集>「ビタミンと遺伝子多型」-ビタミンD-)
- 著者
- 山本 浩範 竹井 悠一郎 香西 美奈 田中 更沙 坂本 達昭 池田 涼子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.9, pp.514-518, 2013-09-25 (Released:2017-08-10)
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D_3, an active form of vitamin D_3, which plays a central role in the regulation of calcium and bone homeostasis through vitamin D receptor (VDR). In 1994, Morrison and colleagues first reported that bone mineral density was associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the intron 8 of human VDR gene. In 1997, we clarified the whole structure of the human VDR genome and reported the relationship between FokI and Cdx-2 SNPs in the human VDR gene and bone density in Japanese women. Osteoporosis is known as one of multifactorial genetic diseases and its occurrence is associated with not only genetic factors but also environmental factors, lifestyle such as diet and exercise, aging, and abnormal bone mineral metabolism. Therefore, it can be expected that the identification of osteoporosis-related genes including the VDR gene will lead to the development of new methods to treat and to protect against osteoporosis, although there are several statistical problems for data analysis.
1 0 0 0 OA ビタミンC はエピジェネティクスによる制御を介して白血病の発症を防ぐ
- 著者
- 佐藤 安訓 石神 昭人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.92, no.8, pp.389-393, 2018-08-25 (Released:2019-08-31)
1 0 0 0 OA 2. 成長期におけるリン・カルシウム摂取量が リン・ビタミン D代謝調節系に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 竹谷 豊 福田 詩織 林 眞由 岸本 麻希 増田 真志 山本 浩範
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.92, no.7, pp.326-327, 2018 (Released:2019-07-31)
1 0 0 0 OA IX.ビタミンE の代謝と栄養 特集 ―脂溶性ビタミン研究70 年―
- 著者
- 池田 彩子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.94, no.3, pp.162-165, 2020-03-25 (Released:2021-03-31)
In the last 30 years, the research on vitamin E metabolism has made great progress. Initially, dietary vitamin E was thought to be absorbed by passive diffusion in the small intestine, but it has become clear that transporter proteins, such as Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 and ATP- binding cassette transporter A1, are involved in at least a part of the intestinal absorption of vitamin E. The α-tocopherol transfer protein (α-TTP) has also been shown to play an important role in maintaining levels of vitamin E in the body. Among vitamin E isoforms, α- tocopherol, which has the highest affinity for α-TTP, is preferentially transported from the liver to extrahepatic tissues. The importance of α -TTP in vitamin E metabolism has influenced the Dietary Reference Intake for Japanese. In addition, carboxyethyl-hydroxychroman was identified as the major metabolite of vitamin E. This finding revealed that vitamin E is metabolized by a kind of drug metabolism reaction.
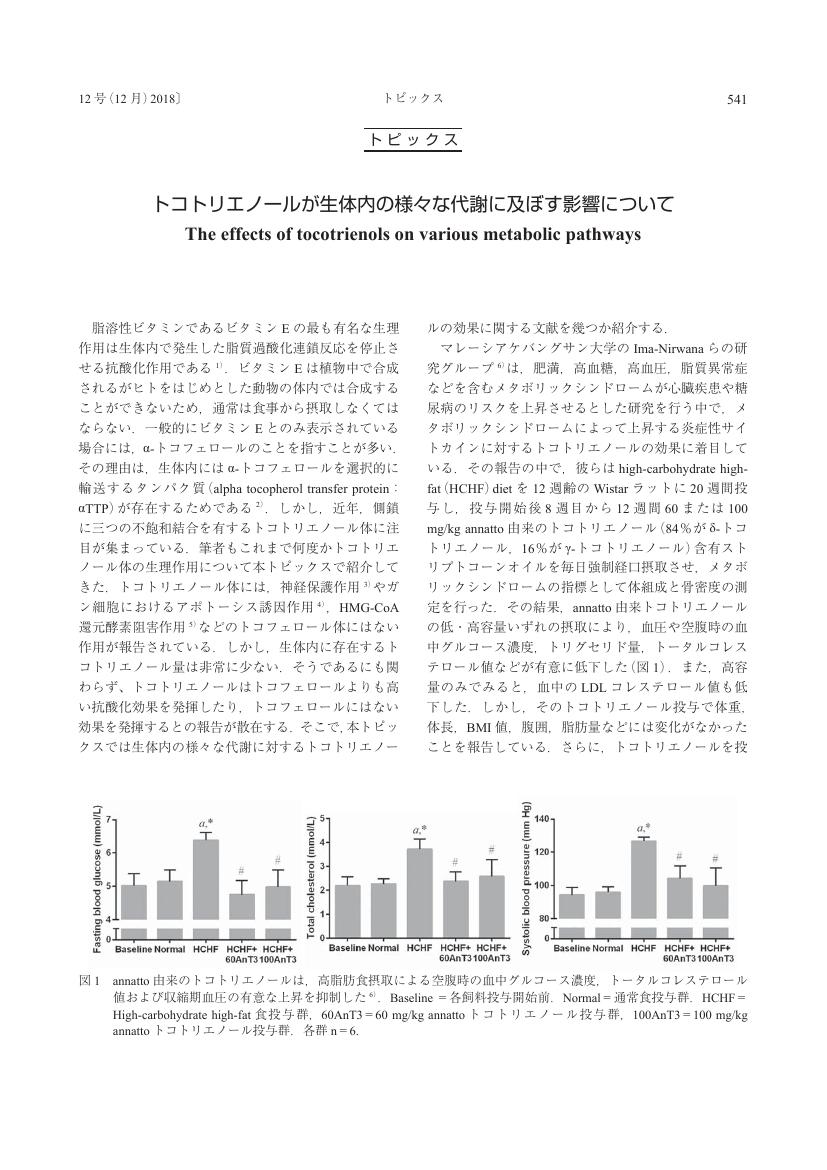
1 0 0 0 OA トコトリエノールが生体内の様々な代謝に及ぼす影響について
- 著者
- 福井 浩二
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.92, no.12, pp.541-544, 2018-12-25 (Released:2019-12-31)
1 0 0 0 OA トコトリエノールのがん抑制作用とその高機能化に関する研究
- 著者
- 永塚 貴弘
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本ビタミン学会
- 雑誌
- ビタミン (ISSN:0006386X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.94, no.12, pp.577-584, 2020-12-25 (Released:2021-12-31)
米ぬかにはトコトリエノール(T3)、フェルラ酸(FA)、γ-オリザノールなどの機能性成分が多く含まれる。不飽和ビタミンEであるT3の高い抗がん活性が注目を集めており、その効果はトコフェロールよりも強いことが知られている。がん細胞や腫瘍組織からテロメラーゼ活性が検出されることから、テロメラーゼはがん治療のターゲットとして期待されている。T3はプロテインキナーゼCの阻害を介してc-mycとテロメラーゼ触媒サブユニット(hTERT)の発現を抑制することでテロメラーゼ活性を阻害することを見出した。また、FAがT3のがん抑制効果(G1期停止を介した細胞増殖阻害とテロメラーゼ阻害)を相乗的に高めることを明らかにした。本研究により、T3によるがん抑制の新たな作用機序が解明され、T3の高い抗がん活性を裏付けた。