4 0 0 0 OA 未成年女子に発生した舌扁平上皮癌の1例
- 著者
- 谷口 紀江 泉 雅浩 香西 雄介 櫻井 孝
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.2, pp.94-98, 2023 (Released:2023-04-06)
- 参考文献数
- 23
The prevalence of oral cancer in Japan is higher in men aged 60 and over, and it is reported that the number is increasing. In recent years, it has been reported that its incidence in women and young people under the age of 40 is also increasing. Young patients generally have a good general condition and are often eligible for radical surgery, which has been reported to have a good prognosis. Early detection and therapeutic intervention are important because oral cancer progresses quickly. The present case was a 17-year-old girl. In April 2018, she visited our hospital with a chief complaint of stomatitis at the base of her tongue. An induration mass with a diameter of 30mm was found on the left tongue edge. She was diagnosed with left tongue cancer (T3N0M0 Stage 3). We performed tongue resection under general anesthesia and abdominal skin graft. Two months after the operation, we found metastatic findings (interval enlargement and internal echo of the left upper internal cervical lymph node) on US examination. On follow-up, there was no change in lymph node size and internal appearance for two months; however, after two months, the lymph nodes were large and swollen, and CT showed typical findings of metastases. We performed left neck dissection. The imaging findings of the present case may be useful for accurate imaging diagnosis in the future.
4 0 0 0 OA いわゆる上顎洞粘液貯留嚢胞のCT像の検討
- 著者
- 代居 敬 金子 雅一 林 宗廣 窪田 秀治 古本 啓一
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.4, pp.213-222, 1992-12-31 (Released:2011-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 16
Six cases of so-called maxillary sinus mucous retention cysts are reported here, focusing mainly on X-ray CT and rotational panoramic examinations. The originating wall and the CT number of the lesions are studied.The results are as follows:1. Alternate positioning of the patient in the CT examination seemed to present valuable information on the origin and the contents.2. The probability of occurence seemed to be more than previously reported because three mucous retention cysts were found during CT examination.3. Mucous retention cysts seem to originate from all of the walls of the maxillary sinus except the upper with equal probability.4. According to the CT number, the mean value seemed to be around 80. There seemed to be a tendency for small mucous retention cysts to have a rather large CT number.It is also reconfirmed that the CT examination seems to be valuable for diagnosing the diseases occuring on the maxillary sinus.
3 0 0 0 OA 歯科用CBCT画像情報の標準化
- 著者
- 勝又 明敏
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.1, pp.22-25, 2015 (Released:2016-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 5
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Standardization of medical image data is an important issue for the both medical and dental radiology. Although almost every medical imaging systems employ DICOM standard, many of dental imaging devices does not adopt to DICOM standard. We evaluated the property of image data that produced from dental cone-beam CT systems using PDI (Portable Data for Images) check tool. As the results, CBCT systems that underwent evaluation adopted DICOM standard. However many incorrect descriptions were found in the tag information of DICOM files. In addition the density value of CBCT images did not correspond with Hounsfield unit.
3 0 0 0 OA 放射線誘発癌: 口蓋血管腫の小線源放射線治療後に生じた粘表皮癌
- 著者
- 花澤 智美 木村 幸紀 蜂須 玲子 関 健次 佐野 司 岡野 友宏 南雲 正男
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.93-97, 1996-06-30 (Released:2011-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 15
A case of radiation-induced cancer is presented. A 59-year-old woman underwent interstitial radiotherapy with radon seeds for the hemangioma of the hard palate 32 years ago. Although a complete response was achieved, the perforation of the hard palate occured 6 years ago because of the induced osteoradionecrosis. An ulcer and swelling in the hard palate was observed around the perforation. CT examination revealed extensive bony destruction of the maxillary sinus walls. Biopsy revealed mucoepidermoid carcinoma. More than 80% of radiation-induced cancer in the head and neck region are squamous cell carcinoma irrespective of the histology of the original lesions. This may be the first case reported of radiation-induced mucoepidermoid carcinoma in the head and neck region.
2 0 0 0 OA 口内法X線撮影法の始祖たち
- 著者
- 小林 馨
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.10-16, 2022 (Released:2022-10-04)
- 参考文献数
- 54
In the present study, we reconsider the pioneers of the intraoral radiography. In intraoral radiography, the bisecting-angle technique was first published by Weston Andrew Valleau Price in 1904, and Antoni Cieszyński devised the same method in 1907. The paralleling technique was first used by Charles Edmund Kells in 1896. Then, in 1911, Franklin W. McCormack introduced the long-distance technique into the paralleling technique and published his findings in 1920. It was integrated and improved, and was popularized by Gordon M. Fitzgerald as a long cone paralleling technique between 1947 and 1950. The author proposes that the above should be the established theory in Japan.
2 0 0 0 OA 頭頸部放射線治療後のう蝕発生リスク因子に関する検討
- 著者
- 曽我 麻里恵 勝良 剛詞 小林 太一 髙村 真貴 黒川 亮 新美 奏恵 田中 恵子 石山 茉佑佳 林 孝文
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.41-46, 2022 (Released:2022-04-06)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Background and Purpose: Dental caries that arise after radiotherapy (radiation caries) can lead to reduced masticatory function caused by tooth loss and osteoradionecrosis caused by dental infections. There are two main opinions regarding the mechanism underlying radiation caries: 1) tooth fragility caused by the direct effects of radiation and 2) a reduction in the physiological effects of saliva due to hyposalivation and a worsening of oral status. However, it has not been clarified which of these mechanisms is the main cause of radiation caries. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the risk factors for radiation caries in patients who had received head and neck radiotherapy. Material and Methods: Forty patients who had received head and neck radiotherapy were enrolled. We retrospectively investigated the relationships between radiation caries and clinical parameters, such as the treated site, irradiation field, radiation dose, and oral status, for 3 years after the completion of radiotherapy. Results: The incidence rate of radiation caries was 85%. Twenty-two percent and 78% of radiation caries occurred within and outside the irradiation field, respectively. The incidence rate of radiation caries among teeth within and outside the radiation field was 41.7% and 57.7%, respectively. The occurrence of radiation caries showed a moderate positive correlation with plaque control records. On the other hand, it was not correlated with the total radiation dose, the mean radiation dose delivered to the parotid gland, or the amount of saliva. Discussion: Our results suggested that radiation caries occur both within and outside the radiation field. It is considered that the risk of radiation caries is affected more by oral status, such as poor oral hygiene, than structural changes in teeth caused by radiation. Therefore, it is important to maintain a good oral status after head and neck radiotherapy to prevent radiation caries.
2 0 0 0 OA 舌骨骨折の2症例
- 著者
- 内田 啓一 馬瀬 直通 深澤 常克 和田 ゆかり 長内 剛 和田 卓郎
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.3, pp.176-181, 1996-09-30 (Released:2011-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 14
The hyoid bone is a bone not directly connected with other bones. Rather it is surrounded by soft tissues, mandible and vertebra. These act a protector to the traumatic injury. We herein report two cases of hyoid bone fracture. A 29- year- old man was tackled during a football game. After the game, he experienced continous pain for a week while swallowing. A plain radiograph did not reveal the cause of his pain at the first examination, but CT images taken more than a week later revealed a hyoid bone injury. The 3D image shows the dislocation of a fragment of the bone. A 46- year- old man had injured his mandible in a traffic accident and thereafter experienced severe pain in his jaw and was unable to open his mouth. The fracture of his mandibular body and ramus was found by radiography. The repositioning operation of the mandibule was considered successful, but the hyoid bone fracture was not discovered at that time. After the operation, the patient complained of gradual pain upon swallowing, and a subsequent radiographic examination showed that the hyoid bone had been fractured. In both cases, it was confirmed that ordinary lateral oblique radiography should be technically modified to some extent, and CT or other images might be necessary for the detection or diagnosis of hyoid bone fracture.
2 0 0 0 OA 涙道閉塞症の診断と治療
- 著者
- 相馬 啓子
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.6-11, 2021 (Released:2021-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 5
I introduce the diagnosis and treatment of the lacrimal drainage system obstruction which causes epiphora.The obstruction of the lacrimal drainage pathway at any point from the punctum to the nasolacrimal duct induces epiphora. Not only ophthalmologic factors but also rhinological factors such as a post-maxillary sinus surgery cause the obstruction.In recent years, a number of researchers have reported the obstruction due to the side effects of oral anticancer drug TS1.Slit lamp microscopy examination, irrigation test, dacryoendoscopy and dacryocystgraphy are used to diagnose this disease. Small-diameter dacryoendoscope enabled us to observe the inside condition of lacrimal passage. Corn Beam CT dacryocystography is available for diagnosis of the obstructed site of tear route and paranasal sinuses disease.Re-opening or making a new tear route through the lacrimal drainage pathway can relieve the epiphora. Dacryoendoscopic surgery for the obstruction without severe inflammation is one of the initial methods to penetrate the stenosis and obstruction of the lacrimal drainage pathway.There are two methods, endoscopic endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy (END-DCR) and external dacryocystorhinostomy (EXT-DCR), which make a new tear route. Both methods have been accepted technique and showed high success rates, especially for obstructions at the nasolacrimal duct. However, clinical comfort defined by patients is higher in END-DCR. A sutureless surgical area with less pain is advantage of this method.
2 0 0 0 OA 顎放線菌症のCT・US所見
- 著者
- 木村 幸紀 荒木 和之 花澤 智美 酒巻 紅美 岡野 友宏
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.4, pp.231-239, 2001-12-30 (Released:2011-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Actinomycosis is an unusual chronic suppurative bacterial infection, predominantly caused by Actinomyces israelii, that most often affects the cervico-facial region, accounting for about 60%. Classically, the clinical presentation is a hard, boardlike mass, multiple abscesses and/or sinus tracts, and trismus. Because of the current lack of familiarity with this disease and its ability to mimic other infections or even neoplasms, actinomycosis of the mandible and/or paramandibular tissue may frequently be misdiagnosed. Recently, we experienced three cases with osteomyelitis of the mandible with actinomycosis, clinically diagnosed as a parotid tumor or nonspecific osteomyelitis, however, not conforming radiologically. The images of actinomycotic mandibular osteomyelitis should be, therefore, critically re-evaluated.Materials and Methods: The CT appearances of two cases with a final diagnosis of actinomycotic mandibular osteomyelitis and nineteen cases diagnosed as non-actinomycotic mandibular osteomyelitis between 1993 and December 2000 were reviewed. The evaluation included bone marrow density changes, sequesta, periosteal reaction, cortical bone thickening, the extent of cortical bone destruction, abscess formation, and soft tissue swelling. Ultrasonography of abscesses from actinomycotic mandibular osteomyelitis was evaluated retrospectively, in two cases (one having received both CT and US examinations). The internal echogenecity of an abscess between the masseter muscle and the ramus of the mandible, and cortical bone destruction were investigated.Results: On CT, no remarkable osteosclerotic and/or osteolytic bone marrow changes, or small punched out radiolucent areas (less than 6mm) of the mandibular ramus accompanied with a well demarked overlying abscess were seen in actinomycotic osteomyelitis. Any other CT findings in actinomycosis of the mandible were nonspecific. Ultrasonography showed a well-defined hypoehoic area, including multiple, relatively large, hyperechoic spots in abscesses from actinomycotic mandibular osteomyelitis. Destruction of the cortex was also seen simultaneously.Conclusion: Actinomycotic mandibular osteomyelitis may be characterized by its CT appearances. Ultrasonography can also be used as an additional diagnostic tool to detect those radiological changes caused by actinomycosis.
2 0 0 0 OA 第28回日本歯科放射線学会抄録
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.2Supplement, pp.225-313, 1987 (Released:2011-09-05)
1 0 0 0 OA AIを用いたパノラマX線画像からのカルテ入力支援システムの開発
- 著者
- 鳥井 浩平 誉田 栄一 北 研二
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.24-34, 2022 (Released:2022-10-04)
- 参考文献数
- 24
Research and development of AI-based diagnostic systems in the medical and dental fields is flourishing worldwide. However, there are few practical dental support systems and dental databases. Support for medical record input is needed to reduce the burden at diagnosis. We have been developing a dental database with detailed annotation information and building an AI system for automatic teeth detection, teeth numbering, teeth contour estimation, and disease diagnosis from panoramic X-ray images since 2019. Three dentists and one expert of dental radiology created our database, which includes teeth number based on FDI method, coordinates of teeth contour, and various dental conditions, using Anotee, a software developed for creating dental databases. Our system consists of multiple deep neural networks that were trained using 1,781 panoramic X-ray images and annotations, which excluded deciduous teeth and rare dental conditions. The deep neural network to classify dental conditions is based on EfficientNetV2-S and can diagnose multiple dental conditions. To verify our system’s usefulness, we evaluated two dental condition classifications for 20 dental conditions and 10 dental conditions such as caries, periodontitis, root canal filling, inlay, composite resin, crown, pontic, implant, and impacted tooth. We performed 5-fold cross validation and calculated precision, sensitivity, and specificity. Experimental results were encouraging. For the diagnosis of 20 conditions, precision was 90.4%, sensitivity was 86.1%, and specificity was 99.4%; for the diagnosis of 10 conditions, precision was 92.9%, sensitivity was 90.0%, and specificity was 99.1%. The system achieved high accuracy, suggesting that AI systems are useful in assisting medical record input support.
1 0 0 0 OA う蝕が認められない歯牙に生じた歯根嚢胞の特異例
- 著者
- 井田 瑞枝 中村 正
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, no.2, pp.131-132, 1972 (Released:2010-10-21)
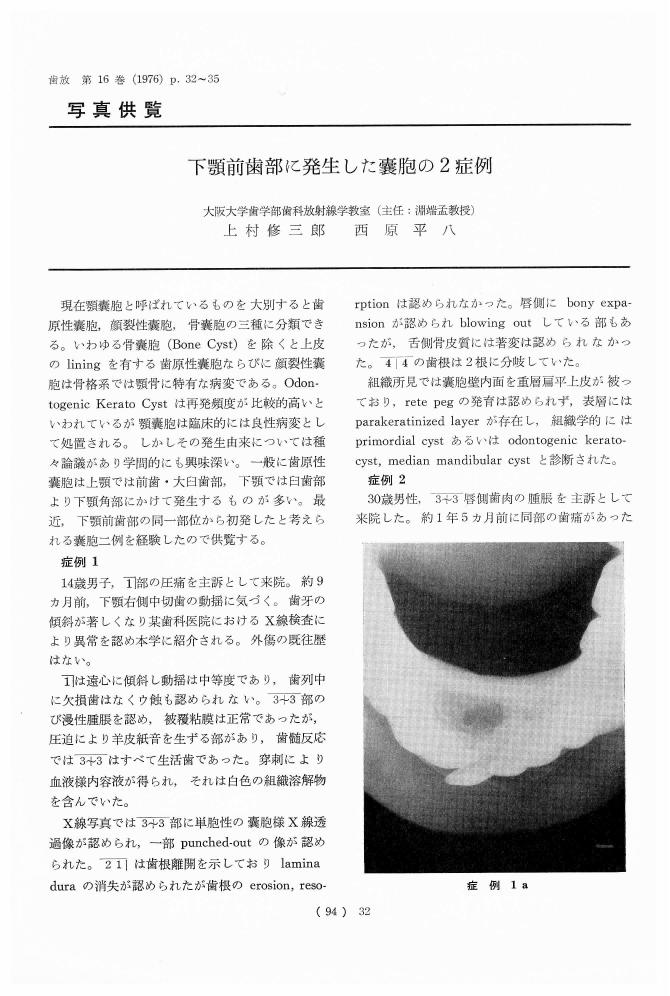
1 0 0 0 OA 下顎前歯部に発生した嚢胞の2症例
- 著者
- 上村 修三郎 西原 平八
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, no.2, pp.94-97, 1976-08-30 (Released:2010-10-21)
1 0 0 0 OA 顎口腔領域疾患におけるサーモグラフィの応用
- 著者
- 早瀬 康博 花田 孝二 片岡 久美子 秋田 和俊 佐藤 眞 藤木 知一 岸 幹二 青野 要
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.1, pp.10-16, 1987-06-22 (Released:2011-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 38
Thermography was clinically applicated in 155 cases of various diseases in oral-maxillo-facial region. An attempt was made to evaluate the detectability of thermogram compared with the one of radiographic examination, the distribution of difference of temperature in various disease, the relationship between pain and the difference of temperature and the relationship between pain after operation and temperature change. Thermography was able to detect the influence of the lesions in soft tissue which was not detectable by radiograph. Thermographic findings was quite in accord with those of clinical symptom but not always with radiographic findings. In the cases of acute inflammation the difference of temperature with the opposite side showed wide range of distribution correlated with clinical symptom. In the cases of chronic inflammation no apparent difference was observed in the range of temperature. In cystic lesions without any acute inflammation the area of lesion was demonstrated as a cold spot. In cases of malignant tumor the area was shown as a hot spot between 0.5°C and 1.5°C In the cases of arthrosis painful areas were shown as localized hot spots. Correlationship was observed between pain and the differences of temperature and it was suggested that thermography might represent the painful area as an objective sign. It was also possible to demonstrate the changes of pathological conditions after operation by using thermography in lapse of time and it was indicated that thermography yielded much useful data as an excellent functional analyzing method.
1 0 0 0 OA 全顎的な歯髄腔の狭窄がみられた ステロイド長期使用患者のX線画像
1 0 0 0 OA 舌悪性腫瘍との鑑別を要した魚骨迷入の1例
- 著者
- 川島 雄介 阿部 浩志 宮腰 昌明 川畑 義裕 犬童 寛子 田中 達朗
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.43-46, 2022 (Released:2022-10-04)
- 参考文献数
- 11
1 0 0 0 OA 低線量放射線の生体影響の解明
- 著者
- 小林 純也
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.1-5, 2021 (Released:2021-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 11
After the accident of Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, many people in Japan have a concern about biological effect with low dose and low dose rate radiation. In such situation, some people also have concerns to radiation usage for diagnostics and therapies. As the current amendment of medical law provides the rules of radiation diagnostics strictly, medical workers, treating radiation for medical, have to understand the biological effects with exposure to ionizing radiation to explain the effects of medical radiation to patients.Acute irradiation of high dose radiation induces several types of DNA damages. Among of them, DNA doble-strand breaks (DSBs) are most serious damages to cells and constructing organs, because remaining of DSB damages could lead to cell death, subsequently dysfunction of organs (deterministic effects). Therefore, living beings are developing DNA repair systems such as non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination. Miss-repair and non-repair could generate gene mutation, and subsequently lead to tumorigenesis (stochastic effects).Exposure of radiation also causes excess accumulation of ROS (reactive oxygen species)/oxidative stress, which may lead to biological effects of low dose rate radiation. We found that mitochondria damage contributed to accumulation of ROS and activation of oxidative stress in human normal fibroblasts under low dose rate irradiation. We also observed that low dose rate irradiation also caused gamma-H2AX positive micronuclei in the presence of ATM inhibitor. As ATM is an important protein kinase of oxidative stress responses as well as DNA damage responses, anti-oxidative stress function may be important to repress micronuclei formation. In order to provide relief to concerning people, we have to clarify the biological effects of low dose and low dose rate radiation more.
1 0 0 0 OA 唾液腺造影像における大舌下腺像の検討
- 著者
- 清水 真弓 湯浅 賢治 神田 重信
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.4, pp.279-284, 1991-12-30 (Released:2011-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 19
On the sialogram of the submandibular gland, ducts and/or glands communicating with Wharton's duct are sometimes seen and considered to be the major sublingual gland or accessory submandibular gland.But no distinct definition of the major sublingual gland image on sialograms is so far given.We defined, therefore, the major sublingual gland image on sialograms mainly referring to anatomical literature. The frequency of appearance of the major sublingual gland image on sialograms was also examined.Our results include:1. The major sublingual gland was defined as follows on the sialogram of the submandibular gland: the gland which has a duct communicating with Wharton's duct within 10mm from the orifice.2. The major sublingual gland was identified on 64 out of 553 submandibular gland sialograms.
1 0 0 0 OA 頭頸部化学放射線治療後に多発う蝕を生じ口腔管理に苦慮した1例
- 著者
- 新垣 理宣 勝良 剛詞 小林 大二郎 道 泰之 北本 佳住 依田 哲也 倉林 亨
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本歯科放射線学会
- 雑誌
- 歯科放射線 (ISSN:03899705)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.53-57, 2022 (Released:2022-04-06)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Introduction: Radiation-induced dental caries is a late oral adverse event that should be considered after head and neck radiotherapy. However, there are no clinical guidelines for dental management after head and neck radiotherapy. We report a case of multiple dental caries that developed after head and neck radiotherapy in a patient in whom symptomatic treatment was challenging. Case: A 67-year-old male was referred to our department with difficulty with oral intake secondary to occlusal insufficiency. He had a history of radiotherapy for hypopharyngeal carcinoma, and nearly all of his teeth only had residual roots. We found multiple carious teeth, including in areas outside of the radiation field. We designed a temporary denture in coordination with a dental office; however, it was difficult to extract all of the patient’s teeth. The patient was followed-up; however, he died of esophageal cancer. Conclusion: Radiation-induced dental caries can even occur in teeth outside of the radiation field. In such cases, continuous preventative measures, such as oral care, are important, even before the start of radiotherapy.