- 著者
- Masahiko Imai Tomohiro Izumisawa Daisuke Saito Shinya Hasegawa Masahiro Yamasaki Noriko Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.5, pp.661-671, 2023-05-01 (Released:2023-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
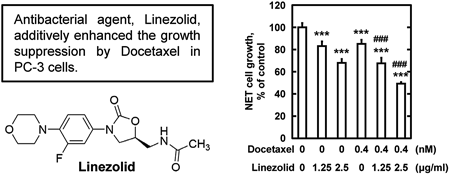
Myelosuppression, a side effect of anticancer drugs, makes people more susceptible to infectious diseases by compromising the immune system. When a cancer patient develops a contagious disease, treatment with an anticancer drug is suspended or postponed to treat the infectious disease. If there was a drug that suppresses the growth of cancer cells among antibacterial agents, it would be possible to treat both infectious diseases and cancer. Therefore, this study investigated the effect of antibacterial agents on cancer cell development. Vancomycin (VAN) had little effect on cell proliferation against the breast cancer cell, MCF-7, prostate cancer cell, PC-3, and gallbladder cancer cell, NOZ C-1. Alternatively, Teicoplanin (TEIC) and Daptomycin (DAP) promoted the growth of some cancer cells. In contrast, Linezolid (LZD) suppressed the proliferation of MCF-7, PC-3, and NOZ C-1 cells. Therefore, we found a drug that affects the growth of cancer cells among antibacterial agents. Next, when we examined the effects of the combined use of existing anticancer and antibacterial agents, we found VAN did not affect the growth suppression by anticancer agents. However, TEIC and DAP attenuated the growth suppression of anticancer agents. In contrast, LZD additively enhanced the growth suppression by Docetaxel in PC-3 cells. Furthermore, we showed that LZD inhibits cancer cell growth by mechanisms that involve phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway suppression. Therefore, LZD might simultaneously treat cancer and infectious diseases.
- 著者
- Yukiko K. Kaneko
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.5, pp.640-646, 2023-05-01 (Released:2023-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Although diabetes is associated with an increased risk of various diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases, no definitive cure has yet been found. Long-term treatment for blood glucose control significantly reduces the QOL. Pancreatic β-cells are the only cells that can lower blood glucose levels by secreting insulin. Therefore, maintaining insulin-secreting β-cells is crucial in preventing the progression of diabetes and improving the QOL. We have investigated the mechanisms for the regulation of insulin secretion, the prevention of β-cell apoptosis, and the increase in β-cell mass. In particular, we have elucidated the involvement of type I diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) in the regulation of insulin secretion and the effects of nitric oxide (NO) signaling and natural products in suppressing β-cell death. In addition, we have elucidated the function of DGKδ as a suppressor of β-cell proliferation. This review introduces the findings of our study leading to development of novel anti-diabetic therapeutics that targets pancreatic β-cells.
- 著者
- Hisashi Shiraishi Maho Fujino Naoki Shirakawa Nanao Ishida Hiroki Funato Ayumu Hirata Noriaki Abe Michiro Iizuka Kohei Jobu Junko Yokota Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.10, pp.1700-1705, 2017-10-01 (Released:2017-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
Minerals are essential for life, as they are a vital part of protein constituents, enzyme cofactors, and other components in living organisms. Deep sea water is characterized by its cleanliness and stable low temperature, and its possible health- and medical benefits are being studied. However, no study has yet evaluated the physical properties of the numerous commercially available deep sea water products, which have varying water sources and production methods. We analyzed these products’ mineral content and investigated their effect on living organism, focusing on immune functions, and investigated the relation between physiological immunoactivities and mineral intake. We qualitatively analyzed the mineral compositions of the deep sea water drinks and evaluated the drinks’ physical properties using principal component analysis, a type of multivariate analysis, of their mineral content. We create an iron and copper-deficient rat model and administered deep sea water drinks for 8 weeks. We then measured their fecal immunoglobulin A (IgA) to evaluate immune function. Principal component analysis suggested that physical properties of deep sea water drinks could be determined by their sources. Administration of deep sea water drinks increased fecal IgA, thus tending to stimulate immune function, but the extent of this effect varied by drink. Of the minerals contained in deep sea water, iron showed positive correlations with the fecal IgA. The principal component analysis used in this study is suitable for evaluating deep sea water containing many minerals, and our results form a useful basis for comparative evaluations of deep sea water’s bioactivity.
- 著者
- Sumihito Togi Misa Togi Satoshi Nagashima Yuichi Kitai Ryuta Muromoto Jun-ichi Kashiwakura Toshiaki Miura Tadashi Matsuda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BPB Reports (ISSN:2434432X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.2, pp.59-63, 2021 (Released:2021-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 2 4
The controlled and moderate oxidative stress such as ozone induces both inflammatory and anti-inflammatory response. This balance is important for homeostasis of living organisms. Furthermore, it has been shown that this conflict response is mainly regulated by two transcriptional factors, nuclear transcriptional factor κB (NF-κB) and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). NF-κB is involved in inflammatory responses by regulating expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and various inflammatory cytokines while Nrf2 is involved in anti-inflammatory responses by controlling expression of numerous antioxidant enzymes such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). We here demonstrate the molecular mechanisms of the crosstalk between NF-κB and Nrf2 activation during the moderate oxidative stress induced by ozone. We first confirmed the activation of NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling during the moderate oxidative stress in HeLa cells. Induction of NF-κB-mediated COX-2 mRNA expression was observed at the early phase after stimulation (30-60 min after ozone treatment). However, induction of HO-1 mRNA expression was observed at the late phase of stimulation (6 h after stimulation). To reveal the crosstalk between NF-κB and Nrf2, we tested whether reduction of NF-κB expression affects ozone-induced Nrf2 activation by knocking down of NF-κB in HeLa cells. Importantly, the HO-1 induction by ozone was remarkably decreased by a reduction in NF-κB expression. These results suggest that the moderate oxidative stress by ozone initially induces NF-κB activation, and this NF-κB activation is required for HO-1 induction at the late phase of the moderate stress.
- 著者
- Qiong Hu Chujun Chen Zhenming Lin Liyao Zhang Sujiuan Guan Xiaoyan Zhuang Guangfu Dong Juan Shen
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3, pp.382-393, 2023-03-01 (Released:2023-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Delayed wound healing is a persistent medical problem mainly caused by decreased angiogenesis. Esculentin-1a(1–21)NH2 [Esc-1a(1–21)NH2], has broad-spectrum antibacterial properties which comes from frog skins. It has shown promise as a treatment for wound healing. However, its effects on angiogenesis as well as the mechanism by which esc-1a(1–21)NH2 enhanced wound healing remained unclear. In this study, we analyzed the structural properties and biocompatibility of esc-1a(1–21)NH2 and evaluated its effect on wound closure using a full-thickness excision model in mice. Our results showed that esc-1a(1–21)NH2 significantly accelerated wound healing by increasing collagen deposition and angiogenesis, characterized by elevated expression levels of platelet, endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Furthermore, the angiogenic activity of esc-1a(1–21)NH2 was confirmed in vitro by various assays. Esc-1a(1–21)NH2 significantly promoted cell migration and cell proliferation in human umbilical vein vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) via activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway, and upregulated the expression of CD31 at both mRNA and protein levels. The effect of esc-1a(1–21)NH2 on angiogenesis was diminished by LY294002, a PI3K pathway inhibitor. Taken together, this study demonstrates that esc-1a(1–21)NH2 accelerates wound closure in mice by promoting angiogenesis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, suggesting its effective application in the treatment of wound healing.
- 著者
- Takehiro Yamada Shuhei Ishikawa Nobuhisa Ishiguro Masaki Kobayashi Ken Iseki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.9, pp.1338-1345, 2020-09-01 (Released:2020-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 2 3
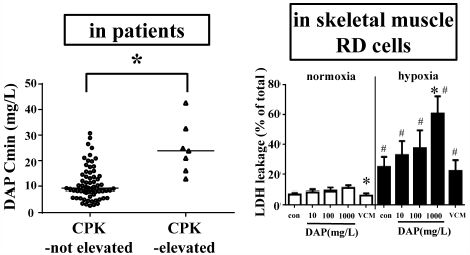
Daptomycin, a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic, has bactericidal activity against Gram-positive organisms and is especially effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Although daptomycin causes unique adverse drug reactions such as elevation of creatine phosphokinase or rhabdomyolysis, the detailed mechanisms underlying these adverse drug reactions in skeletal muscle are unclear. This study aimed to elucidate whether daptomycin causes direct skeletal muscle cell toxicity and investigate the relationship between daptomycin exposure and musculoskeletal toxicity. First, we evaluated the relationship between daptomycin exposure and skeletal muscle toxicity. Of the 38 patients who received daptomycin intravenously, an elevation in creatine phosphokinase levels was observed in five. The median plasma trough concentration of daptomycin in patients with elevated creatine phosphokinase levels was significantly higher than that in patients whose creatine phosphokinase levels were within the normal range, suggesting that increased exposure to daptomycin is related to elevation in creatine phosphokinase levels. In an in vitro study using human rhabdomyosarcoma cells, daptomycin reduced cell viability and increased membrane damage. These effects were more marked under hypoxic conditions. A necroptotic pathway seemed to be involved because phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein expression was enhanced following daptomycin exposure, which was significantly enhanced under hypoxic conditions. These findings indicate that daptomycin elicits cytotoxic effects against skeletal muscle cells via the necroptotic pathway, and the extent of toxicity is enhanced under hypoxic conditions.
1 0 0 0 OA Identification of Risk Factors for Phlebitis in Patients Treated with Nafamostat Mesylate
- 著者
- 小武 和正 田平 明啓 川上 恭弘
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22-00201, (Released:2023-03-07)
- 参考文献数
- 22
The proteolytic enzyme inhibitor nafamostat mesylate is widely used for the treatment of acute pancreatitis and disseminated intravascular coagulation. This drug may be a risk factor for phlebitis, but this risk has not been studied. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the frequency of phlebitis and its risk factors in patients treated with nafamostat mesylate in intensive care units (ICU) or high care units (HCU). During the study period, 83 patients met the inclusion criteria, and 22 of them (27%) experienced phlebitis. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed for severe acute pancreatitis, administration duration, and administration concentration of nafamostat mesylate in the ICU or HCU. As a result, the administration of nafamostat mesylate for ≥ 3 days in the ICU or HCU was an independent predictor of phlebitis caused by nafamostat mesylate (odds ratio, 10.3; 95% confidence interval, 1.28–82.5; p=0.03). This study suggests that the number of days of nafamostat mesylate administration is associated with phlebitis in patients treated with the drug, and it may be necessary to pay attention to its administration for ≥ 3 days in the ICU or HCU.
- 著者
- Tomoko Ishida Mohammad Shahriar Khan Honami Kodama Yukiko Uejima Yumi Kawase Takahiro Matsumoto Yuki Yamamura Nobuyuki Sera Takao Gotou Masaaki Hirakawa Yoshitaka Yano Masayuki Shima Nobuyuki Yamagishi Keiji Wakabayashi Tetsushi Watanabe
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.9, pp.1361-1366, 2020-09-01 (Released:2020-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
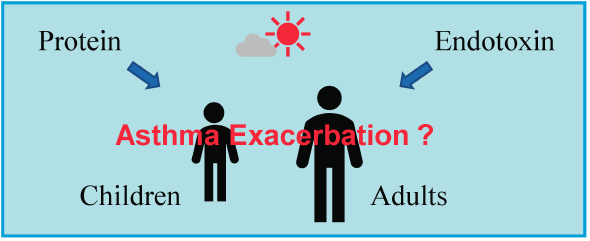
We examined the association of biological components in airborne particles, i.e., proteins and endotoxins, in outdoor air with asthma exacerbation in the Fukuoka metropolitan area, Fukuoka, Japan. Data on emergency department (ED) visits for asthma in children (age, 0–14 years) and adults (age, 15–64 years) were collected at a medical center from December 2014 to November 2015. One hundred eighty-one children and 143 adults visited the ED for asthma, and the weekly number of ED visits in children increased in autumn, i.e., September (second week) to November (first week). Fine (aerodynamic diameter ≤2.5 µm) and coarse (≥2.5 µm) particles were collected for 3 or 4 weeks per month, and protein and endotoxin concentrations were analyzed. Protein was largely prevalent in fine particles (0.34–7.33 µg/m3), and concentrations were high in April, May, June, and October. In contrast, endotoxin was mainly included in coarse particles (0.0010–0.0246 EU/m3), and concentrations were high in September (third week), October (first, second, and fourth weeks), February (fourth week), and July (first week). The results of a Poisson regression analysis indicated that endotoxin (in fine and coarse particles alike) was a significant factor for ED visits related to asthma in children, even after adjusting for meteorological factors, i.e., temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed. However, there was no association between environmental factors and ED visits for asthma in adults. These results suggest that endotoxin in outdoor air is significantly associated with an increased risk of asthma exacerbation in children.
1 0 0 0 OA Thiazolidinediones Are Potent Inducers of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Expression in the Liver
- 著者
- Katsutaka Oishi Tatsunosuke Tomita
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.7, pp.1120-1121, 2011-07-01 (Released:2011-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 被引用文献数
- 21 23
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is an effective metabolic regulator of glucose and lipid homeostasis in the context of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and dyslipidemia in diabetic rodents and monkeys, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) directly induces FGF21 expression in the rodent liver. Recent findings suggest that the effects and regulation of FGF21 qualitatively differ between rodents and humans. Here, we examined the effects of PPARα and PPARγ agonists on FGF21 mRNA expression in the mouse liver and in cultured hepatocytes. Intraperitoneal injection of both bezafibrate and pioglitazone induced FGF21 mRNA expression in the mouse liver. Rosiglitazone and pioglitazone as well as bezafibrate significantly induced FGF21 mRNA expression in cultured mouse hepatocytes. On the other hand, both rosiglitazone and pioglitazone significantly induced, whereas bezafibrate did not affect FGF21 mRNA expression in the human liver carcinoma cell line HepG2. Bezafibrate significantly induced pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 mRNA expression, suggesting that HepG2 cells are sensitive to bezafibrate like the mouse liver. Our findings suggest that PPARγ-activating antidiabetic drugs such as rosiglitazone and pioglitazone induce FGF21 expression in mouse and human hepatocytes, and that PPARγ rather than PPARα might play an important role in human FGF21 production.
- 著者
- Akari Yoshimura Tatsuya Sakakihara Takemi Enomoto Masayuki Seki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.2, pp.200-206, 2022-02-01 (Released:2022-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
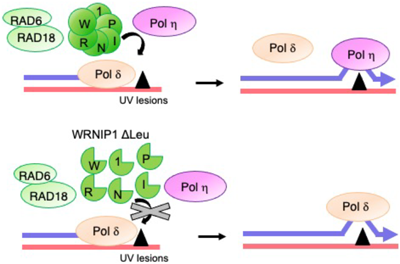
Werner helicase–interacting protein 1 (WRNIP1) belongs to the AAA+ ATPase family and is conserved from Escherichia coli to human. In addition to an ATPase domain in the middle region of WRNIP1, WRNIP1 contains a ubiquitin-binding zinc-finger (UBZ) domain and two leucine zipper motifs in the N-terminal and C-terminal regions, respectively. Here, we report that the UBZ domain of WRNIP1 is responsible for the reduced levels of UV-induced proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) monoubiquitylation in POLH-disrupted (polymerase η (Polη)-deficient) cells, and that the ATPase domain of WRNIP1 is involved in regulating the level of the PrimPol protein. The suppression of UV sensitivity of Polη-deficient cells by deletion of WRNIP1 was abolished by expression of the mutant WRNIP1 lacking the UBZ domain or ATPase domain, but not by the mutant lacking the leucine zipper domain in WRNIP1/POLH double-disrupted cells. The leucine zipper domain of WRNIP1 was required for its interaction with RAD18, a key factor in TLS (DNA translesion synthesis), and DNA polymerase δ catalytic subunit, POLD1. On the basis of these findings, we discuss the possible role of WRNIP1 in TLS.
- 著者
- Masaki Kumondai Masamitsu Maekawa Eiji Hishinuma Yu Sato Toshihiro Sato Masafumi Kikuchi Masahiro Hiratsuka Nariyasu Mano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3, pp.455-463, 2023-03-01 (Released:2023-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 52
CYP3A4, which contributes to the metabolism of more than 30% of clinically used drugs, exhibits high variation in its activity; therefore, predicting CYP3A4 activity before drug treatment is vital for determining the optimal dosage for each patient. We aimed to develop and validate an LC-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method that simultaneously measures the levels of CYP3A4 activity-related predictive biomarkers (6β-hydroxycortisol (6β-OHC), cortisol (C), 1β-hydroxydeoxycholic acid (1β-OHDCA), and deoxycholic acid (DCA)). Chromatographic separation was achieved using a YMC-Triart C18 column and a gradient flow of the mobile phase comprising deionized water/25% ammonia solution (100 : 0.1, v/v) and methanol/acetonitrile/25% ammonia solution (50 : 50 : 0.1, v/v/v). Selective reaction monitoring in the negative-ion mode was used for MS/MS, and run times of 33 min were used. All analytes showed high linearity in the range of 3–3000 ng/mL. Additionally, their concentrations in urine samples derived from volunteers were analyzed via treatment with deconjugation enzymes, ignoring inter-individual differences in the variation of other enzymatic activities. Our method satisfied the analytical validation criteria under clinical conditions. Moreover, the concentrations of each analyte were quantified within the range of calibration curves for all urine samples. The conjugated forms of each analyte were hydrolyzed to accurately examine CYP3A4 activity. Non-invasive urine sampling employed herein is an effective alternative to invasive plasma sampling. The analytically validated simultaneous quantification method developed in this study can be used to predict CYP3A4 activity in precision medicine and investigate the potential clinical applications of CYP3A4 biomarkers (6β-OHC/C and 1β-OHDCA/DCA ratios).
- 著者
- Makoto Oba Mika Shibuya Yuto Yamaberi Hidetomo Yokoo Satoshi Uchida Atsushi Ueda Masakazu Tanaka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.3, pp.250-256, 2023-03-01 (Released:2023-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Amphipathic peptides composed of cationic amino acids and hydrophobic amino acids have cell-penetrating ability and are often used as a delivery tool for membrane-impermeable compounds. Small interfering RNA (siRNAs) are one of the delivery targets for such cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs). Cationic CPPs can associate with anionic siRNAs by electrostatic interactions resulting in the formation of nano-sized complexes, which can deliver siRNAs intracellularly. CPPs containing unnatural amino acids offer promising tools to siRNA delivery. However, the detailed structure–activity relationship in siRNA delivery has been rarely studied. In the current study, we designed peptides containing dipropylglycine (Dpg) and explored the cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of peptide/siRNA complexes. The amphipathic structure of the peptides played a key role in complexation with siRNAs and intracellular siRNA delivery. In the amphipathic peptides, cellular uptake of siRNA increased with increasing peptide length, but cytotoxicity was reduced. A peptide containing four Dpg exhibited an effective gene-silencing effect with small amounts of peptides without cytotoxicity in medium containing serum. These findings will be helpful for the design of novel CPPs for siRNA delivery.
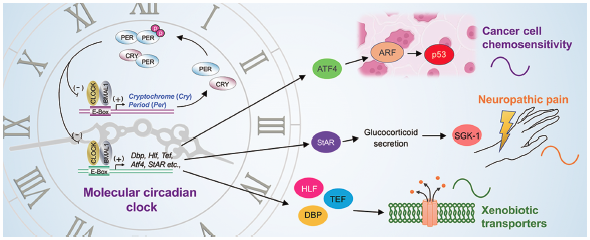
1 0 0 0 OA Chrono-Pharmaceutical Approaches to Optimize Dosing Regimens Based on the Circadian Clock Machinery
- 著者
- Satoru Koyanagi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.11, pp.1577-1584, 2021-11-01 (Released:2021-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 76
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Daily rhythmic variations in biological functions affect the efficacy and/or toxicity of drugs: a large number of drugs cannot be expected to exhibit the same potency at different administration times. The “circadian clock” is an endogenous timing system that broadly regulates metabolism, physiology and behavior. In mammals, this clock governs the oscillatory expression of the majority of genes with a period length of approximately 24 h. Genetic studies have revealed that molecular components of the circadian clock regulate the expression of genes responsible for the sensitivity to drugs and their disposition. The circadian control of pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics enables ‘chrono-pharmaceutical’ applications, namely drug administration at appropriate times of day to optimize the therapeutic index (efficacy vs. toxicity). On the other hand, a variety of pathological conditions also exhibit marked day-night changes in symptom intensity. Currently, novel therapeutic approaches are facilitated by the development of chemical compound targeted to key proteins that cause circadian exacerbation of disease events. This review presents an overview of the current understanding of the role of the circadian biological clock in regulating drug efficacy and disease conditions, and also describes the importance of identifying the difference in the circadian machinery between diurnal and nocturnal animals to select the most appropriate times of day to administer drugs in humans.
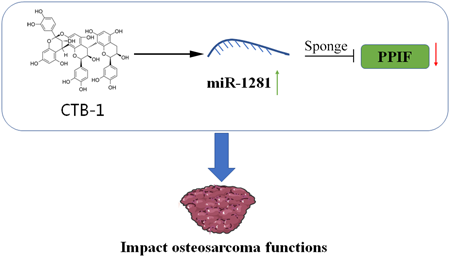
1 0 0 0 OA Cinnamtannin B-1 Inhibits the Progression of Osteosarcoma by Regulating the miR-1281/PPIF Axis
- 著者
- Jun Jia Jiaojiao Xia Weifeng Liu Fengqin Tao Jun Xiao
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.67-73, 2023-01-01 (Released:2023-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Osteosarcoma (OS), one of the bone tumors, occurs mainly during childhood and adolescence and has an incidence rate of 5%. Cinnamtannin B-1 (CTB-1) is a natural trimeric proanthocyanidin compound found in plants Cinnamomum zeylanicum and Laurus nobilis. Previously, several articles have demonstrated that CTB-1 exerts a certain effect on melanoma and cervical cancer. However, their role in OS remains unclear. In this study, CTB-1 was found to inhibit the proliferation of OS cancer cells, with the dose of CTB-1 positively correlated to the survival rate of HOS and MG-63 cells. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs) were also reported to play an important role in tumor proliferation. Hence, we performed the miRNA sequencing analysis after CTB-1 treatment to identify miRNA levels in HOS cells and found that the expression of miR-1281 was significantly upregulated. According to the functional analysis, CTB-1 inhibited the growth and migration of OS by upregulating the expression of miR-1281. Additionally, miR-1281 acted as a sponge for Peptidylprolyl Isomerase F (PPIF), inhibiting its expression levels. The rescue experiments revealed that CTB-1 delayed the development of OS by regulating the miR-1281/PPIF pathway. Hence, our findings suggested that CTB-1 inhibited the cell growth, invasion, and migration of OS by upregulating miR-1281 and inhibiting PPIF expression, thereby providing a possible target drug for OS treatment.
- 著者
- Ren Wu Ding Li Qi Tang Wanchun Wang Guangrong Xie Pengcheng Dou
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.4, pp.458-464, 2018-04-01 (Released:2018-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 12 13
Osteosarcoma (OS) is a typical bone cancer, and most frequently used cancer treatments for OS are limited due to severe drug-related toxicities. Wasp venoms contain functional components that may offer pharmaceutical components for the treatment of cancers. This study aimed to isolate and characterize a novel peptide (venom anti-cancer peptide 1, VACP1) derived from the wasp venom of Vespa ducalis SMITH. Toxins from Vespa ducalis crude venom were separated by gel filtration and purified by C18 reverse-phase HPLC. As examined by Edman degradation, the amino acid sequence of VACP1 is AQKWLKYWKADKVKGFGRKIKKIWFG. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays revealed that VACP1 inhibited the cell proliferation of MG-63, U-2 OS and Saos-2 cells. Furthermore, annexin V and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining revealed that VACP1 could induce the apoptosis of OS cell lines. In addition, VACP1 increased the protein levels of cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), caspase 3, but decreased B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2). Apoptotic signaling pathway screening in MG-63 cells via an antibody array revealed that VACP1 activated the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways. The present study demonstrates that VACP1 potently suppressed cell proliferation and induced the cell apoptosis of OS cells by inducing the activation of the p38 MAPK and JNK signaling pathways, suggesting that VACP1 is a promising agent for OS therapy.
- 著者
- Mayuka Yamada Midori Suzuki Takuya Noguchi Takumi Yokosawa Yuto Sekiguchi Natsumi Mutoh Takashi Toyama Yusuke Hirata Gi-Wook Hwang Atsushi Matsuzawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BPB Reports (ISSN:2434432X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.1, pp.16-21, 2020 (Released:2020-11-26)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 4 7
Both NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) contribute to cellular defense to various stresses, and have emerged as candidates of therapeutic targets to improve or prevent tissue damage. Cefotaxime (CTX), a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, is conceived as a safe drug largely free from side effects. CTX exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, and thereby, is most commonly prescribed for the treatment of infectious diseases induced by Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacteria. In this study, we unexpectedly found the beneficial properties of CTX that upregulate both Nrf2 and HSP70 to the extent that stress-induced damage is ameliorated. Non-toxic levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced by CTX activated the Nrf2 pathway without cytotoxicity, which in turn upregulated HSP70. Interestingly, the cytotoxicity of Fas/CD95 ligand (FasL), a cytotoxic cytokine that strongly induces apoptosis, was significantly ameliorated by pre-treatment with CTX, most likely because of the upregulation of Nrf2 and HSP70. Our results therefore show novel properties of CTX, which raise the possibility that CTX works as a non-toxic therapeutic agent for preventing and repairing tissue damage.
- 著者
- Satoko Notomi Mineaki Kitamura Kosei Yamaguchi Maya Komine Kenji Sawase Tomoya Nishino Satoshi Funakoshi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.2, pp.286-291, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Anorexia is a common symptom in older patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD) and has become a serious problem in dialysis facilities with the aging of patients. Polypharmacy, defined as the prescription of several medications, is known to cause drug-induced anorexia. Although polypharmacy is also common in older patients undergoing HD, only a few studies have examined the association between anorexia and polypharmacy. This study used the Simplified Nutritional Appetite Questionnaire for Japanese Elderly (SNAQ-JE) to evaluate patients’ appetite, and examined its association with medications. This cross-sectional study included 233 patients (aged ≥65 years) who underwent HD in October 2021. Among the 233 patients (median age, 73.0 [interquartile range (IQR), 69.0–80.5] years; men, 57.3%; median dialysis vintage, 62.0 [IQR, 30.0–122.0] months), 116 and 117 were classified into the poor (SNAQ-JE total score ≤14) and good (>14) appetite groups, respectively. Although the total number of medications prescribed was not significantly different between the two groups (p = 0.12), the number of antihypertensive drugs was significantly lower (p = 0.03), and that of sleeping medications was significantly higher (p = 0.002) in the poor appetite group. Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the number of sleeping medications was associated with poor appetite (odds ratio, 2.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.32–3.27; p < 0.001). The findings suggest that the number of sleeping medications is an important contributing factor to poor appetite in older patients undergoing HD. A proper and regular review of prescriptions may be necessary to improve anorexia.
- 著者
- Rio Uno Kyoko Ohkawa Honami Kojima Tamami Haraguchi Minoru Ozeki Ikuo Kawasaki Miyako Yoshida Masaaki Habara Hidekazu Ikezaki Takahiro Uchida
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.2, pp.148-153, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This study aimed to evaluate the bitterness of famotidine (FAM) combined with each of three non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): ibuprofen (IBU), flurbiprofen (FLU), and naproxen (NAP), which have potential as fixed-dose combination (FDC) drugs. We evaluated the bitterness of FAM and each NSAID by taste sensor AN0 and C00, respectively. FAM showed high sensor output representing sensitivity to bitterness, whereas three NSAIDs did not show large sensor output, suggesting that the bitterness intensities of three NSAIDs were lower than that of FAM. The bitterness of FAM on sensor AN0 was suppressed in a concentration-dependent manner when mixed with IBU, FLU, or NAP. Among three NSAIDs, IBU most effectively inhibited bitterness on sensor output, and the gustatory sensation test confirmed that adding IBU to FAM reduced the bitterness of FAM in a concentration-dependent manner. MarvinSketch confirmed that the drugs were mostly present in an ionic solution when FAM was mixed with NSAIDs. The 1H-NMR spectroscopy analysis also revealed the presence of electrostatic interactions between FAM and NSAIDs, suggesting that the electrostatic interaction between FAM and NSAIDs might inhibit the adsorption of FAM on the bitter taste sensor membrane, thereby masking the bitter taste.
- 著者
- Tatsuo Akaki Shinya Nakamura Keiji Nishiwaki Isao Nakanishi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.c22-00866, (Released:2023-02-02)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The fragment molecular orbital (FMO) method is a fast quantum-mechanics method that divides systems into pieces of fragments and performs ab initio calculations. The method has been expected to improve the accuracy of describing protein-ligand interactions by incorporating electronic effects. In this article, FMO calculation with solvation methods were applied to the affinity prediction at the ATP-binding site of PDHK4. As the ionized aspartic acid lies at the center and is involved in the complex hydrogen bond networks, this system has turned out to be a difficult target to describe by traditional molecular-mechanics method. In the FMO calculation with the polarizable continuum model (PCM) solvation method, a considerable amount of charge (-0.27e) was transferred from the ionized aspartate to the surrounding residues. We found that using FMO with the PCM solvation method was important to increase the correlation, and by incorporating the ligand deformation energy, the correlation was improved to R = 0.81 for whole twelve compounds and R= 0.91 without one outlier compound.
- 著者
- Risako Morishita Miki Shimada Minami Nagao Shin Shimizu Noriyasu Kamei Mariko Takeda-Morishita
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.2, pp.343-347, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Owing to their unique physicochemical properties and diverse biological effects, ultrafine bubbles (UFBs) have recently been expected to be utilized for industrial and biological purposes. Thus, this study investigated the biological safety of UFBs in water for living beings in drinking the water with a view to future use in health sciences. In this study, we used H2-filled UFBs (NanoGAS®) that can hold hydrogen in the aqueous phase for a long time. Mice were randomly assigned to one of three groups: those receiving NanoGAS® water, reverse osmosis water, or natural mineral water, and they ingested it ad libitum for one month or three months. As a result, subchronic drinking of NanoGAS® water does not affect either the common blood biochemical parameters or the health of the organs and mucosal membranes. Our results, for the first time, scientifically demonstrated the biological safety of H2-filled UFBs water for subchronic oral consumption.