- 著者
- Miyuki Yuda Shin Aizawa Isao Tsuboi Yoko Hirabayashi Tomonori Harada Hirotsugu Hino Shuichi Hirai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.11, pp.1602-1608, 2022-11-01 (Released:2022-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in senescence-accelerated mice (SAMP1/TA-1), but not in senescence-resistant control mice (SAMR1). SAMP1/TA-1 treated with LPS exhibited functional impairment of the hematopoietic microenvironment, which disrupted the dynamics of hematopoiesis. Macrophages are a major component of the bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic microenvironment, which regulates hematopoiesis. Qualitative and quantitative changes in activated macrophages in LPS-treated SAMP1/TA-1 are thought to contribute to the functional deterioration of the hematopoietic microenvironment. Thus, we examined the polarization of pro-inflammatory (M1) and anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophages, and the dynamics of macrophage production in the BM of SAMP1/TA-1 and SAMR1 after LPS treatment. After LPS treatment, the proportions of M1 and M2 macrophages and the numbers of macrophage progenitor (CFU-M) cells increased in both SAMP1/TA-1 and SAMR1. However, compared to the SAMR1, the increase in the M1 macrophage proportion was prolonged, and the increase in the M2 macrophage proportion was delayed. The increase in the number of CFU-M cells was prolonged in SAMP1/TA-1 after LPS treatment. In addition, the levels of transcripts encoding an M1 macrophage-inducing cytokine (interferon-γ) and macrophage colony-stimulating factor were markedly increased, and the increases in the levels of transcripts encoding M2 macrophage-inducing cytokines (interleukin (IL)-4, IL-10, and IL-13) were delayed in SAMP1/TA-1 when compared to SAMR1. Our results suggest that LPS treatment led to the severely imbalanced polarization of activated M1/M2 macrophages accompanied by a prolonged increase in macrophage production in the BM of SAMP1/TA-1, which led to the impairment of the hematopoietic microenvironment, and disrupted the dynamics of hematopoiesis.
1 0 0 0 OA Feasibility Study of Dendrimer-Based TTR-CRISPR pDNA Polyplex for Ocular Amyloidosis in Vitro
- 著者
- Masamichi Inoue Kyosuke Muta Ahmed Fouad Abdelwahab Mohammed Risako Onodera Taishi Higashi Kenta Ouchi Mitsuharu Ueda Yukio Ando Hidetoshi Arima Hirofumi Jono Keiichi Motoyama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.11, pp.1660-1668, 2022-11-01 (Released:2022-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Hereditary amyloidgenic transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis is caused by a genetic point-mutated transthyretin such as TTR Val30Met (TTR V30M), since it forms protein aggregates called amyloid resulting in the tissue accumulation and functional disorders. In particular, ATTR produced by retinal pigment epithelial cells often causes ATTR ocular amyloidosis, which elicits deterioration of ocular function and ultimately blindness. Therefore, development of novel therapeutic agents is urgently needed. Genome-editing technology using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR associated proteins (CRISPR-Cas9) system is expected to be a therapeutic approach to treat genetic diseases, such as ATTR amyloidosis caused by a point mutation in TTR gene. Previously, we reported that glucuronylglucosyl-β-cyclodextrin conjugated with a polyamidoamine dendrimer (CDE) had excellent gene transfer ability and that underlying dendrimer inhibited TTR aggregation. Conversely, folate receptors are known to be highly expressed in retina; thus, folate has potential as a retinal target ligand. In this study, we prepared a novel folate-modified CDE (FP-CDE) and investigated its potential as a carrier for the retinal delivery of TTR-CRISPR plasmid DNA (pDNA). The results suggested that FP-CDE/TTR-CRISPR pDNA could be taken up by retinal pigment epithelial cells via folate receptors, exhibited TTR V30M amyloid inhibitory effect, and suppressed TTR production via the genome editing effect (knockout of TTR gene). Thus, FP-CDE may be useful as a novel therapeutic TTR-CRISPR pDNA carrier in the treatment of ATTR ocular amyloidosis.
- 著者
- 山尾 忠直 中上 博秋 古濱 和久 小野寺 威 黒崎 勇二 中山 太二 木村 聰城郎
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.5, pp.691-695, 1994-05-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 6 6
The pharmacokinetics of tolbutamide (TB) following intravenous and oral administration was compared between normal rats and rats with experimentally-induced obstructive jaundice (OJ). The plasma concentration-time curve of i.v. administered TB was lower in rats with OJ, in comparison with normal rats. The result of the pharmacokinetic analysis showed no change in the elimination rate constant, but a significant increase in the volume of distribution in the OJ state. The increase in the volume of distribution of TB could be explained by the decreased protein binding in plasma. In the case of oral administration, the elevation of the plasma concentration was slow and the plasma concentration profile was remarkably low in rats with OJ. The rate of TB disappearance from the small-intestinal lumen was delayed in the OJ state, and its marked accumulation in the tissues of the small intestine and the liver was observed. This retarded uptake by the small-intestinal mucosa and subsequent pre-systemic accumulation might, at least in part, be the reason for the slow appearance in the systemic plasma in the OJ state.
- 著者
- 鈴木 久美子 藤本 治宏 山崎 幹夫
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.6, pp.2176-2178, 1983-06-25 (Released:2008-03-31)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 10 17
Fasciculol E and F were identified as the toxic principles of Naematoloma fasciculare (Nigakuritake), a poisonous mushroom. These compounds caused paralysis and death in mice. The LD50 values of fasciculol E and F to mice were determined as 50 mg/kg and 168 mg/kg (i. p.), respectively.
- 著者
- Ayako Tamaki Hidetoshi Hayashi Hironori Nakajima Takemasa Takii Daichi Katagiri Keiji Miyazawa Kunitaka Hirose Kikuo Onozaki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.3, pp.407-410, 2004 (Released:2004-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 45 51
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by proliferation of synoviocytes that produce proinflammatory cytokines, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of the disease. Among the cytokines, IL-1 is the critical mediator of the disease. When human fibroblast-like synoviocytes line, MH7A, was treated with 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC), a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), mRNA of IL-1β was up-regulated. MH7A cells express functional aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) as shown by 3-MC-inducible CYP1A1 mRNA expression. The effect of 3-MC was inhibited by α-napthoflavone, an AhR antagonist, indicating that the effect of 3-MC is mediated via AhR. Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) also up-regulated mRNA level of IL-1β in the cells via AhR. As PAHs are much contained in cigarette smoke, these findings provide the possible basis for epidemiological studies indicating a strong association between heavy cigarette smoking and outcome of RA.
- 著者
- Takashi Ito Yuuki Hanahata Keita Kine Shigeru Murakami Stephen W. Schaffer
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.10, pp.1561-1566, 2018-10-01 (Released:2018-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 9 12
Dietary taurine deficiency results in dilated cardiomyopathy in cats while in mice taurine deficiency produced by knocking out the taurine transporter (TauT) gene leads to a reduction in cardiac function with advancing age. The present study elucidated the involvement of cardiac fibrosis in the aging-dependent cardiac disorder of the TauT-knockout (TauTKO) mouse. Old (18–24-month-old) TauTKO mice, but not young (3–5-month-old) mice, exhibit cardiac fibrosis. Transcriptome microarray analysis revealed an increase in pro-fibrotic genes, such as S100A4, ACTA2 and CTGF, in both young and old TauTKO hearts. Based on transcriptome-pathway analysis the genes involved in “organization of extracellular matrix,” such as LGALS3, are enriched in old TauTKO hearts compared to old wild-type hearts, suggesting the contribution of these genes to fibrosis. In conclusion, taurine depletion predisposes the heart to fibrosis, which leads to cardiac fibrosis upon aging.
- 著者
- Ryota Araki Shoji Nishida Yosuke Hiraki Feng Li Kinzo Matsumoto Takeshi Yabe
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.289-294, 2016-02-01 (Released:2016-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 6 10
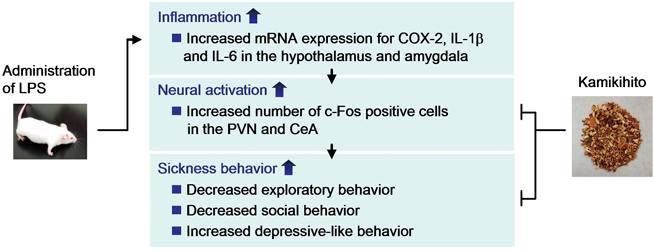
Sickness behavior is a series of behavioral and psychological changes that develop in those stricken with cancers and inflammatory diseases. The etiological mechanism of sickness behavior is not known in detail, and consequently there are no established standard therapies. Kamikihito (KKT), a Kampo (traditional Japanese herbal) medicine composed of 14 herbs, has been used clinically to treat psychiatric dysfunction. Previously, we found that KKT ameliorated sickness behavior in mice inoculated with murine colon 26 adenocarcinoma cells. In this study, we examined the effects of KKT on bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sickness behavior in mice. The administration of LPS caused the emotional aspects of sickness behavior, such as loss of object exploration, social interaction deficit, and depressive-like behavior. LPS also induced mRNA expression for cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, and increased the number of c-Fos immunopositive cells in the hypothalamus and amygdala. KKT ameliorated the behavioral changes and reversed the increases in c-Fos immunopositive cells in the two brain regions, but did not influence the mRNA expression. These results suggest that KKT ameliorates sickness behavior via the suppression of neural activation without anti-inflammatory effects, and that KKT has the potential to treat sickness behavior.
- 著者
- Takuya Murai Shohei Hamada Yusuke Kobayashi Takahiro Sasamori Takumi Furuta
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.9, pp.605-615, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The preparation, optical resolution, and structural investigations of a series of axially chiral biaryl dicarboxylic acids bearing oxygen, sulfur, and selenium atoms were carried out. The crystal structures of sulfur- and selenium-containing derivatives revealed that the carboxy groups of these compounds are located in a co-planar geometry with the fused aromatic rings including the chalcogen atoms. These conformational controls were found to be achieved by chalcogen-bonding interactions between chalcogen atoms in the aromatic rings and oxygen atoms in the carboxy groups. Even in the case of a binaphthofuran derivative, in which the formation of chalcogen-bonding interactions was expected to be negligible, the carboxy groups were also found to be located in a co-planar geometry toward its fused cyclic rings. Natural bond orbital (NBO) analyses of these dicarboxylic acids indicated the formation not only for the chalcogen-bonding interactions for S and Se derivatives, but also the tetrel-bonding interactions between the oxygen atoms in the carboxy groups and the carbon atoms in the fused cyclic rings for all biaryl dicarboxylic acids. These tetrel-bonding interactions were thought to contribute to conformational control in the binaphthofuran derivative. Physical and chiroptical properties such as the racemization barriers and circular dichroism (CD) spectra of these biaryl dicarboxylic acids were also revealed.
- 著者
- Nobutomo Ikarashi Naoki Ogiue Eri Toyoda Marina Nakamura Risako Kon Yoshiki Kusunoki Takashi Aburada Makoto Ishii Yoshikazu Tanaka Yoshiaki Machida Wataru Ochiai Kiyoshi Sugiyama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.10, pp.1615-1621, 2013-10-01 (Released:2013-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 12 14
Aquaporin-3 (AQP3) plays an important role in maintaining the normal water content of the skin. Previously, we revealed that the expression of cutaneous AQP3 increased following oral administration of Gypsum fibrosum (main component: CaSO4) to mice. The purpose of this study is to elucidate the mechanism by which Gypsum fibrosum increases the expression of cutaneous AQP3 in a keratinocyte cell line. Gypsum fibrosum or CaSO4 was added to keratinocytes, and the expression level of AQP3, the Ca concentration, the activity of protein kinase C (PKC), and the degrees of phosphorylation of both extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) were measured. The mRNA and protein expression levels of AQP3 increased significantly 6 h-post addition of Gypsum fibrosum. In keratinocytes treated with Gypsum fibrosum, increases in the concentration of intracellular Ca, PKC activity, and the phosphorylation of ERK and CREB were observed. Pre-treatment with GF109203X, a PKC inhibitor, suppressed the mRNA expression levels of AQP3. Similarly to treatment with Gypsum fibrosum, the addition of CaSO4 led to the same observations in keratinocytes. It is hypothesized that Gypsum fibrosum causes an increase in the intracellular Ca concentration, PKC activity, and the phosphorylation levels of ERK and CREB, resulting in increased AQP3 expression in keratinocytes. In addition, it is possible that the effect of Gypsum fibrosum is attributable to CaSO4, based on the results demonstrating that the mechanisms of action of Gypsum fibrosum and CaSO4 were nearly identical.
- 著者
- Noriko Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1213-1224, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 63
- 被引用文献数
- 3
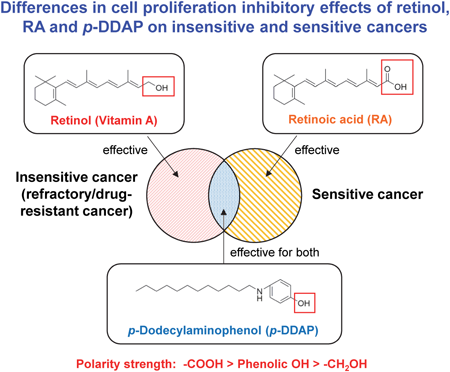
Vitamin A is an important trace essential nutrient. Vitamin A is present as a retinyl ester in animal foods and as β-carotene (provitamin A), which is a precursor of vitamin A, in plant foods such as green and yellow vegetables. After ingestion and absorption in the body, these are converted into retinol and stored as retinyl esters in stellate cells in the liver. The stored retinyl esters are decomposed into retinol as needed, and converted into the aldehyde retinal, which plays an important role in vision. Retinoic acid (RA) has a variety of effects. In particular, RA is used as a therapeutic agent for acute promyelocytic leukemia. This review will cover (1) elucidation of anti-refractory cancer effects of retinol (vitamin A) not mediated by RA receptors, (2) elucidation of anti-cancer effects of RA not mediated by RA receptors and (3) the development of candidate new anti-cancer agents that combine the actions of RA and retinol. Lessons learned from these findings are that vitamin A has anti-cancer activity not mediated by RA receptors; that nutritional management of vitamin A leads to prevention and treatment of cancer, and that new compounds developed from RA derivatives represent good anti-cancer drug candidates that are in various stages of clinical trials.
- 著者
- Kenji Momo Takeo Yasu Seiichiro Kuroda Sonoe Higashino Eiko Mitsugi Hiromasa Ishimaru Kazumi Goto Atsuko Eguchi Kuniyoshi Sato Masahiro Matsumoto Takashi Shiga Hideki Kobayashi Reisuke Seki Mikako Nakano Yoshiki Yashiro Takuya Nagata Hiroshi Yamazaki Shou Ishida Naoki Watanabe Mihoko Tagomori Noboru Sotoishi Daisuke Sato Kengo Kuroda Dai Harada Hitoshi Nagasawa Takashi Kawakubo Yuta Miyazawa Kyoko Aoyagi Sachiko Kanauchi Kiyoshi Okuyama Satoshi Kohsaka Kohtaro Ono Yoshiyasu Terayama Hiroshi Matsuzawa Mikio Shirota
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.10, pp.1489-1494, 2022-10-01 (Released:2022-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The aim of this study was to determine the proportion of near-miss dispensing errors in hospital pharmacies in Japan. A prospective multi-center observational study was conducted between December 2018 and March 2019. The primary objective was to determine the proportion of near-miss dispensing errors in hospital pharmacy departments. The secondary objective was to determine the predictive factors for near-miss dispensing errors using multiple logistic regression analysis. The study was approved by the ethical committee at The Institute of Medical Sciences, University of Tokyo, Japan. A multi-center prospective observational study was conducted in 20 hospitals comprising 8862 beds. Across the 20 hospitals, we assessed data from 553 pharmacists and 53039 prescriptions. A near-miss dispensing error proportion of 0.87% (n = 461) was observed in the study. We found predictive factors for dispensing errors in day-time shifts: a higher number of drugs in a prescription, higher number of quantified drugs, such as liquid or powder formula, in a prescription, and higher number of topical agents in a prescription; but we did not observe for career experience level for clinical pharmacists. For night-time and weekend shifts, we observed a negative correlation of near-miss dispensing errors with clinical pharmacist experience level. We found an overall incidence of near-miss dispensing errors of 0.87%. Predictive factors for errors in night-time and weekend shifts was inexperienced pharmacists. We recommended that pharmacy managers should consider education or improved work flow to avoid near-miss dispensing errors by younger pharmacists, especially those working night or weekend shifts.
- 著者
- Tomoko Yamaguchi Misae Nishijima Kenji Kawabata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.10, pp.1525-1530, 2022-10-01 (Released:2022-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) are essential component of the blood–brain barrier (BBB). BMECs strictly regulate the entry of various molecules into the central nervous system from the peripheral circulation by forming tight junctions and expressing various influx/efflux transporters and receptors. In vitro BBB models have been widely reported with primary BMECs isolated from animals, although it is known that the expression patterns and levels of transporters and receptors in BMECs differ between humans and animals. Recently, several methods to differentiate BMECs from human induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cell have been developed. However, the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which is a key efflux transporter, in hiPS cell-derived BMECs was detected at a relatively low level compared with primary human BMECs. In this study, we examined the involvement of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, which contributes to the development of BBB formation, in the regulation of P-gp expression in hiPS cell-derived BMECs. We found that the barrier integrity was significantly enhanced in hiPS cell-derived BMECs treated with glycogen synthase kinase-3ß (GSK-3ß) inhibitors, which are known to positively regulate the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. In addition, our data also showed P-gp expression level was increased by treatment with GSK-3ß inhibitors. In conclusion, physiological barrier function and P-gp expression in BMECs can be enhanced by the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Our results may be useful for promoting the development of drugs for central nervous system diseases using in vitro BBB model.
- 著者
- Kouya Yamaki Kiyoe Ohta Norihiro Kobayashi Izumi Morita Yuki Kiguchi Hiroyuki Oyama Ken Ito Asuka Nanbo Hirozo Oh-oka Yutaka Koyama Yoshiki Kawata Hirotaka Fujisawa Mitsuhiro Ohta
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.8, pp.1022-1026, 2022-08-01 (Released:2022-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
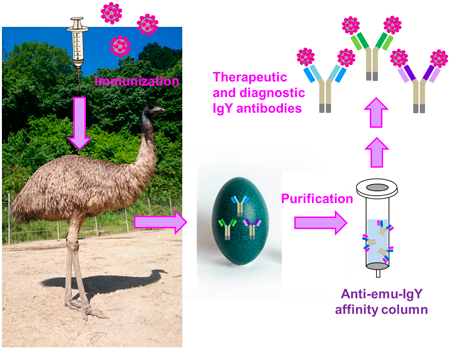
The emu is the second largest ratite; thus, their sera and egg yolks, obtained after immunization, could provide therapeutic and diagnostically important immunoglobulins with improved production efficiency. Reliable purification tools are required to establish a pipeline for supplying practical emu-derived antibodies, the majority of which belongs to the immunoglobulin Y (IgY) class. Therefore, we generated a monoclonal secondary antibody specific to emu IgY. Initially, we immunized an emu with bovine serum albumin multiply haptenized with 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) groups. Polyclonal emu anti-DNP antibodies were partially purified using conventional precipitation method and used as antigen for immunizing a BALB/c mouse. Splenocytes were fused with myeloma cells and a hybridoma clone secreting a desirable secondary antibody (mAb#2-16) was established. The secondary antibody bound specifically to emu-derived IgY, distinguishing IgYs from chicken, duck, ostrich, quail, and turkey, as well as human IgGs. Affinity columns immobilizing the mAb#2-16 antibodies enabled purification of emu IgY fractions from sera and egg yolks via simple protocols, with which we succeeded in producing IgYs specific to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein with a practical binding ability. We expect that the presented purification method, and the secondary antibody produced in this study, will facilitate the utilization of emus as a novel source of therapeutic and diagnostic antibodies.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Inazumi Yukihiko Sugimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.8, pp.992-997, 2022-08-01 (Released:2022-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 63
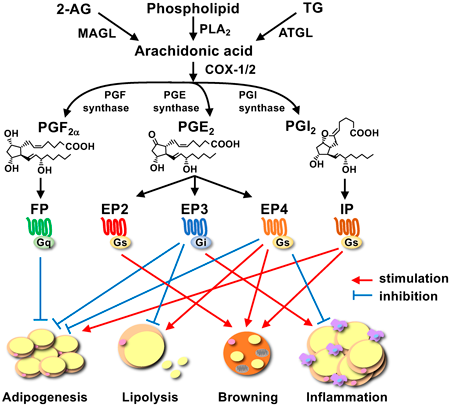
Prostanoids are a group of typical lipid mediators that are biosynthesized from arachidonic acid by the actions of cyclooxygenases and their subsequent terminal synthases. Prostanoids exert a wide variety of actions through their specific membrane receptors on target cells. In addition to their classical actions, including fever, pain, and inflammation, prostanoids have been shown to play pivotal roles in various biological processes, such as female reproduction and the maintenance of vascular and gut homeostasis. Moreover, recent research using mice deficient in each of the prostanoid receptors, or using agonists/antagonists specific for each receptor clarified novel actions of prostanoids that had long been unknown, and the mechanisms therein. In this review, we introduce recent advances in the fields of metabolic control by prostanoid receptors such as in adipocyte differentiation, lipolysis, and adipocyte browning in adipose tissues, and discuss the potential of prostanoid receptors as a treatment target for metabolic disorders.
- 著者
- Yu Sakurai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.8, pp.972-977, 2022-08-01 (Released:2022-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 2
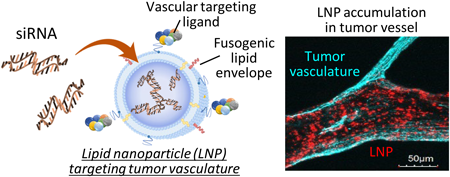
Nucleic acid drugs can control gene expression and function in a manner different from that of conventional compounds. On the other hand, nucleic acids can be easily degraded in the in vivo circumstances. In addition, nucleic acids cannot penetrate cell membranes. Therefore, a drug delivery system (DDS) is essential to protect nucleic acid molecules until they reach the target cell and to release them efficiently inside the cell. In order to apply nucleic acid drugs to new cancer therapeutic strategies, the author has been developing a DDS that enables functional control of vascular endothelial cells that consist of the tumor microenvironment. The aim of my study is to develop lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) were modified with functional molecules that control their pharmacokinetics in vivo and intracellular fate to delivered small interfering RNA (siRNA) to tumor vasculature. By imparting pH-responsive membrane fusion properties to lipid nanoparticles, I have developed a system that responds to acidification in endosomes within cells and subsequently efficiently releases siRNA into the cytoplasm via membrane fusion, where siRNA molecules exhibit their function. In addition, by developing a method for presenting functional molecules, such as peptides, saccharides and so on, that recognize target cells on the surface of LNPs, I succeeded in establishing LNPs which internalize more efficiently into specific cells than off-target cells. Finally, by integrating these technologies, I developed an in vivo siRNA DDS that enables in vivo control of genes of interest in tumor vascular endothelial cells and succeeded in cancer therapy by regulating vascular function.
- 著者
- Takahiko Aoyama Toshinori Hirai Yasuhiro Tsuji Aoi Miyamoto Toshimasa Itoh Takuya Iwamoto Yoshiaki Matsumoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.1, pp.136-142, 2022-01-01 (Released:2022-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Warfarin is a representative anticoagulant with large interindividual variability. The published kinetic-pharmacodynamic (K-PD) model allows the prediction of warfarin dose requirement in Swedish patients; however, its applicability in Japanese patients is not known. We evaluated the model’s predictive performance in Japanese patients with various backgrounds and relationships using Bayesian parameter estimation and sampling times. A single-center retrospective observational study was conducted at Tokyo Women’s Medical University, Medical Center East. The study population consisted of adult patients aged >20 years who commenced warfarin with a prothrombin time-international normalized ratio (PT-INR) from June 2015 to June 2019. The published K-PD model modified by Wright and Duffull was assessed using prediction-corrected visual predictive checks, focusing on clinical characteristics, including age, renal function, and individual prediction error. The external dataset included 232 patients who received an initial warfarin daily dose of 3.2 ± 1.28 mg with 2278 PT-INR points (median [range] follow-up period of 23 d [7–28]). Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks carried a propensity for underprediction. Additionally, age >60 years, body mass index ≤25 kg/m2, and estimated glomerular filtration rate ≤60 mL/min/1.73 m2 had a pronounced tendency to underpredict PT-INR. However, Bayesian prediction using four prior observations reduced underprediction. To improve the prediction performance of these special populations, further studies are required to construct a model to predict warfarin dose requirements in Japanese patients.
- 著者
- Michihisa Tohda Hiroshi Watanabe
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.11, pp.1627-1631, 2018-11-01 (Released:2018-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 3 5
This review article mentions about the following points, and proposes its importance and positive thinking. 1) Wakan-yaku (Japanese oriental medicines) is covered by the national health insurance system in Japan as therapeutic drugs to be actively used in medical practice to treat illness. 2) Applications of Wakan-yaku is accomplished based on the reliable own theories which are established with long histories. 3) Promotion of studies based on these theories will be highly expected to find novel view points which breaks conventional concepts and to novel standards for developing new medicinal drugs. Although studies based on the reliable Wakan-yaku theories are not advancing satisfactorily till now, the possibilities to obtain the advanced resources for drugs and novel viewpoints for experiments by studies about Wakan-yaku theories are discussed in this review.
- 著者
- 三村 務 前田 和宏 辻坊 裕 佐竹 幹雄 藤田 孝夫
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.4, pp.1508-1512, 1982-04-25 (Released:2008-03-31)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 5 5
Octopus melanin obtained from ink bags of Octopus vulgaris CUVIER was found to inhibit gastric secretion in rats in the same way as that from Ommastrephes bartrami LESUEL. The molecular weight of this melanin fraction (which has an indole skeleton) was estimated to be over 200000 by gel filtration on Sephadex G-200, and the Octopus melanin fraction (Fr. OM) released several kinds of proteins in the presence of SDS. The chemical composition of Fr. OM was melanin pigment 79%, protein 17.5% and sugar 1.7%, so Fr. OM was considered to be a melanoprotein. Fr. OM significantly reduced gastric secretion in rats at the dose of 1 mg/kg, i.p., and also prevented both ulcer formation in pylorusligated rats and aspirin-induced ulcer.
- 著者
- Wei Zhe Naomi Hoshina Yukihiro Itoh Toshifumi Tojo Takayoshi Suzuki Koji Hase Daisuke Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1364-1372, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1
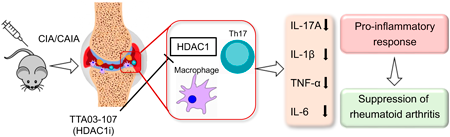
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is systemic autoimmune arthritis that causes joint inflammation and destruction. Accumulating evidence has shown that inhibitors of class I histone deacetylases (HDACs) (i.e., HDAC1, 2, 3, and 8) are potential therapeutic candidates as targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs). Nevertheless, the inhibition of class I HDACs has severe adverse effects because of their broad spectrum. We evaluated the therapeutic effect of a novel selective HDAC1 inhibitor TTA03-107 for collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) models in mice. We also examined the effect of TTA03-107 in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells in vitro. Here, we delineate that TTA03-107 reduced the severity of autoimmune arthritis without obvious adverse effects in CIA and CAIA models. Moreover, TTA03-107 suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-17A, in serum and joint tissue. In vitro treatment of BMDMs with TTA03-107 dampened the M1 differentiation and inflammatory cytokine production. TTA03-107 also suppressed the differentiation of Th17 cells. These results demonstrate that TTA03-107 can attenuate the development of arthritis in experimental RA models by inhibiting the differentiation and activation of macrophages and Th17 cells. Therefore, TTA03-107 is a potential tsDMARD candidate.
- 著者
- Taisuke Konno Hiroyuki Suzuki Hitoshi Nakamura Yuriko Murai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1225-1231, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
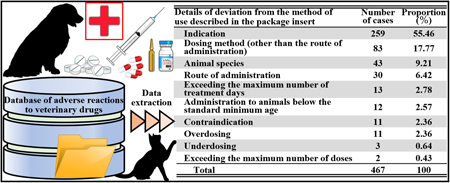
In veterinary medicine, various drugs are used on a daily basis. Using inappropriate medications poses health hazards to companion animals and humans; thus, assessing adverse events in veterinary medicine has great social significance but remains an untapped area of research. In this study, to promote the appropriate use of veterinary drugs and clarify common pharmaceutical issues in Japanese veterinary medicine, we analyzed information in the Veterinary Drug Side Effects Database (National Veterinary Assay Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan). We found that the number of reports has been increasing annually, including those on high-risk drugs, molecular-targeted drugs, and antibody-based drugs. The details of the reports were similar to those from the United States, including the misadministration of veterinary drugs to humans, improper drug management, and re-administering drugs with a history of side effects. Furthermore, 46.50% of all reports mentioned the administration of one or more drugs, with the highest number of concomitant drugs being 10. In addition, 37.78% of all reports described the use of drugs in manners deviating from the intended use indicated in the package insert. Therefore, to avoid adverse events, pharmacists may have to be involved in dispensing and aseptically preparing veterinary medicines and providing drug information and medication guidance. To optimize pharmacotherapy for ill companion animals, “veterinary pharmacy” and “veterinary medicine pharmacy” must be developed in line with clinical situations in Japan, while considering knowledge from countries that are advanced in terms of veterinary medicine.