1 0 0 0 OA 物体表面電荷の測定
- 著者
- 村田 雄司
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.2, pp.98-103, 1987-06-20 (Released:2011-06-28)
- 参考文献数
- 4
1 0 0 0 エアロゾルと飛沫感染・空気感染
- 著者
- 竹川 暢之
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1, pp.65-74, 2021
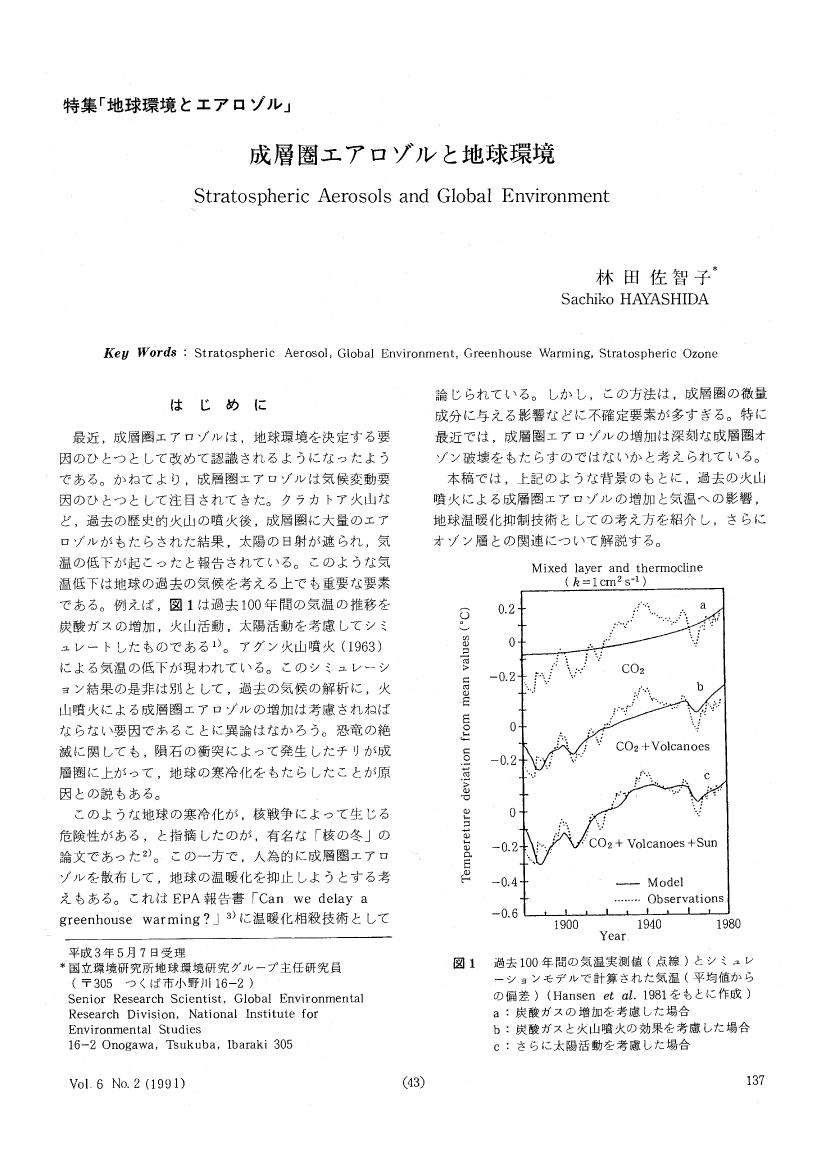
1 0 0 0 OA 成層圏エアロゾルと地球環境
- 著者
- 林田 佐智子
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, no.2, pp.137-142, 1991-06-20 (Released:2011-06-09)
- 参考文献数
- 27
1 0 0 0 OA 月面ダストの生体影響
- 著者
- 森本 泰夫 三木 猛生 東 敏昭 明星 敏彦 田中 一成 向井 千秋
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.2, pp.129-134, 2009-06-20 (Released:2009-06-24)
- 参考文献数
- 22
We reviewed the effect of lunar dust (regolith) on humans from technological and biological point of views. In physicochemical properties of lunar dust, hazard-related factors are that silicon occupies about 50 % in composition, and that fibrous materials and nanoparticles are included. Animal exposure studies have been performed using a simulant of lunar dust, and it was speculated that the harmful effect of simulant lies between crystalline silica (positive control) and titanium dioxide (negative control). Fibrous materials may not have low solubility judging from the component. The nanoparticle in lunar dusts may have harmful potentials by the components. In microgravity, the deposition of particles with less than 1 μm in human lung did not decreased, but the deposition of particles with diameter of several μm decreased linearly with reducing the gravity. In microgravity the functions of macrophage including phagocytosis were suppressed. These data on the deposition of particles and the function of macrophage suggested that fine and ultrafine particles may be accumulated in the lung in microgravity. The researches on lunar dust and microgravity are preliminary and very much limited, therefore it is necessary to perform lots of researches in this field.
1 0 0 0 OA 論文特集にあたって
- 著者
- 足立 元明
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, no.2, pp.78, 2008-06-20 (Released:2008-06-25)
1 0 0 0 OA 能動型測器「ライダー」を用いたエアロゾルの観測研究
- 著者
- 西澤 智明 杉本 伸夫
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.4, pp.242-249, 2009-12-20 (Released:2009-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Vertical distributions of aerosol optical properties derived from lidar measurements are essential information for evaluating climate change. The recent development of lidar, communication, and computer technologies has enabled us to conduct ground-based network observations and satellite borne, ship borne, and airborne measurements with multichannel lidar. These lidar observations and related data analyses have provided detailed aerosol information. This paper reports the current status of aerosol observations conducted with lidars by the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES) and those performed around the world. Several up-to-date developed algorithms that estimate aerosol optical and microphysical properties using multichannel lidar data are also reported. NIES future strategies for lidar observation and aerosol retrieval algorithms are also presented based on the current status.
1 0 0 0 OA 室内空気汚染とエアロゾル
- 著者
- 呂 俊民
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.7, no.4, pp.309-311, 1992-12-20 (Released:2011-06-09)
- 参考文献数
- 7
1 0 0 0 OA オフィスにおけるエアロゾル
1 0 0 0 OA 風成塵から眺めた古気候研究
- 著者
- 長島 佳菜 豊田 新
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.3, pp.284-291, 2012 (Released:2013-01-18)
- 参考文献数
- 42
The eolian dust in the sediments of North Pacific and marginal seas of the northwestern Pacific has potential to record past climate changes. For example, the variability of eolian dust flux estimated from North Pacific sediments have been interpreted as recording past aridity changes of the eolian source region of the East Asia. However, recent observations revealed large effects of the wind-systems on the amount of dust transported to the North Pacific and marginal seas. Therefore, it is important to consider both effects of the wind-systems and aridity changes when we interpret eolian dust parameters. Recently, we estimated provenance of eolian dust in Japan Sea sediments and reconstructed its variations during the last glacial period based on a newly developed provenance-tracing method, a combination of electron spin resonance intensity and the crystallinity of quartz. The result revealed millennial-scale provenance changes in accordance with so-called Dansgaard-Oeschger (D-O) events, with dominance of quartz from the Mongolian Gobi during cold intervals of D-O events, whereas dominance of quartz from the Taklimakan Desert during warm intervals of D-O events. These provenance variations seem to mainly represent latitudinal displacement of the subtropical jet path in harmony with D-O events.
1 0 0 0 電子顕微鏡による微粒子の測定
- 著者
- 飯島 澄男
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.3, pp.168-174, 1989
1 0 0 0 OA 大気中の硫酸塩、硝酸塩粒子の挙動
- 著者
- 大喜多 敏一
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.2, pp.90-98, 1986-06-20 (Released:2011-06-28)
- 参考文献数
- 37
1 0 0 0 OA 噴霧液滴のPDA計測
1 0 0 0 OA 病院における室内空気と微生物汚染
1 0 0 0 OA エアロゾルを用いた微粒子の静電捕集
- 著者
- 中島 耀二
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.2, pp.92-97, 2003-06-20 (Released:2007-10-16)
- 参考文献数
- 16
1 0 0 0 OA 船舶排ガス用電気集塵装置の研究開発
- 著者
- 瑞慶覧 章朝 乾 貴誌
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.2, pp.85-92, 2015-06-20 (Released:2015-06-27)
- 参考文献数
- 22
Abstract Exhaust gases emitted from ships were regulated in MARPOL Treaty 73/78 Annex VI of IMO for air pollution control. In this paper, results of a fundamental development for an electrostatic precipitation (ESP) and a demonstration test for cleaning exhaust gases were described. In fundamental research, the characteristics of ESP with a heat exchanger were explained. It was described that ESP without a heat exchanger was able to remove dry soot and nano-particles, which were included with exhaust gas, in high efficiency. It was also indicated that particulate matters were generated due to condensation of gaseous soluble organic fraction and sulphate in the case of gas cooled by a heat exchanger, whereby these were also removed by ESP. In demonstration test, it was confirmed that high removal efficiency for 24 hours in ESP pilot plant was possible.
1 0 0 0 OA ラジカル捕獲剤を用いたα-ピネン由来二次有機エアロゾル雰囲気下の活性種の捕獲と分析
- 著者
- 斎藤 弘樹 木浪 由菜 川畑 未夢 大原 伊織 藤谷 雄二 五東 弘昭 榊原 和久
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.4, pp.278-286, 2016-12-20 (Released:2017-01-06)
- 参考文献数
- 24
In order to clarify the mechanism to induce biologically hazardous phenomena in the environment by the reaction of the Secondary Organic Aerosol (SOA) and to identify reactive species in SOA atmosphere (particles and gaseous constituents are coexisting), experiments of capturing reactive species in the gas chamber where SOAs were generated via the reaction of ambient air containing α-pinene with ozone have been carried out by taking advantage of radical scavenging reagents. The obtained adducts in SOA atmosphere were analyzed by ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) and LC/MS (Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry). ESR signal intensities of the radical scavenging samples exposed by SOA atmosphere were smaller than those of the control sample due to the formation of diamagnetic adducts. And new peculiar peaks (α-pinene radical adducts produced by the trapping reactions with radical scavenging reagents) were detected by LC/MS. Thus, it is plausible that reactive species in ambient air can be identified surely from analytical approach of the adducts formed with radical scavenging reagents.
1 0 0 0 OA シリカの物理化学的性質と作業環境測定方法
1 0 0 0 OA 自然放射能からみた東アジアにおけるレスと風成塵起源土壌の特徴
- 著者
- 古川 雅英 赤田 尚史 卓 維海 郭 秋菊 楢崎 幸範 床次 眞司
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.4, pp.306-312, 2005 (Released:2007-01-12)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 2
In order to investigate the characteristics on natural radioactivity of loess, desert sand and eolian dust origin soil distributed in East Asia, analyses for 238U, 232Th and 40K concentrations by ICP-MS and ICP-AES, and for major chemical composition, SiO2, Al2O3, K2O, etc., by XRF have been performed on 48 samples collected from the wide area of China and three prefectures of Japan. The results for loess samples indicated that the concentrations of natural radioactive elements and major chemical composition are almost homogeneous over Chinese Loess Plateau. Also the results suggested that the basic material of the red soils developed on Quaternary limestone in Okinawa prefecture, southwestern part of Japan, is not weathering residual from the base rock, but the eolian dust from the high background radiation area in the southeastern part of China. These observations could give important keys to understand the origin place of the eolian dust in East Asia during the Quaternary.
1 0 0 0 ニューカレドニアにおけるエアロゾル中ニッケルおよび元素組成の特徴
- 著者
- 奥田 知明 榎本 太吉
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.1, pp.29-34, 2019-03-20 (Released:2019-04-09)
- 参考文献数
- 19
Characteristics of the elemental composition were investigated for PM10 samples at four sites in Noumea, New Caledonia, where health effects due to nickel production activities such as mining and refining were concerned. The concentration of nickel in the aerosol sample collected in New Caledonia was approximately the same level in Japan while those of other elements were lower in comparing to Japan. Enrichment factor of nickel in aerosol in New Caledonia was approximately 250 which was about 20 times greater than that in Japan. The reasons for this were thought to be (1) influence of soil particles that have relatively higher nickel content from surrounding sampling site, and (2) influence of emission from nickel smelter near the sampling site; however, there was no clear evidence to prove them. Alternatively, the nickel-enriched particles, which were generated as a result of nickel production activities such as a refinement of laterite-nickel ore, could be contributed as a potential source of the aerosol in this area.
1 0 0 0 OA 黄砂とアレルギー疾患
- 著者
- 東 朋美 神林 康弘 藤村 政樹 大倉 徳幸 吉崎 智一 中西 清香 西條 清史 早川 和一 小林 史尚 道上 義正 人見 嘉哲 中村 裕之
- 出版者
- 日本エアロゾル学会
- 雑誌
- エアロゾル研究 (ISSN:09122834)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.S1, pp.s212-s217, 2014-02-20 (Released:2014-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 33
The frequency and scale of Asian dust events have increased rapidly in East Asia since 2000. In connection with this, the effects of Asian dust (kosa) on human health, especially on allergic diseases, are major concern in Japan. We herein discuss the effects of kosa on allergic diseases, including asthma, chronic cough and Japanese cedar pollinosis. Epidemiological studies, as well as experimental studies, have demonstrated the association between kosa and the exacerbation of asthma and allergic diseases.The kosa particles increase airway inflammation as one of the major sources of atmospheric particulate matter. Furthermore the kosa particles absorb various atmospheric gases, including air pollution. Such environmental pollution enhances the response to allergens, including Japanese cedar pollen. Recently, some epidemiological studies used the kosa data obtained by the light detection and ranging (LIDAR) system, which distinguish between mineral dust and other spherical particles, by identifying differences in the shape of the particles. Further studies using the LIDAR system will help to identify the kosa aerosol components that have adverse health effects, leading to provide new strategies to prevent environmentally induced allergic diseases.