1 0 0 0 OA 心停止患者に対する救命処置 ~心停止後症候群の転帰改善に関わる因子の検討~
- 著者
- 木下 浩作
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.73, no.1, pp.41-44, 2014-02-01 (Released:2015-05-22)
- 参考文献数
- 9
1 0 0 0 OA 慢性心不全に対する心臓リハビリテーション
- 著者
- 関野 久邦
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.4, pp.231-234, 2020-08-01 (Released:2020-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 14
I report the effects of and a program and instructions for cardiac rehabilitation and the current status of cardiac rehabilitation for heart failure at our hospital.
1 0 0 0 OA 離脱期に心筋症を発症したリチウム中毒症の 1 例
- 著者
- 新保 暁
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.6, pp.351-355, 2008-12-01 (Released:2011-11-28)
- 参考文献数
- 16
症例は 81 歳女性.炭酸リチウム (600 mg/日) を約 3 年間内服していたが,下痢,食思不振,悪心,嘔吐に続いて無言・無動となり入院となった.臨床症状および血中リチウム濃度高値 (2.02 mEq/L) から,本例を慢性リチウム中毒症と診断し,治療を開始した.入院第 6 日目に 38°C 台の発熱および胸部苦悶が出現し,翌日には心電図上著明な広範囲陰性T波の出現を認めた.リチウム中毒症離脱過程の心筋症および心不全の出現と考えられた.
1 0 0 0 OA 微小な毛は生命と進化の立役者
- 著者
- 野田 直紀
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.2, pp.117-118, 2022-04-01 (Released:2022-06-09)
- 参考文献数
- 7
1 0 0 0 OA 死亡診断書の除外規定について
- 著者
- 内ヶ崎 西作
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.1, pp.44-45, 2015-02-01 (Released:2021-01-21)
- 参考文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 宇宙医学
- 著者
- 岩崎 賢一
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.1, pp.60-63, 2008-10-25 (Released:2009-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 著者
- 長野 伸彦
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.4, pp.237-241, 2022-08-01 (Released:2022-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 33
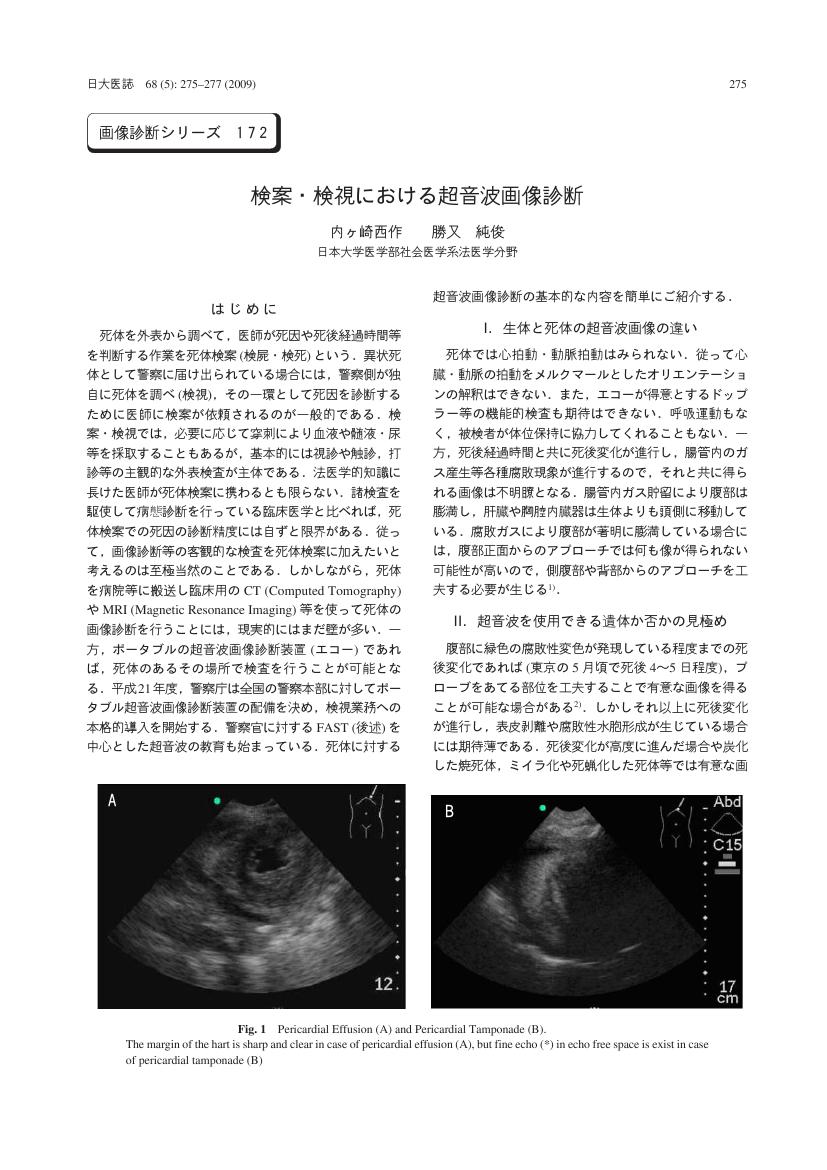
1 0 0 0 OA 検案・検視における超音波画像診断
- 著者
- 植田 雄一 牧野 裕子 西田 卓弘 落合 昂一郎 丸塚 浩助 盛口 清香 大友 直樹
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.3, pp.155-159, 2022-06-01 (Released:2022-08-11)
- 参考文献数
- 8
42 歳の女性.HER2 陰性転移性乳癌に対する標準治療 が終了後,遺伝子パネル検査 FoundationOne®CDx を施行 した.ERBB2 遺伝子の増幅を認めた.また,生検検体 での HER2 IHC 法で 2+ であったため,FISH 法を施行し たところ陽性であった.抗 HER2 療法を開始したところ, 部分奏功を認めた.既存の HER2 テストでは抗 HER2 療 法の適応とならなかった症例でも,遺伝子パネル検査を 行うことで,抗 HER2 剤の適応となる症例を拾い上げる ことが可能であり,一部の乳癌患者の予後を大きく変え る可能性がある.
1 0 0 0 「睡眠障害をめぐって」不眠症と過眠症
- 著者
- 内山 真
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.1, pp.11-16, 2010
Epidemiologic studies have clearly shown that sleep problems are common in the general population. A survey, conducted in Japan, reported that 21.4% of adults had complaints of insomnia and that 14.9% complained of hypersomnia (excessive daytime sleepiness). In the primary care setting, however, few patients present with overt sleep complaints but rather generally present with symptoms of fatigue, excessive sleepiness, and impaired waking. Therefore, it is important for physicians to understand how to differentiate and manage the sleep complaints of the patient. Herein, the author reviewed the clinical management of insomnia and hypersomnia, together with recent pathophysiological findings on these disorders. Insomnia is currently defined as an inability to obtain an adequate amount of sleep, to feel restored and refreshed in the morning, and to function adequately in the daytime. The differential diagnosis of difficulty in sleeping includes psychophysiological, neurological and circadian causes. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions are combined in the treatment of insomnia. Sleep deprivation is the most frequent cause of excessive daytime sleepiness. Narcolepsy is the most prevalent type of hypersomnia with sleep attack and cataplexy. Recent studies have indicated the pathogenetic importance of orexin/hypocretin (a peptide hormone produced in the lateral hypothalamus) dysfunction in narcolepsy.
1 0 0 0 OA 軽度低体温循環停止,急速冷却復温による脳保護効果に関する実験的検討
- 著者
- 猪野 崇 秦 光賢 本間 琢 中田 金一 谷口 由樹 折目 由紀彦 秋山 謙次 三俣 昌子 塩野 元美
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.72, no.6, pp.312-319, 2013-12-01 (Released:2014-12-30)
- 参考文献数
- 28
目的: 今回我々は大動脈外科における新しい 脳保護法及び体外循環法として軽度低体温循環停止・急速冷却復温法を考案した.従来法は,20°C の超低体温とし,復温も緩徐に行うことが一般的であった.我々は 28°C の軽度低体温・循環停止からの急速な温度変化によっ ても脳に対して影響しないと推測し,実験的検討を行った.方法:体重,約 40 kg のブタを用いて完全体外循環モデルを作成し,実験モデルを以下の 3 群 (各 n = 10) に分類した.A 群:直腸温 20°C の高度低体温で 20 分間の循環停止後,直腸温と人工心肺送血温の差を 5°C 以内に保ち,緩徐に 37°C まで復温する.B 群:28°C の軽度低体温で 20 分の循環停止後 A 群と同様に復温する. C 群:28°C 軽度低体温で 20 分の循環停止度後,38°C に加温した血液を送血することにより急速に復温する.人工心肺開始前,冷却完了時,復温開始時,復温完了時の 4 時点における血液生化学検査,CK-BB, S-100 及び脳組織血流,脳酸素分圧,頸静脈酸素飽和度について比較検討し,実験終了時に大脳皮質・海馬組織を採取し,病理学的に検討した.結果: 血小板数は復温完了時において A 群 が他の 2 群に比較し有意に低値であった.各測定時において BUN, Cr は群間に有意差はなかったが,復温完了時において AST は C 群が他の 2 群に比して有意に低値であり,LDH は A 群が他の 2 群と比較して有意に高値であった.CK-BB, S-100 は血中,髄液中ともに A 群が他の 2 群と比較して有意に高値であった.脳組織血流量は冷却完了時,復温開始時,復温完了時において A 群が他の 2 群と比較して有意に低値であった.脳酸素分圧に関しては復温開始時において,A 群が他の 2 群と比較して有意に低値であった.脳組織における細胞変性数は 3 群間で有意差は認められなかった.結論:28°C の軽度低体温循環停止に続く急速復温法は脳組織に対する影響は少なく,血液凝固障害の予防のためにもより有効な方法であると考えられた.
1 0 0 0 OA トンネルナノチューブを介した細胞間ミトコンドリア移送
- 著者
- 三木 敏生
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.5, pp.313-315, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-11-26)
- 参考文献数
- 22
1 0 0 0 OA 遷延性意識障害に対する脳脊髄刺激療法
- 著者
- 山本 隆充 深谷 親 吉野 篤緒 片山 容一
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.73, no.2, pp.109-111, 2014-04-01 (Released:2015-05-22)
- 参考文献数
- 14
要旨 遷延性意識障害では,vegetative state (VS) とminimally conscious state (MCS) を明確に区別する必要がある.VS には視床CM-pf complex をターゲットとする脳深部刺激療法,MCS には上位頚髄刺激療法を用いてきた.視床CM-pf complex 刺激では,大脳皮質への広範投射系を賦活することにより,刺激開始直後から激しい覚醒反応と脳血流の増加を認める.また,5 Hz の上位頚髄刺激では上肢のmuscle twitch を誘発し,脳血流を増加させる.手術適応を決定するためには残存する脳機能を正確に評価する必要があり,神経学的評価と電気生理学的評価が有用である.VS は脳深部刺激療法によって植物状態から脱却してもベッド上生活であったが,上位脊髄刺激によってMCS から回復した症例では運動機能の回復も良好で,特に上肢の運動機能回復が著しかった.脊髄刺激によって繰り返しmuscle twitch を誘発することは,関節拘縮や筋の廃用性萎縮を予防するとともに,運動機能回復に有用であり,新たなニューロモデュレーション技術として期待される.
1 0 0 0 OA 性感染症
- 著者
- 早川 智
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.3, pp.141-143, 2018-06-01 (Released:2018-07-23)
- 参考文献数
- 18
1 0 0 0 OA オートファジーからみたCOPD の病態
- 著者
- 水村 賢司
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.2, pp.115-117, 2018-04-01 (Released:2018-06-05)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 著者
- 岸野 明洋
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.2, pp.87-94, 2019-04-01 (Released:2019-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 22
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is the most common type of peripheral vertigo. BPPV occurs when calcium carbonate crystals (otoconia) in the utricle dislodge and migrate into the semicircular canals. There are two pathogeneses of BPPV: canalolithiasis and cupulolithiasis. Canalolithiasis involves to the presence of free cumulates of otoconia in the semicircular canals. When they become displaced in response to head movements, an endolymphatic flow is generated that abnormally stimulates the cupula, leading to vertigo. Cupulolithiasis involves a deposit of otolith nests that adhere to the cupula of the semicircular canal; thus, changing its specific gravity. Thus, the cupula is sensitized to linear accelerations, such as gravitational acceleration. The canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is used to treat BPPV by moving the otoconia from the semicircular canal to the utricle. Although BPPV can resolve spontaneously, BPPV treated with CRP is resolved more quickly than untreated BPPV. In order to treat BPPV appropriately with the CRP, we must ensure its appropriate diagnosis.
1 0 0 0 OA 肥満症の食事療法とその管理
- 著者
- 藤城 緑
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.4, pp.223-229, 2019-08-01 (Released:2019-09-20)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Sedentary lifestyles and dietary changes have resulted in an increasing number of obese subjects in Japan, as in Western countries. The number of complications affecting Japanese adults increases in relation to the body mass index (BMI), with a progressive increase in BMI ≥ 25, as well as 100 cm2 or greater visceral fat area. Thus, the Japan Society for the Study of Obesity has defined obesity as a BMI ≥ 25 and coined the term ‘obesity disease’ as a condition characterized by the presence of associated complications or their likely occurrence in an obese person. What is critically important is that a person in this situation needs to lose weight for medical reasons. To achieve clinically meaningful weight loss, lifestyle interventions together with reducing dietary calories, regardless of which macronutrients the patients emphasize, is the optimal approach. Herein, we explain how to treat people with obesity disease using diet therapy in Japan.
1 0 0 0 OA スポーツと肺機能
- 著者
- 伊藤 玲子
- 出版者
- 日本大学医学会
- 雑誌
- 日大医学雑誌 (ISSN:00290424)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.80, no.1, pp.21-25, 2021-02-01 (Released:2021-04-22)
- 参考文献数
- 16
It is expected that knowledge on the relationship between respiration and sports is beneficial for promoting both physical and mental health. With that knowledge, we can learn to exercise effectively every day. We supply oxygen to tissues by breathing. During exercise, respiration and circulation work closely together to carry oxygen to the mitochondria in muscles to generate energy. Exercise increases oxygen demand and carbon dioxide emissions. We increase the minute ventilation volume (MVV), thereby increasing V̇ O2 (oxygen consumption) as the exercise intensity increases. Endurance athletes exhibit higher levels of these parameters. MVV (maximum voluntary ventilation), which is a parameter used for evaluating the strength and endurance of inspiratory and expiratory muscles, improves after strength training. Strength training is thought to be effective in increasing the strength of the respiratory muscles. The combination of endurance training and strength training can improve lung function. Not only strengthening the respiratory muscles but also increasing the elastic contraction force of the lungs by training can improve respiratory ability. There are diseases in which sports affect lung function. Attention should be paid to exercise-induced asthma, vocal cord dysfunction, and COPD (chronic obstructive disease).