- 著者
- Toshihiro Tsuchiyama Takayuki Sakamoto Shohei Tanaka Takuro Masumura
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.12, pp.2954-2962, 2020-12-15 (Released:2020-12-16)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Medium manganese steel (Fe-5.0%Mn-1.2%Si-0.10%C alloy) was subjected to interrupted quenching from the austenite single-phase region to a temperature between Ms and Mf followed by intercritical annealing in the ferrite and austenite dual-phase region at 923 K. As a result, a core-shell type second phase, which consisted of a fresh martensite core surrounded by a film-like retained austenite shell, was formed. The mechanism and kinetics of reversion for the interrupted-quenched specimens were analyzed with DICTRA simulation and TEM observation. With regard to the effect of the core-shell type second phase on mechanical properties, it was inferred that the fresh martensite core functioned as a hard second phase and enhanced work hardening by stress partitioning similar to DP steel, while the film-like retained austenite contributed to improved ductility due to the TRIP effect. As the interrupted quenching temperature decreased, the volume fraction of the fresh martensite core decreased, while the stability of the retained austenite shell increased. This showed potential for controlling the strength and ductility balance of medium manganese steel. A possible beneficial effect of the core-shell type second phase on the ductile fracture behavior was also discussed in terms of stress/strain relaxation at the interfaces between hard martensite and ferrite matrix.
3 0 0 0 OA 溶融亜鉛めっきスパングルの結晶方位および元素分布
- 著者
- 福居 康 甲田 満 広瀬 祐輔
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.7, pp.939-946, 1991-07-01 (Released:2009-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 5 5
Spangles formed at hot-dip galvanized steel were classified and the distribution of Pb and Al, which were impurity and additional element respectively in molten zinc bath, on the spangle surface was investigated. The hot-dip galvanized Al-killed steel was produced with gas reduction type hot dipping testing aparatus in which steel sheet was cleaned by heating in reducing atmosphere and dipped into molten zinc bath which contained 0.25 wt%Pb and 0.17 wt%Al. X-ray Laue method was used for determination of crystal orientation and EPMA was used for the measurement of distribution of Pb and Al at the spangles.The main results of the study are follows:(1) The spangles are classified from the point of view of the crystal orientation and the appearance into the seven types as follows, Fern I, Fern II, Mirror, Frost, Half fern, Feather, Triangle.(2) The direction of the straight boundary of the spangles coincide with the projected direction of preferred crystal growth orientation (<1010>) on the spangle surface.(3) Spangles are classified into α type and β type from the point of view of the inclination of c-axis (<0001>). The c-axis of α type spangle is inclined to the straight boundary of the spangles and the c-axis of β type spangle is inclined to the reverse direction.(4) The amounts of Pb and Al at the spangle surface vary with the types of the spangle.(5) The spangle with the larger amounts of Pb and Al has less brilliance.
3 0 0 0 OA 主要元素に基づいた古代遺跡出土鉄滓の識別
- 著者
- 松本 建速
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.91, no.1, pp.55-61, 2005-01-01 (Released:2009-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 14
To identify the process of iron production, some indicators are proposed by using the chemical components of excavated slag. Especially, the ratio of Ti/Fe and V/Fe are useful for this purpose. All indicators, however, are not always appropriate for the distinguishable procedure between bowl-shaped slag and other slag. It is not yet fundamentally explained that major elements of iron-making slag caused from any materials.In this article, ten major elements which are constituent of iron-making slag as Silicon (Si), Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Titanium (Ti), Manganese (Mn), Magnesium (Mg), Calcium (Ca), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K) and Phosphorus (P) are considered by using the released analytical data. Every element has been normalized against Si, and the correlation diagrams are plotted. The correlation diagram with Si can be distinguished as 3 groups.( 1 ) Elements Al, Ca, Na, K and P have positive correlation with Si.( 2 ) Elements Ti, Mn, and Mg do not correlate with Si.( 3 ) Fe has negative correlation with Si.Elements of group (1) as Ca, Na, K and P increase the content in any slag during the smelting, refining and forging processes. Thus, it is obvious that these four elements can not be utilized for the distinguishable procedure of ancient iron-making slag.On the other hand, elements of group (2) as Ti, Mn and Mg are appropriate to be indicators for the distinguishable procedure of two types slag between forging slag (sometimes in refining process) and other slag (normally in smelting process). On the basis of concentration of the 3 elements, it is indicated that bowl-shaped slag is formed in forging (sometimes in refining), and other slag is done in smelting.As the result of this study, the ratio of element as Mn/Ti, Mn/Si, Mg/Ti and Mg/Si are suggested to be useful as indicators for the distinguishable procedure between bowl-shaped slag and other slag.
3 0 0 0 OA 熔鋼に於ける炭素と酸素との平衡並に水素還元に依る鋼中の酸素定量法
- 著者
- 的場 幸雄
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鐵と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.12, pp.837-847, 1934-12-25 (Released:2009-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 3
In the main part, author treats the equilibrium of Fe-C-O2-system at steel making temperatures by melting carbon and oxygen bearing iron in the gas stream of carbon mono-oxide and dioxide mixture. As the results of his experiment, it was proved that the oxygen content of the molten steel in equilibrium with the gas phase, is proportional to the ratio pco2/pco, and carbon content to p2co/pco2. On these accounts, he proposed that the two equilibriums, FeO(Fe)+CO=Fe+CO2 and C(Fe)+CO2=2CO, should be considered simultaneously as the carbon-oxygen equilibrium in steel making process instead of FeO(Fe)+C(Fe)=Fe+CO as was usually accepted. Further he constructed also the equilibrium diagram of Fe-C-O2-system qualitatively in the region of molten steel.As an appendix of his main paper, he described the hydrogen reduction method of oxygen determination in iron and steel. Some remarkable points of his method of determination are in the treatment of reduction products, H2O, CO2 and CO. Here H2O was absorbed by P2O5 and CO2 by soda lime as usually, CO is oxidized by I2O5 to CO2 selectively and after retaining free iodine with metallic copper chips, secondary formed CO2 absorbed by soda lime and weighed.
3 0 0 0 宇宙線ミュオン測定による高炉の炉内検知
- 著者
- 篠竹 昭彦 松崎 眞六 国友 和也 内藤 誠章 橋本 操 圃中 朝夫 長根 利弘 永嶺 謙忠 田中 宏幸
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.95, no.10, pp.665-671, 2009
- 被引用文献数
- 1 7
The visualization of the inner state of a blast furnace was investigated by exploiting the feature of cosmic-ray muon that attenuates according to the density and the thickness of the object through which it penetrates. The distribution of the cosmic-ray muon accumulated in an object in a blast furnace during a certain period has been determined by a probing system provided with two sets of a pair of panels with plastic scintillation counters segmented in parallel along each direction of both sides. First, measurement was performed in the furnace hearth structure that had been taken out after the shutdown of Oita No. 2 Blast Furnace repaired in 2004. Next, another measurement was performed in the same manner in the renewed furnace hearth of Oita No. 2 Blast Furnace which had just started working after its repairs. The density of the material at the iron-rich portion inside the hearth was estimated from the accumulation ratio obtained from the relation between the intensity of the muon channel passing through the iron-rich part in the hearth and that passing through its opposite channel symmetric to the coordinate origin. Then, the level of the furnace bottom brick, meaning its eroded thickness, was estimated from those accumulation ratios in relation to each channel crossing both the iron-rich part and the furnace bottom brick. The possibility of the density distribution of the material inside a blast furnace and the remaining thickness of bricks being estimated by this measurement method was identified.
2 0 0 0 OA 新技術開発部会直接還元法分科会報告日本における鉄鉱石直接還元技術の推移
- 著者
- 遠藤 勝治郎 松下 幸雄
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.6, pp.796-802, 1962-05-01 (Released:2010-02-22)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 1
2 0 0 0 OA Optimum Water Content Estimation for Wet Granulation of Iron Ore Powders with Quicklime Binder
- 著者
- Shota Yokokawa Hideya Nakamura Tomotaka Otsu Shuji Ohsaki Satoru Watano Shohei Fujiwara Takahide Higuchi
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ISIJINT-2022-498, (Released:2023-01-19)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Wet granulation plays an important role in the processing of fine ore powder. Water content is a critical process parameter that determines the granule properties during wet granulation. However, in the ironmaking industry, various types of iron ore powder imported from different regions are blended, quicklime powder is added as a binder, and used as raw materials. Therefore, the physicochemical properties of the raw powders are not always consistent, which makes it difficult to determine the optimum water content. In this study, we present a method to determine the optimum water content using the agitation torque of wet ore powder blended with quicklime. First, we investigated the agitation torque for blending of various types and ratios of ore powders and quicklime. Two types of torque profiles were observed: a unimodal torque profile (Type I) and a torque profile with a plateau region (Type II). From the agitation torque profile, the characteristic water content (
2 0 0 0 OA ステンレス鋼の常温におけるクリープ変形挙動
- 著者
- 天藤 雅之 竹下 哲郎 中澤 崇徳 木村 英隆 安保 秀雄
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.1, pp.98-104, 1993-01-01 (Released:2009-06-30)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 14 21
Room temperature creep behavior has been investigated for typical stainless steels (SUS304, SUS430, SUS410L). The mechanism of creep is discussed in comparison with creep data on a carbon steel (SM400).The results are summerized as follows:1) Stainless steels showed creep deformation at a stress around 0.2% proof stress. Though creep rate decreased monotonously with increase in time, deformation did not ceased even at a time 1000 h. The creep curve of SUS304 steel followed a logarithmic creep law.2) No creep was observed in steel SM400 below a critical strain rate at around 10-8S-1.3) The facts that interstitial free steels showed room temperature creep, and that SUS304 steel showed no creep at 300°C suggest that the suppression of creep can be attributed to the dynamic strain aging due to the interaction between dislocation and interstitial carbon and nitrogen atoms.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Uchima Masayoshi Kumagai Junzo Shimbe Akihiro Tanabe Yuta Mizuno Yusuke Onuki
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.5, pp.998-1003, 2022-05-15 (Released:2022-05-24)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 9
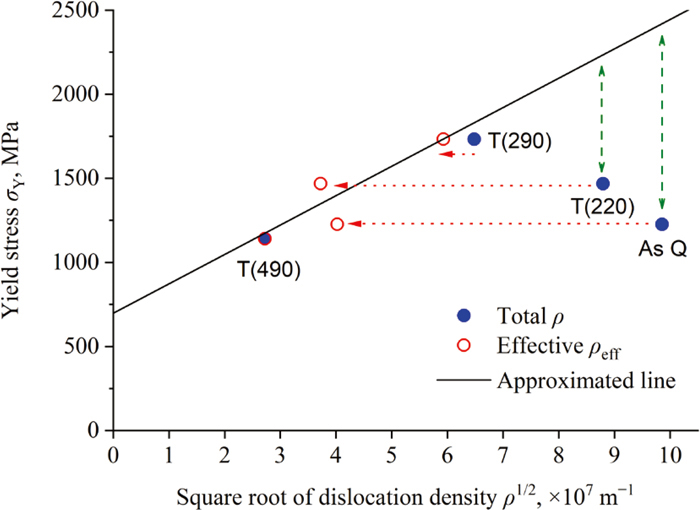
Middle-carbon martensite steels are vital materials for mechanical components and their mechanical properties have attracted significant interest. However, the decrease in the elastic limit of the as-quenched materials is one of the remaining puzzles. Herein, we quantitatively characterized the dislocation density and its structure in the as-quenched and tempered martensite steel by neutron diffraction line profile analysis and discussed their impact on the yield stress. The dislocation density in the as-quenched specimen was the highest at 9.7 × 1015 m−2, while it decreased with an increase in the tempering temperature. In addition, the component ratios of edge and screw dislocations decreased and increased, respectively, depending on the increase in the tempering temperature. The dislocation arrangement parameter (M) varied between the tempering temperatures of 220 and 290°C. Although there was a large difference between the yield stress obtained from the tensile test and that estimated from the dislocation density, the experimental results could be explained by correcting them with the inverse of M value as an index showing the effective dislocation density ratio.
2 0 0 0 OA Determining Optimum Water Content for Iron Ore Granulation using Agitation Torque of Wet Ore Powder
- 著者
- Tomotaka Otsu Hideya Nakamura Shuji Ohsaki Satoru Watano Shohei Fujiwara Takahide Higuchi
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ISIJINT-2022-009, (Released:2022-03-12)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Wet granulation of iron ore powders is a key process in ironmaking. In wet granulation, it is important to determine the optimum content of water added to the original ore powders. To determine the optimum water content, it is important to understand the saturation state in wet ore powder, which can be done by measuring the agitation torque of the wet powder. This study proposes a methodology for determining the optimum water content of various iron ore powders using the agitation torque of wet ore powders. First, measurement of the agitation torque and wet granulation of various iron ore powders were conducted. By comparing the results, it was found that the optimum water content, which was defined as the minimum water content required to diminish fine particles in the original powder, corresponded to the water content exhibiting the maximum agitation torque, regardless of the original powder. Using the agitation torque at different water contents, the saturation degree S, which is the volume ratio of water to the interparticle voids, was calculated, resulting in a range of 0.999 ≤ S ≤ 1.173 at the optimum water content. This suggests that the state between the funicular and capillary states is a suitable saturation state for the wet granulation of ore powders. Consequently, it was demonstrated that it is possible to determine the optimum water content for wet granulation of various iron ore powders based on the water content exhibiting the maximum agitation torque of wet ore powders.
2 0 0 0 OA 砂鉄および砂鉄銑について
- 著者
- 市川 直雄
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1204-1216, 1958-10-01 (Released:2009-05-26)
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Uchima Masayoshi Kumagai Junzo Shimbe Akihiro Tanabe Yuta Mizuno Yusuke Onuki
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ISIJINT-2021-443, (Released:2022-01-07)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Middle-carbon martensite steels are vital materials for mechanical components and their mechanical properties have attracted significant interest. However, the decrease in the elastic limit of the as-quenched materials is one of the remaining puzzles. Herein, we quantitatively characterized the dislocation density and its structure in the as-quenched and tempered martensite steel by neutron diffraction line profile analysis and discussed their impact on the yield stress. The dislocation density in the as-quenched specimen was the highest at 9.7 × 1015 m-2, while it decreased with an increase in the tempering temperature. In addition, the component ratios of edge and screw dislocations decreased and increased, respectively, depending on the increase in the tempering temperature. The dislocation arrangement parameter (M) varied between the tempering temperatures of 220 and 290°C. Although there was a large difference between the yield stress obtained from the tensile test and that estimated from the dislocation density, the experimental results could be explained by correcting them with the inverse of M value as an index showing the effective dislocation density ratio.
2 0 0 0 OA 鋼材の火花試驗に關する研究(II)
- 著者
- 三島 徳七 三橋 鐵太郎
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鐵と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.9, pp.959-968, 1942-09-25 (Released:2009-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 2
Die Untersuchungen erstreckten sick auf C-Stähle, Cr-Stähle, Cr-Ni-Stähle, Cr-Mo-Stähle, die in Form von geschmiedeten and gegossenen Rundstangen sind. Versuche uber den Einfluss von Schmieden auf Funkbarkeit von C-Stähle. Versuche uber den Einfluss allerleien Warmebehandlungen auf Funkbarkeit von Ni-Cr-Stäble. Versuche über die Wirkung des Cr-, Mooder Ni-gehaltes auf Funkbarkeit der C-Stähle.
2 0 0 0 OA Comparison of Microstructure and Hardness between High-carbon and High-nitrogen Martensites
- 著者
- Toshihiro Tsuchiyama Kurato Inoue Katsutoshi Hyodo Daichi Akama Nobuo Nakada Setsuo Takaki Tamotsu Koyano
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.1, pp.161-168, 2019-01-15 (Released:2019-01-17)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 9 16
The microstructure and hardness of martensite in Fe–C and Fe–N alloys with up to 7.5 at% contents of carbon and nitrogen, respectively, were compared. Their difference in hardness was discussed based on four strengthening mechanisms. The martensitic structures of Fe–C and Fe–N alloys with equal contents of carbon and nitrogen, respectively, were nearly identical, except for the amount of retained austenite. Furthermore, Fe–C alloy was considerably harder than Fe–N alloy. This discrepancy gradually increased with carbon and nitrogen contents. The enhanced hardness of Fe–C alloy martensite was attributed to its higher dislocation density and the stronger pinning force of interstitial carbon atoms on dislocations.
2 0 0 0 OA 特種鋼材の二三の性質に就て
- 著者
- 佐々川 清
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鐵と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, no.3, pp.201-224, 1929-03-25 (Released:2009-07-09)
According to the industrial progress, it is evident that the demand is going up to get large steel mass having the great stiffness and toughness. This problem will be solved by using some alloy steels in spite of plain carbon steel. To have good alloy steel it is necessary that the large mass is thoroughly uniform.Some special properties of alloy steels are investigated and described here.1) Mass effect;: -Steels used are plain C-steel, Ni-steel, Cr-steel, Ni-Cr-steel, Ni-Cr-mo steel, long rods of various diameters are forged from ingots, Annealed and quenched in water and in oil from hardening temperature. Hardeness change through the sectional area is measured, Theoretical interpretation is made on the phenomene of mass effect, concerning to the chemical composition, cooling velocity and the mass, 2) Residual stresss due to heat treatment;: -Several methods to measure the internal stress are described, Some experiments are made to research the residual stress due to heat treatment in using large mass of alloy steels, Some methods to eliminate the residual stress are discussed, 3) Temper-brittleness;: -The phenomene of temper-brittleness is described, To ascertain the relation between the temper-brittleness and tempering temperature, some experiments are made, Conclusion;: -To have good alloy steels of large mass, it is necessary to select the steel without or least mass effect. To avoid the effect of residual stress due to tempering, it must be reheated to a high temperature for some hours, but the temperature must be selected that no temper-brittleness well occur.
2 0 0 0 OA 橋梁における高力ボルトの遅れ破壊
- 著者
- 松山 晋作
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.8, pp.903-912, 1983-06-01 (Released:2009-06-30)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 6 8
実橋における高力ボルトの遅れ破壊に関する事例解析結果をまとめると次のようになる.1) 橋梁の桁構造別にみると箱桁における損傷例が多かつた.これは桁内部に水が溜まるために日照時には高温高湿条件となり腐食反応が生じやすいためである.したがつて,箱桁には水抜き孔を設けて桁内部が乾燥状態を保つようにすることが破損防止上必要である.2) 橋梁によつて破損が上フランジ,ウェブ,下フランジなどのある箇所に集中する傾向が認められた.この原因は明らかではないが,ボルトの遊びねじ長さ,水滴の溜まりやすさ,温度上昇度など,ボルトの製造ロット別に生ずる材質的差異以外の要因が考えられる.3) ボルトの破断部位は不完全ねじ部が一般的には多いが,橋梁によつては首下破断が多発する場合もあつた.規格上は首下はねじ部より強い筈であるから,首下破断を生ずる理由には,第一に頭が下向きの場合首下に水滴が溜まりやすいこと,第二に首下の丸み部に座金の角があたり荷重が集中したことが考えられる.とくに後者の場合には座金が遅れ破壊してボルト孔内部への水の浸入を容易にすることもある10)ので,座金の内側隅は十分面とりする必要がある.4) F 13T (No.4)を適用した唯一の橋梁で約15年間にわたりボルトの破損傾向を追跡調査した.その結果ボルト破損の確率分布は二母数ワイブル分布に従うことが認められた.継手のすべりに対する安全率を考えると,破損の補修をしなかつた場合にはこの橋梁は約40年で変状を生ずると推定された.5) F 11Tを使用した橋梁で最初の破損を生ずるまでの寿命分布も二母数ワイブル分布で表され,故障率が時間と共に低下する傾向を示した。現在F 11Tの使用は中止されているから,すでにF 11Tを使用している既設の橋梁での遅れ破壊事例は今後減少傾向にあると推定される.6) 高力ボルトを適用した初期の橋梁や遅れ破壊を発生した橋梁についてボルトを採取して軸部の鉄さびの分析を行つた.直接雨に曝された箇所や箱桁ではボルトが湿つた状態にあるものが多かつたが,鉄さびの組成からも水の存在が認められた.遅れ破壊は水の存在下で腐食反応の結果生ずる水素により誘起されるもので,乾燥状態で使用されていれば遅れ破壊は生じない.7) 破面の破壊起点部には旧オーステナイト粒界割れがみられた.材料によつては破壊途中で圧延方向にミクロ偏析帯に沿つて粒界割れを生ずる縦割れが認められた.8) 遅れ破壊を生じたボルトの最小硬さはHRC 37.5であつた.従来の実験から得られた遅れ破壊を生ずる限界硬さはHRC 41であるから,HRC<41で破損したボルトは材質的鋭敏化原因があつたと考えられる.その原因として,浸炭による表面硬化, Pの粒界偏析, Bの粒界における存在などが考えられた.これらの原因の検討から,熱処理炉の雰囲気は脱炭傾向にすること,可能な限り低燐の高純度鋼を用いること, B添加は必要最少量にすることなどが高力ボルトの信頼度を高めるために必要であると結論される.しかし市販鋼では高純化には限度があるから粒界炭化物が十分凝集するまで焼もどし温度を高めることが必要である.9) 一般に炭素量が多いと焼もどし軟化曲線の勾配が急になり,焼もどし温度変化の硬さへの影響が大きくなるから,炭素量の多い鋼種で高強度化するのは望ましいことではない.またバッチ型焼もどし炉のように装入方法によつては温度むらを生ずる場合には,一部に焼もどしが不十分で硬さの高い製品が混入する可能性があるので注意が必要である.
2 0 0 0 OA ボルトの遅れ破壊
- 著者
- 中里 福和
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.10, pp.606-611, 2002 (Released:2009-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 54
- 被引用文献数
- 12 14
This review article on delayed fracture of bolts covers the following topics: general features of delayed fracture, case histories of in-service failures of high-strength bolts, existing demands for higher-strength bolts and their background, increasing needs for standardization of delayed fracture susceptibility evaluation method, and approaches so-far taken to prevent delayed fracture. The author emphasizes that, thanks to the recent intensive R&D activities, overcoming delayed fracture is now very close to the reality.
2 0 0 0 OA たたら製鉄の炉内反応機構と操業技術
- 著者
- 永田 和宏 鈴木 卓夫
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.1, pp.64-71, 2000-01-01 (Released:2009-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 8
- 被引用文献数
- 7 6
"Tatara" was a traditional box-type furnace in Japan and had produced steel and pig iron directly until 1923. After then, because of the low productivity, Tatara was not commercially operated but only for producing the materials of Japanese sword in little. In 1977 with the blank ages after the World War II, Japan Institute of Art Japanese Sword reconstructed the Tatara furnace, called "Nittoho Tatara". Then, Mr. Yoshizo Abe as a leader "Murage" realized his own technique for the Tatara operation because of the technique transfer only by oral instruction to the Murage's family. The 3rd Tatara operation in 1999 winter has been studied on the effect of fire flame (so called "Hose") and sound from furnace, the color and viscosity of slag (so called "Noro") flowed out from furnace and the condition of tuyers to the productivity of "Kera" including steel (so called "Tamahagane") and pig iron (so called "Zuku"), etc. This operation met the trouble of air blowing to the furnace in the final stage. Though many efforts had been made to recover the stable operation, the activity of furnace was stopped in shorter operation time than the other two operations. From the experiences of the recover, the fundamental treatments to make the operation stable have been cleared and also the reaction mechanisms to produce.
2 0 0 0 OA 自動車車体外板の樹脂化の動向
- 著者
- 井出 正 佐野 実 新井 重男
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.72, no.11, pp.1674-1680, 1986-09-01 (Released:2010-02-15)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 著者
- Harshad Kumar Dharamshi Hansraj Bhadeshia
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.1, pp.24-36, 2016-01-15 (Released:2016-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 169
- 被引用文献数
- 118 400
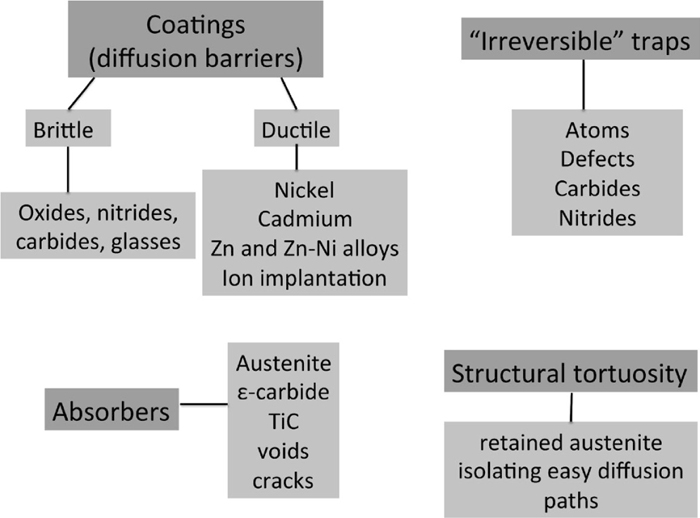
The essential facts about the nature of the hydrogen embrittlement of steels have now been known for 140 years. It is diffusible hydrogen that is harmful to the toughness of iron. It follows, therefore, that the harmful influence of diffusible hydrogen can be mitigated by preventing its entry into steel or by rendering it immobile once it penetrates the material. This review deals with the methods that might be implemented to design steels and components that resist hydrogen embrittlement by reducing the intake of hydrogen or rendering it innocuous when it does penetrate the steel.