1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[100], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[99], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[98], 1800
- 著者
- Natsu Takayanagi Mai Mukai Munetaka Sugiyama Misato Ohtani
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.329-333, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 18
During organ regeneration, differentiated cells acquire cell proliferation competence before the re-start of cell division. In Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), CDKA;1, a cyclin-dependent kinase, RID1, a DEAH-box RNA helicase, and SRD2, a small nuclear RNA transcription factor, are implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation competence. Here, we report phytohormonal transcriptional regulation of these cell proliferation competence-associated genes during callus initiation. We can induce the callus initiation from Arabidopsis hypocotyl explants by the culture on the auxin-containing medium. By RT-quantitative PCR analysis, we observed higher mRNA accumulation of CDKA;1, RID1, and SRD2 in culture on the auxin-containing medium than in culture on the auxin-free medium. Promoter-reporter analysis showed that the CDKA;1, RID1, and SRD2 expression was induced in the stele regions containing pericycle cells, where cell division would be resumed to make callus, by the culture in the medium containing auxin and/or cytokinin. However, the expression levels of these genes in cortical and epidermal cells, which would not originate callus cells, were variable by genes and phytohormonal conditions. We also found that the rid1-1 mutation greatly decreased the expression levels of CDKA;1 and SRD2 during callus initiation specifically at 28°C (restrictive temperature), while the srd2-1 mutation did not obviously decrease the expression levels of CDKA;1 and RID1 regardless of temperature conditions but rather even increased them at 22°C (permissive temperature). Together, our results implicated the phytohormonal and differential regulation of cell proliferation competence-associated genes in the multistep regulation of cell proliferation competence.
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[96], 1800
- 著者
- Takashi Nobusawa Hiroshi Yamatani Makoto Kusaba
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.317-321, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Controlling the flowering time is crucial for propagating plant species and crop production. ALTERED MERISTEM PROGRAM1 (AMP1) in Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a putative carboxypeptidase, and an AMP1 mutant (amp1) was found to cause highly pleiotropic phenotypes including a short plastochron, an enlarged shoot apical meristem, and reduced apical dominance. Although amp1 also shows an early flowering phenotype, its mechanism has not been investigated in detail. The most important floral integrator or florigen gene, FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), has a close relative, TWIN SISTER OF FT (TSF). In this report, we generated a new allele of tsf using a genome-editing technique and produced ft tsf double and amp1 ft tsf triple mutants. The flowering time of amp1 ft tsf was equally as late as ft tsf under long-day conditions. In addition, the expression level of FT in amp1 was 2.4-fold higher than that in wild-type, even five days after germination under long-day conditions. These results suggest that the elevated expression level of FT is responsible for the early flowering phenotype of amp1. Furthermore, expression of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), a negative regulator of FT expression, is severely repressed in amp1, raising the possibility that low expression levels of FLC contributes to upregulation of FT expression and the early flowering phenotype of amp1.
- 著者
- Sho Takeda Taisuke Togawa Kei-ichiro Mishiba Katsuyuki T. Yamato Yuji Iwata Nozomu Koizumi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.303-310, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 2
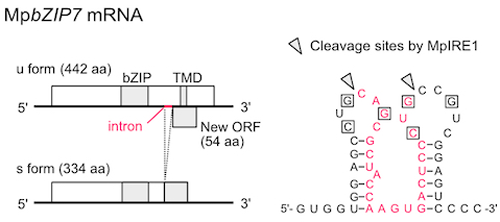
The unfolded protein response (UPR) or the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response is a homeostatic cellular response conserved in eukaryotes to alleviate the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER. In the present study, we characterized the UPR in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha to obtain insights into the conservation and divergence of the UPR in the land plants. We demonstrate that the most conserved UPR transducer in eukaryotes, IRE1, is conserved in M. polymorpha, which harbors a single gene encoding IRE1. We showed that MpIRE1 mediates cytoplasmic splicing of mRNA encoding MpbZIP7, a M. polymorpha homolog of bZIP60 in flowering plants, and upregulation of ER chaperone genes in response to the ER stress inducer tunicamycin. We further showed that MpIRE1 also mediates downregulation of genes encoding secretory and membrane proteins in response to ER stress, indicating the conservation of regulated IRE1-dependent decay of mRNA. Consistent with their roles in the UPR, Mpire1ge and Mpbzip7ge mutants exhibited higher sensitivity to ER stress. Furthermore, an Mpire1ge mutant also exhibited retarded growth even without ER stress inducers, indicating the importance of MpIRE1 for vegetative growth in addition to alleviation of ER stress. The present study provides insights into the evolution of the UPR in land plants.
- 著者
- Edjohn Aaron Macauyag Hiroyuki Kajiura Takao Ohashi Ryo Misaki Kazuhito Fujiyama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.291-301, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 56
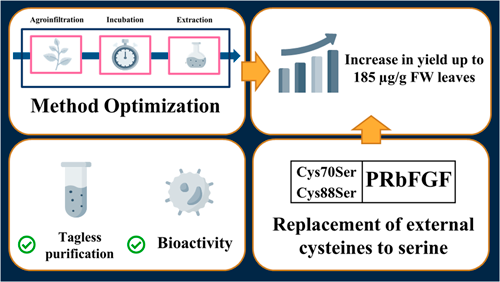
The human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is a protein that plays a pivotal role in cellular processes like cell proliferation and development. As a result, it has become an important component in cell culture systems, with applications in biomedical engineering, cosmetics, and research. Alternative production techniques, such as transient production in plants, are becoming a feasible option as the demand continues to grow. High-level bFGF production was achieved in this study employing an optimized Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression system, which yielded about a 3-fold increase in production over a conventional system. This yield was further doubled at about 185 µg g−1 FW using a mutant protease-resistant version that degraded/aggregated at a three-fold slower rate in leaf crude extracts. To achieve a pure product, a two-step purification technique was applied. The capacity of the pure protease-resistant bFGF (PRbFGF) to stimulate cell proliferation was tested and was found to be comparable to that of E. coli-produced bFGF in HepG2 and CHO-K1 cells. Overall, this study demonstrates a high-level transient production system of functional PRbFGF in N. benthamiana leaves as well as an efficient tag-less purification technique of leaf crude extracts.
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[94], 1800
- 著者
- Yoshiki Tanahara Kaho Yamanaka Kentaro Kawai Yukiko Ando Takashi Nakatsuka
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.273-280, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
Matthiola incana is an important floricultural plant that blooms from winter to spring, and had been desired to be established a transformation system. This study successfully obtained stable transgenic plants from M. incana. We used Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring a binary vector containing the β-glucuronidase gene (GUS) under the control of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter to evaluate the transformation frequency of M. incana. We observed that cocultivation with the A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 for 5 days effectively enhanced the infection frequency, assessed through a transient GUS expression area in the seedling. Furthermore, the addition of 100 µM acetosyringone was necessary for Agrobacterium infection. However, we could not obtain transgenic plants on a shoot formation medium supplemented with 1 mg l−1 6-benzyladenine (BA). For callus formation from the leaf sections, a medium supplemented with 1–50 µM fipexide (FPX), a novel callus induction chemical, was employed. Then, the callus formation was observed after 2 weeks, and an earlier response was detected than that in the BA medium (4–6 weeks). Results also showed that cultivation in a selection medium supplemented with 12.5 µM FPX obtained hygromycin-resistant calli. Thus, this protocol achieved a 0.7% transformation frequency. Similarly, progenies from one transgenic line were observed on the basis of GUS stains on their leaves, revealing that the transgenes were also inherited stably. Hence, FPX is considered a breakthrough for establishing the transformation protocol of M. incana, and its use is proposed in recalcitrant plants.
- 著者
- Shilian Huang Yanchun Qiao Xinmin Lv Jianguang Li Dongmei Han Dongliang Guo
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.259-272, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 61
Potassium chlorate can promote off-season flowering in longan, but the molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, four-year-old ‘Shixia’ longan trees were injected in the trunk with potassium chlorate, and terminal buds were sampled and analyzed using transcriptomics and bioinformatics tools. To generate a reference longan transcriptome, we obtained 207,734 paired-end reads covering a total of 58,514,149 bp, which we assembled into 114,445 unigenes. Using this resource, we identified 3,265 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that were regulated in longan terminal buds in response to potassium chlorate treatment for 2, 6 or 30 days, including 179 transcription factor genes. By reference to the Arabidopsis literature, we then defined 38 longan genes involved in flowering, from which we constructed the longan flowering pathway. According to RNA-seq data, at least 24 of these genes, which participate in multiple signaling pathways, are involved in potassium chlorate-stimulated floral induction, and the differential regulation in terminal buds of ten floral pathway genes (GI, CO, GID1, GA4, GA5, FLC, AP1, LFY, FT and SOC1) was confirmed by qRT-PCR. These data will contribute to an improved understanding of the functions of key genes involved in longan floral induction by potassium chlorate.
- 著者
- Zhe-Yu Liu Jiao-Jiao Ji Feng Jiang Xing-Rui Tian Jian-Kuan Li Jian-Ping Gao
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.251-257, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Codonopsis pilosula, a traditional Chinese medicinal and edible plant, contains several bioactive components. However, the biosynthetic mechanism is unclear because of the difficulties associated with functional gene analysis. Therefore, it is important to establish an efficient genetic transformation system for gene function analysis. In this study, we established a highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated callus genetic transformation system for C. pilosula using stems as explants. After being pre-cultured for 3 days, the explants were infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 harboring pCAMBIA1381-35S::GUS at an OD600 value of 0.3 for 15 min, followed by co-cultivation on MS induction medium for 1 day and delayed cultivation on medium supplemented with 250 mg l−1 cefotaxime sodium for 12 days. The transformed calli were selected on screening medium supplemented with 250 mg l−1 cefotaxime sodium and 2.0 mg l−1 hygromycin and further confirmed by PCR amplification of the GUS gene and histochemical GUS assay. Based on the optimal protocol, the induction and transformation efficiency of calli reached a maximum of 91.07%. The establishment of a genetic transformation system for C. pilosula calli lays the foundation for the functional analysis of genes related to bioactive components through genetic engineering technology.
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[93], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[92], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[91], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[90], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[89], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[88], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[87], 1800
1 0 0 0 OA [青山延于・延光書簡]
- 著者
- [青山延于, 青山延光] [著]
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.[86], 1800