2 0 0 0 OA 武田友加著『現代ロシアの貧困研究』
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- ロシア・東欧学会
- 雑誌
- ロシア・東欧研究 (ISSN:13486497)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2011, no.40, pp.98-100, 2011 (Released:2013-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 5
1 0 0 0 OA トランプ現象とロシア経済
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- ロシア・東欧学会
- 雑誌
- ロシア・東欧研究 (ISSN:13486497)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2017, no.46, pp.7-26, 2017 (Released:2019-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 51
The present study discusses the two problems in Putin’s Russia, namely that of protective trade measures and that of social disparities, both of which have been attracting attention from a lot of researchers and journalists under the circumstance of the Trump phenomenon. Therefore it examines the problems in comparison with the situation of the two problems in the USA under the Trump administration. For the first problem, it argues that Russia is rather faithful to the rule of the game of international system, while the Trump administration has an inclination to destroy it. However, there is a kind of deception in this attitude of Russia because it applies double standards when it treats trade problems with the USA, Western Europe and Japan on the one hand and the problems with the former Soviet states on the other. It emphasizes that Trump’s trade policies would play a role that gives an indulgence to the double standards of Russia. For the second problem, we argue that the residents in Russia are divided into small interest groups as a result of the survival of the “Soviet social system”. What ties together the people there is the patriotism of the citizens surrounded by “enemies”. Also in the United States, a specific income group does not support Trump’s regime, but a wider cross-hierarchical ideology, “anti-intellectualism” supports it. According to our view it is important to pay an attention to the relationship between the hierarchical structure and the patriotism or ideology in order to estimate the sustainability of the both regimes in the future.
1 0 0 0 OA 金融危機・石油価格下落下のロシア経済
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association for Russian and East European Studies
- 雑誌
- ロシア・東欧研究 (ISSN:13486497)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2009, no.38, pp.4-16, 2009 (Released:2011-10-14)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
There are three conundrums as for the relation between the Russian economy and the Sub-Prime financial crisis. Firstly, it is not clear why Russia’s GDP has been damaged so severely after the crisis comparing with other leading countries including China. Secondly, we have not yet found out a main process through which the American crisis reached Russia. Because Russian financial institutions did not have Sub-Prime-related securities so much, it does not stand to reason that they suffered the same kind of turbulence as British or German banks had. Thirdly, why such a basically financial affair as the Sub-Prime crisis has had a serious effect on economic real sectors of Russia is not easy to understand. In the case of the financial crisis in 1998 the real sectors of Russia did not have close connections with its financial sectors and therefore they did not receive serious damages from the financial sectors. Have the connections between the real sectors and financial sectors in Russia strengthened considerably in the last ten years? Among these three conundrums this article tries to answer to the last two and give a hint to the first one. As for the second conundrum the author insists that foreign financial institutions, which had held much Sub-Prime-related assets, withdrew their capital from Russia to compensate their losses in the crisis, which in turn brought Russian financial institutions into a difficult situation. As for the third one it is emphasized that the real and financial sectors in Russia have not yet achieved modern close relationship and that we must find another factor that led to economic difficulties of the real sectors of Russia. For example, the so-called financial deepening cannot be considered to have proceeded sufficiently in Russia if compared to Japan, England, Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland. As for the first one the author suggests that decrease of “terms of trade effect” after the crisis, which occurred because of oil price decline, might have been one of the important factors for GDP setback. By explaining about these three conundrums the author clarifies a special economic structure of Russia: vulnerability to foreign shocks.
1 0 0 0 OA ロシア経済の回復, その原因と今後の展望
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- ロシア・東欧学会
- 雑誌
- ロシア・東欧研究 (ISSN:13486497)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2004, no.33, pp.4-15, 2004 (Released:2010-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 23
The economic recovery of Russia after the financial crisis in August 1998 has been driven by a large amount of “net export”. The “net export” was produced by low exchange rate of ruble and high price of oil. Using rough estimates of the future trend of the exchange rate and oil price, we can conclude that the Russian economic boom will not suffer a serious setback in the near future. In the longer term, however, Russia will face political and economic difficulties if Russians cannot restructure the oil-gas monoculture, which has been existed at the core of the economic recovery until now.
1 0 0 0 OA ポーランド労働者調査報告
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- 比較経済体制学会
- 雑誌
- 社会主義経済学会会報 (ISSN:18839789)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1991, no.28, pp.43-44, 1991-03-20 (Released:2009-07-31)
1 0 0 0 OA ルーマニア経済の西側接近とその帰結
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- 比較経済体制学会
- 雑誌
- 社会主義経済学会会報 (ISSN:18839789)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1986, no.24, pp.7-10, 1986-10-20 (Released:2009-07-31)
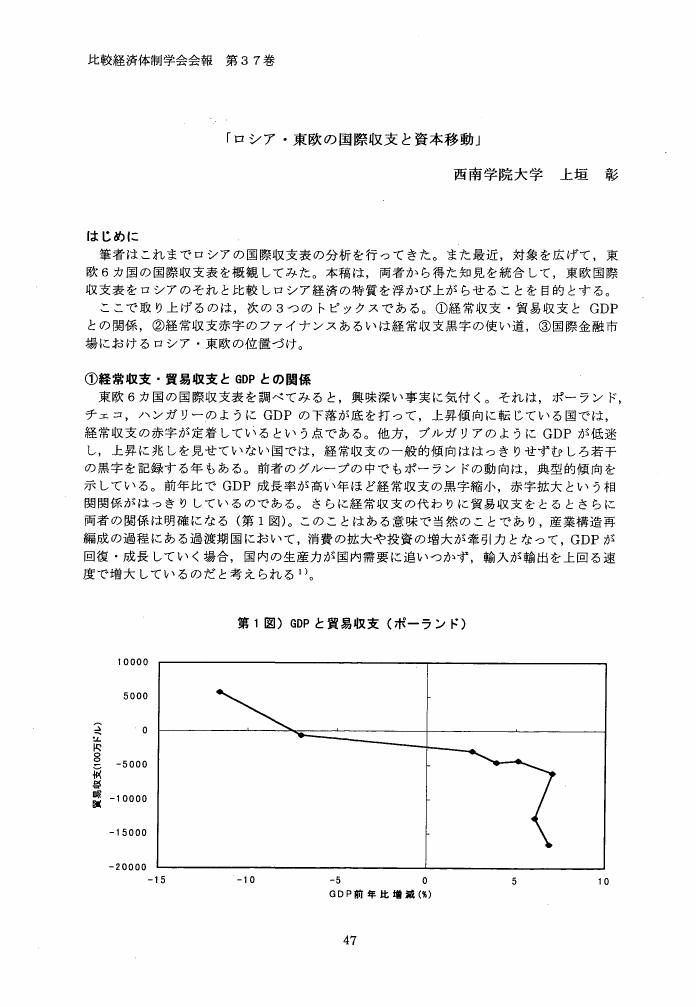
1 0 0 0 OA 「ロシア・東欧の国際収支と資本移動」
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- 比較経済体制学会
- 雑誌
- 比較経済体制学会会報 (ISSN:18839797)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.1, pp.47-54, 2000-01-30 (Released:2009-07-31)
1 0 0 0 OA ロシア連邦の国際収支表:その特徴と若干の分析
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- 比較経済体制学会
- 雑誌
- 比較経済体制学会会報 (ISSN:18839797)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.1, pp.67-75, 1998-02-01 (Released:2009-07-31)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- Japan Association for Comparative Economic Studies
- 雑誌
- 比較経済体制学会年報 (ISSN:13484060)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.110-112, 2003-01-01 (Released:2009-07-31)
- 参考文献数
- 2
1 0 0 0 OA 市場経済移行類型化の試み:貿易関係自由化の側面から
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- Japan Association for Comparative Economic Studies
- 雑誌
- 比較経済体制学会年報 (ISSN:13484060)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.1, pp.52-64,204, 2002 (Released:2009-07-31)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Russia and Eastern European countries (excluding Albania and former Yugoslav states) can be divided into three groups. The first group includes Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Slovakia, which have successfully coordinated macro economic stabilization and liberalization of foreign trade. The second group includes Bulgaria and Romania, where half measures of liberalization have been adopted under the circumstance of vicious spiral of inflation and depreciation of currency. The third group consists of Russia. Russia keeps old complicated organizations in the half liberalized system. One interesting point here is that the first and the third group experienced real currency appreciation in the first years of the transition whereas the currencies of the second group were depreciated considerably.
- 著者
- 上垣 彰
- 出版者
- ロシア史研究会
- 雑誌
- ロシア史研究 (ISSN:03869229)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, pp.40-60, 1978
1 0 0 0 OA 持続的経済発展の可能性
1 0 0 0 OA 黒海地域の国際関係-4次元分析における学際的総合研究
- 著者
- 六鹿 茂夫 廣瀬 陽子 黛 秋津 佐藤 真千子 小窪 千早 梅本 哲也 吉川 元 上垣 彰 大西 富士夫 西山 克典 小久保 康之 吉村 貴之 中島 崇文 末澤 恵美 服部 倫卓 木村 真
- 出版者
- 静岡県立大学
- 雑誌
- 基盤研究(A)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2008
黒海地域の国際関係を歴史、経済、域内国際関係、域外国際関係の4次元から分析し、国際会議をボアジチ大学(イスタンブール)と静岡県立大学にて開催して学際的総合化に努めた。その結果、1.黒海としての地域性、2.地政学的重要性、3.黒海地域の特殊性と地域特有のイシュー(エネルギー、民主化、凍結された紛争)、4.黒海地域の構造とその変動、5.黒海地域と広域ヨーロッパおよび世界政治との相互連関性が明らかにされた。