- 著者
- Kozo Hotta Ryoji Taniguchi Hiroyuki Nakayama Fumitaka Yamaguchi Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- International Heart Journal Association
- 雑誌
- International Heart Journal (ISSN:13492365)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.6, pp.1342-1347, 2021-11-29 (Released:2021-11-30)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 5
The aim of the present study was to determine whether the addition of an oral nutritional supplement with whey peptides and branched-chain amino acids for cardiac rehabilitation improves cardiopulmonary function, skeletal muscle function, and metabolism in CHF patients.In this randomized, parallel-group comparative pilot study, 20 CHF patients were randomly assigned to the nutrition group (n = 10) or the control group (n = 10). At baseline and 12 weeks, we performed physical examinations, motor function evaluation, clinical laboratory tests, nutritional status assessment, and echocardiography. The primary outcome was exercise tolerance, as determined by the cardiopulmonary stress test (CPX), 6-minute walking test (6MWT), and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels.During follow-up, body weight, body mass index, total muscle mass, and total lean mass did not change significantly in either group. The total fat mass significantly increased in the nutrition group (14.3 ± 5.4 kg versus 16.1 ± 5.5 kg, P < 0.001) but did not change in the control group, and the difference in the changes in total fat mass between groups was significant (−0.26 ± 0.96 kg versus 1.49 ± 0.63 kg, P < 0.001). The peakVO2 and 6-minute walk test (6 MWT) significantly increased in the nutrition group (14.6 ± 3.4 mL/minute/kg versus 15.8 ± 3.8 mL/minute/kg, P = 0.029; 346.9 ± 103.1 m versus 382.7 ± 102.1 m, P = 0.048; respectively) but did not change in the control group. The changes in peakVO2 and 6MWT did not significantly differ between the groups.The oral nutritional supplement for the treatment of CHF was effective for cardiac rehabilitation in terms of fat mass and exercise capacity.The present study demonstrated that oral nutritional supplements with whey peptides and branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) for cardiac rehabilitation in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) increased fat mass and exercise capacity. We conclude that whey peptides and BCAA supplementation may be a useful treatment for CHF patients.
- 著者
- Takashi Kuragaichi Yuma Kurozumi Shogo Ohishi Yasuo Sugano Akihiro Sakashita Norihiko Kotooka Makoto Suzuki Taiki Higo Dai Yumino Yasuko Takada Seiko Maeda Saori Yamabe Koichi Washida Tomonori Takahashi Tomohito Ohtani Yasushi Sakata Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.5, pp.1336-1343, 2018-04-25 (Released:2018-04-25)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 16 26
Background:Palliative care for heart failure (HF) patients is recommended in Western guidelines, so this study aimed to clarify the current status of palliative care for HF patients in Japan.Methods and Results:A survey was sent to all Japanese Circulation Society-authorized cardiology training hospitals (n=1,004) in August 2016. A total of 544 institutions (54%) returned the questionnaire. Of them, 527 (98%) answered that palliative care is necessary for patients with HF. A total of 227 (42%) institutions held a palliative care conference for patients with HF, and 79% of the institutions had <10 cases per year. Drug therapy as palliative care was administered at 403 (76%) institutions; morphine (87%) was most frequently used. Among sedatives, dexmedetomidine (33%) was administered more often than midazolam (29%) or propofol (20%). Regarding the timing of end-of-life care, most institutions (84%) reported having considered palliative care when a patient reached the terminal stage of HF. Most frequently, the reason for the decision at the terminal stage was “difficulty in discontinuing cardiotonics.” A major impediment to the delivery of palliative care was “difficulty predicting an accurate prognosis.”Conclusions:This large-scale survey showed the characteristics of palliative care for HF in Japan. The present findings may aid in the development of effective end-of-life care systems.
- 著者
- Kentaro Kamiya Takanobu Yamamoto Miyuki Tsuchihashi-Makaya Toshimi Ikegame Tetsuya Takahashi Yukihito Sato Norihiko Kotooka Yoshihiko Saito Hiroyuki Tsutsui Hiroaki Miyata Mitsuaki Isobe
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.7, pp.1546-1552, 2019-06-25 (Released:2019-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 15 70
Background:The purpose of this study was to clarify the implementation rate of multidisciplinary heart failure (HF) care and cardiac rehabilitation (CR) in Japan, as well as the relationship between implementation rates and characteristics of the facility.Methods and Results:Survey participants were cardiologists who are members of the Japan Heart Failure Society and belonged to 1 of 845 medical institutions that are members of the Japan Heart Failure Society, as of April 2016. A total of 288 institutions (34.1%) returned the questionnaire. The percentages of hospitals implementing multidisciplinary HF care were 78.5% for inpatients and 32.6% for outpatients with HF. Inpatient and outpatient CR for HF had implementation rates of 80.4% and 56.5%, respectively. In addition, very few HF patients (7.3%, 3,741/51,323 patients) received outpatient CR. Both the presence of nurses certified in chronic HF care and registered CR instructors on staff were consistently associated with implementation of multidisciplinary HF care, and Japanese Circulation Society training hospitals, lower number of hospital beds, and presence of registered CR instructors on staff were consistently associated with implementation of CR.Conclusions:This first nationwide survey demonstrated that the implementation rates of multidisciplinary care and CR for HF, especially for outpatients, are low in Japan. Skilled healthcare professionals are expected to play important roles in the widespread implementation of this type of HF care in Japan.
- 著者
- Kazuhiro Yamamoto Miyuki Tsuchihashi-Makaya Yoshiharu Kinugasa Yuki Iida Kentaro Kamiya Yasuki Kihara Yuji Kono Yukihito Sato Norio Suzuki Harumi Takeuchi Taiki Higo Yasushi Miyazawa Isao Miyajima Akira Yamashina Katsushi Yoshita Koichi Washida Masafumi Kuzuya Tetsuya Takahashi Yutaka Nakaya Naoyuki Hasebe Hiroyuki Tsutsui on behalf of The Japanese Heart Failure Society Expert Consensus Writing Committee
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-20-0322, (Released:2020-07-10)
- 参考文献数
- 206
- 被引用文献数
- 21
- 著者
- Kanae Su Takao Kato Mamoru Toyofuku Takeshi Morimoto Hidenori Yaku Yasutaka Inuzuka Yodo Tamaki Neiko Ozasa Erika Yamamoto Yusuke Yoshikawa Yasuyo Motohashi Hiroki Watanabe Takeshi Kitai Ryoji Taniguchi Moritake Iguchi Masashi Kato Kazuya Nagao Takafumi Kawai Akihiro Komasa Ryusuke Nishikawa Yuichi Kawase Takashi Morinaga Toshikazu Jinnai Mitsunori Kawato Yukihito Sato Koichiro Kuwahara Takashi Tamura Takeshi Kimura KCHF Registry Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.11, pp.517-524, 2019-11-08 (Released:2019-11-08)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Background:We sought to explore the effects of previous heart failure (HF) hospitalization on mortality in patients hospitalized for acute decompensated HF (ADHF) in a large Japanese contemporary observational database.Methods and Results:We prospectively enrolled consecutive patients with ADHF in 19 participating hospitals between October 2014 and March 2016. Of 4,056 patients, 1,442 patients (35.4%) had at least 1 previous HF hospitalization (previous hospitalization group), while 2,614 patients (64.5%) did not have a history of HF hospitalization (de novo hospitalization group). Patients with previous hospitalization were older and more often had comorbidities such as anemia, and renal failure than those without. The cumulative 1-year incidence of all-cause death was significantly higher in the previous hospitalization group than in the de novo hospitalization group (28% vs. 19%, P<0.001). After adjusting confounders, the excess risk of the previous hospitalization group relative to the de novo hospitalization group for all-cause death remained significant (HR, 1.28; 95% CI: 1.10–1.50, P=0.001). The excess risk was significant in patients without advanced age, anemia, or renal failure, but not significant in patients with these comorbidities, with significant interaction. Increase in the number of hospitalizations was associated with an increased risk for mortality.Conclusions:In a contemporary ADHF cohort in Japan, repeated hospitalization was associated with an increasing, higher risk for 1-year mortality.
- 著者
- Kentaro Kamiya Takanobu Yamamoto Miyuki Tsuchihashi-Makaya Toshimi Ikegame Tetsuya Takahashi Yukihito Sato Norihiko Kotooka Yoshihiko Saito Hiroyuki Tsutsui Hiroaki Miyata Mitsuaki Isobe
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-19-0241, (Released:2019-06-11)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 70
Background:The purpose of this study was to clarify the implementation rate of multidisciplinary heart failure (HF) care and cardiac rehabilitation (CR) in Japan, as well as the relationship between implementation rates and characteristics of the facility.Methods and Results:Survey participants were cardiologists who are members of the Japan Heart Failure Society and belonged to 1 of 845 medical institutions that are members of the Japan Heart Failure Society, as of April 2016. A total of 288 institutions (34.1%) returned the questionnaire. The percentages of hospitals implementing multidisciplinary HF care were 78.5% for inpatients and 32.6% for outpatients with HF. Inpatient and outpatient CR for HF had implementation rates of 80.4% and 56.5%, respectively. In addition, very few HF patients (7.3%, 3,741/51,323 patients) received outpatient CR. Both the presence of nurses certified in chronic HF care and registered CR instructors on staff were consistently associated with implementation of multidisciplinary HF care, and Japanese Circulation Society training hospitals, lower number of hospital beds, and presence of registered CR instructors on staff were consistently associated with implementation of CR.Conclusions:This first nationwide survey demonstrated that the implementation rates of multidisciplinary care and CR for HF, especially for outpatients, are low in Japan. Skilled healthcare professionals are expected to play important roles in the widespread implementation of this type of HF care in Japan.
- 著者
- Takashi Kuragaichi Yuma Kurozumi Shogo Ohishi Yasuo Sugano Akihiro Sakashita Norihiko Kotooka Makoto Suzuki Taiki Higo Dai Yumino Yasuko Takada Seiko Maeda Saori Yamabe Koichi Washida Tomonori Takahashi Tomohito Ohtani Yasushi Sakata Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-17-1305, (Released:2018-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 26
Background:Palliative care for heart failure (HF) patients is recommended in Western guidelines, so this study aimed to clarify the current status of palliative care for HF patients in Japan.Methods and Results:A survey was sent to all Japanese Circulation Society-authorized cardiology training hospitals (n=1,004) in August 2016. A total of 544 institutions (54%) returned the questionnaire. Of them, 527 (98%) answered that palliative care is necessary for patients with HF. A total of 227 (42%) institutions held a palliative care conference for patients with HF, and 79% of the institutions had <10 cases per year. Drug therapy as palliative care was administered at 403 (76%) institutions; morphine (87%) was most frequently used. Among sedatives, dexmedetomidine (33%) was administered more often than midazolam (29%) or propofol (20%). Regarding the timing of end-of-life care, most institutions (84%) reported having considered palliative care when a patient reached the terminal stage of HF. Most frequently, the reason for the decision at the terminal stage was “difficulty in discontinuing cardiotonics.” A major impediment to the delivery of palliative care was “difficulty predicting an accurate prognosis.”Conclusions:This large-scale survey showed the characteristics of palliative care for HF in Japan. The present findings may aid in the development of effective end-of-life care systems.
4 0 0 0 OA Developing Multidisciplinary Management of Heart Failure in the Super-Aging Society of Japan
- 著者
- Yukihito Sato Takashi Kuragaichi Hiroyuki Nakayama Kozo Hotta Yuji Nishimoto Takao Kato Ryoji Taniguchi Koichi Washida
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0675, (Released:2022-12-23)
- 参考文献数
- 81
- 被引用文献数
- 3
The Japanese population is rapidly aging because of its long life expectancy and low birth rate; additionally, the number of patients with heart failure (HF) is increasing to the extent that HF is now considered a pandemic. According to a recent HF registry study, Japanese patients with HF have both medical and care-related problems. Although hospitalization is used to provide medical services, and institutionalization is used to provide care for frail older adults, it can be difficult to distinguish between them. In this context, multidisciplinary management of HF has become increasingly important in preventing hospital readmissions and maintaining a patient’s quality of life. Academia has promoted an increase in the number of certified HF nurses and educators. Researchers have issued numerous guidelines or statements on topics such as cardiac rehabilitation, nutrition, and palliative care, in addition to the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF. Moreover, the Japanese government has created incentives through various medical and long-term care systems adjustments to increase collaboration between these two fields. This review summarizes current epidemiological registries that focus not only on medical but also care-related problems and the 10 years of multidisciplinary management experience in Japanese medical and long-term care systems.
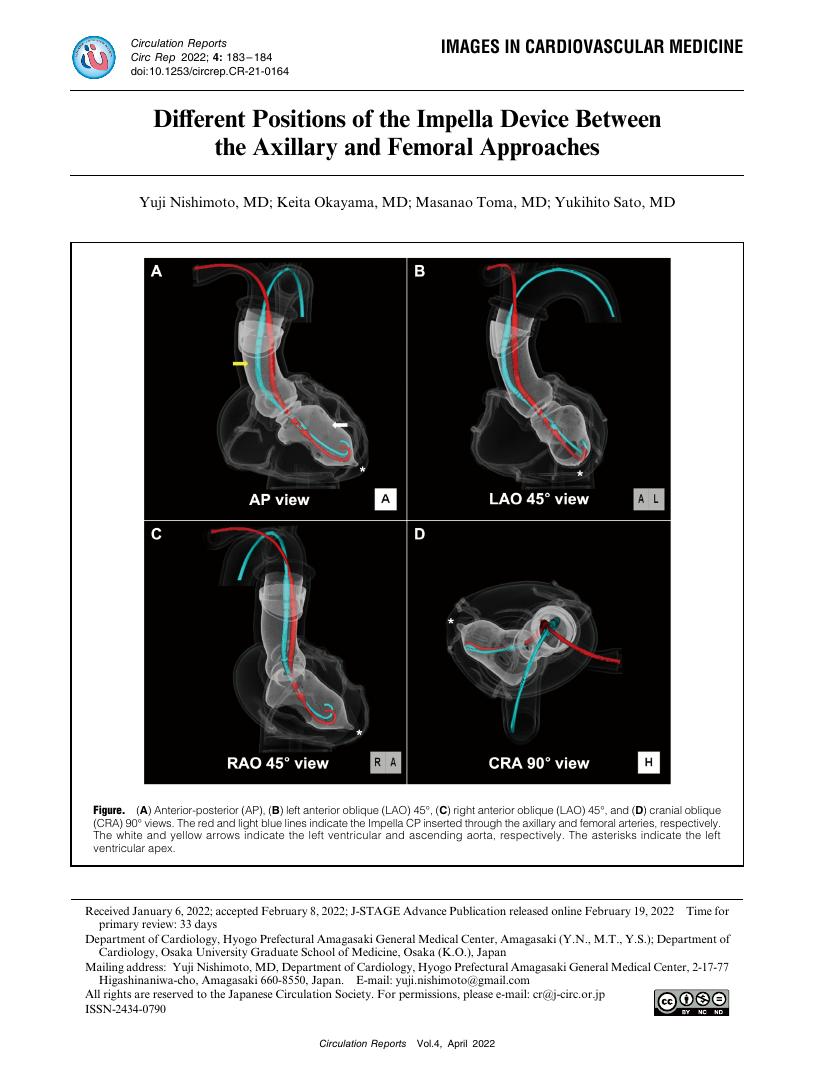
- 著者
- Yuji Nishimoto Ryosuke Hara Ryoji Taniguchi Masanao Toma Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.12, pp.742-743, 2021-12-10 (Released:2021-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Shuhei Tsuji Satoshi Koyama Ryoji Taniguchi Takako Fujiwara Hisayoshi Fujiwara Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.10, pp.456-461, 2019-10-10 (Released:2019-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background:Decreased skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) is a major complication of severe chronic heart failure (HF), but no appropriate indices have been developed to predict decreased SMI.Methods and Results:We enrolled patients with a structural heart disease or history of HF and collected body composition and blood sample data, including serum amino acid concentration. On multivariate logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, serum branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) concentration was a significant predictor of decreased SMI at 1-year follow-up.Conclusions:Serum BCAA concentration at baseline was significantly associated with decreased SMI at 1-year follow-up.
- 著者
- Yuji Nishimoto Keita Okayama Masanao Toma Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.4, pp.183-184, 2022-04-08 (Released:2022-04-08)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Yuji Nishimoto Yugo Yamashita Kitae Kim Takeshi Morimoto Syunsuke Saga Hidewo Amano Toru Takase Seiichi Hiramori Maki Oi Masaharu Akao Yohei Kobayashi Mamoru Toyofuku Toshiaki Izumi Tomohisa Tada Po-Min Chen Koichiro Murata Yoshiaki Tsuyuki Tomoki Sasa Jiro Sakamoto Minako Kinoshita Kiyonori Togi Hiroshi Mabuchi Kensuke Takabayashi Yusuke Yoshikawa Hiroki Shiomi Takao Kato Takeru Makiyama Koh Ono Yukihito Sato Takeshi Kimura on behalf of the COMMAND VTE Registry Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.11, pp.2006-2014, 2020-10-23 (Released:2020-10-23)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 21
Background:Patients with cancer-associated venous thromboembolism (VTE) are at high risk for recurrent VTE and are recommended to receive prolonged anticoagulation therapy if they are at a low risk for bleeding. However, there are no established risk factors for bleeding during anticoagulation therapy.Methods and Results:The COMMAND VTE Registry is a multicenter retrospective registry enrolling 3,027 consecutive patients with acute symptomatic VTE among 29 Japanese centers. The present study population consisted of 592 cancer-associated VTE patients with anticoagulation therapy. We constructed a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of the potential risk factors for major bleeding. During a median follow-up period of 199 days, major bleeding occurred in 72 patients. The cumulative incidence of major bleeding was 5.8% at 3 months, 13.8% at 1 year, 17.5% at 2 years, and 28.1% at 5 years. The most frequent major bleeding site was gastrointestinal tract (47%). Terminal cancer (adjusted HR, 4.17; 95% CI, 2.22–7.85, P<0.001), chronic kidney disease (adjusted HR, 1.89; 95% CI 1.06–3.37, P=0.031), and gastrointestinal cancer (adjusted HR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.04–3.04, P=0.037) were independently associated with an increased risk of major bleeding.Conclusions:Major bleeding events were common during anticoagulation therapy in real-world cancer-associated VTE patients. Terminal cancer, chronic kidney disease, and gastrointestinal cancer were the independent risk factors for major bleeding.
- 著者
- Yuta Seko Takao Kato Takeshi Morimoto Hidenori Yaku Yasutaka Inuzuka Yodo Tamaki Neiko Ozasa Masayuki Shiba Erika Yamamoto Yusuke Yoshikawa Yugo Yamashita Takeshi Kitai Ryoji Taniguchi Moritake Iguchi Kazuya Nagao Takafumi Kawai Akihiro Komasa Ryusuke Nishikawa Yuichi Kawase Takashi Morinaga Mamoru Toyofuku Yutaka Furukawa Kenji Ando Kazushige Kadota Yukihito Sato Koichiro Kuwahara Takeshi Kimura for the KCHF Study Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.10, pp.1547-1558, 2022-09-22 (Released:2022-09-22)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background: The clinical benefits of neurohormonal antagonists for patients with heart failure (HF) with mid-range and preserved ejection fraction (HFmrEF and HFpEF) are uncertain.Methods and Results: This study analyzed 858 consecutive patients with HFmrEF (EF: 40–49%) or HFpEF (EF ≥50%), who were hospitalized for acute HF, and who were discharged alive, and were not taking angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE)-I/ angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB) or β-blockers at admission. The study population was classified into 4 groups according to the status of prescription of ACE-I/ARB and β-blocker at discharge: no neurohormonal antagonist (n=342, 39.9%), ACE-I/ARB only (n=128, 14.9%), β-blocker only (n=189, 22.0%), and both ACE-I/ARB and β-blocker (n=199, 23.2%) groups. The primary outcome measure was a composite of all-cause death or HF hospitalization. The cumulative 1-year incidence of the primary outcome measure was 41.2% in the no neurohormonal antagonist group, 34.0% in the ACE-I/ARB only group, 28.6% in the β-blocker only group, and 16.4% in the both ACE-I/ARB and β-blocker group (P<0.001). Compared with the no neurohormonal antagonist group, both the ACE-I/ARB and β-blocker groups were associated with a significantly lower risk for a composite of all-cause death or HF hospitalization (HR: 0.46, 95% CI: 0.28–0.76, P=0.002).Conclusions: In hospitalized patients with HFmrEF and HFpEF, starting both ACE-I/ARB and a β-blocker was associated with a reduced risk of the composite of all-cause death or HF hospitalization compared with patients not starting on an ACE-I/ARB or β-blocker.
1 0 0 0 OA Concomitant Mitral Regurgitation in Severe Aortic Stenosis ― A Report From the CURRENT AS Registry ―
- 著者
- Ryosuke Murai Yuichi Kawase Tomohiko Taniguchi Takeshi Morimoto Kazushige Kadota Masanobu Ohya Takenobu Shimada Takeshi Maruo Yasushi Fuku Tatsuhiko Komiya Kenji Ando Michiya Hanyu Norio Kanamori Takeshi Aoyama Koichiro Murata Tomoya Onodera Fumio Yamazaki Takeshi Kitai Yutaka Furukawa Tadaaki Koyama Makoto Miyake Chisato Izumi Yoshihisa Nakagawa Kazuo Yamanaka Hirokazu Mitsuoka Manabu Shirotani Masashi Kato Shinji Miki Hiroyuki Nakajima Yutaka Hirano Shunichi Miyazaki Toshihiko Saga Sachiko Sugioka Shintaro Matsuda Mitsuo Matsuda Tatsuya Ogawa Kazuya Nagao Tsukasa Inada Shogo Nakayama Hiroshi Mabuchi Yasuyo Takeuchi Hiroki Sakamoto Genichi Sakaguchi Keiichiro Yamane Hiroshi Eizawa Mamoru Toyofuku Takashi Tamura Atsushi Iwakura Mitsuru Ishii Masaharu Akao Kotaro Shiraga Eri Minamino-Muta Takao Kato Moriaki Inoko Koji Ueyama Tomoyuki Ikeda Yoshihiro Himura Akihiro Komasa Katsuhisa Ishii Kozo Hotta Yukihito Sato Keiichi Fujiwara Yoshihiro Kato Ichiro Kouchi Yasutaka Inuzuka Shigeru Ikeguchi Senri Miwa Chiyo Maeda Eiji Shinoda Junichiro Nishizawa Toshikazu Jinnai Nobuya Higashitani Mitsuru Kitano Yuko Morikami Shouji Kitaguchi Kenji Minatoya Takeshi Kimura on behalf of the CURRENT AS Registry Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.3, pp.427-437, 2022-02-25 (Released:2022-02-25)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background:The clinical significance of concomitant mitral regurgitation (MR) has not been well addressed in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS).Methods and Results:We analyzed 3,815 patients from a retrospective multicenter registry of severe AS in Japan (CURRENT AS registry). We compared the clinical outcomes between patients with moderate/severe MR and with none/mild MR according to the initial treatment strategy (initial aortic valve replacement [AVR] or conservative strategy). The primary outcome measure was a composite of aortic valve-related death or heart failure hospitalization. At baseline, moderate/severe MR was present in 227/1,197 (19%) patients with initial AVR strategy and in 536/2,618 (20%) patients with a conservative strategy. The crude cumulative 5-year incidence of the primary outcome measure was significantly higher in patients with moderate/severe MR than in those with none/mild MR, regardless of the initial treatment strategy (25.2% vs. 14.4%, P<0.001 in the initial AVR strategy, and 63.3% vs. 40.7%, P<0.001 in the conservative strategy). After adjusting confounders, moderate/severe MR was not independently associated with higher risk for the primary outcome measure in the initial AVR strategy (hazard ratio [HR] 1.11, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.67–1.83, P=0.69), and in the conservative strategy (HR 1.13, 95% CI 0.93–1.37, P=0.22).Conclusions:Concomitant moderate/severe MR was not independently associated with higher risk for the primary outcome measure regardless of the initial treatment strategy.
- 著者
- Kozo Hotta Ryoji Taniguchi Hiroyuki Nakayama Fumitaka Yamaguchi Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- International Heart Journal Association
- 雑誌
- International Heart Journal (ISSN:13492365)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.21-102, (Released:2021-11-17)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 5
The aim of the present study was to determine whether the addition of an oral nutritional supplement with whey peptides and branched-chain amino acids for cardiac rehabilitation improves cardiopulmonary function, skeletal muscle function, and metabolism in CHF patients.In this randomized, parallel-group comparative pilot study, 20 CHF patients were randomly assigned to the nutrition group (n = 10) or the control group (n = 10). At baseline and 12 weeks, we performed physical examinations, motor function evaluation, clinical laboratory tests, nutritional status assessment, and echocardiography. The primary outcome was exercise tolerance, as determined by the cardiopulmonary stress test (CPX), 6-minute walking test (6MWT), and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels.During follow-up, body weight, body mass index, total muscle mass, and total lean mass did not change significantly in either group. The total fat mass significantly increased in the nutrition group (14.3 ± 5.4 kg versus 16.1 ± 5.5 kg, P < 0.001) but did not change in the control group, and the difference in the changes in total fat mass between groups was significant (−0.26 ± 0.96 kg versus 1.49 ± 0.63 kg, P < 0.001). The peakVO2 and 6-minute walk test (6 MWT) significantly increased in the nutrition group (14.6 ± 3.4 mL/minute/kg versus 15.8 ± 3.8 mL/minute/kg, P = 0.029; 346.9 ± 103.1 m versus 382.7 ± 102.1 m, P = 0.048; respectively) but did not change in the control group. The changes in peakVO2 and 6MWT did not significantly differ between the groups.The oral nutritional supplement for the treatment of CHF was effective for cardiac rehabilitation in terms of fat mass and exercise capacity.The present study demonstrated that oral nutritional supplements with whey peptides and branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) for cardiac rehabilitation in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) increased fat mass and exercise capacity. We conclude that whey peptides and BCAA supplementation may be a useful treatment for CHF patients.
- 著者
- Masahiro Natsuaki Takeshi Morimoto Hiroki Shiomi Ko Yamamoto Kyohei Yamaji Hirotoshi Watanabe Takashi Uegaito Mitsuo Matsuda Toshihiro Tamura Ryoji Taniguchi Moriaki Inoko Hiroshi Mabuchi Teruki Takeda Takenori Domei Manabu Shirotani Natsuhiko Ehara Hiroshi Eizawa Katsuhisa Ishii Masaru Tanaka Tsukasa Inada Tomoya Onodera Ryuzo Nawada Eiji Shinoda Miho Yamada Takashi Yamamoto Hiroshi Sakai Mamoru Toyofuku Takashi Tamura Mamoru Takahashi Tomohisa Tada Hiroki Sakamoto Takeshi Tada Kazuhisa Kaneda Shinji Miki Takeshi Aoyama Satoru Suwa Yukihito Sato Kenji Ando Yutaka Furukawa Yoshihisa Nakagawa Kazushige Kadota Takeshi Kimura on behalf of the CREDO-Kyoto PCI/CABG Registry Cohort-Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0526, (Released:2021-09-16)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background:Optimal intensity is unclear for P2Y12receptor blocker therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in real-world clinical practice.Methods and Results:From the CREDO-Kyoto Registry, the current study population consisted of 25,419 patients (Cohort-2: n=12,161 and Cohort-3: n=13,258) who underwent their first PCI. P2Y12receptor blocker therapies were reduced dose of ticlopidine (200 mg/day), and global dose of clopidogrel (75 mg/day) in 87.7% and 94.8% of patients in Cohort-2 and Cohort-3, respectively. Cumulative 3-year incidence of GUSTO moderate/severe bleeding was significantly higher in Cohort-3 than in Cohort-2 (12.1% and 9.0%, P<0.0001). After adjusting 17 demographic factors and 9 management factors potentially related to the bleeding events other than the type of P2Y12receptor blocker, the higher bleeding risk in Cohort-3 relative to Cohort-2 remained significant (hazard ratio (HR): 1.52 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.37–1.68, P<0.0001). Cohort-3 compared with Cohort-2 was not associated with lower adjusted risk for myocardial infarction/ischemic stroke (HR: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.87–1.06, P=0.44).Conclusions:In this historical comparative study, Cohort-3 compared with Cohort-2 was associated with excess bleeding risk, which might be at least partly explained by the difference in P2Y12receptor blockers.