- 著者
- Tomofumi Nakatsukasa Tomoko Ishizu Masumi Ouchi Nobuyuki Murakoshi Kimi Sato Masayoshi Yamamoto Kunio Kawanishi Yoshihiro Seo Masaki Ieda
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.12, pp.2029-2039, 2022-11-25 (Released:2022-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background: Elevated central venous pressure (CVP) in heart failure causes renal congestion, which deteriorates prognosis. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2-i) improves kidney function and heart failure prognosis; however, it is unknown whether they affect renal congestion. This study investigated the effect of SGLT2-i on the kidney and left ventricle using model rats with hypertensive heart failure.Methods and Results: Eight rats were fed a 0.3% low-salt diet (n=7), and 24 rats were fed an 8% high-salt diet, and they were divided into 3 groups of untreated (n=6), SGLT2-i (canagliflozin; n=6), and loop diuretic (furosemide; n=5) groups after 11 weeks of age. At 18 weeks of age, CVP and renal intramedullary pressure (RMP) were monitored directly by catheterization. We performed contrast-enhanced ultrasonography to evaluate intrarenal perfusion. In all high-salt fed groups, systolic blood pressure was elevated (P=0.287). The left ventricular ejection fraction did not differ among high-salt groups. Although CVP decreased in both the furosemide (P=0.032) and the canagliflozin groups (P=0.030), RMP reduction (P=0.003) and preserved renal medulla perfusion were only observed in the canagliflozin group (P=0.001). Histological analysis showed less cast formation in the intrarenal tubule (P=0.032), left ventricle fibrosis (P<0.001), and myocyte thickness (P<0.001) in the canagliflozin group than in the control group.Conclusions: These results suggest that SGLT2-i causes renal decongestion and prevents left ventricular hypertrophy, fibrosis, and dysfunction
- 著者
- Tomohiko Taniguchi Yuhei Hasegawa Kitae Kim Natsuhiko Ehara Yutaka Furukawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0205, (Released:2023-05-24)
2 0 0 0 OA Coronary Artery Aneurysm After Drug-Coated Balloon Angioplasty for Chronic Total Occlusion
- 著者
- Taishi Miyata Hiroyuki Yamamoto Tomofumi Takaya
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0149, (Released:2023-05-17)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Ikuo Fukuda Atsushi Hirayama Kazuo Kawasugi Takao Kobayashi Hideaki Maeda Mashio Nakamura Norikazu Yamada Tsubasa Tajima Michiya Tachiiri Yutaka Okayama Toshiyuki Sunaya Kazufumi Hirano Takanori Hayasaki
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0104, (Released:2023-05-27)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: The incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE; pulmonary embolism [PE] and/or deep vein thrombosis [DVT]) in Japan is increasing, but relatively small numbers of patients from Japan have been included in studies investigating rivaroxaban (a direct factor Xa inhibitor) for the treatment of VTE and preventing its recurrence.Methods and Results: An open-label, prospective, observational study (XASSENT [NCT02558465]) investigated the safety profile and effectiveness of rivaroxaban for ≤2 years in the treatment of VTE and prevention of its recurrence in Japanese clinical practice. Primary outcomes were major bleeding and symptomatic recurrent VTE. Statistical analyses were exploratory and descriptive. Overall, 2,540 patients were enrolled (safety analysis population [SAP], n=2,387; effectiveness analysis population [EAP], n=2,386). In the SAP, >80% of patients received the approved rivaroxaban dose, the mean (standard deviation) age was 66.6 (15.0) years, ≈74% were >50 kg, and 43% had a creatinine clearance ≥80 mL/min. PE+DVT, PE only, and DVT only were reported in 42%, 8%, and 50% of patients, respectively, and active cancer in 17% of patients. Major bleeding was reported in 69 patients (2.89%; 3.60%/patient-year; SAP) and symptomatic PE/DVT recurrence in 26 patients (1.09%; 1.36%/patient-year; EAP) during the treatment period.Conclusions: XASSENT provided information on the expected proportions of bleeding and VTE recurrence during rivaroxaban treatment in Japanese clinical practice; no new concerns of safety or effectiveness were found.
2 0 0 0 OA Acute Coronary Syndrome and Cancer ― Cardio-Oncology in the Super Aged Society in Japan ―
- 著者
- Hideki Ishii
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0203, (Released:2023-04-14)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 著者
- Taro Takeuchi Shumpei Kosugi Yasunori Ueda Kuniyasu Ikeoka Haruya Yamane Kohtaro Takayasu Takuya Ohashi Takashi Fukushima Kohei Horiuchi Takashi Iehara Mai Sakamoto Kazuho Ukai Shinya Minami Yuuki Mizumori Naoya Muraoka Masayuki Nakamura Tatsuhisa Ozaki Tsuyoshi Mishima Haruhiko Abe Koichi Inoue Yasushi Matsumura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0838, (Released:2023-04-12)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: It remains controversial whether a cancer history increases the risk of cardiovascular (CV) events among patients with myocardial infarction (MI) who undergo revascularization.Methods and Results: Patients who were confirmed as type 1 acute MI (AMI) by coronary angiography were retrospectively analyzed. Patients who died in hospital or those not undergoing revascularization were excluded. Patients with a cancer history were compared with those without it. A cancer history was examined in the in-hospital cancer registry. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiac death, recurrent type 1 MI, post-discharge coronary revascularization, heart failure hospitalization, and stroke. Among 551 AMI patients, 55 had a cancer history (cancer group) and 496 did not (non-cancer group). Cox proportional hazards model revealed that the risk of composite endpoint was significantly higher in the cancer group than in the non-cancer group (adjusted hazard ratio [HR]: 1.78; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.13–2.82). Among the cancer group, patients who were diagnosed as AMI within 6 months after the cancer diagnosis had a higher risk of the composite endpoint than those who were diagnosed as AMI 6 months or later after the cancer diagnosis (adjusted HR: 5.43; 95% CI: 1.55–19.07).Conclusions: A cancer history increased the risk of CV events after discharge among AMI patients after revascularization.
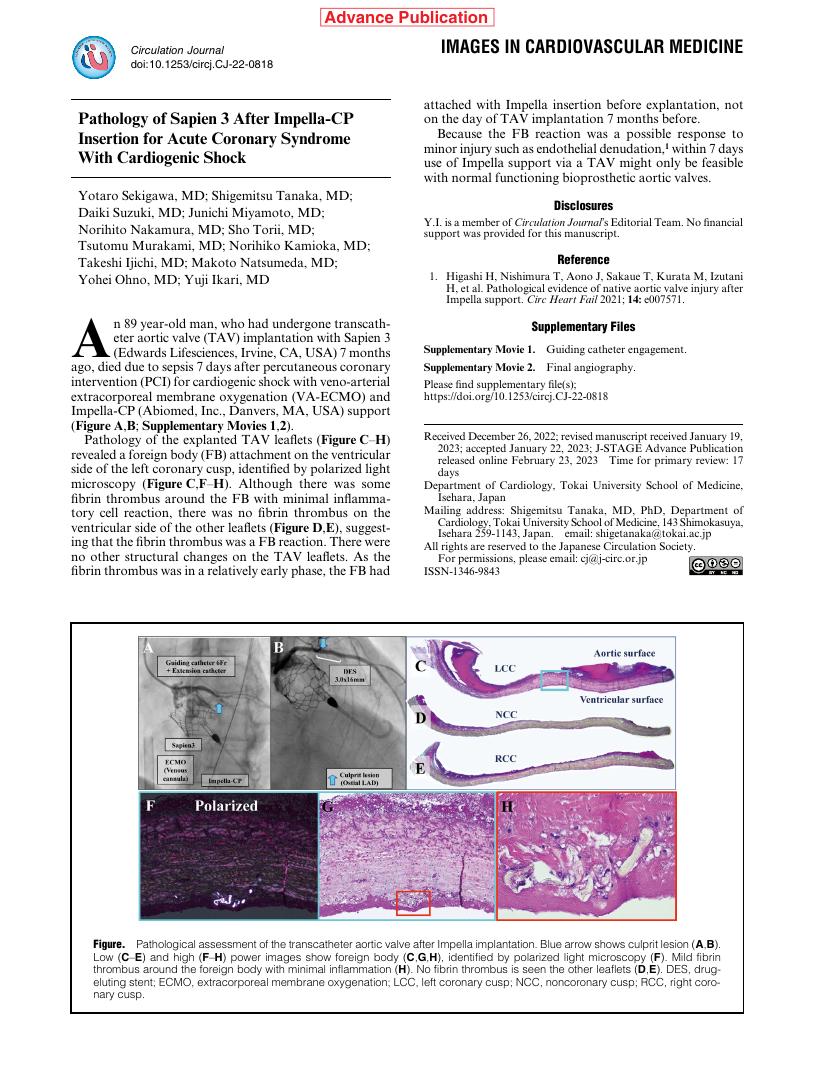
2 0 0 0 OA Pathology of Sapien 3 After Impella-CP Insertion for Acute Coronary Syndrome With Cardiogenic Shock
- 著者
- Yotaro Sekigawa Shigemitsu Tanaka Daiki Suzuki Junichi Miyamoto Norihito Nakamura Sho Torii Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Natsumeda Yohei Ohno Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0818, (Released:2023-02-23)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Koichi Inoue Tomoyuki Fujita Daisuke Yoshioka Kohei Tonai Yusuke Yanagino Takashi Kakuta Naoki Tadokoro Naonori Kawamoto Kizuku Yamashita Ai Kawamura Ryohei Matsuura Takuji Kawamura Tetsuya Saito Masashi Kawamura Satoshi Kainuma Satsuki Fukushima Koichi Toda Shigeru Miyagawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.12, pp.1961-1967, 2022-11-25 (Released:2022-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: The superiority of a fully magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow left ventricular assist device (LVAD) in terms of overall survival, stroke events and pump thrombosis has been demonstrated in previous international analyses, so we evaluated a Japanese cohort for the same.Methods and Results: This retrospective observational study was conducted at Osaka University Medical Hospital and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan. A total of 75 consecutive patients who underwent HeartMate3 (HM3) implantation were included. The primary endpoint was on-device survival, and the secondary endpoint was the incidence of LVAD-related complications at 2 years. All parameters were compared with those of the previously performed HeartMate II (HMII) implantation in 197 cases. The on-device survival rates were 94.7% and 92.3% in the HM3 and HMII groups, respectively, at the 2-year follow-up (P=0.62). The rehospitalization-free rate after implantation was 61.8% in the HM3 group, which was significantly higher than that in the HMII group (relative risk, 0.35; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.23–0.55; P<0.0001). Event-free survival rates from cerebral cerebrovascular events and pump thrombosis in the HM3 group were significantly higher than those in the HMII group, at 97.2% and 100%, respectively (relative risk, 0.14; 95% CI 0.03–0.58); P=0.0015 and relative risk, not calculated; P=0.049, respectively).Conclusions: Satisfactory short-term outcomes were observed after HM3 implantation in a Japanese cohort.
- 著者
- Hon-Kan Yip Pei-wen Wang Li-Teh Chang Ali A. Youssef Jiunn-Jye Sheu Fan-Yen Lee Chiung-Jen Wu
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.8, pp.1213-1218, 2007 (Released:2007-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 8 9
Background Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) is a particularly important molecule in down-regulating T-cell expansion and cytokine production. The purpose of the present study was to determine the frequency distribution of an A/G single nucleotide polymorphism at position 49 in exon 1 of the CTLA-4 gene, which may be a functional related-genetic risk marker for the development of ST-segment elevation (ST-se) acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Methods and Results A total of 503 consecutive patients, consisting of 250 ST-se AMI patients undergoing primary coronary angioplasty (group 1), 203 angina pectoris patients undergoing elective coronary angioplasty (group 2) and 50 patients with chest pain and normal coronary angiographic findings (group 3), were enrolled in the present study. The frequency of the G/G genotype was significantly higher in group 1 (53.2%) than in groups 2 (33.0%) and 3 (36.0%) (p=0.0005). In group 1, patients with a G/G genotype had significantly higher levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and white blood cell counts, and much higher incidences of multi-vessel disease, greater lesion lengths, advanced congestive heart failure (≥ class 3) and 30-day mortality, than patients with G/A or A/A genotypes (p values<0.05 in all cases). Multivariate analysis of the enrolled baseline variables (age, gender, diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) and the genotypes (G/G, A/G and A/A) demonstrated that G/G genotype is the only independent predictor of development of AMI (p<0.0001). Conclusion The G/G genotype polymorphism of the CTLA-4 gene is associated with increased risk of AMI. (Circ J 2007; 71: 1213 - 1218)
- 著者
- Hiroki Ikenaga Yukiko Nakano
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0014, (Released:2023-02-08)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 著者
- Takeshi Yagyu Sayaka Funabashi Shuichi Yoneda Teruo Noguchi Satoshi Yasuda
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.11, pp.1990-1998, 2020-10-23 (Released:2020-10-23)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 4 10
Background:Duplex ultrasound scanning (DUS) plays a major role in less invasive diagnosis and assessment of lesion severity in lower extremity peripheral artery disease (PAD). In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of each DUS parameter measured in patients with PAD and established a simple method for PAD evaluation.Methods and Results:We retrospectively investigated 211 patients (270 limbs) who underwent assessment with both angiography and DUS. During DUS of the common femoral artery (CFA) and popliteal artery, we measured 3 parameters: acceleration time (AcT), peak systolic velocity (PSV), and waveform contour. We compared these parameters with the degree of angiographic stenosis. AcT at the CFA had a significantly higher value in prediction of aortoiliac artery lesions with >50% stenosis (c-index, 0.85; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.79–0.91), with a sensitivity of 0.82 and specificity of 0.76 at the best cutoff point, compared with PSV and waveform contour (P<0.001, respectively). For femoropopliteal lesions, the ratio of AcT at the popliteal artery to AcT at the CFA is the most predictive parameter, with sensitivity of 0.86 and specificity of 0.92 at the best cutoff point (c-index, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.90–0.97), compared with others (P<0.001, respectively).Conclusions:For the assessment of PAD with DUS, AcT and AcT ratio are simple and reliable parameters for evaluating aortoiliac and femoropopliteal artery disease.
- 著者
- Yuji Mizuno Seiji Hokimoto Eisaku Harada Kenji Kinoshita Michihiro Yoshimura Hirofumi Yasue
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-16-0969, (Released:2016-11-29)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 16 22
Background:Coronary spastic angina (CSA) is common among East Asians and tobacco smoking (TS) is an established risk factor for CSA. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) plays a key role in removing reactive toxic aldehydes and a deficient variant ALDH2 genotype (ALDH2*2) is prevalent among East Asians. We examined the interaction between TS andALDH2*2as a risk factor for CSA to better understand the disease pathogenesis.Methods and Results:The study subjects comprised 410 patients (258 men, 152 women; mean age, 66.3±11.5) in whom intracoronary injection of acetylcholine was performed on suspicion of CSA.ALDH2genotyping was performed by direct application of the Taqman polymerase chain reaction system. Of the study subjects, 244 had CSA proven and 166 were non-CSA. The frequencies of male sex,ALDH2*2, alcohol flushing syndrome, TS, coronary organic stenosis, and plasma levels of uric acid were higher (P<0.001, P<0.001, P<0.001, P<0.001, P<0.001, and P=0.015, respectively) and that of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol lower (P=0.002) in the CSA than non-CSA group. Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed thatALDH2*2and TS were significant risk factors for CSA (P<0.001 and P=0.002, respectively).ALDH2*2exacerbated TS risk for CSA more than the multiplicative effects of each.Conclusions:ALDH2*2synergistically exacerbates TS risk for CSA, probably through aldehydes.
- 著者
- Toyonobu Tsuda Takeshi Kato Keisuke Usuda Takashi Kusayama Soichiro Usui Kenji Sakata Kenshi Hayashi Masa-aki Kawashiri Masakazu Yamagishi Masayuki Takamura Takayuki Otsuka Shinya Suzuki Akio Hirata Masato Murakami Mitsuru Takami Masaomi Kimura Hidehira Fukaya Shiro Nakahara Wataru Shimizu Yu-ki Iwasaki Hiroshi Hayashi Tomoo Harada Ikutaro Nakajima Ken Okumura Junjiroh Koyama Michifumi Tokuda Teiichi Yamane Yukihiko Momiyama Kojiro Tanimoto Kyoko Soejima Noriko Nonoguchi Koichiro Ejima Nobuhisa Hagiwara Masahide Harada Kazumasa Sonoda Masaru Inoue Koji Kumagai Hidemori Hayashi Kazuhiro Satomi Yoshinao Yazaki Yuji Watari Masaru Arai Ryuta Watanabe Katsuaki Yokoyama Naoya Matsumoto Koichi Nagashima Yasuo Okumura on behalf of the AF Ablation Frontier Registry and the Hokuriku-Plus AF Registry Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0461, (Released:2022-12-02)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Background: A recent randomized trial demonstrated that catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (EF) is associated with a reduction in death or heart failure. However, the effect of catheter ablation for AF in patients with heart failure with mid-range or preserved EF is unclear.Methods and Results: We screened 899 AF patients (72.4% male, mean age 68.4 years) with heart failure and left ventricular EF ≥40% from 2 Japanese multicenter AF registries: the Atrial Fibrillation registry to Follow the long-teRm Outcomes and use of aNTIcoagulants aftER Ablation (AF Frontier Ablation Registry) as the ablation group (525 patients who underwent ablation) and the Hokuriku-Plus AF Registry as the medical therapy group (374 patients who did not undergo ablation). Propensity score matching was performed in these 2 registries to yield 106 matched patient pairs. The primary endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure. At 24.6 months, the ablation group had a significantly lower incidence of the primary endpoint (hazard ratio 0.32; 95% confidence interval 0.13–0.70; P=0.004) than the medical therapy group.Conclusions: Compared with medical therapy, catheter ablation for AF in patients with heart failure and mid-range or preserved EF was associated with a significantly lower incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure.
- 著者
- Yoichi Hisata Akihiko Tanigawa Takafumi Yamada
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0391, (Released:2022-08-30)
- 参考文献数
- 2
- 著者
- Christian-Hendrik Heeger Kentaro Hayashi Karl-Heinz Kuck Feifan Ouyang
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.80, no.5, pp.1073-1086, 2016-04-25 (Released:2016-04-25)
- 参考文献数
- 53
- 被引用文献数
- 21 34
Ventricular arrhythmias (VA), like premature ventricular contractions (PVC) and ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients without structural heart disease (idiopathic VA), mainly arise from the right and left ventricular outflow tracts (RVOT/LVOT). The prognosis for OT VA is generally good in the majority of patients, but there is potential for developing dilated cardiomyopathies from the high burden of VA, as well as a certain risk for sudden cardiac death because of fast monomorphic VT or polymorphic VT triggered by short-coupling PVC. Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) has evolved into a widely accepted treatment strategy for patients suffering from VAs. A detailed knowledge of surface ECGs and complex cardiac anatomy, especially within the ventricular OTs, is essential for the understanding of cardiac OT-VAs and highly related to safe and successful RFCA procedures. This review article focuses on RFCA of idiopathic VA arising from the cardiac OT as well as adjacent regions and will illustrate recent insights and technical issues. (Circ J 2016; 80: 1073–1086)
- 著者
- Hideo Fujita
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.10, pp.1488-1489, 2022-09-22 (Released:2022-09-22)
- 参考文献数
- 9
2 0 0 0 OA Practice and Safety of Static Balloon Atrial Septostomy Based on a Nationwide Registry Data
- 著者
- Ryo Inuzuka Hisateru Tachimori Sung-Hae Kim Hikoro Matsui Tohru Kobayashi Atsuko Kato Takanari Fujii Mami Ho Hanako Morikawa Sara Takahashi Haruki Shirato Yuji Haishima Yoshihiro Okamoto Hideyuki Sakoda Hideshi Tomita
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0185, (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Balloon atrial septostomy (BAS) is an essential catheterization procedure for congenital heart lesions. Recently, a balloon catheter for static BAS was approved for the first time in Japan as an alternative to the conventional pull-through BAS. Despite the expected increase in the use of static BAS, reports on its safety are scarce worldwide.Methods and Results: Data on static and pull-through BAS registered in a national registry between 2016 and 2018 were collected. During the study period, 247 sessions of static BAS and 588 sessions of pull-through BAS were performed on a total of 674 patients. Patients who underwent static BAS were older (P<0.001). The incidence of serious adverse events (4.3% vs. 0.9%, P=0.03) and the overall incidence of adverse events (8.1% vs. 3.2%, P=0.03) were higher in static BAS than in pull-through BAS. Among patients who underwent static BAS, the risk factor for adverse events was a body weight <3 kg at the time of the procedure (odds ratio: 4.3 [confidence interval: 1.7–11], P=0.003).Conclusions: This nationwide study revealed differences in patient background between static and pull-through BAS, as well as a higher incidence of adverse events related to static BAS. Patients weighing <3 kg are at high risk for adverse events after static BAS and may require surgical and circulatory support backup.
- 著者
- Albert Youngwoo Jang Minsu Kim Pyung Chun Oh Soon Yong Suh Kyounghoon Lee Woong Chol Kang Ki Hong Choi Young Bin Song Hyeon-Cheol Gwon Hyo-Soo Kim Woo Jung Chun Seung-Ho Hur Seung-Woon Rha In-Ho Chae Jin-Ok Jeong Jung Ho Heo Junghan Yoon Soon Jun Hong Jong-Seon Park Myeong-Ki Hong Joon-Hyung Doh Kwang Soo Cha Doo-Il Kim Sang Yeub Lee Kiyuk Chang Byung-Hee Hwang So-Yeon Choi Myung Ho Jeong Chang-Wook Nam Bon-Kwon Koo Seung Hwan Han
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.9, pp.1365-1375, 2022-08-25 (Released:2022-08-25)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Background: Differences in the impact of the 1- or 2-stent strategy in similar coronary bifurcation lesion conditions are not well understood. This study investigated the clinical outcomes and its predictors between 1 or 2 stents in propensity score-matched (PSM) complex bifurcation lesions.Methods and Results: We analyzed the data of patients with bifurcation lesions, obtained from a multicenter registry of 2,648 patients (median follow up, 53 months). The patients were treated by second generation drug-eluting stents (DESs). The primary outcome was target lesion failure (TLF), composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (TVMI), and ischemia-driven target lesion revascularization (TLR). PSM was performed to balance baseline clinical and angiographic discrepancies between 1 and 2 stents. After PSM (N=333 from each group), the 2-stent group had more TLRs (hazard ratio [HR] 3.14, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.42–6.97, P=0.005) and fewer hard endpoints (composite of cardiac death and TVMI; HR 0.44, 95% CI 0.19–1.01, P=0.054), which resulted in a similar TLF rate (HR 1.40, 95% CI 0.83–2.37, P=0.209) compared to the 1-stent group. Compared with 1-stent, the 2-stent technique was more frequently associated with less TLF in the presence of main vessel (pinteraction=0.008) and side branch calcification (pinteraction=0.010).Conclusions: The 2-stent strategy should be considered to reduce hard clinical endpoints in complex bifurcation lesions, particularly those with calcifications.
- 著者
- Yasuhiro Hamatani Yasuko Takada Yoshihiro Miyamoto Yukie Kawano Yuta Anchi Tatsuhiro Shibata Atsushi Suzuki Mitsunori Nishikawa Hiroto Ito Masashi Kato Tsuyoshi Shiga Yoshihiro Fukumoto Chisato Izumi Satoshi Yasuda Hisao Ogawa Yasuo Sugano Toshihisa Anzai
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.4, pp.584-591, 2020-03-25 (Released:2020-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 13 17
Background:Palliative care is highly relevant for patients with heart failure (HF), and there is a need for quantitative information on quality of care. Accordingly, this study aimed to develop a set of quality indicators (QIs) for palliative care of HF patients, and to conduct a practical pilot measurement of the proposed QIs in clinical practice.Methods and Results:We used a modified Delphi technique, a consensus method that involves a comprehensive literature review, face-to-face multidisciplinary panel meeting, and anonymous rating in 2 rounds. A 15-member multidisciplinary expert panel individually rated each potential indicator on a scale of 1 (lowest) to 9 (highest) for appropriateness. All indicators receiving a median score ≥7 without significant disagreement were included in the final set of QIs. Through the consensus-building process, 35 QIs were proposed for palliative care in HF patients. Practical measurement in HF patients (n=131) from 3 teaching hospitals revealed that all of the proposed QIs could be obtained retrospectively from medical records, and the following QIs had low performance (<10%): “Intervention by multidisciplinary team”, “Opioid therapy for patients with refractory dyspnea”, and “Screening for psychological symptoms”.Conclusions:The first set of QIs for palliative care of HF patients was developed and could clarify quantitative information and might improve the quality of care.
- 著者
- Keisuke Miyake Nobuyoshi Azuma Chugo Rinoie Shusaku Maeda Akima Harada Liu Li Itsunari Minami Shigeru Miyagawa Yoshiki Sawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0257, (Released:2022-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Although regenerative cell therapy is expected to be an alternative treatment for peripheral artery disease (PAD), many regenerative cell therapies have failed to show sufficient efficacy in clinical trials. Most preclinical studies have used acute ischemia models, despite PAD being a chronic disease. In addition, aging and atherosclerosis decrease the quality of a patient’s stem cells. Therefore, using a non-acute ischemic preclinical model and stem cells with high regenerative potency are important for the development of effective regenerative therapy. In this study, we assessed the tissue regenerative potential of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (UCMSCs), which could potentially be an ideal cell source, in a rat model of established ischemia.Methods and Results: The regenerative capacity of UCMSCs was analyzed in terms of angiogenesis and muscle regeneration. In vitro analysis showed that UCMSCs secrete high amounts of cytokines associated with angiogenesis and muscle regeneration. In vivo experiments in a rat non-acute ischemia model showed significant improvement in blood perfusion after intravenous injection of UCMSCs compared with injection of culture medium or saline. Histological analysis revealed UCMSCs injection enhanced angiogenesis, with an increased number of von Willebrand factor-positive microcapillaries, and improved muscle regeneration.Conclusions: These results suggest that intravenous administration of UCMSCs may be useful for treating patients with PAD.