- 著者
- Teruhiko Imamura Shintaro Kinugawa Toshihiro Muramatsu Tsuyoshi Shiga Akiyoshi Ogimoto Toshihisa Anzai Nobuhisa Hagiwara Hiroyuki Tsutsui Issei Komuro Koichiro Kinugawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.10, pp.431-437, 2019-10-10 (Released:2019-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 8
Background:The vasopressin type-2 receptor antagonist tolvaptan is an essential tool in the management of decompensated heart failure (HF) in the inpatient setting for short-term use with careful monitoring. There is conflicting evidence, however, for its long-term use.Methods and Results:In this prospective, multi-center, open-labeled, randomized control trial, Assessment of QUAlity of life during long-term treatment of ToLVaptan in refractory HF (AQUA-TLV study), patients with congestive HF refractory to furosemide ≥60 mg/day were randomly assigned to a control group or tolvaptan add-on group and followed for 6 months, after confirmation of baseline urine osmolality ≥350 mOsm/L. Twenty-nine patients (median age, 60 years; 22 male) were enrolled and assigned to a control group (n=16) or a tolvaptan group (n=13). Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire score improved significantly in the tolvaptan group (from 58 to 10, P=0.030). In the tolvaptan group, diuretics dose reduced (P=0.001), serum creatinine decreased (P=0.040), and hyponatremia tended to improve (P=0.12). The tolvaptan group had a lower HF readmission rate compared with the control group (0.213 vs. 1.242 events/year, P=0.13).Conclusions:Six-month tolvaptan therapy improved quality of life and renal function and reduced HF readmissions, when given to the estimated responders (UMIN Clinical Trial Registry Number: UMIN 000009604).
- 著者
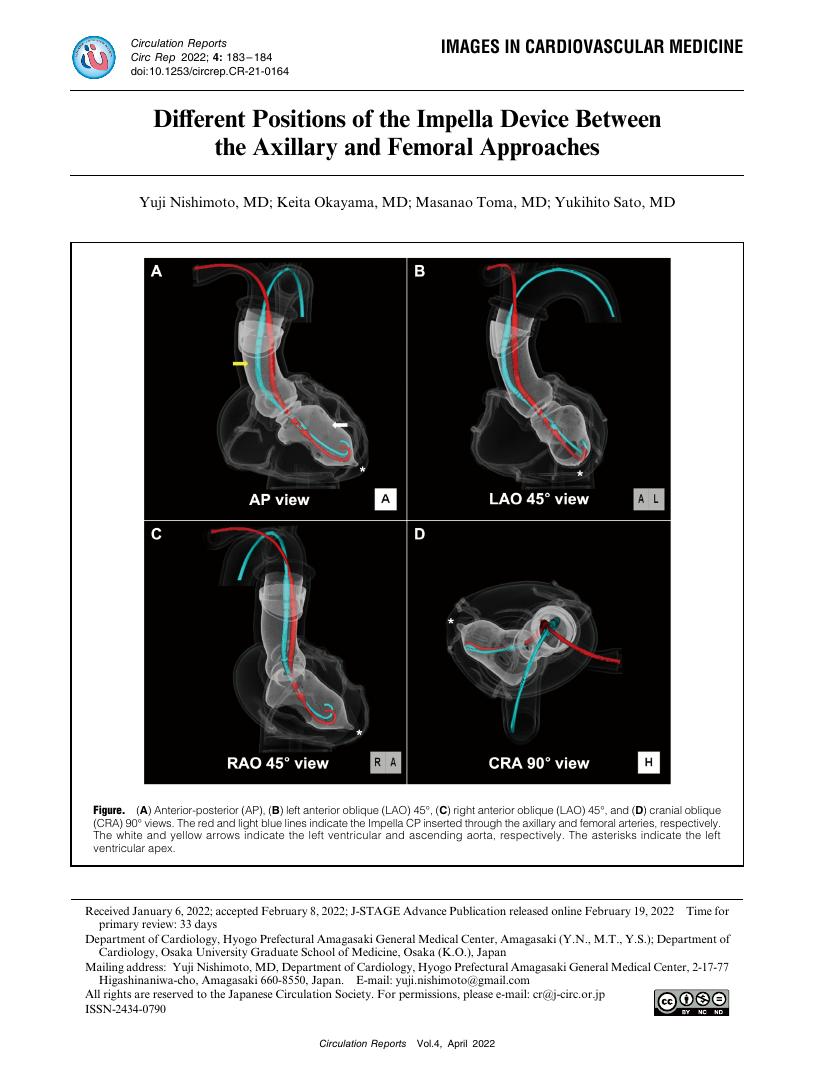
- Yuji Nishimoto Keita Okayama Masanao Toma Yukihito Sato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.4, pp.183-184, 2022-04-08 (Released:2022-04-08)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Takahiro Sakamoto Akihiro Endo Hiroyuki Yoshitomi Kazuaki Tanabe
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.7, pp.382-383, 2020-07-10 (Released:2020-07-10)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Yayoi Tetsuou Tsukada Eitaro Kodani Kuniya Asai Masahiro Yasutake Yoshihiko Seino Wataru Shimizu
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.2, pp.77-85, 2021-02-10 (Released:2021-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Background:Given the high prevalence of heart failure (HF) in the elderly, it is essential to establish medical coordination between general practitioners (GPs) and acute care hospitals (ACHs) in an aging society. The aim of this study was to elucidate the status of acceptance of elderly patients with HF and their management requirements in a comprehensive community health system. Furthermore, we investigated GPs’ interest in using information and communications technology (ICT) in patient care.Methods and Results:We sent a questionnaire survey to 1,800 GPs in January 2015 and received 392 replies. The overall prevalence of home visits was 55%, with no differences according to GP background characteristics or geographic area. However, less than half (44%) reported accepting patients with symptomatic HF for treatment in their clinic. In addition, only 3 GPs reported accepting and providing emergency visits for patients with refractory HF. In particular, GPs who were not certificated cardiologists, female, and older showed poorer acceptance of symptomatic HF patients. More than half the GPs wanted the prompt acceptance by ACHs of emergency patients, followed by strengthening of home care support at discharge and support for end-of-life care. Half the GPs were interested in telemedicine.Conclusions:ACHs must promptly accept patients with HF in cases of emergency and strengthen nursing care support at discharge. It is also necessary to consider how to support older and female GPs.
- 著者
- Tomoyuki Kabutoya Takeshi Mitsuhashi Akihiko Shimizu Takashi Nitta Hideo Mitamura Takashi Kurita Haruhiko Abe Yuji Nakazato Naokata Sumitomo Kazushige Kadota Kazuo Kimura Ken Okumura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.2, pp.69-76, 2021-02-10 (Released:2021-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background:There has been no large multicenter clinical trial on the prognosis of implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac resynchronization therapy with a defibrillator (CRT-D) in Japanese patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). The aim of the present study was to compare differences in the prognoses of Japanese patients with CAD between primary and secondary prevention, and to identify potential predictors of prognosis.Methods and Results:We investigated 392 CAD patients (median age 69 years, 90% male) treated with ICD/CRT-D enrolled in the Japan Implantable Devices in CAD (JID-CAD) Registry. The primary endpoint was all-cause death, and the secondary endpoint was appropriate ICD therapies. Endpoints were assessed by dividing patients into primary prevention (n=165) and secondary prevention (n=227) groups. The mean (±SD) follow-up period was 2.1±0.9 years. The primary endpoint was similar in the 2 groups (P=0.350).Conclusions:The mortality rate in Japanese patients with CAD who underwent ICD/CRT-D implantation as primary prevention was not lower than that of patients who underwent ICD/CRT-D implantation as secondary prevention, despite the lower cardiac function in the patients undergoing ICD/CRT-D implantation as primary prevention.
- 著者
- Takeshi Yamashita Yukiko Nakasu Hiroto Mizutani Kenji Sumitani
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.1, pp.34-43, 2021-01-08 (Released:2021-01-08)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background:The aim of the prospective post-marketing AF-CHF Landiolol Survey was to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of landiolol for the treatment of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter in patients with cardiac dysfunction in clinical practice in Japan. This analysis reports mid-term prognoses with a focus on switching from landiolol to oral β-blockers.Methods and Results:The AF-CHF Landiolol Survey took place between June 2014 and May 2016 and involved 1,121 patients with cardiac dysfunction and atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter. Data collected about switching from landiolol to oral β-blockers were analyzed in relation to all-cause mortality within 180 days after landiolol initiation. Among 1,002 patients with available follow-up data, the 6-month all-cause mortality rate was 14. 6% (n=146 patients), of whom 39.7% had died from heart failure (HF). Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed significantly longer survival in patients who had switched to oral β-blockers vs. those who had not, with hazard ratios of 0.39 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.28–0.55) for all-cause mortality and 0.40 (95% CI: 0.23–0.70) for death from HF. Only male sex and advanced age were independently associated with all-cause mortality and death from HF.Conclusions:This large-scale routine practice survey of landiolol in HF patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter showed high mid-term all-cause mortality. Switching from landiolol to oral β-blockers was apparently, although not independently, associated with lower all-cause mortality and death from HF.
- 著者
- Miho Nishitani-Yokoyama Hiroyuki Daida Kazunori Shimada Akiko Ushijima Keisuke Kida Yuji Kono Yasuhiko Sakata Masatoshi Nagayama Yutaka Furukawa Nagaharu Fukuma Keijiro Saku Shin-ichiro Miura Yusuke Ohya Youichi Goto Shigeru Makita for the Japanese Association of Cardiac Rehabilitation (JACR) Registration Committee
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.12, pp.715-721, 2020-12-10 (Released:2020-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background:Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is categorized as a Class I recommendation in guidelines for the management of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS); however, nationwide studies on CR in patients with ACS remain limited in Japan.Methods and Results:The Japanese Association of Cardiac Rehabilitation (JACR) Registry is a nationwide, real-world database for patients participating in CR. From the JACR Registry database, we analyzed 924 patients participating in Phase II CR in 7 hospitals between September 2014 and December 2016. The mean age of patients was 65.9±12.0 years, and 80% were male. The prevalence of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-STEMI (NSTEMI), and unstable angina pectoris (UAP) was 58%, 9%, and 33%, respectively. The prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, current smoking, and a family history was 55%, 27%, 67%, 21%, and 10%, respectively. Among the entire CR cohort at baseline, 96%, 78%, and 92% were treated with aspirin, β-blockers, and statins, respectively. After CR, the values of body mass index, the lipid profile, and exercise capacity significantly improved in the STEMI, NSTEMI and UAP groups.Conclusions:In the JACR Registry, a high rate of guideline-recommended medications at baseline and improvements in both coronary risk factors and exercise capacity after CR were observed in patients with ACS.
- 著者
- Bolrathanak Oeun Daisaku Nakatani Shungo Hikoso Takayuki Kojima Tomoharu Dohi Tetsuhisa Kitamura Katsuki Okada Akihiro Sunaga Hirota Kida Takahisa Yamada Masaaki Uematsu Yoshio Yasumura Yoshiharu Higuchi Toshiaki Mano Yoshiyuki Nagai Hisakazu Fuji Hiroya Mizuno Yasushi Sakata for the Osaka CardioVascular Conference (OCVC) Heart Failure Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.8, pp.400-408, 2020-08-07 (Released:2020-08-07)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background:Little is known about factors associated with elevated N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) at the convalescent stage and their effects on 1-year outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).Methods and Results:This study included 469 patients with HFpEF. Elevated NT-proBNP was defined as the highest quartile. The first 3 quartiles (Q1–Q3) were combined together for comparison with the fourth quartile (Q4). Median NT-proBNP concentrations in Q1–Q3 and Q4 were 669 and 3,504 pg/mL, respectively. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that low albumin (odds ratio [OR] 2.44; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.35–4.39; P=0.003), low estimated glomerular filtration rate (OR 5.83; 95% CI 3.46–9.83; P<0.001), high C-reactive protein (OR 2.09; 95% CI 1.21–3.63; P=0.009), and atrial fibrillation at discharge (OR 2.33; 95% CI 1.40–3.89; P=0.001) were associated with elevated NT-proBNP. Cumulative rates of all-cause mortality and heart failure rehospitalization were significantly higher in Q4 than in Q1–Q3 (P=0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). Incidence and hazard ratios of these adverse events increased when the number of associated factors for elevated NT-proBNP clustered together (P<0.001 and P=0.002, respectively).Conclusions:In addition to atrial fibrillation, extracardiac factors (malnutrition, renal impairment and inflammation) were associated with elevated NT-proBNP at the convalescent stage, and led to poor prognosis in patients with HFpEF.
- 著者
- Yoshito Kadoya Masahiko Hara Kosuke Takahari Yoko Ishida Masatake Tamaki
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.7, pp.351-356, 2020-07-10 (Released:2020-07-10)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Background:The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has tried to promote telemedicine since 2018, but faces difficulties in increasing the use of telemedicine partly due to a lack of clinical evidence. This study investigated the disease control status and safety of telemedicine, which, in Japan, is provided under the National Health Insurance system, for the treatment of lifestyle diseases under the present legal restraints.Methods and Results:This multicenter prospective observational study started in April 2018 and enrolled 34 patients with lifestyle diseases, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes. Primary and secondary outcome measures included control status, serial changes in clinical indices, and the safety of telemedicine 6 months after implementation. Control status was assessed by the attending physician, and differences in blood pressure (BP), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), or HbA1c levels were evaluated. Of the 34 patients, 29 were successfully introduced to telemedicine and followed-up for 6 months. Median patient age was 77 years, 14 (48.3%) were men, 24 (82.8%) had hypertension, 17 (58.6%) had dyslipidemia, and 9 (31.0%) had diabetes. At the 6-month follow-up, no patients had experienced exacerbation of underlying diseases, with no significant changes in BP, LDL-C, or HbA1c. Moreover, no telemedicine-associated adverse events were observed.Conclusions:Telemedicine can be a safe and feasible option for managing lifestyle diseases under the present legal restraints.
- 著者
- Jonathan Yap Fang Yi Lim Fei Gao Sinead Z. Wang Shoen C.S. Low Thu Thao Le Ru-San Tan
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.6, pp.306-313, 2020-06-10 (Released:2020-06-10)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background:Myocardial viability assessment in revascularization of ischemic heart failure remains controversial. This study evaluated the prognostic utility of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in ischemic heart failure.Methods and Results:This study retrospectively analyzed subjects with ischemic heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤35%, who underwent CMR at a single center in 2004–2014 before undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or optimal medical therapy (OMT). Analyses were stratified by treatment. Myocardial segments were deemed non-viable if LGE exceeded 50% wall thickness. Overall and anterior viability were assessed. Outcomes were all-cause mortality, cardiovascular (CV) mortality and major adverse CV events. Among 165 subjects (mean (±SD) age 57.5±8.5 years, 152 males), 79 underwent CABG and 86 received OMT. A greater number of non-viable segments was significantly associated with higher all-cause and CV mortality in the CABG group (adjusted hazard ratios 1.17 [95% confidence interval {CI} 1.01–1.37; P=0.04] and 1.25 [95% CI 1.01–1.56; P=0.045], respectively), but not in the OMT (P>0.05) group. Anterior wall viability did not affect outcomes.Conclusions:The extent of myocardial viability assessed by LGE appeared to identify patients with a differential survival benefit from CABG in this retrospective, small cohort study. These findings raise interesting hypotheses that need to be validated in larger prospective studies.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Kobayashi Yohei Sotomi Akio Hirata Yasushi Sakata Atsushi Hirayama Yoshiharu Higuchi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.6, pp.289-296, 2020-06-10 (Released:2020-06-10)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Background:The association between direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) dose and clinical outcomes when used with antiplatelets still remains to be investigated.Methods and Results:We conducted a prospective registry of non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) patients with DOAC: the DIRECT registry (n=2,216; follow-up, 407±388 days). We analyzed patients taking standard dose (n=907) and off-label reduced dose (n=338) DOAC in this sub-analysis. These patients were further stratified by add-on antiplatelets. Because DOAC dose was not randomly selected, potential confounding factors were eliminated through a propensity score-matching technique. The primary endpoint was clinically significant bleeding. The secondary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE; composite of all-cause death, all myocardial infarction, and stroke/systemic embolism). In patients with DOAC only/DOAC+antiplatelets, we successfully matched 212/62 patients who received off-label reduced dose DOAC with 212/62 standard dose patients. Off-label DOAC dose reduction did not have a significant impact on bleeding (HR, 1.123; 95% CI: 0.730–1.728, P=0.596) or MACE (HR, 1.107; 95% CI: 0.463–2.648, P=0.819) in patients with DOAC only, whereas in patients with add-on antiplatelets, off-label dose reduction significantly reduced bleeding (HR, 0.429; 95% CI: 0.212–0.868, P=0.019) without increasing MACE (HR, 2.205; 95% CI: 0.424–11.477, P=0.348).Conclusions:Reduced DOAC dose in combination with antiplatelet agents was associated with fewer bleeding complications than standard-dose therapy with no reduction in efficacy.
- 著者
- Yuji Nishizaki Hiroyuki Daida
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.4, pp.260-264, 2020-04-10 (Released:2020-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background:The n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), represented by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid, have anti-atherogenic effects (e.g., neutral fat-lowering effects) and other beneficial effects such as antiplatelet, anti-inflammatory, plaque stabilizing, vascular endothelial function ameliorative, antihypertensive, and anti-arrhythmic effects. Epidemiological studies and clinical trials have assessed the inhibitory effects of n-3 PUFA on cardiovascular events.Methods and Results:Studies that reported positive outcomes, such as the Japan EPA Lipid intervention Study (JELIS) and the Cardiovascular Risk Reduction with Icosapent Ethyl for Hypertriglyceridemia (REDUCE-IT), noted a tendency toward the use of high-dose n-3 PUFA (1.8–4 g/day). The Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell’Infarto Miocardico-Prevenzione (GISSI-Prevenzione) trial and the JELIS had high EPA/arachidonic acid (AA) baseline ratios. In contrast, negative outcome studies, such as the Outcome Reduction with an Initial Glargine Intervention (ORIGIN) trial, Risk and Prevention study, A Study of Cardiovascular Events in Diabetes (ASCEND), and the Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial (VITAL) had participants who tended to use low-dose n-3 PUFA (0.84–1 g/day) and to have low baseline EPA/AA.Conclusions:Differences in baseline EPA/AA ratio and the EPA/AA ratio threshold for the prevention of cardiovascular events seem to contribute to the different outcomes, together with the dose of n-3 PUFA.
- 著者
- Nobuhiro Nakanishi Koichi Kaikita Masanobu Ishii Yu Oimatsu Tatsuro Mitsuse Miwa Ito Kenshi Yamanaga Koichiro Fujisue Hisanori Kanazawa Daisuke Sueta Seiji Takashio Yuichiro Arima Satoshi Araki Taishi Nakamura Kenji Sakamoto Satoru Suzuki Eiichiro Yamamoto Hirofumi Soejima Kenichi Tsujita
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.3, pp.158-166, 2020-03-10 (Released:2020-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 51
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Background:Direct-activated factor X (FXa) plays an important role in thrombosis and is also involved in inflammation via the protease-activated receptor (PAR)-1 and PAR-2 pathway. We hypothesized that rivaroxaban protects against cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction (MI).Methods and Results:MI was induced in wild-type mice by permanent ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery. At day 1 after MI, mice were randomly assigned to the rivaroxaban and vehicle groups. Mice in the rivaroxaban group were provided with a regular chow diet plus rivaroxaban. We evaluated cardiac function by echocardiography, pathology, expression of mRNA and protein at day 7 after MI. Rivaroxaban significantly improved cardiac systolic function, decreased infarct size and cardiac mass compared with the vehicle. Rivaroxaban also downregulated the mRNA expression levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, transforming growth factor-β, PAR-1 and PAR-2 in the infarcted area, and both A-type and B-type natriuretic peptides in the non-infarcted area compared with the vehicle. Furthermore, rivaroxaban attenuated cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the non-infarcted area compared with the vehicle.Conclusions:Rivaroxaban protected against cardiac dysfunction in MI model mice. Reduction of PAR-1, PAR-2 and proinflammatory cytokines in the infarcted area may be involved in its cardioprotective effects.
- 著者
- Mitsuru Matsukura Junji Mochizuki Shinya Misawa Yoshiki Hata
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.12, pp.630-631, 2019-12-10 (Released:2019-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Ningyan Wong Khung Keong Yeo
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.10, pp.397-400, 2019-10-10 (Released:2019-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 7
In the United States and Europe, percutaneous edge-to-edge repair of the mitral valve with the MitraClip device for patients with severe degenerative mitral regurgitation who are at prohibitive surgical risk has been well-established. Recent randomized controlled trials have also demonstrated significant clinical benefits with the use of the device in selected patients with functional mitral regurgitation. Thus far, >80,000 patients in more than 50 countries have undergone the MitraClip procedure. Despite the exponential growth worldwide, the rate of MitraClip adoption in Asia has been more gradual. In addition, very few publications describe the use of MitraClip in Asian populations. This review aims to describe the Asian experience with the MitraClip device and the challenges faced.
- 著者
- Risako Nakao Michinobu Nagao Kenji Fukushima Akiko Sakai Eri Watanabe Masateru Kawakubo Shuji Sakai Nobuhisa Hagiwara
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-18-0024, (Released:2019-07-26)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background:We investigated the association between left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) and vortex flow (VF), and whether cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) response can be predicted using VF mapping (VFM) in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).Methods and Results:Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging data for 20 patients with heart failure (HF) with LVEF ≥40% and 25 patients with DCM with LVEF <40%, scheduled for CRT, were retrospectively analyzed. The maximum VF (MVF) on short-axis, long-axis and 4-chamber LV cine imaging were calculated using VFM. Summed MVF was used as a representative value for each case and was significantly greater for patients with DCM than for patients with HF with LVEF ≥40% (25.2±19.2% vs. 12.1±15.4%, P<0.005). Summed MVF was significantly greater for CRT responders (n=12, 35.8±22.7%) than for non-responders (n=13, 15.8±8.7%, P=0.04) during the mean follow-up period of 38.4 months after CRT. Patients with summed MVF ≥31.3% had a significantly higher major adverse cardiac event-free rate than those with MVF <31.3% (log-rank=4.51, P<0.05).Conclusions:On VFM analysis, LV VF interrupted efficient ejection in HF. Summed MVF can predict CRT response in DCM.
- 著者
- Taro Narumi Tetsu Watanabe Shigehiko Kato Harutoshi Tamura Satoshi Nishiyama Hiroki Takahashi Takanori Arimoto Tetsuro Shishido Masafumi Watanabe
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.6, pp.255-260, 2019-06-10 (Released:2019-06-10)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background:Insulin resistance as assessed using homeostasis model assessment ratio (HOMA-R) is associated with latent myocardial damage in apparently healthy subjects in health check. Meanwhile, diabetes mellitus (DM) is an unfavorable prognostic risk factor in patients with heart failure (HF). We examined the impact of pancreatic β-cell dysfunction on clinical outcomes in HF patients without DM.Methods and Results:This study enrolled 312 HF patients without DM. Pancreatic β-cell dysfunction was defined as HOMA-β <30%. A total of 108 patients (35%) had β-cell dysfunction. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide was higher in patients with pancreatic β-cell dysfunction compared with those without (625.2 vs. 399.0 pg/mL, P<0.001). On Kaplan-Meier analysis, a significantly higher cardiovascular events rate was observed in patients with pancreatic β-cell dysfunction (log-rank test, P=0.001), but there was no significant difference between patients with and without insulin resistance. On Cox hazard analysis, pancreatic β-cell dysfunction was independently associated with cardiovascular events after adjustment for confounding factors (HR, 1.58; 95% CI: 1.02–2.45), whereas insulin resistance was not associated with cardiovascular events.Conclusions:Pancreatic β-cell dysfunction, but not insulin resistance, was associated with unfavorable outcome in HF patients without DM.
- 著者
- Masaharu Kataoka Toru Satoh Hiromi Matsubara Koji Yamamoto Tsukasa Inada Kazunari Umezawa Tomohiko Takahashi Atsushi Nakano Keiichi Fukuda
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.6, pp.268-275, 2019-06-10 (Released:2019-06-10)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background:This retrospective study was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ambrisentan combination therapy with phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors in Japanese patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).Methods and Results:PAH patients who received ambrisentan for the first time in combination with a PDE5 inhibitor between January 2013 and the end of August 2015 were included in this study. Adverse drug reaction (ADR) safety analysis, as well as the efficacy analysis focusing on changes in clinical parameters, were investigated for overall cases and cases stratified by patient background. Forty-eight consecutive patients (n=21, 43.8% with idiopathic PAH; male/female, 18/30; average age, 43.3±17.4 years; World Health Organization functional class III/IV, n=22, 45.8%) who were treated with ambrisentan and a PDE5 inhibitor in Japan underwent the safety analysis. A total of 14 ADR occurred in 10 patients (20.8%). ADR included headache (8.3%), face edema (4.2%), angina pectoris (2.1%), hyperemia (2.1%), dyspnea (2.1%), pulmonary hypertension (i.e., worsening of PAH, 2.1%), nausea (2.1%), hepatic function abnormal (2.1%), edema (2.1%), and sudden death (2.1%). On analysis of hemodynamics parameters, there was a significant improvement in the mean pulmonary arterial pressure (−13.5 mmHg, P=0.0001) and pulmonary vascular resistance (−563.53 dyn·s·cm−5, P=0.0033).Conclusions:Ambrisentan combination therapy is safe and effective in hemodynamics improvement.
- 著者
- Takashi Yamauchi Hiroshi Takano Hiroaki Miyata Noboru Motomura Shinichi Takamoto
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.3, pp.131-136, 2019-03-08 (Released:2019-03-08)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: The aim of this study was to determine adequate indication for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). We analyzed risk factors of surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) not only for mortality, but also for morbidity, including long hospital stay (≥90 days) and patient activity at discharge, in patients who underwent SAVR for aortic stenosis (AS). Methods and Results: Using the Japan Adult Cardiovascular Surgery Database (JCVSD), 13,961 patients with or without coronary artery bypass grafting who underwent elective SAVR for AS were identified from January 2008 to December 2012. The hospital mortality rate was 3.1%. The percentage of patients who had long hospital stay (≥90 days) and who had moderately or severely decompressed activity at discharge (modified Rankin scale ≥4) was 2.9% and 6.5%, respectively. Eleven and 20 preoperative predictors of hospital mortality and morbidity, respectively, including long hospital stay and compromised status at discharge, were identified. Based on these risk factors, the risk model predicted hospital mortality (area under the curve [AUC], 0.732) and morbidity (AUC, 0.694). Conclusions: Using JCVSD, a risk model of SAVR was developed for AS. This model can identify patients at high risk not only for mortality, but also for mortality and morbidity, including long hospital stay and status at discharge.
- 著者
- Hirokazu Shimono Akihiro Tokushige Daisuke Kanda Ayaka Ohno Ryo Arikawa Hideto Chaen Hideki Okui Naoya Oketani Mitsuru Ohishi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-23-0087, (Released:2023-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 30
Background: This study aimed to compare the discriminative ability of the Japanese Version of High Bleeding Risk (J-HBR), Academic Research Consortium for High Bleeding Risk (ARC-HBR), and Predicting Bleeding Complications in Patients Undergoing Stent Implantation and Subsequent Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (PRECISE-DAPT) scores for predicting major bleeding events.Methods and Results: Between January 2017 and December 2020, 646 consecutive patients who underwent successful percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) were enrolled. We scored the ARC-HBR and J-HBR criteria by assigning 1 point to each major criterion and 0.5 point to each minor criterion. The primary outcome was major bleeding events, defined as Bleeding Academic Research Consortium type 3 or 5 bleeding events. According to the J-HBR, ARC-HBR, and PRECISE-DAPT scores, 428 (66.3%), 319 (49.4%), and 282 (43.7%) patients respectively had a high bleeding risk. During the follow-up period (median, 974 days), 44 patients experienced major bleeding events. The area under the curve (AUC) using the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curve for major bleeding events was 0.84, 0.82, and 0.83 within 30 days and 0.86, 0.83, and 0.80 within 2 years for the J-HBR, ARC-HBR, and PRECISE-DAPT scores, respectively. The AUC values did not differ significantly among the 3 bleeding risk scores.Conclusions: The J-HBR score had a discriminative ability similar to the ARC-HBR and PRECISE-DAPT scores for predicting short- and mid-term major bleeding events.