1 0 0 0 OA 教育講演 がん検診における血清CEA値の有用性に関する検討
- 著者
- 袁 萍 高橋 為生 関原 絹子 日野原 茂雄 岡崎 勲 藤森 一平
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本総合健診医学会誌 (ISSN:09111840)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.4, pp.385-390, 1993-12-20 (Released:2010-09-09)
- 参考文献数
- 17
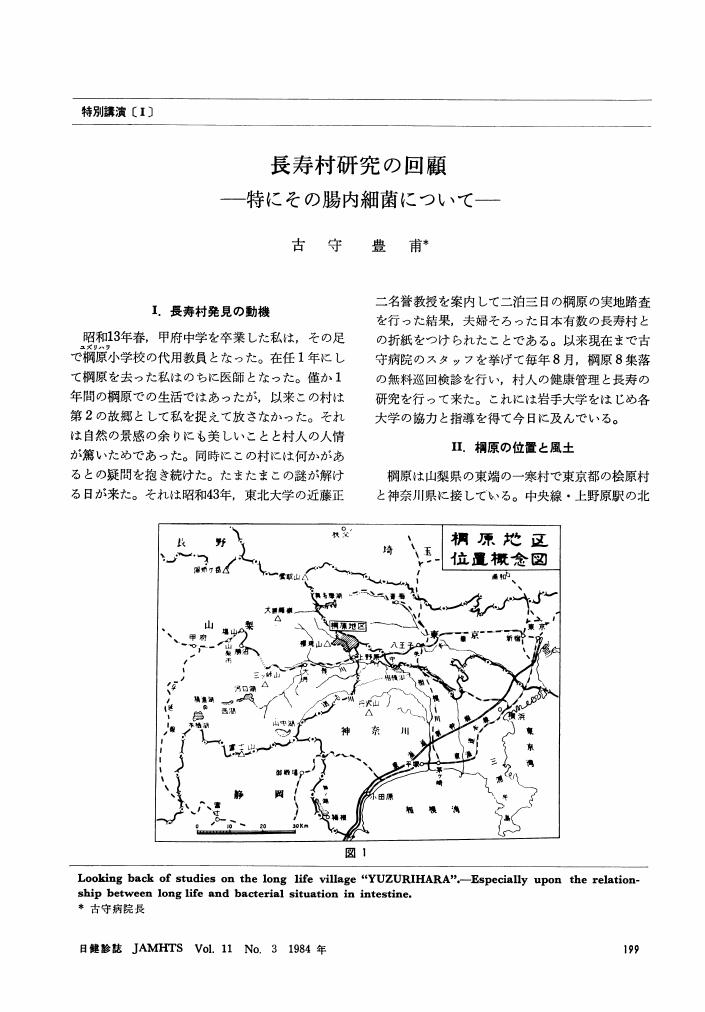
1 0 0 0 OA 特別講演 長寿村研究の回顧 ―特にその腸内細菌について―
- 著者
- 古守 豊甫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本自動化健診学会々誌 (ISSN:0386135X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.11, no.3, pp.199-209, 1984-09-25 (Released:2010-09-09)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 日本総合健診医学会第38回大会―特別講演1― 疫学と健診の接点
- 著者
- 田中 平三
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.6, pp.649-656, 2010 (Released:2013-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
According to UK National Screening Committee, screening is a public health service in which members of a defined population, who do not necessarily perceive that they are at risk of, or are already affected by, a disease or its complications, are asked a question or offered a test to identify those who are more likely to be helped than harmed by further tests or treatment to reduce the risk of disease or its complications. In Japan, the screening program to detect and control risk factors for stroke and coronary heart disease are established. Sensitivity, specificity and ROC curves should be applied to a test with continuous variable and a detectable preclinical phase of cancer. The only design that effectively eliminates the effect of lead time, length time, overdiagnosis and selection biases is the randomized controlled trial, but only if person-years mortality is used as the endpoint. In Japan, practically, the case-control study is a second-best method. In screening, those who are approached to participate are not patients and most of them do not become patients. The screener must build up a core of ethical principles that govern the relationship between screenee and screener like that between patient and physician.
1 0 0 0 OA 抗加齢医学の過去、現在、そして未来(総論)
- 著者
- 川北 哲也 坪田 一男
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.2, pp.212-222, 2011 (Released:2013-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 4
抗加齢医学(アンチエイジング医学)とは、加齢という生物学的プロセスに介入を行い、加齢に伴う動脈硬化や、がんのような加齢関連疾患の発症確率を下げ、健康長寿をめざす医学である。アンチエイジング医学が注目されてきた背景には、老化研究が進んだことにより老化が科学的に解明されはじめたことによる。 老化は避けられないものではなく、細胞生物学的なプロセスのひとつとであり、介入することにより遅らせることができる可能性があることがわかってきた。1980 年代までは、加齢のプロセスは非常に複雑で、とても介入など不可能であると考えられていた。現在でも加齢のメカニズムに関してはさまざまな説があるが、次第に研究や情報の整理により、徐々に加齢のメインメカニズムが解明されてきている。 現時点においては、酸化ストレスが老化のメカニズムに関わり、カロリーリストリクションにより介入できることは老化のサイエンスとして認識されてきている。 ヒトにおいては、カロリーリストリクションが寿命を延長するという確実なエビデンスはいまだ存在しないが、最近では、長寿の代謝マーカーとして低体温、低インシュリン血症、高DHEA-s 血症が、カロリーリストリクションをしたサルに認められたことが報告された。1)このカロリーリストリクションによる寿命延長には、Sir2/SirT1 というNAD 依存症ヒストン脱アセチル化酵素が重要な役割を果たしていることが明らかになってきた。運動に関しても、自発的な運動をさせたラットで約10%の寿命延長が観察されている。これらは、食事制限や適度な運動によって、老化過程で認められる動脈硬化などの病的現象が抑制される可能性を示している。 食事制限や適度な運動といった生活習慣の改善はヒトにおいても寿命を延長し、また健康にとってプラスになることが示唆されている。今後も老化に関するメカニズムが少しずつ明らかになり、ヒトの健康寿命の延長に貢献し、日本が健康大国となることを願ってやまない。
1 0 0 0 OA 総合健診における遺伝子関連検査
- 著者
- 山上 孝司
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.49, no.2, pp.255-262, 2022-03-10 (Released:2022-04-20)
- 参考文献数
- 10
遺伝性疾患として単一遺伝子病と多因子疾患の例を取り上げ、現在における遺伝子検査の現状、今後の課題について述べた。単一遺伝子病の中の遺伝性乳がん卵巣がん症候群については、BRCA1/2遺伝子の変異を持っている場合についての対策と、必要と思われる人にはこの遺伝子の検査を勧めて行くことが今後求められる。多因子疾患における遺伝要因の解析方法であるGWASの説明と、その1つの活用法であるPRSについて説明した。今後は、日本人のゲノムを使って各疾患ごとのGWASの解析とPRSの作成を行っていくことにより、日本人特有の遺伝要因の解析が進んでいくと思われる。 多因子疾患のうちのアルツハイマー病については、今後APOE遺伝子のアレルを調べる人が増えると思われ、リスクの高い人に対する生活上の注意点について述べた。冠動脈疾患については、たとえGWASやPRSによってリスクが高いと判定されても、生活習慣を望ましくすることで発症リスクを下げられることを受診者に話す必要がある。 多因子疾患の遺伝要因を説明するためには、ゲノムの構造だけでなくエピゲノムの変化も大事である。エピゲノムの変化は運動や喫煙、ストレスなどの生活習慣要因によって起こることを受診者に理解してもらい、行動変容に結び付けてもらうことが必要である。 総合健診に従事するものとして、家族歴、GWAS、PRSなどの結果から遺伝要因が強いと思われる受診者に対しては、その疾患の早期発見につながる検査を受診することを奨励するとともに、遺伝要因が強くても生活習慣の改善によって疾病の先送りが可能であることをよく説明して、環境整備やナッジも行使して、望ましい生活習慣の実践を後押しし、遺伝子関連検査が受診者にとってよいものとなるように常に研鑽を積む必要がある。
1 0 0 0 OA 全ゲノム情報を活用した世界の医療の現状
- 著者
- 岡﨑 康司
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.49, no.2, pp.271-277, 2022-03-10 (Released:2022-04-20)
- 参考文献数
- 14
臨床の現場においてエキソームや全ゲノムシーケンスを用いた精密医療が指数関数的に成長し、多くのラボでシーケンシングを検査のポートフォリオに入れつつある。全ゲノムシーケンスのコストは1人当たり10万円を切るようになってきたが、その解析を行い、臨床的意義について解釈するためには、膨大なデータを迅速かつ正確に処理する必要があり、ここには、シーケンス自体のコストの数倍のコストがかかる。全ゲノムシーケンスを用いたクリニカルシーケンスなどで、先頭を走る米国の施設を中心に、いくつかの事例を紹介し、Genomics Englandのプロジェクトについても解説する。全ゲノム情報を用いた解析から、最終的に臨床の現場で用いられるレポート作成までを行うツールは種々開発されつつあるが、本稿では、Genomics Englandのプロジェクトにおいて評価を得た、Fabric Genomics社が開発したツールを中心に、クリニカルシーケンスの現状についても紹介する。
- 著者
- 堀江 正知 中田 博文 上野 しおん 川波 祥子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.6, pp.671-678, 2016 (Released:2017-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 50
健康診断は、19世紀のアメリカ合衆国で、移民の感染症スクリーニングや保険加入者の資格審査として始まり、その後、健康志向のある会社役員の疾病予防対策として発展した。わが国では各種の法令で規定された結核対策として発展し、現在は、事実上、がんや循環器疾病のリスクに対する保健指導の機会となっている。科学論文のレビューによれば、対象疾病を特定せずに多項目の健康診断を行っても総死亡率が下がる確証はない。受診者に有益となる科学的根拠がなくても、一般市民、医療職、行政担当者は健康診断に大きな期待を寄せている。一方、本来の語意である健康度を診断する検査法は普及していない。労働衛生分野の健康診断は、「職場環境による曝露や影響を監視するサーベイランス」又は「職業性疾病を発見するスクリーニング」の機能を果たすべきである。生体試料を用いるサーベイランスは生物学的モニタリングとも呼ばれ、ILOや学術団体が示すガイドラインに準じて、心身への侵襲性がなるべく低い検査法を選択し、その結果は作業環境測定結果とも合わせて総合的に評価する。労働者に症状や所見を認めた場合は、職場や作業の実態を調査して関連性を評価し、職業性疾病を見逃さないように留意する。なお、雇入れ前に採用候補者を選別する健康診断は実施すべきでない。健康診断の関係者は、その企画、実施、結果報告、情報管理の各工程で、バイオエシックスに配慮して、受診者の自律、利益、安全、公平性を侵害しないように努める。特に、法定項目でない検査を行う際は本人の同意を取得する仕組みを確立する。また、安易に過剰な検査を実施しないように配慮し、ミスや誤診の防止対策を徹底する。適切な質を保障するには、健康診断を専門とする医療職が企画する段階から参画して、最新の科学を適用し、検査の精度を維持し、受診者がその結果を疾病予防や健康増進に役立てるよう促すことが望ましい。
1 0 0 0 OA 健康診断時の心電図自動診断で見逃したブルガダ症候群の一例
- 著者
- 岸谷 望加 山本 晃之 熊谷 宗晃 安田 洋二 西村 浩美
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.620-625, 2017 (Released:2017-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 17
【はじめに】ブルガダ症候群とは、心電図の右側前胸部誘導に特徴的なST上昇を呈し、突然に心室頻拍・心室細動を生じて、失神や突然死を生じる疾患として知られている。健診時の心電図で異常なしとされていたが、突然の心室細動にて救急搬送されブルガダ症候群が診断された一例を経験したので報告する。【症例】45歳、男性。2014年より継続して当施設の定期健康診断を受診していた。2014年2月初診時、身体所見に異常を認めなかった。また、自覚症状、既往歴とも特記すべき事はなかった。検査結果では、胸部X線所見は正常で、生化学検査ではT-cho: 256mg/dL、LDL-cho: 180mg/dL、TG: 161mg/dLと軽度高値を認める以外に異常を認めなかった。心電図は初回の2014年2月、2014年9月、2015年9月と3度受けていたが、いずれも心電図自動診断にて正常とされていた。2016年4月、夜間就寝時に突然意識消失をきたしているところを家人が発見し救急搬送となった。搬送先の病院にてブルガダ症候群と診断された。専門病院に転院後、植込み型除細動器の手術を受け、無事退院となった。【考察】健診時の心電図自動診断では異常なしとされており、saddle backタイプのブルガダ型心電図の波形が正常と診断されていた。最近の心電図自動診断のソフトはブルガダ型心電図の自動診断基準に対応しているが、そういった心電計においてもしばしばブルガダ型心電図が見逃され、不完全右脚ブロックやRSR’パターン等の判定にされる場合がある。ブルガダ型心電図の健診時の検出率は、0.14%~0.9%との報告があり、決して稀ではない。ブルガダ型心電図が疑われる場合には、実波形を確認すること、V1・V2誘導の一肋間上の誘導の波形を確認すること、以前の心電図とST部分の変化を確認することが、健診でブルガダ型心電図の見落としを防ぐために重要であると考えられた。
1 0 0 0 OA うつ病の新しい考え方
- 著者
- 大野 裕
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.2, pp.359-365, 2018 (Released:2018-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 4
うつ病などの精神疾患が単一の要因による疾患ではなく、複数の要因が関与した症状群だからである。したがって、治療に役立つ診断になるためには、単に症状だけに目を向けるだけではなく、発症に関与した可能性のある社会的、心理的、生物学的な要因を考慮し、一人の人として総合的に判断する“みたて”が極めて重要になってくる。そこで本稿では、世界的に用いられているアメリカ精神医学会の「精神疾患の診断・統計マニュアル第5版(DSM-5)」をもとに、うつ病の診断と治療の新しい考え方を紹介し、さらに職域における予防の可能性についても論じることにしたい。
1 0 0 0 採血による血管迷走神経反応の実態調査ならびにその対応について
- 著者
- 粟田 有紀 川﨑 エミ 大谷 美幸 酒田 伴子 新城 泰子 長田 三枝 大野 秀樹 大橋 秀一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.6, pp.623-628, 2015
【背景】血管迷走神経反応(vasovagal reaction: VVR)は、採血中や採血後に迷走神経興奮によって生じる諸症状を総称する。血圧低下、徐脈、吐き気などを示し、重症の場合には、意識消失、痙攣、失禁にいたる。不安や緊張によって起こりやすいと言われており、採血の副作用としては最も発生頻度が高いとされている。<br>【目的】健保連大阪中央病院健康管理センターにおけるVVRの実態調査を行い、対応策を作成する。<br>【方法】2012年11月から2013年10月までの1年間に、総受診者55,150名中VVRを発症した144名を対象として、発症率・性別・年齢・程度・採血体位・回復時間を調べた。程度の判定基準には厚生労働省の「血管迷走神経反応による症状群の程度別分類」を用いた。さらに看護師20名の意識調査を行い、これらを総合的に検討した。<br>【結果】VVR発症率は0.26%、男女比では女性が、年齢別では若年層が高い傾向となった。程度別では最も軽いⅠ度が128名(88.9%)、Ⅱ度が9名(6.3%)、Ⅲ度が7名(4.9%)となった。採血体位ではベッド上採血が全てⅠ度にとどまり、重症化を防いでいる事が分かった。回復時間は106名(73.6%)が5分以内に回復し、離床上の有用な目安となった。また、看護師の意識調査からⅡ度以上は15分間のベッド上安静が適切であると判断した。<br>【結語】健診での採血時VVRは高頻度ではないが特に若年者、女性に注意することが重要である。また離床上の目安としては5分毎のバイタルサイン測定を織り込んだ「採血によるVVR対応策」を作成することによって、一定の安全対策が確立できた。
1 0 0 0 OA 肺の構造と感染様式、臨床経過および重症化リスクについて
- 著者
- 桑平 一郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.2, pp.213-219, 2021-03-10 (Released:2021-04-20)
- 参考文献数
- 11
ヒトの肺には3億から5億の肺胞があり、肺胞の表面を肺胞上皮細胞が覆う。この中のⅡ型肺胞上皮細胞に、SARS-CoV-2 がドッキングする受容体であるアンギオテンシン変換酵素2(ACE2)が発現する。ウイルスはここから宿主細胞に侵入、感染が広がり肺炎を発症する。 発熱、全身倦怠感、咽頭痛、咳嗽、筋肉痛など風邪やインフルエンザのような症状が出現するが、下痢などの消化器症状や味覚障害や嗅覚障害もみられる。WHOによれば潜伏期間は1~14日間で、曝露から5日程度で発症することが多い。ヒトへの感染可能期間は、発症前2日から発症後7~14日間程度である。咳嗽やくしゃみなどを介する飛沫感染と接触感染が主体であり、一部エアロゾルも関与する。最近の報告では無症候者からの感染も40%あるいはそれ以上あるのではないかと言われる。厚生労働省による「新型コロナウイルス感染症(COVID-19)診療の手引き」によれば、発症から1週間程度で軽症のまま経過し改善する症例が80%、肺炎が悪化して入院を要する症例が残りの20%、そのうちICUでの加療を要する症例が5%、救命できない症例が2~3%と報告される。 重症化のリスク因子としては、65歳以上の高齢、基礎疾患としての悪性腫瘍、慢性閉塞性肺疾患(COPD)、慢性腎臓病、2型糖尿病、高血圧、高脂血症、固形臓器移植後の免疫不全の存在、そして肥満(BMI 30以上)、喫煙習慣などが挙げられる。性別では、男性の方が女性よりも死亡率が高い。 回復した後も、倦怠感、息切れ、関節痛、胸痛、慢性咳嗽が遷延する場合があり、味覚障害、嗅覚障害、口腔乾燥も認められる。ACE2受容体が全身臓器に分布することを考えれば、多様な症状が出現し、後遺症として残ることも理解できよう。これまでの普通の風邪とは様子が異なることも印象的である。
1 0 0 0 肺の構造と感染様式、臨床経過および重症化リスクについて
- 著者
- 桑平 一郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.2, pp.213-219, 2021
<p> ヒトの肺には3億から5億の肺胞があり、肺胞の表面を肺胞上皮細胞が覆う。この中のⅡ型肺胞上皮細胞に、SARS-CoV-2 がドッキングする受容体であるアンギオテンシン変換酵素2(ACE2)が発現する。ウイルスはここから宿主細胞に侵入、感染が広がり肺炎を発症する。</p><p> 発熱、全身倦怠感、咽頭痛、咳嗽、筋肉痛など風邪やインフルエンザのような症状が出現するが、下痢などの消化器症状や味覚障害や嗅覚障害もみられる。WHOによれば潜伏期間は1~14日間で、曝露から5日程度で発症することが多い。ヒトへの感染可能期間は、発症前2日から発症後7~14日間程度である。咳嗽やくしゃみなどを介する飛沫感染と接触感染が主体であり、一部エアロゾルも関与する。最近の報告では無症候者からの感染も40%あるいはそれ以上あるのではないかと言われる。厚生労働省による「新型コロナウイルス感染症(COVID-19)診療の手引き」によれば、発症から1週間程度で軽症のまま経過し改善する症例が80%、肺炎が悪化して入院を要する症例が残りの20%、そのうちICUでの加療を要する症例が5%、救命できない症例が2~3%と報告される。</p><p> 重症化のリスク因子としては、65歳以上の高齢、基礎疾患としての悪性腫瘍、慢性閉塞性肺疾患(COPD)、慢性腎臓病、2型糖尿病、高血圧、高脂血症、固形臓器移植後の免疫不全の存在、そして肥満(BMI 30以上)、喫煙習慣などが挙げられる。性別では、男性の方が女性よりも死亡率が高い。</p><p> 回復した後も、倦怠感、息切れ、関節痛、胸痛、慢性咳嗽が遷延する場合があり、味覚障害、嗅覚障害、口腔乾燥も認められる。ACE2受容体が全身臓器に分布することを考えれば、多様な症状が出現し、後遺症として残ることも理解できよう。これまでの普通の風邪とは様子が異なることも印象的である。</p>
1 0 0 0 OA 新型コロナウイルス感染症の基礎知識
- 著者
- 忽那 賢志
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.2, pp.220-228, 2021-03-10 (Released:2021-04-20)
- 参考文献数
- 52
1 0 0 0 OA 第19回日本総合健診医学会学術大会講演抄録集 協栄生命助成研究 肥満者における生活習慣と性格上の特徴, および血圧と肥満の関連について: 有効性の高い減量指導法のための基礎的検討
- 著者
- 久代 登志男 奥村 英孝 高橋 行子 平野 真澄 柳井 晴夫 山越 一恵
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本総合健診医学会誌 (ISSN:09111840)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.2, pp.175-177, 1991-06-05 (Released:2010-09-09)
- 参考文献数
- 4
1 0 0 0 OA 肥満と肥満症の診断基準
- 著者
- 小川 渉 宮崎 滋
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.2, pp.301-306, 2015 (Released:2015-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 10 17
肥満は2型糖尿病や脂質代謝異常症、高血圧に代表されるような動脈硬化性疾患のリスク因子に加え、蛋白尿や非アルコール性脂肪肝(non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: NAFLD)、高尿酸血症など様々な疾患・病態の発症基盤となることから、肥満をどのように診断し、どのような対象に介入を行うかは重要である。わが国では欧米のような高度の肥満者は少ないにも関わらず、2型糖尿病や脂質異常症、高血圧などの肥満に関連する疾患の有病率は比較的高いことから、欧米より厳しい基準で肥満を診断することは妥当と考えられる。日本肥満学会では、肥満に関連する健康障害の有病率に関する疫学調査などから、BMI18.5以上25未満を普通体重とし、これを超えるものを肥満、下回る者を低体重と定義している。また、肥満の中でも、医学的に減量を必要とする病態を肥満症と呼び一つの疾患単位として捉えることを提唱してきた。肥満症の考え方として、現在健康障害を持つものだけではなく、将来健康障害を発症する可能性が高いものを含む点が重要である。内臓脂肪型肥満が健康障害を伴いやすいハイリスク肥満であることは知られている。内臓脂肪型肥満の診断手順は、ウェスト周囲長によるスクリーニングの後、腹部CT検査により内臓脂肪面積を測定する。一方、日本人間ドック学会・健康保険組合連合会により公表された「新たな検診の基本検査の基準範囲」は、特定の疾患を持たず、特定の疾患の薬物治療を受けていない集団の平均的なBMIの分布範囲を示したものにすぎない。この基準範囲にはハイリスク肥満である内臓脂肪型肥満が含まれており、これらは減量介入が必要な肥満症患者であることを強調したい。健診や人間ドックに従事される方は、これらの診断基準や基準範囲の設定の手法、目的の差異を十分に理解の上、業務にあたられたい。
- 著者
- 久代 登志男 奥村 英孝 高橋 行子 平野 真澄 柳井 晴夫 山越 一恵
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本総合健診医学会誌 (ISSN:09111840)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.2, pp.175-177, 1991
1 0 0 0 OA 精度管理研修記録 個人データの変動要因 ―健診結果の解釈―
- 著者
- 田内 一民
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本総合健診医学会誌 (ISSN:09111840)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.3, pp.384-390, 2001-09-30 (Released:2010-09-09)
- 参考文献数
- 5
検体検査の健診結果の判定は基準範囲から設定した判定基準に照らし合わせ, 受診者の臨床症状を考慮し受診者に報告する。しかし, 個人データを経時的に観察し, 個人差を考慮すればより細かい判定が可能である。検査データの変動は生活習慣の変化が要因になっている場合が多い。予防医学的な見地からは基準範囲内の変化であっても生活習慣を改善することが必要な場合も出てくる。
1 0 0 0 OA 日本総合健診医学会 第44回大会・シンポジウム1 総合健診とロコモティブシンドローム:総合健診における高齢者健診の実施に向けて 総合健診における高齢者健診の必要性:フレイルとサルコペニアを中心にして
- 著者
- 道場 信孝 久代 登志男 日野原 重明
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.3, pp.447-454, 2016 (Released:2016-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
今日、高齢者の健康評価においてフレイルが主要な関心事になってきている。フレイルは2014年に日本老年医学会がfrailtyの訳語として決めた表現であるが、これはfrailtyのスクリーニングのために以下の単語の頭文字を並べたものと思われる:F(fatigue)、R(resistance: inability to walk up a flight of stairs)、A(ambulation: inability to walk a short distance)、I(Illnesses:5種以上の疾病)、L(Loss of body mass:5%以上の体重減)。今回はfrailtyとsarcopeniaの概略を述べるが、まずフレイルについてはFriedら(2001)が臨床の実在として挙げた5項目(体重の減少、サルコペニア、握力、疲れやすさ、歩行速度の低下)の基準と生存曲線に基づくフレイルの診断基準の正当性、次いで身体・精神・社会的機能と恒常性の維持機能との関わりにおけるフレイルの理解(Langら:2013)、そしてRockwoodら(2005)のCanadian Study for Health and Agingにもとづくフレイルの重症度診断(clinical frailty scale)について述べる。Sarcopeniaについては、European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Oldr People(EWGSOP, 2010)によって示されたコンセプト、研究および臨床における評価基準、そして診断基準について解説する。サルコペニアはフレイルのコンセプトの中で最も重要な位置づけにあり、その評価は量と質の両面からなされなければならないが、特に臨床診断では徒手法が極めて有用であり、その手法の習得は十分な臨床経験を通じて培われる。最後に、近年注目されるようになったsarcopenic obesityは重要な健康障害であり、これは脂肪が筋肉の中に浸潤する現象であって筋肉の機能を著しく障害する。脂肪細胞はそれ自体activeな内分泌器官であり、そこからは炎症性のサイトカインやホルモンが放出され、それらによって筋肉は質・量ともに変化する。フレイルに対する予防と治療の戦略においては食事と運動が主要であり、その他インフルエンザ、肺炎球菌による肺炎、帯状疱疹などに対するワクチン療法が勧められる。同時に諸種の併存病を適切に治療しておかなければならない。
1 0 0 0 OA 当院健診受診者における血中亜鉛濃度の世代別調査について
- 著者
- 吉永 眞人 池田 裕子 樽井 里佳 松永 朋子 上村 雄一郎 横田 真弓
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.2, pp.273-275, 2019-03-10 (Released:2019-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 被引用文献数
- 1
【はじめに】100種類以上の酵素の構成要因として生体の様々な代謝系の調整に関与し、重要な微量元素の一つとされる亜鉛は、蛋白質合成・代謝などの生命維持に関係し、亜鉛の摂取については肉類・魚類・種実類からが主とされる。特に亜鉛欠乏症においては味覚障害・舌痛・貧血・食欲不振など様々な症状が表れ、近年注目される指標の一つとされるが、各医療機関において、あまり測定されていないのが現状である。今回、我々は当院健診受診者を対象に血中亜鉛濃度を測定し、世代別に有意な差が存在するか検討した。【対象者および対象期間】2017年7月から12月までの当院健診受診者を対象とした。【測定方法】採血は原則空腹時の早朝採血(午前8:30~9:30)。 血清亜鉛値の測定は、生化学自動分析器LABOSPECT008(株式会社日立ハイテクノロジーズ)およびアキュラスオートZn(株式会社シノテスト)を使用。各年代別の血清を用い比較した。【検討方法】 ①年代別および男女別で血清亜鉛値を比較 ②「亜鉛欠乏症の診療指針」に挙げられる血清ALP活性値・血清亜鉛値について比較 ③炎症マーカー(CRP)と血清亜鉛値との比較【結果および考察】各年代別に血清亜鉛値を比較した場合、20代男性が最も高く40代女性が最も低い結果であったが、年代別および男女別で明らかな有意差は認めなかった。 亜鉛欠乏が疑われる血清ALP活性値が 150U/L以下では血清亜鉛値基準値下限 80μg/dLを下回る割合が多く、活性値低下の一つの要因になっているのではないかと推測された。また、女性の20代から40代および60歳以上では約4割近くで、潜在性亜鉛欠乏が疑われた。 炎症マーカー(CRP)と血清亜鉛値は負の相関関係を認めた。 日本人の1日当たりの亜鉛摂取推奨量は、成人男性 10mg女性 8mgとされるが、その摂取量は男女ともに不足ぎみで、症状はなくとも日頃の食生活の偏りで亜鉛欠乏は潜在的に起こりうる。食生活を意識的に改善することが重要であり、それを知る上で血清亜鉛測定の有用性が示唆された。
- 著者
- 井部 俊子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本総合健診医学会
- 雑誌
- 総合健診 (ISSN:13470086)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.3, pp.443-446, 2016
健診事業を受診者の視点で捉え、「健診サービス」の特徴をサービスビジネスとして検討した。<br> サービスの特徴は、①無形性、②生産と消費の同時性、③異質性、④結果と過程、⑤共同生産であり、とりわけ顧客との共同生産は、サービス内容の決定や品質管理、学習、マーケティングの機能があることを述べた。<br> では、健診サービスを受ける顧客(受診者)はどのような経験をしているのかを探るため受診者にインタビューを実施した。4人のナラティブからみえてきたことは、①受診者はそれぞれの思い(受診理由)がある。②受診者は健診結果に関心を集中している。③健診サービス提供者との関係は「ドライな距離感」がよい。④しかし、「今年もお会いできてよかった」と言ってくれるつながりがあると保健指導の価値が高まる。