- 著者
- Ai Ebisui Ryo Inose Yoshiki Kusama Ryuji Koizumi Ayako Kawabe Saki Ishii Ryota Goto Masahiro Ishikane Tetsuya Yagi Norio Ohmagari Yuichi Muraki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.6, pp.816-821, 2021-06-01 (Released:2021-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance is a major issue worldwide. Drug resistance is related to inappropriate antibiotic use. Because antipseudomonal agents have a wide spectrum, they must be used appropriately. The purpose of this study was to clarify the trends in antipseudomonal agent use in Japan based on sales data from 2006 to 2015. The total antipseudomonal agent use was increased significantly (r = 0.10, Pfor trend = 0.00040). The proportion of fluoroquinolones use was the highest throughout the year, accounting for 88.6–91.4%. The use of piperacillin/tazobactam significantly increased. The increased use of these drugs may be due to the launch of higher doses and additional indications. On the other hand, for antipseudomonal agents, parenteral carbapenems use was 2.7–3.7%, but it has remained unchanged over the years. In Japan, permit and notification systems have been introduced to prevent the inappropriate use of parenteral carbapenems in medical institutions. It was speculated that these efforts suppressed the inappropriate use of parenteral carbapenems. This study clarified the trend of antipseudomonal agent use in Japan from 2006 to 2015. It is important to continue monitoring antipseudomonal agents use to conduct appropriate antimicrobial resistance measures.
- 著者
- Chieri Fujino Seigo Sanoh Toshiya Katsura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.11, pp.1617-1634, 2021-11-01 (Released:2021-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 219
- 被引用文献数
- 18
The CYP3A subfamily, which includes isoforms CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7 in humans, plays important roles in the metabolism of various endogenous and exogenous substances. Gene and protein expression of CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7 show large inter-individual differences, which are caused by many endogenous and exogenous factors. Inter-individual differences can cause negative outcomes, such as adverse drug events and disease development. Therefore, it is important to understand the variations in CYP3A expression caused by endo- and exogenous factors, as well as the variation in the metabolism and kinetics of endo- and exogenous substrates. In this review, we summarize the factors regulating CYP3A expression, such as bile acids, hormones, microRNA, inflammatory cytokines, drugs, environmental chemicals, and dietary factors. In addition, variations in CYP3A expression under pathological conditions, such as coronavirus disease 2019 and liver diseases, are described as examples of the physiological effects of endogenous factors. We also summarize endogenous and exogenous substrates metabolized by CYP3A isoforms, such as cholesterol, bile acids, hormones, arachidonic acid, vitamin D, and drugs. The relationship between the changes in the kinetics of these substrates and the toxicological effects in our bodies are discussed. The usefulness of these substrates and metabolites as endogenous biomarkers for CYP3A activity is also discussed. Notably, we focused on discrimination between CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7 to understand inter-individual differences in CYP3A expression and function.
- 著者
- Da Hye Hong Hongliang Li Han Sol Kim Hye Won Kim Sung Eun Shin Won-Kyo Jung Sung Hun Na Il-Whan Choi Amy Leanne Firth Won Sun Park Dae-Joong Kim
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.8, pp.1208-1213, 2015-08-01 (Released:2015-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 10 10
We demonstrated the inhibitory effect of fluvoxamine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), on voltage-dependent K+ (Kv) channels in freshly isolated rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells using a whole-cell patch clamp technique. Fluvoxamine reduced the amplitude of Kv currents in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 3.71±1.09 µM and a Hill coefficient of 0.62±0.14. Although fluvoxamine did not significantly affect the steady-state activation curve, it shifted the steady-state inactivation curve toward a more negative potential. Pretreatment with another SSRI, paroxetine, did not affect the basal Kv current and did not alter the inhibitory effect of fluvoxamine on Kv channels. We concluded that fluvoxamine inhibits the Kv current in a concentration-dependent manner and in a closed (inactivated) state of the Kv channels independent of serotonin reuptake inhibition.
- 著者
- Yoichi Sunagawa Nobuko Okamura Yusuke Miyazaki Kana Shimizu Mai Genpei Masafumi Funamoto Satoshi Shimizu Yasufumi Katanasaka Eriko Morimoto Hajime Yamakage Maki Komiyama Noriko Satoh-Asahara Hiromichi Wada Mika Suzuki Koji Hasegawa Tatsuya Morimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.4, pp.504-509, 2018-04-01 (Released:2018-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 2 7
Neck and shoulder stiffness is a typical subjective symptom in developed countries. This stiffness is caused by factors such as muscle tension and poor blood flow, leading to reduce work efficiency and diminish QOL. NKCP®, a natto-derived dietary food supplement whose main component is bacillopeptidase F, has antithrombotic, fibrinolytic, and blood viscosity-lowering effects. Here, we investigated the effect of NKCP® on neck and shoulder stiffness in a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized crossover study. Thirty subjects with neck and shoulder stiffness were randomly divided into 2 groups and ingested 250 mg of NKCP® or placebo daily for 4 weeks. Headache score significantly improved in the NKCP® group compared to the placebo group. Moreover, NKCP® significantly improved the score of visual analogue scale for neck and shoulder stiffness and pain, reduced muscle stiffness of the neck, and increased the skin surface temperature of neck and shoulders, compared to before ingestion. No adverse effects were observed during this study. These results suggest that NKCP® may alleviate headaches and chronic neck and shoulder stiffness and pain.
- 著者
- Hayato Akimoto Takuya Nagashima Kimino Minagawa Takashi Hayakawa Yasuo Takahashi Satoshi Asai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1514-1523, 2021-10-01 (Released:2021-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 57
- 被引用文献数
- 8
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a common adverse drug event. Spontaneous reporting systems such as the Japanese Adverse Event Report Database (JADER) have been used to evaluate the association between drugs and adverse drug events. However, the association of drugs with adverse drug events may be overestimated due to reporting biases. Therefore, it is important to objectively evaluate the association using liver function test values. The aim of the present study was to predict potential hepatotoxic drugs using real-world data including electronic medical records and the JADER database. A total of 70009 (2779 with DILI and 67230 without DILI) and 438515 (10235 with DILI and 428280 without DILI) Japanese adult patients were extracted from electronic medical records and the JADER database, respectively. Drugs with ≥100 DILI patients in both of the two databases were regarded as suspected drugs for DILI. We used multivariate logistic regression to evaluate the association between the suspected drugs and increased risk of DILI. Among the suspected drugs, broad-spectrum antibiotics such as meropenem, tazobactam/piperacillin and ceftriaxone were significantly associated with an increased risk of DILI, and meropenem had a greater risk of DILI in both of the two databases. Additionally, there were significant associations of mosapride and L-carbocisteine with increased risk of DILI. In addition to well-known associations between antibiotic drugs and DILI, mosapride and L-carbocisteine were found to be new potential signals of drugs causing hepatotoxicity. This study indicates potential hepatotoxic drugs that require further causality assessment.
- 著者
- Shungo Imai Yasuyuki Nasuhara Kenji Momo Hiromitsu Oki Hitoshi Kashiwagi Yuki Sato Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1499-1505, 2021-10-01 (Released:2021-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 4
A major adverse effect of benzbromarone is hepatotoxicity. Therefore, periodic liver function tests are required at least for the first 6 months of benzbromarone administration. However, it is not clear whether the relevant blood tests are implemented appropriately. Here, we performed a cross-sectional survey of the implementation status of liver function tests in patients who were newly prescribed benzbromarone, using the Japanese large claims database. Male patients who were newly prescribed benzbromarone from January 2010 to December 2016 were included. We targeted patients who continued benzbromarone during the observation period (up to 180 d from the start of administration). The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients in whom periodic liver function tests were implemented. A periodic liver function test was defined as one or more liver function tests performed during both 1–90 and 91–180 d of initial benzbromarone administration. We labeled the tests as a “periodic test” or “non-periodic test” based on whether periodic liver function tests were performed or not, respectively. Furthermore, factors influencing non-periodic test were analyzed. Periodic testing was implemented only in 28.7% of patients. Additionally, factors such as number of hospital beds ≤19 (compared to 100–199 beds) and duration of the first prescription of benzbromarone were associated with non-periodic testing. Our study revealed that periodic liver function tests are not performed sufficiently in Japan. Thus, clinicians prescribing benzbromarone should be educated about the test. Our blood-test-based approach should be applied to other drugs and countries in future research.
- 著者
- Yu Inoue Seiji Hasegawa Yuichi Hasebe Mika Kawagishi-Hotta Ryosuke Okuno Takaaki Yamada Hiroaki Adachi Katsuma Miyachi Yoshie Ishii Kazumitsu Sugiura Hirohiko Akamatsu
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1403-1412, 2021-10-01 (Released:2021-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Currently, human-skin derived cell culture is a basic technique essential for dermatological research, cellular engineering research, drug development, and cosmetic development. But the number of donors is limited, and primary cell function reduces through cell passage. In particular, since adult stem cells are present in a small amount in living tissues, it has been difficult to obtain a large amount of stem cells and to stably culture them. In this study, skin derived cells were isolated from the epidermis, dermis, and adipose tissue collected from single donor, and immortalization was induced through gene transfer. Subsequently, cell lines that could be used as stem cell models were selected using the differentiation potential and the expression of stem cell markers as indices, and it was confirmed that these could be stably cultured. The immortalized cell lines established in this study have the potential to be applied not only to basic dermatological research but also to a wide range of fields such as drug screening and cell engineering.
1 0 0 0 OA Claudin-5: A Pharmacological Target to Modify the Permeability of the Blood–Brain Barrier
- 著者
- Yosuke Hashimoto Matthew Campbell Keisuke Tachibana Yoshiaki Okada Masuo Kondoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1380-1390, 2021-10-01 (Released:2021-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 110
- 被引用文献数
- 18
Claudin-5 is the dominant tight junction protein in brain endothelial cells and exclusively limits the paracellular permeability of molecules larger than 400 Da across the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Its pathological impairment or sustained down-regulation has been shown to lead to the progression of psychiatric and neurological disorders, whereas its expression under physiological conditions prevents the passage of drugs across the BBB. While claudin-5 enhancers could potentially act as vascular stabilizers to treat neurological diseases, claudin-5 inhibitors could function as delivery systems to enhance the brain uptake of hydrophilic small-molecular-weight drugs. Therefore, the effects of claudin-5 manipulation on modulating the BBB in different neurological diseases requires further examination. To manipulate claudin-5 expression levels and function, several claudin-5 modulating molecules have been developed. In this review, we first describe the molecular, cellular and pathological aspects of claudin-5 to highlight the mechanisms of claudin-5 enhancers/inhibitors. We then discuss recently developed claudin-5 enhancers/inhibitors and new methods to discover these molecules.
- 著者
- Kazuaki Matoba Nobuo N. Noda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.9, pp.1337-1343, 2021-09-01 (Released:2021-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation system regulating cellular homeostasis. The two ubiquitin-like modification systems named the Atg8 system and the Atg12 system are essential for autophagy. Atg8 and Atg12 are ubiquitin-like proteins covalently conjugated with a phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and Atg5, respectively, via enzymatic reactions. The Atg8–PE conjugate binds to autophagic membranes and recruits various proteins through direct interaction, whereas the Atg12–Atg5 conjugate recognizes Atg3, the E2 enzyme for Atg8, and facilitates Atg8–PE conjugation by functioning as the E3 enzyme. Although structural and biochemical analyses have well established the Atg8-family interacting motif (AIM), studies on the interacting sequence for Atg12 are rare (only one example for human ATG12–ATG3), thereby making it challenging to define a binding motif. Here we determined the crystal structure of the plant ATG12b as a complex with the ATG12b-binding region of ATG3 and revealed that ATG12b recognizes the aspartic acid (Asp)–methionine (Met) motif in ATG3 via a hydrophobic pocket and a basic residue, which we confirmed critical for the complex formation by mutational analysis. This recognition mode is similar to that reported between human ATG12 and ATG3, suggesting that the Asp–Met sequence is a conserved Atg12-interacting motif (AIM12). These data suggest that AIM12 mediates E2-E3 interaction during Atg8 lipidation and provide structural basis for developing chemicals that regulate autophagy by targeting Atg12-family proteins.
- 著者
- Kenroh Sasaki Fumihiko Yoshizaki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.6, pp.806-808, 2002 (Released:2002-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 28 34
A tyrosinase inhibitor was isolated from the peel of Citrus fruit by activity-guided fractionation, and identified as 3′,4′,5,6,7,8-hexamethoxyflavone (nobiletin) by comparison with reported spectral data. Nobiletin (IC50 of; 46.2 μM) exhibited more potency than Kojic acid (IC50; 77.4 μM) used as a positive control, and it was found to be potentially an effective inhibitor of the production of melanin.
- 著者
- Dalia Seleem Veronica Santana Freitas-Blanco Juliana Noguti Bruna Raquel Zancope Vanessa Pardi Ramiro Mendonça Murata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.8, pp.1299-1302, 2018-08-01 (Released:2018-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1 6
Monolaurin is a natural compound that has been known for its broad antimicrobial activities. We evaluate the antifungal activity of monolaurin against Candida albicans biofilms in vivo using a novel bioluminescent model to longitudinally monitor oral fungal infection. Oral fungal infection in vivo was performed using bioluminescent engineered C. albicans (SKCa23-ActgLUC) biofilms on Balb/c mice. The antifungal activity of monolaurin was determined by comparing three groups of mice (n=5/group): monolaurin, vehicle control, and positive control (nystatin). All mice were immunosuppressed with cortisone acetate and oral topical treatments were applied for 5 d. In vivo imaging system (IVIS) imaging was used to monitor the progression of infection over a 5-d period. Total photon flux and ex vivo microbiological analysis of the excised tongues were used to determine the overall fungal burden. Oral topical treatments of monolaurin have resulted in a significant decrease (p<0.05) in the total photon flux over 4 and 5 d post-infection in comparison to the vehicle control group. Furthermore, monolaurin treated group had a significant decrease in colony formation unit of tongue tissue compared to the vehicle control. Our findings support monolaurin as a promising antifungal compound in vivo, which may translate to its future use in the treatment of oral candidiasis.
- 著者
- Kazuya Ooi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.8, pp.1037-1043, 2021-08-01 (Released:2021-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Dry skin is a common symptom of various conditions, and elderly individuals commonly exhibit this physiological symptom. Dry skin develops owing to sebum deficiency; however, the use of moisturizers can typically overcome this issue, particularly in patients in whom there are no other skin problems. If dry skin is left untreated, itching and eczema can occur, resulting in skin damage. Additionally, hemodialysis patients exhibit reduced barrier function and can experience pain associated with repeated needle insertion; the repeated use of lidocaine tape to manage the pain can cause further skin damage. To reduce the occurrence of dry skin, the skin is hydrated using moisturizers. Dry skin is also prominent in patients with varicose veins in the lower extremities, and many biochemical studies have shown that skin immunity is altered in patients with dry skin. Moreover, the incidences of dry skin and pruritus differ in male and female patients. Furthermore, in elderly patients, zinc deficiency is likely to cause dry skin, and zinc supplementation may maintain skin hydration. To date, few reports have described dry skin from a clinical point of view. In this review, research on dry skin is presented, and the findings of basic research studies are integrated.
- 著者
- Iqbal Julian Takuya Iwamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.8, pp.1050-1059, 2021-08-01 (Released:2021-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 1
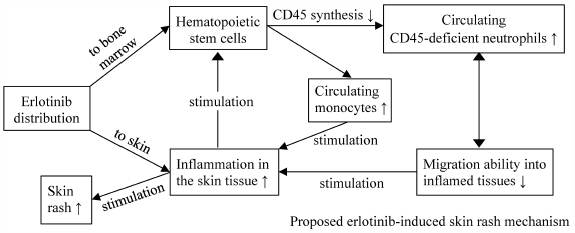
Skin rash is a common adverse event associated with erlotinib therapy. In severe conditions, the rash could affect patients’ QOL. If the rash occurrence can be predicted, erlotinib treatment failures can be prevented. We designed an in vivo study that applied erlotinib regimens resembling its clinical application to evaluate possible erlotinib-induced skin rash biomarkers for humans and simultaneously observe the effects of erlotinib discontinuation, followed with or without dose reduction, on rash development. Rats were divided into four groups: placebo, constant (erlotinib 35 mg/kg on d1–d21), intermittent (erlotinib 70 mg/kg on d1–d7 and d15–d21), and mimic (erlotinib 70 mg/kg on d1–d7 and erlotinib 35 mg/kg on d15–d21). Blood sampling was performed on d1, d8, d15, and d22. The samples were used to measure erlotinib concentrations, the level of hepatic and renal function markers, immune cell percentages, and immune cells’ CD45 expression levels. Erlotinib 70 mg/kg generated high mean circulating erlotinib concentrations (>1800 ng/mL) that led to severe rashes. Erlotinib dose reduction following rash occurrence reduced circulating erlotinib concentration and rash severity. After the treatment, the escalation of neutrophil percentages and reduction of neutrophils’ CD45 expression levels were observed, which were significantly correlated with the rash occurrence. This study is the first to show that erlotinib-induced skin rash may be affected by the reduction of neutrophils’ CD45 expression levels, and this is a valuable finding to elucidate the erlotinib-induced skin rash formation mechanism.
- 著者
- Tomoki Nakayoshi Koichi Kato Eiji Kurimoto Akifumi Oda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.7, pp.967-975, 2021-07-01 (Released:2021-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 39
- 被引用文献数
- 1
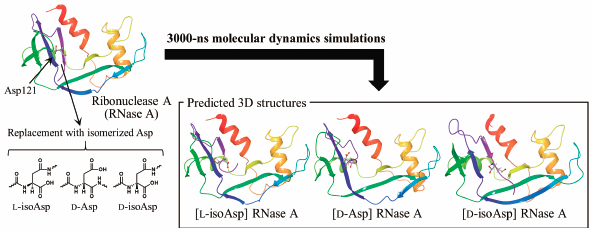
Isomerized aspartic acid (Asp) residues have previously been identified in various aging tissues, and are suspected to contribute to age-related diseases. Asp-residue isomerization occurs nonenzymatically under physiological conditions, resulting in the formation of three types of isomerized Asp (i.e., L-isoAsp, D-Asp, and D-isoAsp) residues. Asp-residue isomerization often accelerates protein aggregation and insolubilization, making structural biology analyses difficult. Recently, Sakaue et al. reported the synthesis of a ribonuclease A (RNase A) in which Asp121 was artificially replaced with different isomerized Asp residues, and experimentally demonstrated that the enzymatic activities of these artificial mutants were completely lost. However, their structural features have not yet been elucidated. In the present study, the three-dimensional (3D) structures of these artificial-mutant RNases A were predicted using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The 3D structures of wild-type and artificial-mutant RNases A were converged by 3000-ns MD simulations. Our computational data show that the structures of the active site and the formation frequencies of the appropriate catalytic dyad structures in the artificial-mutant RNases A were quite different from wild-type RNase A. These computational findings may provide an explanation for the experimental data which show that artificial-mutant RNases A lack enzymatic activity. Herein, MD simulations have been used to evaluate the influences of isomerized Asp residues on the 3D structures of proteins.
- 著者
- Keita Kitamura Kenta Umehara Ryo Ito Yoshiyuki Yamaura Takafumi Komori Hanae Morio Hidetaka Akita Tomomi Furihata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.7, pp.984-991, 2021-07-01 (Released:2021-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 9
In vitro blood–brain barrier (BBB) models are essential research tools for use in developing brain-targeted drugs and understanding the physiological and pathophysiological functions of the BBB. To develop BBB models with better functionalities, three-dimensional (3D) culture methods have gained significant attention as a promising approach. In this study, we report on the development of a human conditionally immortalized cell-based multicellular spheroidal BBB (hiMCS-BBB) model. After being seeded into non-attachment culture wells, HASTR/ci35 (astrocytes) and HBPC/ci37 cells (brain pericytes) self-assemble to form a spheroid core that is then covered with an outer monolayer of HBMEC/ci18 cells (brain microvascular endothelial cells). The results of immunocytochemistry showed the protein expression of several cellular junction and BBB-enriched transporter genes in HBMEC/ci18 cells of the spheroid model. The permeability assays showed that the hiMCS-BBB model exhibited barrier functions against the penetration of dextran (5 and 70 kDa) and rhodamine123 (a P-glycoprotein substrate) into the core. On the other hand, facilitation of 2-(N-[7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl]amino)-2-deoxyglucose (2-NBDG; a fluorescent glucose analog) uptake was observed in the hiMCS-BBB model. Furthermore, tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment elicited an inflammatory response in HBMEC/ci18 cells, thereby suggesting that BBB inflammation can be recapitulated in the hiMCS-BBB model. To summarize, we have developed an hiMCS-BBB model that possesses fundamental BBB properties, which can be expected to provide a useful and highly accessible experimental platform for accelerating various BBB studies.
- 著者
- Kodai Ishida Tomohiro Yako Miruto Tanaka Wataru Otsu Shinsuke Nakamura Masamitsu Shimazawa Hideshi Tsusaki Hideaki Hara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.7, pp.937-946, 2021-07-01 (Released:2021-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 4
The corneal epithelium is continuously exposed to oxygen, light, and environmental substances. Excessive exposure to those stresses is thought to be a risk factor for eye diseases. Photokeratitis is damage to the corneal epithelium resulting in a painful eye condition caused by unprotected exposure to UV rays, usually from sunlight, and is often found in people who spend a long time outdoors. In modern life, human eyes are exposed to artificial light from light-emitting diode (LED) displays of computers and smartphones, and it has been shown that short-wavelength (blue) LED light can damage eyes, especially photoreceptors. However, the effect of blue LED light on the cornea is less understood. In addition, it is important to develop new treatments for preserving human eyesight and eye health from light stress. Here, we used human corneal epithelial cells-transformed (HCE-T) cells as an in-vitro model to investigate the protective effect of NSP-116, an imidazolyl aniline derivative, against the oxidative stress induced by light in the corneal epithelium. Treatment with 10 µM NSP-116 significantly increased the cell viability and reduced the death ratio following UV or blue LED light exposure. Furthermore, NSP-116 treatment decreased light-induced reactive oxygen species production and preserved the mitochondrial membrane potential. Immunoblotting data showed that NSP-116 suppressed the stress response pathway. Finally, NSP-116 treatment prevented corneal epithelial apoptosis induced by blue LED light in an in-vivo mouse model. In conclusion, NSP-116 has a protective effect against oxidative stress and corneal cell death from both UV and blue LED light exposure.
- 著者
- Akiko Omori Yuki Fujisawa Shotaro Sasaki Kazumi Shimono Takashi Kikukawa Seiji Miyauchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.678-685, 2021-05-01 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 6
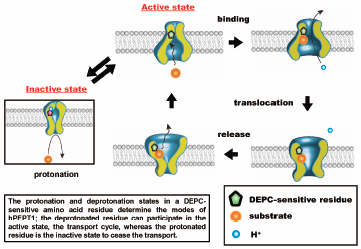
To clarify the role of an amino acid residue in the pH-dependent efflux process in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing the human oligopeptide transporter hPEPT1 (CHO/hPEPT1), we determined the effect of extracellular pH on the hPEPT1-mediated efflux process. The efflux of glycylsarcosine (Gly-Sar), a typical substrate for hPEPT1, was determined using an infinite dilution method after cells were preloaded with [3H]-Gly-Sar. The efflux of [3H]-Gly-Sar was stimulated by 5 mM unlabeled hPEPT1 substrates in the medium. This trans-stimulation phenomenon showed that hPEPT1 mediated the efflux of [3H]-Gly-Sar from CHO/hPEPT1 and that hPEPT1 is a bi-directional transporter. We then determined the effect of extracellular pH (varying from 8.0 to 3.5) on the efflux activity. The efflux activity by hPEPT1 decreased with the decrease in extracellular pH. The Henderson–Hasselbälch-type equation, which fitted well to the pH-profile of efflux activity, indicated that a single amino acid residue with a pKa value of approximately 5.7 regulates the efflux activity. The pH-profile of the efflux activity remained almost unchanged irrespective of the proton gradient across the plasma membrane. In addition, the chemical modification of the histidine residue with diethylpyrocarbonate completely abolished the efflux activity from cells, which could be prevented by the presence of 10 mM Gly-Sar. These data indicate that the efflux process of hPEPT1 is also regulated in a pH-dependent manner by the protonation state of a histidine residue located at or near the substrate recognition site facing the extracellular space.
- 著者
- Shigeru Ishida Ken Masuguchi Takehiro Kawashiri Toshikazu Tsuji Hiroyuki Watanabe Sayuri Akiyoshi Makoto Kubo Satohiro Masuda Nobuaki Egashira
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.4, pp.663-668, 2020-04-01 (Released:2020-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, are common side effects associated with docetaxel treatment in breast cancer patients. However, preventive measures have not yet been established. In this study, we retrospectively analyzed the risk factors for developing anaphylaxis in 182 female breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel. We found that 6.6% of all patients (n = 12) experienced anaphylaxis. Multivariate analyses indicated that concentration of docetaxel higher than 0.275 mg/m2/mL, docetaxel dose rate higher than 1.15 mg/m2/min, and white blood cell count less than 4290 cells/mL are risk factors for developing docetaxel-related anaphylaxis. In particular, concentrations of docetaxel or doses per administration time were associated with a high odds ratio (11.88 or 11.60) for docetaxel-related anaphylaxis. Moreover, patients receiving doses in 250 mL volume experienced anaphylaxis more frequently than those receiving doses in 500 mL (7.0 vs. 0.9%, p = 0.0236). Additionally, patients receiving treatments over 60 min tended to experience anaphylaxis more frequently than those who were treated over 90 min (6.7 vs. 1.1%, p = 0.0637). The present results indicate that high docetaxel concentrations, high dose rates, and low white blood cell counts are risk factors for developing docetaxel-related anaphylaxis, and administering docetaxel diluted in 500 mL over 90 min may limit docetaxel-induced hypersensitivity reactions.
1 0 0 0 OA Inhibition of the Antibody Production by Acetaminophen Independent of Liver Injury in Mice
- 著者
- Katsunori Yamaura Kohei Ogawa Taeko Yonekawa Tomonori Nakamura Shingo Yano Koichi Ueno
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.2, pp.201-205, 2002 (Released:2002-04-27)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 10 18
The causal relationship between the inhibition of antibody production and liver injury induced by single doses of acetaminophen (APAP) was investigated in mice. The liver injury and antibody production were evaluated using the serum transaminase activity and the number of antibody forming cells against sheep red blood cells (SRBC), respectively. The relevance of APAP hepatotoxicity with inhibiting antibody production was elucidated in fasted and fed mice treated with a single oral administration of APAP. In fasted mice, the oral administration of APAP produced serious liver injury, while it was not the case in the fed mice. As the antibody production was measured under these conditions, APAP significantly depressed the antibody production in fed mice as well as in fasted mice. The rate of B220 positive cells in the splenocytes was significantly decreased by APAP administration in both the fasted and fed mice. Splenocytes proliferative responses following mitogenic stimulation with concanavalin A or lipopolysaccharide were inhibited by APAP. Moreover, APAP added directly to the splenocyte culture also inhibited the in vitro antibody-producing response to SRBC. These findings indicate that the APAP-induced depression of antibody production may not be a secondary response to APAP-hepatitis, but may be a primary response to APAP.
- 著者
- Kazumasa Kotake Takashi Hongo Akihiro Tahira Nana Niimi Ikue Haisa Yasuhiro Kawakami
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.605-610, 2021-05-01 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 36
Recombinant human thrombomodulin (rhTM) is an anti-coagulant used to treat disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). The efficacy of rhTM in patients with sepsis-induced DIC has been proved in some clinical trials, but the determining factors are not known. The aim of this study was to identify patients for whom rhTM will be effective and the factors that determine rhTM efficacy in alleviating DIC. A single-center, retrospective, observational study was conducted in patients with sepsis-induced DIC who were treated with rhTM in Okayama Saiseikai General Hospital (Okayama, Japan) between January 2010 and December 2019. Among 67 patients who were treated with rhTM, DIC was resolved in 24 patients. The multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that age (odds ratio (OR) 1.05; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.00–1.10; p < 0.05) and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II scores (OR 0.88; 95% CI 0.78–0.98; p < 0.05) were factors that determined rhTM efficacy in alleviating DIC. Overall, our study provides valuable information on factors that should be considered before rhTM administration to patients with sepsis-induced DIC for a better management of healthcare costs.