- 著者
- Hiroyuki Tsutsui Shin-ichi Momomura Yoshihiko Saito Hiroshi Ito Kazuhiro Yamamoto Yasushi Sakata Akshay Suvas Desai Tomomi Ohishi Takayuki Iimori Toshihito Kitamura Weinong Guo on behalf of the PARALLEL-HF Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-20-0854, (Released:2021-03-16)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 37
Background:In the Prospective Comparison of angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) With ACEi to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM-HF) study, treatment with sacubitril/valsartan reduced the primary outcome of cardiovascular (CV) death and heart failure (HF) hospitalization compared with enalapril in patients with chronic HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). A prospective randomized trial was conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan in Japanese HFrEF patients.Methods and Results:In the Prospective comparison of ARNI with ACEi to determine the noveL beneficiaL trEatment vaLue in Japanese Heart Failure patients (PARALLEL-HF) study, 225 Japanese HFrEF patients (New York Heart Association [NYHA] class II–IV, left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] ≤35%) were randomized (1 : 1) to receive sacubitril/valsartan 200 mg bid or enalapril 10 mg bid. Over a median follow up of 33.9 months, no significant between-group difference was observed for the primary composite outcome of CV death and HF hospitalization (HR 1.09; 95% CI 0.65–1.82; P=0.6260). Early and sustained reductions in N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) from baseline were observed with sacubitril/valsartan compared with enalapril (between-group difference: Week 2: 25.7%, P<0.01; Month 6: 18.9%, P=0.01, favoring sacubitril/valsartan). There was no significant difference in the changes in NYHA class and Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) clinical summary score at Week 8 and Month 6. Sacubitril/valsartan was well tolerated with fewer study drug discontinuations due to adverse events, although the sacubitril/valsartan group had a higher proportion of patients with hypotension.Conclusions:In Japanese patients with HFrEF, there was no difference in reduction in the risk of CV death or HF hospitalization between sacubitril/valsartan and enalapril, and sacubitril/valsartan was safe and well tolerated.
- 著者
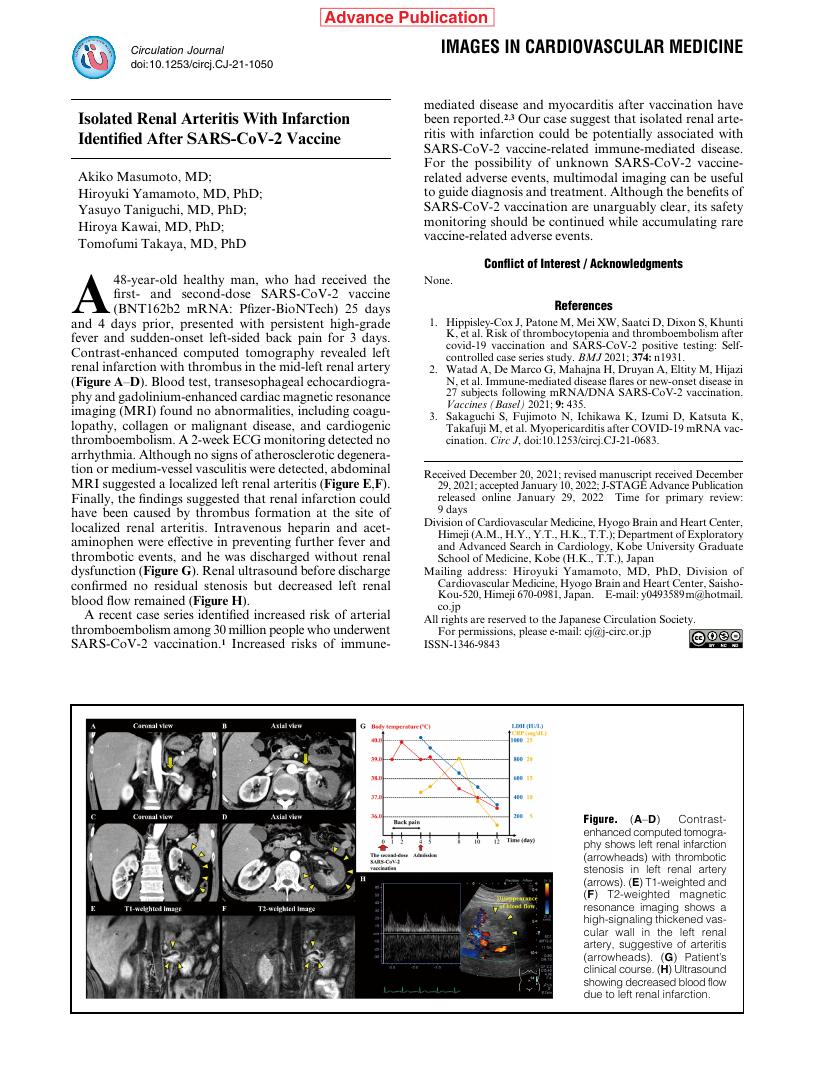
- Akiko Masumoto Hiroyuki Yamamoto Yasuyo Taniguchi Hiroya Kawai Tomofumi Takaya
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-1050, (Released:2022-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 被引用文献数
- 2
- 著者
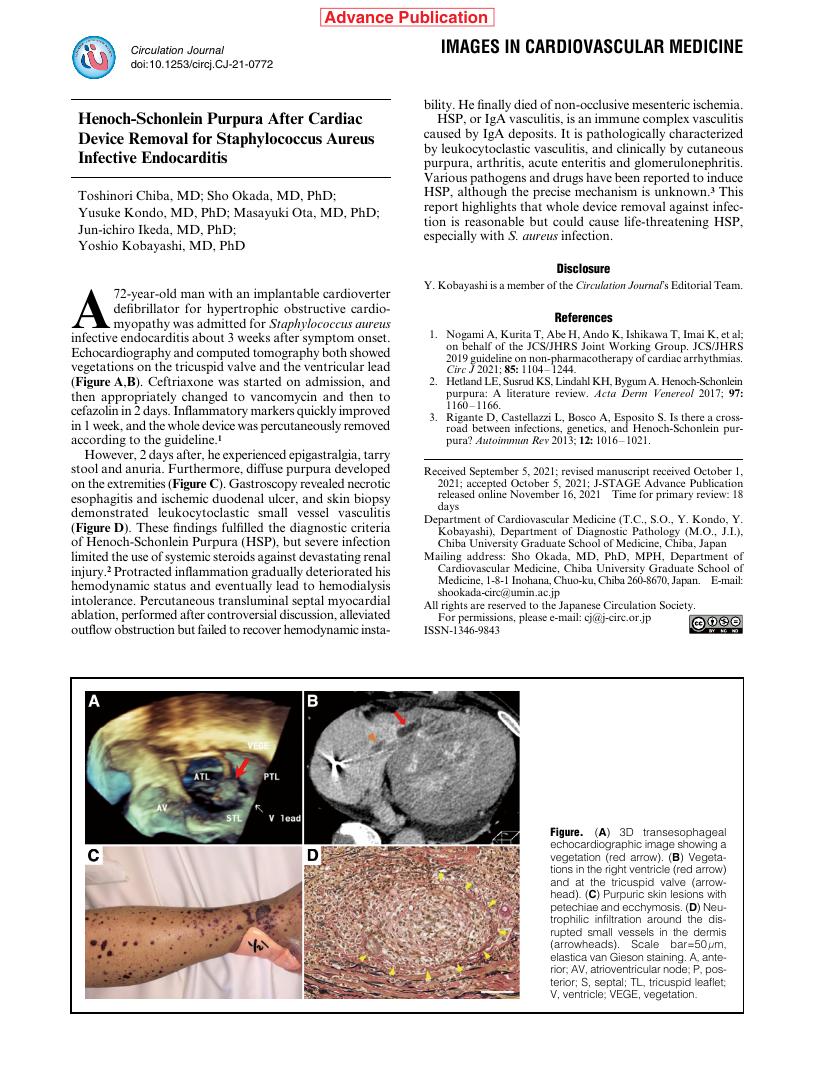
- Toshinori Chiba Sho Okada Yusuke Kondo Masayuki Ota Jun-ichiro Ikeda Yoshio Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0772, (Released:2021-11-16)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Kazuhiro Nakao Teruo Noguchi Chris P Gale
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0662, (Released:2021-08-28)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 著者
- Anthony C. Keech Kazuma Oyama Peter S. Sever Minao Tang Sabina A. Murphy Atsushi Hirayama Chen Lu Leslie Tay Prakash C. Deedwania Chung-Wah Siu Armando Lira Pineda Donghoon Choi Min-Ji Charng John Amerena Wan Azman Wan Ahmad Vijay K. Chopra Terje R. Pedersen Robert P. Giugliano Marc S. Sabatine on behalf of the FOURIER Study Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-20-1051, (Released:2021-05-12)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Background:There are concerns that Asian patients respond differently to some medications. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of evolocumab among Asian vs. other subjects in the FOURIER trial, which randomized stable atherosclerosis patients to receive either evolocumab or placebo.Methods and Results:Effects of adding evolocumab vs. placebo to background statin therapy on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reductions, cardiovascular outcomes, and adverse events were compared among 27,564 participants with atherosclerotic disease, according to self-reported Asian (n=2,723) vs. other (n=24,841) races followed for a median of 2.2 years in the FOURIER trial. The primary endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or coronary revascularization. At randomization, Asians had slightly lower LDL-C (median 89 [IQR 78–104] mg/dL vs. 92 [80–109] mg/dL; P<0.001) and were much less likely to be on a high-intensity statin (33.3% vs. 73.3%; P<0.001). Evolocumab lowered LDL-C more in Asians than in others (66% vs. 58%; P<0.001). The effect of evolocumab on the primary endpoint was similar in Asians (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.61–1.03) and others (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.79–0.93; P interaction=0.55). There was no excess of serious adverse events with evolocumab among Asians over others.Conclusions:Use of evolocumab robustly lowers LDL-C and is equally efficacious in lowering the risk of cardiovascular events and safe in Asians as it is in others.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Omori Hideaki Ota Takuya Mizukami Yoshiaki Kawase Toru Tanigaki Tetsuo Hirata Munenori Okubo Masanori Kawasaki Hitoshi Matsuo
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.85, no.8, pp.1404, 2021-07-21 (Released:2021-07-21)
- 参考文献数
- 2
- 被引用文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Soichi Komaki Masanobu Ishii Kazumasa Kurogi Nobuyasu Yamamoto
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0039, (Released:2021-04-22)
- 参考文献数
- 2
- 被引用文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Mitsuru Takami Koji Fukuzawa Kunihiko Kiuchi Makoto Takemoto Toshihiro Nakamura Jun Sakai Atsusuke Yatomi Kazutaka Nakasone Yusuke Sonoda Kyoko Yamamoto Hiroyuki Takahara Yuya Suzuki Kenichi Tani Ken-ichi Hirata
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.5, pp.294-299, 2021-05-10 (Released:2021-05-10)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background:Demand is growing for remote electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring systems in the COVID-19 era in Japan. This study describes initial experiences with a small wireless ECG monitoring device and the utility of delivery via the postal service for outpatient care in Japan.Methods and Results:Long-term ECG monitoring following postal delivery of the small ECG device was evaluated in 25 patients. The patients had no difficulties with either the postal delivery or self-fitting and wearing the devices. A median of 57 h monitoring per patient was performed. Arrhythmic events were detected in 8 patients. Most patients were satisfied with both the ECG devices and postal delivery.Conclusions:Postal delivery of ECG devices could be used in clinical practice to achieve less or no in-person contact during the COVID-19 era.
- 著者
- Roland Richard Tilz Roza Meyer-Saraei Charlotte Eitel Thomas Fink Vanessa Sciacca Lisbeth Delgado Lopez Bettina Kirstein Michael Schlüter Julia Vogler Karl-Heinz Kuck Christian-H. Heeger
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0094, (Released:2021-04-13)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 28
Background:The arctic front cryoballoon (AF-CB) provides effective and durable pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) associated with encouraging clinical outcome. The POLARx cryoballoon incorporates unique features and design changes that may translate into improved efficacy, safety and further simplified balloon-based procedures. Efficacy and safety of the novel POLARx cryoballoon was compared to the fourth generation AF-CB (AF-CB4).Methods and Results:Twenty-five consecutive patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation were prospectively enrolled, underwent POLARx-based PVI (POLARx group) and were compared to 25 consecutive patients treated with the AF-CB4 (AF-CB4 group). All PVs were successfully isolated utilizing the POLARx and AF-CB4. A significant difference regarding the mean minimal cryoballoon temperatures reached using the AF-CB4 and POLARx (−50±6℃ vs. −57±7℃, P=0.004) was observed. Real-time PVI was visualized in 81% of POLARx patients and 42% of AF-CB4 patients (P<0.001). Utilizing the POLARx, a trend towards shorter median procedure time (POLARx: 45 [39, 53] min vs. AF-CB4: 55 [50, 60] min; P=0.062) was found. No differences were observed between AF-CB4 and POLARx concerning catheter maneuverability, catheter stability and periprocedural complications.Conclusions:The novel POLARx showed similar safety and efficacy compared to the AF-CB4. A higher rate of real-time PV recordings and significantly lower minimal balloon temperatures were observed using the POLARx.
- 著者
- Yuji Ikari Yuya Matsue Sho Torii Misaki Hasegawa Kazuki Aihara Shunsuke Kuroda Takahide Sano Takeshi Kitai Taishi Yonetsu Shun Kohsaka Takuya Kishi Issei Komuro Ken-ichi Hirata Koichi Node Shingo Matsumoto
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0087, (Released:2021-04-29)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Background:Cardiovascular diseases and/or risk factors (CVDRF) have been reported as risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Methods and Results:In total, we selected 693 patients with CVDRF from the CLAVIS-COVID database of 1,518 cases in Japan. The mean age was 68 years (35% females). Statin use was reported by 31% patients at admission. Statin users exhibited lower incidence of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) insertion (1.4% vs. 4.6%, odds ratio [OR]: 0.295, P=0.037) and septic shock (1.4% vs. 6.5%, OR: 0.205, P=0.004) despite having more comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus.Conclusions:This study suggests the potential benefits of statins use against COVID-19.
7 0 0 0 OA Relationship Between Serum Uric Acid Concentration and Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome
- 著者
- Tae Woo Yoo Ki Chul Sung Hun Sub Shin Byung Jin Kim Bum Soo Kim Jin Ho Kang Man Ho Lee Jung Ro Park Hyang Kim Eun Jung Rhee Won Young Lee Sun Woo Kim Seung Ho Ryu Dong Geuk Keum
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.8, pp.928-933, 2005 (Released:2005-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 215 267
Background Associations between hyperuricemia, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes have been reported, but few of the studies have been conducted in the Korean population. The present study examined a Korean adult population with respect to the relationships between serum uric acid concentrations and hypertension, insulin resistance, and the risk factors of metabolic syndrome. Methods and Results A total of 53,477 subjects were divided into 4 groups according to serum uric acid quartiles. The incidence of hypertension in all subjects was higher in the first quartile than in the third plus fourth quartile (odds ratio (OR) 1.192, p<0.001). Homeostasis model assessment index was found to be associated with serum uric acid concentration in all subjects (OR 1.193, p<0.001), and the serum uric acid concentration was positively correlated with the risk factors of metabolic syndrome. In addition, the number of metabolic syndrome variables increased as serum uric acid concentration increased. Conclusions Serum uric acid concentration was found to be independently correlated with hypertension, insulin resistance and the risk factors of metabolic syndrome. In addition, even those with a serum uric acid concentration in the normal range showed an increased risk of metabolic syndrome as serum uric acid concentration increased. (Circ J 2005; 69: 928 -933)
- 著者
- Kodai Momoki Hikoro Matsui
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-20-0108, (Released:2021-01-26)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 被引用文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Keitaro Senoo Tomonori Miki Takashi Okura Hirokazu Shiraishi Takeshi Shirayama Keiji Inoue Tomohiko Sakatani Ken Kakita Tetsuhisa Hattori Kentaro Nakai Takanori Ikeda Satoaki Matoba
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.7, pp.345-350, 2020-07-10 (Released:2020-07-10)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background:Hypertension in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) is a known independent risk factor for stroke. The Complete blood pressure (BP) monitor (Omron Healthcare, Kyoto, Japan) was developed as the first BP monitor with electrocardiogram (ECG) capability in a single device to simultaneously monitor ECG and BP readings. This study investigated whether the Complete can accurately differentiate sinus rhythm (SR) from AF during BP measurement.Methods and Results:Fifty-six consecutive patients with persistent AF admitted for catheter ablation were enrolled in the study (mean age 65.8 years; 83.9% male). In all patients, 12-lead ECGs and simultaneous Complete recordings were acquired before and after ablation. The Complete interpretations were compared with physician-reviewed ECGs, whereas Complete recordings were reviewed by cardiologists in a blinded manner and compared with ECG interpretations. Sensitivity, specificity, and κ coefficient were also determined. In all, 164 Complete and ECG recordings were simultaneously acquired from the 56 patients. After excluding unclassified recordings, the Complete automated algorithm performed well, with 100% sensitivity, 86% specificity, and a κ coefficient of 0.87 compared with physician-interpreted ECGs. Physician-interpreted Complete recordings performed well, with 99% sensitivity, 85% specificity, and a κ coefficient of 0.85 compared with physician-interpreted ECGs.Conclusions:The Complete, which combines BP and ECG monitoring, can accurately differentiate SR from AF during BP measurement.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Tsutsui Shin-ichi Momomura Yoshihiko Saito Hiroshi Ito Kazuhiro Yamamoto Yasushi Sakata Tomomi Ohishi Takayuki Iimori Toshihito Kitamura on behalf of the PARALLEL-HF Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0349, (Released:2023-11-21)
- 参考文献数
- 18
Background: Lower systolic blood pressure (SBP) is known to be associated with poor prognosis in heart failure (HF). We evaluated the efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan according to baseline SBP tertiles in Japanese patients from the PARALLEL-HF study.Methods and Results: In all, 223 patients were stratified into tertiles according to baseline SBP (≤114 mmHg: n=75; >114 and ≤130 mmHg: n=76; and >130 mmHg: n=72). Patients with lower SBP (≤114 mmHg) had the highest median N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations at baseline (P=0.0184). No significant difference was observed between sacubitril/valsartan and enalapril for the composite outcome of cardiovascular death and HF hospitalization across SBP tertiles (P-interaction=0.2682). Although the P-interaction value was not significant (0.2106), a greater reduction in NT-proBNP with sacubitril/valsartan compared with enalapril was observed in patients with SBP >130 mmHg (P=0.0076). The incidence of hypotension-related events and reduction or discontinuation of treatment due to hypotension-related events was higher in the lower SBP subgroup, and these events were more frequent in the sacubitril/valsartan than enalapril group.Conclusions: The efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan compared with enalapril was consistent across baseline SBP tertiles in Japanese patients from the PARALLEL-HF study. Hypotension-related events were more common in patients treated with sacubitril/valsartan with lower SBP.
- 著者
- Shunsuke Tatebe Satoshi Yasuda Ryo Konno Yasuhiko Sakata Koichiro Sugimura Kimio Satoh Takashi Shiroto Satoshi Miyata Osamu Adachi Masato Kimura Yoshiko Mizuno Junko Enomoto Shigeru Tateno Hiromichi Nakajima Kotaro Oyama Yoshikatsu Saiki Hiroaki Shimokawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0383, (Released:2023-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Little is known about clinical or sociodemographic factors that influence health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with adult congenital heart disease (ACHD).Methods and Results: We conducted a nationwide prospective cross-sectional multicenter study at 4 large ACHD centers in Japan. From November 2016 to June 2018, we enrolled 1,223 ACHD patients; 1,025 patients had an HRQoL score. Patients completed a questionnaire survey, including sociodemographic characteristics, and the 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). To determine factors associated with HRQoL, correlations between 2 SF-36 summary scores (i.e., physical component score [PCS] and mental component score [MCS]) and other clinical or sociodemographic variables were examined using linear regression analysis. In multivariable analysis, poorer PCS was significantly associated with 11 variables, including older age, higher New York Heart Association class, previous cerebral infarction, being unemployed, and limited participation in physical education classes and sports clubs. Poorer MCS was associated with congenital heart disease of great complexity, being part of a non-sports club, current smoking, and social drinking. Student status and a higher number of family members were positively correlated with MCS.Conclusions: This study demonstrates that HRQoL in ACHD patients is associated with various clinical and sociodemographic factors. Further studies are needed to clarify whether some of these factors could be targets for future intervention programs to improve HRQoL outcomes.
- 著者
- Taishi Okuno Masaki Izumo Noriko Shiokawa Shingo Kuwata Yuki Ishibashi Yukio Sato Masashi Koga Kazuaki Okuyama Norio Suzuki Keisuke Kida Yasuhiro Tanabe Yoshihiro J. Akashi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0503, (Released:2023-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Background: The MitraClip G4 system is a new iteration of the transcatheter edge-to-edge repair system. We assessed the impact of the G4 system on routine practice and outcomes in secondary mitral regurgitation (2°MR).Methods and Results: Consecutive patients with 2°MR treated with either the MitraClip G2 (n=89) or G4 (n=63) system between 2018 and 2021 were included. Baseline characteristics, procedures, and outcomes were compared. Inverse probability of treatment weighting and Cox regression were used to adjust for baseline differences. Baseline characteristics were similar, except for a lower surgical risk in the G4 group (Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality ≥8: 38.1% vs. 56.2%; P=0.03). In the G4 group, more patients had short (≤2 mm) coaptation length (83.7% vs. 54.0%; P<0.001) and fewer clips were used (17.5% vs. 36.0%; P=0.02). Acceptable MR reduction was observed in nearly all patients, with no difference between the G4 and G2 groups (100% vs. 97.8%, respectively; P=0.51). The G4 group had fewer patients with high transmitral gradients (>5mmHg; 3.3% vs. 13.6%; P=0.03). At 1 year, there was no significant difference between groups in the composite endpoint (death or heart failure rehospitalization) after baseline adjustment (10.5% vs. 20.2%; hazard ratio 0.39; 95% confidence interval 0.11–1.32; P=0.13).Conclusions: The G4 system achieved comparable device outcomes to the early-generation G2, despite treating more challenging 2°MR with fewer clips.
- 著者
- Mitsuru Takami Koji Fukuzawa Kunihiko Kiuchi Hiroyuki Takahara Kimitake Imamura Toshihiro Nakamura Yusuke Sonoda Kazutaka Nakasone Kyoko Yamamoto Yuya Suzuki Kenichi Tani Hidehiro Iwai Yusuke Nakanishi Mitsuhiko Shoda Atsushi Murakami Shogo Yonehara Ken-ichi Hirata
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-23-0083, (Released:2023-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 11
Background: There is a strong demand for remote monitoring systems to gather health data. This study investigated the safety, usefulness, and patient satisfaction in outpatient care using telehealth with real-time electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring after catheter ablation.Methods and Results: In all, 38 patients who underwent catheter ablation were followed up using telehealth. At the 3- and 6-month follow-up, a self-fitted Duranta ECG monitoring device was sent to the patient’s home before the online consultation. Patients attached the devices themselves, and the doctors viewed the patients by video chat and performed real-time ECG monitoring. The frequency of hospital visits and the ECG monitoring duration were compared with conventional in-person follow-up data (n=102). The completion rate for telehealth follow-up was 32 of 38 patients (84%). The number of hospital visits during the 6 months was significantly lower with telehealth follow-up than with conventional follow-up (median [interquartile range] 1 [1–1] vs. 5 [3–5]; P<0.0001). However, the ECG monitoring duration was approximately 4-fold longer for the telehealth follow-up (median [interquartile range] 89 [64–117] vs. 24 [0.1–24] h; P<0.0001). No major adverse events were observed during the telehealth follow-up. Patient surveys showed high satisfaction with telehealth follow-up due to reduced hospital visits.Conclusions: A combination of telehealth follow-up with real-time ECG monitoring increased the ECG monitoring duration and patient satisfaction without any adverse events.
- 著者
- Raisuke Iijima
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0720, (Released:2023-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 著者
- Xue Feng Yishuo Xu Ming Zeng Yuhan Qin Ziqian Weng Yanli Sun Zhanqun Gao Luping He Chen Zhao Ning Wang Dirui Zhang Chao Wang Yini Wang Lulu Li Chao Fang Jiannan Dai Haibo Jia Bo Yu
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0200, (Released:2023-07-04)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Microvascular reperfusion following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is associated with the prognosis of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). We investigated how plaque characteristics detected by optical coherence tomography (OCT) in STEMI patients affect the status of the microcirculation during PCI.Methods and Results: This retrospective, single-center study was a post hoc analysis basedon the multicenter SALVAGE randomized control trial (NCT03581513) that enrolled 629 STEMI patients, and finally we enrolled 235 patients who underwent PCI and pre-intervention OCT. Microvascular perfusion was evaluated using the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) myocardial perfusion frame count (TMPFC). Patients were divided into 3 groups based on the change in TMPFC from before to after PCI: improving TMPFC (n=11; 4.7%), stable TMPFC (n=182; 77.4%), and worsening TMPFC group (n=42; 17.9%). The proportion of patients with a microcirculation dysfunction before reperfusion was 11.9%, which increased significantly by (P=0.079) 8.5% to 20.4% after reperfusion. Compared with plaque characteristics in the stable and worsening TMPFC groups, the improving TMPFC group had fewer thrombi (90.7% and 90.5% vs. 89.4%, respectively; P=0.018), a lower proportion of plaque rupture (66.5% and 66.3% vs. 54.5%, respectively; P=0.029), and a lower proportion of lipid-rich plaques (89.6% and 88.1% vs. 63.6%, respectively; P=0.036).Conclusions: PCI may not always achieve complete myocardial reperfusion. Thrombi, plaque rupture, and lipid-rich plaques detected by OCT can indicate microcirculation dysfunction during the reperfusion period.
- 著者
- Shiro Nakahara Yuichi Hori Reiko Fukuda Hirotsugu Sato Hideyuki Aoki Tetsuya Ishikawa Yuji Itabashi Sayuki Kobayashi Isao Taguchi Yasuo Okumura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-23-0073, (Released:2023-09-16)
- 参考文献数
- 25
Background: Adverse atrial remodeling, including epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) deposition in the left atrium (LA), is implicated in atrial fibrillation (AF). Radiofrequency hotballoon (RHB) ablation can produce wide planar lesions because the balloon is highly compliant; however, chronic effects of RHB ablation on structural remodeling remain unknown. This clinical-experimental investigation characterized chronic effects of RHB ablation on EAT in persistent AF (PsAF).Methods and Results: The clinical study involved 91 patients (obese, n=30; non-obese, n=61) undergoing RHB ablation for PsAF. LA-EAT was assessed from computed tomography images obtained before ablation and 6 months later. Tissue effects of RHB ablation were explored in a chronic swine model. RHB ablation significantly reduced LA volume (mean [±SD] 177.7±29.7 vs. 138.4±29.6 mL; P<0.001) and LA-EAT volume (median [interquartile range] 22.0 [12.4–33.3] vs. 16.5 [7.9–25.8] mL; P<0.001). The reduction in EAT was significantly greater in the pulmonary vein (PV) antrum than in other LA regions (37.9% vs. 15.8%; P<0.001). The percentage reduction in PV antrum EAT was equivalent between obese and non-obese patients, as was the postablation success rate (73% vs. 70%; P=0.77). RHB ablation produced transmural lesions reaching the pigs’ epicardial fat region.Conclusions: RHB-based planar-transmural lesions altered the structurally remodeled LA, including EAT. Further studies are needed to determine whether factors other than PV isolation contribute to the clinical success of RHB ablation.