1 0 0 0 OA 無酸素性運動能力の評価 ―ウインゲート無酸素性テストを中心に―
- 著者
- 岩田 学 近藤 和泉 細川 賀乃子
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.12, pp.880-887, 2005 (Released:2006-09-22)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 1
It has been generally considered that physical fitness is represented by exercise performance under aerobic conditions. However, we are often required to exert highly powerful movements momentarily or within a few seconds in daily life. Therefore, when we evaluate physical fitness, it appears important to evaluate physical fitness not only under aerobic conditions, but also under anaerobic conditions, with the latter being represented by maximal muscle power. In the daily living of people with physical disabilities, whether or not they can achieve a specific activity (for example, standing up, getting up from the floor and sitting down, etc.) is considered to depend on their performance under anaerobic conditions rather than under aerobic conditions. The Wingate anaerobic test (WAnT) has been developed as one of the most precise tests to evaluate anaerobic exercise performance. The WAnT, established at the Wingate Institute in Israel in 1970s, is a test incorporating bicycle riding with a maximal effort for 30 seconds. An ergometer with equipment to load an examinee with a constant resistance from a suspended weight is used in this test. The WAnT is measured as the changes in mechanical power that are yielded by multiplying the resistance produced from a suspended weight by the rotation speed of pedaling during a period of 30 seconds. The WAnT has not been usually applied so far to disabled people due to some technical problems. However, we have been improving the test to overcome those problems so that we can adopt the WAnT in the field of rehabilitation. We expect that this modified WAnT would contribute to a comprehensive evaluation of physical fitness in people with disabilities.
1 0 0 0 文部省科学研究費細目「リハビリテーション科学」誕生のお知らせ
- 著者
- 米本 恭三 佐藤 徳太郎
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.9, pp.597, 1997
1 0 0 0 OA 急性期リハビリテーションにおけるラクナ梗塞の治療成績の検討
- 著者
- 佐藤 貴子 町田 隆一 大塚 功 原 寛美
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.9, pp.620-624, 2006 (Released:2006-10-26)
- 参考文献数
- 12
急性期脳卒中リハビリテーションでのラクナ梗塞の治療成績について調査した.対象は2004 年1 月から2005 年5 月までに当院へ入院し,リハビリテーション科へ入院あるいは経過で転科し,急性期リハビリテーションを実施した急性期ラクナ梗塞患者51例で,電子カルテより後方視的に調査した.その結果,患者全体の平均在院日数は31.9±15.6日であった.入院時のmotor FIM平均は41.0±18.4 点で退院時のmotor FIMの平均は68.7±19.9 点,motor FIM gainの平均は,27.7±15.3 点で,motor FIM gain/dayは1.3±0.9であった.ADLは,入院時は82%がmodified Rankin Scale(mRS)4以上の症例であったが,退院時はmRS3以下86%の歩行獲得率であった.退院時の転帰は51 例中43 例(84%)が自宅退院,残り8 例が回復期リハ病棟へ転院という結果であった.今回の調査から,ラクナ梗塞では早期にリハビリを処方し離床開始を実施することで約1 カ月の入院期間で歩行獲得および自宅復帰までが十分可能であると推察された.
1 0 0 0 OA 脳卒中リハビリテーション研究の25年 リハビリテーションの効果と障害学を中心に
- 著者
- 上田 敏
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.6, pp.466-473, 1988-11-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 113
1 0 0 0 OA 損傷後の中枢神経軸索再生の分子機構 金魚視神経をモデルとして
- 著者
- 加藤 聖
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.Supplement, pp.S88, 2004-05-18 (Released:2010-02-25)
1 0 0 0 OA 脳卒中リハビリと韓国鍼灸
- 著者
- 鄭 宇相 Ki-Ho Cho
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.Supplement, pp.S129, 2004-05-18 (Released:2010-02-25)
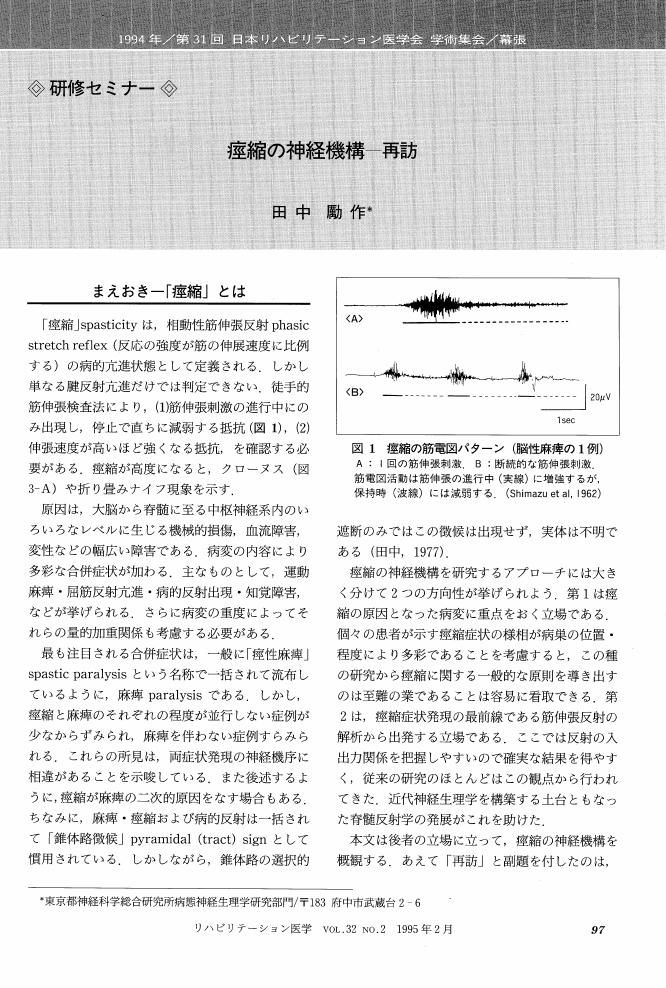
1 0 0 0 OA 痙縮の神経機構 再訪
- 著者
- 田中 勵作
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.2, pp.97-105, 1995-02-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 10 4
1 0 0 0 OA 成人脳性麻痺の臨床像 ―痙性と筋力の影響―
- 著者
- 丸石 正治 黒瀬 靖郎 片山 昭太郎
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.8, pp.564-572, 2005 (Released:2006-09-22)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disorder that results from a nonprogressive brain lesion that occurs during prenatal or perinatal development. As motor function in patients with CP changes with brain development, it may be more suitable to make a quantitative evaluation during adulthood than childhood. But until now there has been little information available about adult CP. In this review, we investigate the clinical characteristics and ADL scores in adult CP patients from our series of clinical experience. From our previous study that assessed the clinical characteristics of adult CP using uniform scale, a population of adult CP patients showed markedly increased muscle tone and moderate muscle weakness. These two factors did not correlate with each other, and were independently responsible for worse ADL scores. Decreased functional ability and secondary muscloskeletal problems such as cervical spondylosis are common in adult CP patients. We therefore added a review of them such reports from the literatures.
1 0 0 0 OA 腰椎の特徴と腰背筋の筋力増強
- 著者
- 大井 淑雄
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.1, pp.15-17, 1993-01-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 患者の自己決定権
- 著者
- 加藤 一郎
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.1, pp.21-27, 1990-01-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 神経心理学的テスト
- 著者
- 山下 光 山鳥 重
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.9, pp.651-658, 1994-09-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
- 著者
- 小坂 健二 中村 隆一
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.2, pp.93-100, 1983
筋電図反応時間(EMG-RT)は肢位変化によって変化することが知られている.例えば上腕三頭筋のEMG-RTは,促通肢位で短縮する.このEMG-RTの肢位依存性は,小脳障害患者で消失するがPNFによって一時的に回復する.このPNFの効果の神経機序を検討するために,サルの大脳皮質運動野刺激によって惹起されるEMGの潜時の肢位依存性について検討し,小脳核の破壊前と破壊後の肢位依存性の変化を比較検討した.さらに破壊後,皮質反復刺激を行なった.<br>皮質上肢運動野の連続電気刺激によるEMGの潜時は,肩のretraction肢位と比較するprotraction肢位で短縮した.この潜時の肢位依存性は,小脳核破壊によって消失した.試行間隔を短縮し,皮質刺激を反復すると,消失した肢位依存性は回復した.これらの神経機序については次のように考えられる.潜時の肢位依存性は,肢位変化による運動感覚入力が皮質運動野の興奮性を変化させた結果の現象である.小脳はこの運動感覚の入力系と運動の出力系に対してmodulatorとして作用しており,その破壊によって肢位依存性は消失する.この肢位依存性の回復には,試行間隔を短縮して皮質刺激を反復することでおこる上位中枢への運動感覚情報のより強力な入力が有効である.<br>このことからPNF治療には,最大抵抗下における随意運動の反復によって上位中枢への運動感覚入力を強化させることが重要である.
1 0 0 0 OA リハビリテーションと歩行分析
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.10, no.4, pp.247-270, 1973-10-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 手の機能解剖
- 著者
- 室田 景久
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.4, pp.257-261, 1992-04-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 被引用文献数
- 2 1
1 0 0 0 OA 能力低下の評価法について
- 著者
- 園田 茂 千野 直一
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.7, pp.491-500, 1993-07-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
1 0 0 0 OA 失語症訓練の技法とその効果
- 著者
- 綿森 淑子
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.2, pp.103-107, 1996-02-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 著者
- 里宇 明元
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.8, pp.531-539, 2004
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 歩行能力とバランス機能の関係
- 著者
- 猪飼 哲夫 辰濃 尚 宮野 佐年
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.12, pp.828-833, 2006 (Released:2006-12-29)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 20 27
バランス機能は歩行能力に影響する因子の一つと考えられる.そこで歩行能力の代表的な評価法である最大歩行速度 (Maximum Walking Speed: MWS) と各種バランス検査を,若年者群と高齢者群で検討した.身長は若年者群ではMWS, Functional reach (FR),タンデム肢位での重心動揺,Timed Up and Go test (TUG) と相関したが,高齢者群では関係は認められなかった.若年者群ではMWSは,タンデム肢位外周面積,TUGと相関したが,これは身長の影響によると考えられた.高齢者群ではMWSは,FR,タンデム肢位総軌跡長,TUGと相関した.高齢者では歩行能力は静的・動的両者のバランス機能に影響されることが示唆された.
1 0 0 0 OA 変形性膝関節症における大腿四頭筋の筋力増強訓練の効果
- 著者
- 橘内 勇 小野沢 敏弘 山下 泉 鈴木 伸治 宮津 誠 井上 秀美
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, no.2, pp.82-84, 1986-03-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 4
変形性膝関節症(以下膝OA)患者および健常中高齢者に対し,膝伸展筋力増大を図る目的で同一方法による等運動性筋力訓練を行い,以下の結果を得た.1)4週間の訓練により最大膝伸展筋力は,健常成年男子は平均4.63kg・m,女子3.19kg・mの増加をみたが,老年女性では0.93kg・m,膝OA女性では0.50kg・mの微増にとどまった.2)老年女性および膝OA女性グループでは,3週以降はむしろ減少傾向が認められた.3)高齢者および膝OA例の筋力増強は,筋肥大によるものより神経性因子によるものが大きいと考えられる.4)筋機能の評価には最大収縮力だけでなく,持久力あるいは神経制御機能を含めた方法が必要となる.
1 0 0 0 OA 嚥下障害のリハビリテーションにおけるvideofluorographyの応用
- 著者
- 才藤 栄一 木村 彰男 矢守 茂 森 ひろみ 出江 紳一 千野 直一
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, no.3, pp.121-124, 1986-05-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 8 8
嚥下障害の治療指向的評価法としてvideofluorography検査を26例の機能的嚥下障害が疑われた患者に施行し,嚥下障害のリハビリアプローチ上,重要な-むせの意義,体位の影響,食物形態の影響-について検討した.誤嚥とむせは,約3分の1の症例で相関せず,むせのないことが安全な嚥下とはいえなかった.体位では従来,体幹垂直位が推奨されてきたが,体幹後屈位の方が誤嚥の程度が軽く,より嚥下しやすい体位であった.食物形態については,固形物は口腔期障害を増悪し,咽頭期障害(誤嚥)を軽減した.