- 著者
- Takaki Kamiya Daiki Hira Ryo Nakajima Kazuha Shinoda Atsuko Motomochi Aya Morikochi Yoshito Ikeda Tetsuichiro Isono Michiya Akabane Satoshi Ueshima Mikio Kakumoto Shinji Imai Shin-ya Morita Tomohiro Terada
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.7, pp.907-913, 2023-07-01 (Released:2023-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Tramadol is metabolized by CYP2D6 to an active metabolite, which in turn acts as an analgesic. This study aimed to investigate the impact of CYP2D6 genotype on the analgesic effect of tramadol in clinical practice. A retrospective cohort study was performed in patients treated with tramadol for postoperative pain after arthroscopic surgery for rotator cuff injury during April 2017–March 2019. The impact of CYP2D6 genotypes on the analgesic effects was assessed by the numeric rating scale (NRS) pain scoring and analyzed by the Mann–Whitney U test. Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis was performed to identify predictive factors for the area under the time-NRS curve (NRS-AUC), which was calculated using the linear trapezoidal method. Among the 85 enrolled Japanese patients, the number of phenotypes with CYP2D6 normal metabolizer (NM) and intermediate metabolizer (IM) was n = 69 (81.1%) and n = 16 (18.9%), respectively. The NRS and NRS-AUC in the IM group were significantly higher than those in the NM group until Day 7 (p < 0.05). The multiple linear regression analysis indicated that the CYP2D6 polymorphism was a prediction factor of the high NRS-AUC levels in Days 0–7 (β = 9.52, 95% CI 1.30–17.7). In IM patients, the analgesic effect of tramadol was significantly reduced one week after orthopedic surgery in clinical practice. Therefore, dose escalation of tramadol or the use of alternative analgesic medications can be recommended for IM patients.
- 著者
- Lu Lin Shunsuke Kataoka Kiichi Hirayama Ryozo Shibuya Kenji Watanabe Hiroyuki Morimoto Takashi Ohshima
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.2, pp.101-106, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 53
Catalytic control of chemoselectivity is crucial in the synthesis of highly functionalized compounds. Although there are reports of efficient chemoselective reactions of alcohols and amines as nucleophiles, there are no reports of the chemoselective activation of alcohols and amines as electrophiles. In this study, highly O- and N-selective electrophilic activation of allylic alcohols and amines was achieved in Pd-catalyzed direct allylic alkylation. Allylamines were inherently more reactive than allylic alcohols (N-selectivity). On the other hand, the addition of catalytic amounts of 9-phenanthreneboronic acid preferentially activated allylic alcohols over allylamines (O-selectivity). Density functional theory (DFT) calculations suggested that the N-selectivity is due to the selective activation of allylic amines with ammonium cations, and boronate formation accelerates the activation of allylic alcohols.
- 著者
- Taisuke Konno Hiroyuki Suzuki Hitoshi Nakamura Yuriko Murai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b22-00050, (Released:2022-06-29)
- 参考文献数
- 15
In veterinary medicine, various drugs are used on a daily basis. Using inappropriate medications poses health hazards to companion animals and humans; thus, assessing adverse events in veterinary medicine has great social significance but remains an untapped area of research. In this study, to promote the appropriate use of veterinary drugs and clarify common pharmaceutical issues in Japanese veterinary medicine, we analyzed information in the Veterinary Drug Side Effects Database (National Veterinary Assay Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan). We found that the number of reports has been increasing annually, including those on high-risk drugs, molecular-targeted drugs, and antibody-based drugs. The details of the reports were similar to those from the United States, including the misadministration of veterinary drugs to humans, improper drug management, and re-administering drugs with a history of side effects. Furthermore, 46.50% of all reports mentioned the administration of one or more drugs, with the highest number of concomitant drugs being 10. In addition, 37.78% of all reports described the use of drugs in manners deviating from the intended use indicated in the package insert. Therefore, to avoid adverse events, pharmacists may have to be involved in dispensing and aseptically preparing veterinary medicines and providing drug information and medication guidance. To optimize pharmacotherapy for ill companion animals, "veterinary pharmacy" and "veterinary medicine pharmacy" must be developed in line with clinical situations in Japan, while considering knowledge from countries that are advanced in terms of veterinary medicine.
- 著者
- Toshihiko Tashima
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.4, pp.316-325, 2020-04-01 (Released:2020-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 59
- 被引用文献数
- 23 55
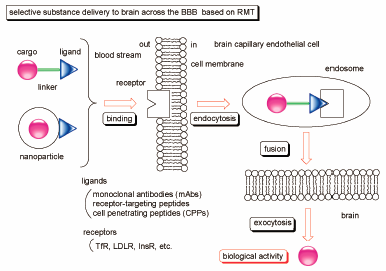
Discriminatory drug delivery into target cells is essential to effectively elicit the drug activity and to avoid off-target side effects; however, transporting drugs across the cell membrane is difficult due to factors such as molecular size, hydrophilicity, intercellular adhesiveness, and efflux transporters, particularly, in the brain capillary endothelial cells. Drug delivery into the brain is blocked by the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Thus, developing drugs for the central nervous system (CNS) diseases remains a challenge. The approach based on receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) can overcome this impassable problem at the BBB. Well-designed molecules for RMT form conjugates with the ligand and drugs via linkers or nanoparticles. Cell penetrating peptides (CPPs), receptor-targeting peptides, and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are often used as ligands. The binding of ligand to the receptor on the endothelial cell surface induces endocytosis. Existing exosomes comprising the conjugates move in the cytoplasm and fuse with the opposite plasma membrane to release them. Subsequently, the transcytosed conjugate-loaded drugs or released drugs from the conjugates elicit activity in the brain. As receptors, transferrin receptor (TfR), low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), and insulin receptor (InsR) have been used to intendedly induce transcytosis. Presently, several clinical trials on CNS drugs for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson disease are hindered due to poor drug distribution into the brain. Therefore, this strategy based on RMT is a promising method for CNS drugs to be transported into the brain. In this review, I introduce the practicality and possibility of drug delivery into brain across the BBB using RMT.
- 著者
- Fan Zhang Mu-rong Liu Hai-tong Wan
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.3, pp.335-339, 2014-03-01 (Released:2014-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 72
- 被引用文献数
- 63 101
PEGylation changes the physical and chemical properties of the biomedical molecule, such as its conformation, electrostatic binding, and hydrophobicity, and results in an improvement in the pharmacokinetic behavior of the drug, while it also causes some disadvantages of which cannot be neglected. The available data manifests that polyethylene glycol (PEG) itself shows potential risk, such as immunogenicity of the PEG and PEG-containing vacuoles in cells observed with PEGylated biologicals. Decreased activity and heterogeneity are also the negative aspects of PEGylation. The unfavorable impacts which are brought by the PEGylation are described here with examples of modified therapeutic proteins on the market and used in the clinical trials.
- 著者
- Ryota Tanaka Daiki Eto Koji Goto Yoshifumi Ohchi Norihisa Yasuda Yosuke Suzuki Ryosuke Tatsuta Takaaki Kitano Hiroki Itoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.737-741, 2021-05-01 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 5
For intensive care unit (ICU) patients, injectable voriconazole (VRCZ) is difficult to use because the patients often develop acute kidney injury. Since many ICU patients have consciousness disturbance, oral ingestion of tablet formulation is also difficult, and administration of a suspension via enteral feeding tube is required when using VRCZ. In this study, we investigated the in vitro adsorption property of oral VRCZ to feeding tube and performed pharmacokinetic analysis of VRCZ prepared by powdering and simple suspension for ICU patients. VRCZ was tube-administered to five ICU patients at a loading dose of 300 mg and plasma VRCZ concentrations before and at 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 h after the first dose were measured using HPLC. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated by non-compartmental model analysis. The recovery rate of VRCZ after infusion of the suspension through feeding tube was 89.8 ± 8.3%, but the cumulative rates after the first and second re-infusion were 102.7 ± 20.7 and 99.3 ± 10.3%, respectively, suggesting almost no residual drug in the tube after re-infusion. Metabolic phenotype was extensive metabolizer (EM) in two patients and intermediate metabolizer (IM) in three patients. The values of total clearance (CLtot/F) calculated by moment analysis were 0.51 and 0.55 L/h/kg in two EM patients, and 0.09, 0.29 and 0.31 L/h/kg in three IM patients. The CLtot/F was apparently lower in IM patients compared to EM. In conclusion, powdered and suspended VRCZ administered via enteral feeding tube showed pharmacokinetics depending on CYP2C19 gene polymorphism, similar to that observed in usual oral administration.
- 著者
- 柳澤 裕之
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.128, no.3, pp.333-339, 2008 (Released:2008-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 35 51
Zinc is an essential trace element and serves as the active center of approximately 300 enzymes. Therefore, zinc deficiency may be associated with a variety of clinical features such as hypogeusia, hyposmia, growth retardation, dermatitis, alopecia, gonadal hypofunction, abnormal pregnancy, susceptibility to infections, delayed wound healing, impaired glucose tolerance, and increased carcinogenesis. Zinc deficiency was reported to be on the increase in the Nagano Study conducted from 2003 to 2005. Zinc therapy is classified into two categories, zinc-supplementary and -specific treatments. Ordinarily, zinc-supplementary therapy is carried out for the symptoms and diseases caused by zinc deficiency. On the other hand, zinc-specific therapy is applied to obtain copper- and iron-chelating, antifibrotic, and antidiabetic effects. The availability of zinc-specific therapy is now confirmed in humans and animals. Hereafter, the safety of zinc therapy needs to be examined further.
- 著者
- Kosuke Kusamori
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.8, pp.1029-1036, 2021-08-01 (Released:2021-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 70
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Cell-based therapy for disease treatment involves the transplantation of cells obtained either from self or others into relevant patients. While cells constituting the body tissues maintain homeostasis by performing remarkable functions through complicated cell–cell interactions, transplanted cells, which are generally cultured as a monolayer, are unable to recapitulate similar interactions in vivo. The regulation of cell–cell interactions can immensely increase the function and therapeutic effect of transplanted cells. This review aims to summarize the methods of regulating cell–cell interactions that could significantly increase the therapeutic effects of transplanted cells. The first method involves the generation of multicellular spheroids by three-dimensional cell culture. Spheroid formation greatly improved the survival and therapeutic effects of insulin-secreting cells in diabetic mice after transplantation. Moreover, mixed multicellular spheroids, composed of insulin-secreting cells and aorta endothelial cells or fibroblasts, were found to significantly improve insulin secretion. Secondly, adhesamine derivatives, which are low-molecular-weight compounds that accelerate cell adhesion and avoid anoikis and anchorage-dependent apoptosis, have been used to improve the survival of bone marrow-derived cells and significantly enhanced the therapeutic effects in a diabetic mouse model of delayed wound healing. Finally, the avidin-biotin complex method, a cell surface modification method, has been applied to endow tumor-homing mesenchymal stem cells with anti-tumor ability by modifying them with doxorubicin-encapsulated liposomes. The modified cells showed excellent effectiveness in cell-based cancer-targeting therapy. The discussed methods can be useful tools for advanced cell-based therapy, promising future clinical applications.
- 著者
- Kazuyuki Niki Maki Yasui Maika Iguchi Tomomi Isono Hiroto Kageyama Mikiko Ueda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.2, pp.279-282, 2021-02-01 (Released:2021-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Taking bitter-tasting drugs can be stressful for children who have underdeveloped swallowing skills and do not understand the meaning of medication. Furthermore, the senses of vision and smell are known to majorly influence taste. This pilot study was aimed at determining the effect of visual stimulation by immersive virtual reality (iVR) on taste and the safety of this approach for developing a new method to assist children with taking medication. Ten subjects participated in this study, and their mean (standard deviation (S.D.)) age was 21.8 (0.8) years. The subjects tasted the bitter aqueous solution (quinine 0.00375%) while viewing two different VR images (strawberry sponge cake and orange juice) alternately and received sensory tests immediately after the tasting and again 30 s later. In addition, nausea was assessed 30 s after tasting for each VR image. The primary endpoint was the difference in sensory test scores immediately after the tasting and 30 s later, between the two images. There were no significant differences in the sensory test scores between the placebo and either strawberry sponge cake or orange juice immediately after tasting. However, 30 s after tasting, the scores changed significantly to a tendency to perceive sweetness from the strawberry sponge cake and orange juice images compared with the placebo. No subject experienced nausea. Therefore, the findings of this study suggest that displaying images of sweet foods by using iVR to stimulate visual perception could safely reduce the sense of bitterness.
- 著者
- Yoshitaka Saito Kazuki Uchiyama Tatsuhiko Sakamoto Kosei Kubota Hiromitsu Oki Miwako Iwai Yoh Takekuma Yoshito Komatsu Mitsuru Sugawara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.3, pp.293-297, 2021-03-01 (Released:2021-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Chemotherapy regimen management is one of the most important oncology pharmacy practices, because chemotherapy is conducted according to the registered regimens. In this study, we evaluated the pharmaceutical practice that assumes the initial confirmation of chemotherapy regimens and the quality of practice sharing between oncology-specialized and non-specialized pharmacists in regimen management committee. Pharmacists initially confirmed the applied regimen prescribed by physicians regarding chemotherapeutic agents and prophylactic supportive care medicines. Following confirmation, the regimens were reviewed by the Hokkaido University Hospital Regimen Management Committee. A total of 233 regimens were reviewed by the committee over three years. In total, 110 pharmaceutical inquiries were conducted, 45% of inquiries were concerning chemotherapeutic agents, of which approximately half were regarding supportive care medicines. Most inquiries were regarding premedication, followed by those on administration time, solvent of infusion medicines, and dosage. Correction was performed for 84.5% of inquiries. There was no significant difference in inquiry rates between practice and trial regimens. We have entrusted the first basic regimen review according to the checklist, creation of the chemotherapy plan document, and registry of the adopted regimens in the ordering system from oncology-certified pharmacists to non-certified pharmacists. Basic regimen review was well conducted by a non-certified pharmacist, and a more advanced review was additionally performed by certified pharmacists. In conclusion, we demonstrated the utility of pharmaceutical confirmation in a chemotherapeutic regimen review, suitable review coverage, and quality practice sharing between oncology-certified and non-certified pharmacists, which is one of the recommended methods in chemotherapy regimen review.
- 著者
- Shungo Imai Kenji Momo Hitoshi Kashiwagi Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.10, pp.1519-1525, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 7
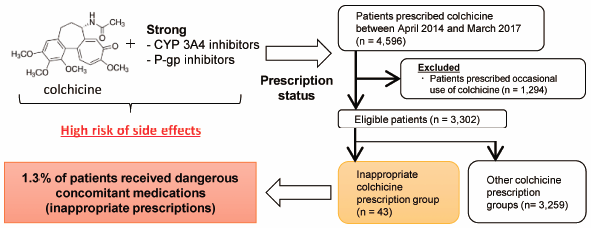
The anti-inflammatory agent colchicine may cause toxic effects such as rhabdomyolysis, pancytopenia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome in cases of overdose and when patients have renal or liver impairment. As colchicine is a substrate for CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), drug–drug interactions are important factors that cause fatal colchicine-related side effects. Thus, we conducted a nation-wide survey to determine the status of inappropriate colchicine prescriptions in Japan. Patients prescribed the regular use of colchicine from April 2014 to March 2017 were identified using the Japanese large health insurance claims database. As the primary endpoint, we evaluated the concomitant prescription proportions of strong CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inhibitors classified as “contraindications for co-administration” with colchicine in patients with renal or liver impairment. We defined these cases as “inappropriate colchicine prescriptions.” Additionally, factors affecting inappropriate colchicine prescriptions were analyzed. Among the 3302 enrolled patients, 43 (1.30%) were inappropriately prescribed colchicine. Of these 43 patients, 11 had baseline renal and/or liver impairment. By multiple regression analysis, the primary diseases “gout” and “Behçet’s disease” were extracted as independent factors for inappropriate colchicine prescriptions with odds ratios of 0.40 (95% confidence interval: 0.19–0.84) and 4.93 (95% confidence interval: 2.12–11.5), respectively. We found that approximately 1% of patients had important colchicine interactions. Particularly, Behçet’s disease was a risk factor for inappropriate prescriptions, with approximately 25% of patients showing renal and/or liver impairment (classified as “contraindications for co-administration”). These findings may be useful for medical professionals who prescribe colchicine therapy.
4 0 0 0 OA Foreword
- 著者
- Koyo Nishida
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.7, pp.559, 2020-07-01 (Released:2020-07-01)
4 0 0 0 OA Revolution of Small Molecule Drug Discovery by Affinity Selection-Mass Spectrometry Technology
- 著者
- Takashi Motoyaji
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.3, pp.191-193, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 15
Affinity selection (AS)-MS is a label-free binding assay technology for the analysis of interactions between targets and small drug molecules, which does not require modification of targets or compounds. AS-MS technology has been used in drug discovery research for more than 10 years, and is currently one of the most important affinity-based screening techniques. As such, it may be the driving force for novel small molecule drug discovery. This review introduces the principles of AS-MS technology and its use in high-throughput screening (HTS), then discusses strategies for its use in drug discovery and its application in target identification.
- 著者
- Katsuhiko Sekimata Tomohiro Sato Naoki Sakai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.3, pp.194-200, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 70
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) are diseases that typically manifest in childhood and are associated with severely reduced life expectancy. However, there are currently no effective therapies for these diseases, which remain incurable. Activin receptor-like kinase-2 (ALK2), encoded by the ACVR1 gene, is a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type-I receptor subtype that plays an important physiological role in the development of bones, muscles, brain, and other organs. Constitutively active mutants of ALK2 have been identified as causative of FOP and involved in the tumorigenesis of DIPG owing to abnormal activation of BMP signaling, and therefore have emerged as promising treatment targets. Here, we describe these two diseases, along with the link to ALK2 signal transduction, and highlight potential ALK2 inhibitors that are under development to offer new hope for patients with FOP and DIPG.
- 著者
- Atsushi Yoshimori Enzo Kawasaki Chisato Kanai Tomohiko Tasaka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.3, pp.227-233, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 15
The goal of drug design is to discover molecular structures that have suitable pharmacological properties in vast chemical space. In recent years, the use of deep generative models (DGMs) is getting a lot of attention as an effective method of generating new molecules with desired properties. However, most of the properties do not have three-dimensional (3D) information, such as shape and pharmacophore. In drug discovery, pharmacophores are valuable clues in finding active compounds. In this study, we propose a computational strategy based on deep reinforcement learning for generating molecular structures with a desired pharmacophore. In addition, to extract selective molecules against a target protein, chemical genomics-based virtual screening (CGBVS) is used as post-processing method of deep reinforcement learning. As an example study, we have employed this strategy to generate molecular structures of selective TIE2 inhibitors. This strategy can be adopted into general use for generating selective molecules with a desired pharmacophore.
- 著者
- Takumi Matsuzaki Masao Nakamura Takehide Nogita Atsushi Sato
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.6, pp.989-995, 2019-06-01 (Released:2019-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 21
An Intact form of lactoferrin (LF) is known to be absorbed from the small intestine and transported into the blood circulation. We reevaluated the cellular uptake and release of LF using an enterocyte model of human small intestinal cells derived from the Caco-2 cell line. In contrast to a previous report, we observed that intact bovine LF was taken up into seven and 21 d-cultured Caco-2 cells and successfully released back into the culture medium, even though the human intestinal LF receptor, intelectin-1, was not immunochemically detectable. Similar observations were made for human LF and its derivatives (the N-terminal half of LF designated N-lobe and Fc fusions). These observations regarding the uptake and release of intact LF in Caco-2 cells were consistent with in vivo observations. Therefore, we propose that the uptake and release of intact LF by Caco-2 cells should be assessed as a potential in vitro model of in vivo LF absorption in human intestines.
- 著者
- Masao Toyota Takuji Shimamura Hikari Ishii Matt Renner John Braggins Yoshinori Asakawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.10, pp.1390-1392, 2002 (Released:2002-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 5
- 被引用文献数
- 26 74
The ether extract of the New Zealand liverwort Radula marginata afforded a new cannabinoid type bibenzyl compound named perrottetinenic acid, and two new bibenzyls, together with a known cannabinoid, perrottetinene. Their structures were established by two dimensional (2D) NMR spectral data. The structure of perrottetinenic acid was a similar to that of Δ1-tetrahydrocannabinol, a known hallucinogen. Cannabinoid type bibenzyls have been isolated from liverwort Radula perrottetii, though have not previously been reported from the liverwort R. marginata.
- 著者
- Ghazi Mohamed Eisa Hussein Hisashi Matsuda Seikou Nakamura Makoto Hamao Toshihito Akiyama Kouhei Tamura Masayuki Yoshikawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.12, pp.1849-1855, 2011-12-01 (Released:2011-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 39 52
We previously investigated the effects of an aqueous extract of maté (mate) tea, made from the leaves of Ilex paraguariensis, on the diabesity and metabolic syndrome features in a mouse model. Mate induced significant decreases in body weight (BW), body mass index, and food intake (FI). In this study, to verify the mode of action of mate on FI and consequently on BW, we examined the anorexic effects of mate on the appetite and satiety markers glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and leptin in high-fat diet-fed ddY mice. GLP-1 is a peptide signal generated by the gastrointestinal tract, which regulates appetite and influences BW, whereas leptin is an afferent signal from the periphery to the brain in a homeostatic feedback loop that regulates adipose tissue mass, thus leading to decreased appetite and FI and increased energy expenditure. Chronic administration of mate (50, 100 mg/kg) for 3 weeks significantly reduced FI, BW, and ameliorated blood fats, liver fats, and adipose tissue. Mate induced significant increases in GLP-1 levels and leptin levels compared with the control. Acute administration of major constituents of mate showed significant increases in GLP-1 levels by dicaffeoyl quinic acids and matesaponins, and significant induction of satiety by caffeoyl quinic acids and caffeine in ddY mice. These findings suggest that mate may induce anorexic effects by direct induction of satiety and by stimulation of GLP-1 secretion and modulation of serum leptin levels.
- 著者
- Kohei Tsuji Takuya Kobayakawa Takahiro Ishii Nobuyo Higashi-Kuwata Chika Azuma Kouki Shinohara Yutaro Miura Kenichi Yamamoto Soshi Nishimura Shin-ichiro Hattori Haydar Bulut Hiroaki Mitsuya Hirokazu Tamamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.12, pp.879-886, 2023-12-01 (Released:2023-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 53
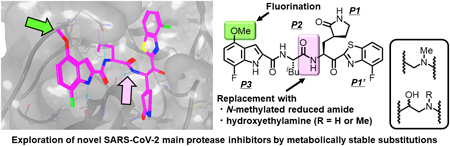
In the development of anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) drugs, its main protease (Mpro), which is an essential enzyme for viral replication, is a promising target. To date, the Mpro inhibitors, nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir, have been clinically developed by Pfizer Inc. and Shionogi & Co., Ltd., respectively, as orally administrable drugs to treat coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19). We have also developed several potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro that include compounds 4, 5, TKB245 (6), and TKB248 (7), which possesses a 4-fluorobenzothiazole ketone moiety as a reactive warhead. In compounds 5 and TKB248 (7) we have also found that replacement of the P1-P2 amide of compounds 4 and TKB245 (6) with the corresponding thioamide improved their pharmacokinetics (PK) profile in mice. Here, we report the design, synthesis and evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors with replacement of a digestible amide bond by surrogates (9–11, 33, and 34) and introduction of fluorine atoms in a metabolically reactive methyl group on the indole moiety (8). As the results, these compounds showed comparable or less potency compared to the corresponding parent compounds, YH-53/5h (2) and 4. These results should provide useful information for further development of Mpro inhibitors.
3 0 0 0 OA Chloroform Fraction of Panax Ginseng Extract Enhances Zip4-Mediated Zinc Influx into the Cytosol
- 著者
- Yoshito Ikeda Mizuki Kawakami Yasuyuki Yamada Masayuki Munekane Kohei Sano Takahiro Mukai Taiho Kambe Nobukazu Shitan
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BPB Reports (ISSN:2434432X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, no.3, pp.108-114, 2023 (Released:2023-06-14)
- 参考文献数
- 24
Zinc is an essential nutrient with important biological functions, and its deficiency can lead to several diseases. The zinc transporter families, ZIP and ZNT, play essential roles in regulating zinc homeostasis and dynamics in the body and cells. Specifically, ZIP4 is the primary zinc transporter responsible for zinc absorption in the small intestine. Previous studies have shown that Panax ginseng (P. ginseng) extract can promote mouse Zip4 expression, and ginsenosides, including Rc and Re, enhance zinc uptake. However, the effects of other metabolites present in P. ginseng extract remain unclear. Therefore, we fractionated P. ginseng extract using chloroform, ethyl acetate, and n-butyl alcohol, and evaluated the effect of each fraction on zinc uptake using mouse Hepa and Hepa/MRE-Luc cells that stably expressed luciferase under the promoter of metal-responsive elements. Luciferase activity assays demonstrated that the chloroform (F1), ethyl acetate (F2), and n-butyl alcohol (F3) fractions increased cellular zinc uptake. In particular, F1 fraction was found to induce Zip4 mRNA and protein expressions, which significantly enhanced zinc uptake. Ginsenosides were mainly present in the F2 and F3 fractions, indicating that metabolites other than ginsenosides in the F1 fraction would enhance zinc uptake by inducing Zip4 mRNA and protein expressions. Our study offers novel insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying zinc uptake by P. ginseng.