15 0 0 0 OA 亀岡断層帯の第四紀断層運動と地下構造
- 著者
- 岡田 篤正 植村 善博 東郷 正美 竹村 恵二 吉岡 敏和 堤 浩之 梅田 康弘 尾池 和夫 松井 和夫 杉森 辰次 杉山 直紀 園田 玉紀 梅田 孝行 松村 法行 山田 浩二 古澤 明
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本活断層学会
- 雑誌
- 活断層研究 (ISSN:09181024)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2005, no.25, pp.93-108, 2005-06-30 (Released:2012-11-13)
- 参考文献数
- 36
The Kameoka basin is located to the west of the Kyoto basin. On the northeast side of the basin, two faults trending the northwest to southeast direction exist along the foot and the former edge of a mountain, respectively. They compose of the Kameoka fault zone with the length of about 13km (Okada&Togo ed.,2000).To elucidate such characteristics as distribution, subsurface structure and activity of those faults, we have carried out seismic reflections (P-waves) and deep drilling surveys across the faults. Volcanic ash and pollen analysis were also performed using core samples obtained by drillings. In this paper, we report the results of these surveys, especially about the characteristics of the concealed faults related to basin formation.By these surveys, three faults were detected along the three sections by the seismic reflection crossing the eastern half of the Kameoka basin, named as Fl, F2 and F3 faults from west to east. All faults incline to the northeast to form the reverse fault type uplifting to the northeast side.The Fl fault is concealed under the alluvial plain of the Katsura River and is an active fault having remarkable displacement of vertical direction to a few hundreds of meters. An accumulation of the displacement in the vertical direction is plainly recognized on the topographical and geological sections.The F2 fault appears in the wide deformation zone on the hanging. wall of Fl fault and is thought to be a subordinate fault of the F1 fault. From the distribution, the F2 fault is corresponded to be an active fault described by Okada&Togo ed. (2000) and identified at former edge of a mountain in the Kameoka basin. In this paper, we will call the Fl fault and the F2 fault as“ the Kameoka fault within the basin”. It is surely distributed about 4.6 km from the Umaji to the Hozu settlements in the southeast direction.Of the Kawarabayashi reflection profile, one reflection layer C has vertical displacement of 65m resulted from the activity of“ the Kameoka fault within the basin”. A pure seam from core samples of the layer is confirmed as so-called Oda Volcanic ash at 420-450ka. Therefore, the average slip rate of the vertical displacement is estimated at 0.15m per thousand of years or less, during the last about 430,000 years.We also found a fault scarplet (relative height 1.5-2.5m) on a low terrace. It seems to be formed by the F2 faulting since about 20,000 years ago. Hence the faulting of“ the Kameoka fault within the basin” since the late Pleistocene is certain, and also there is a possibility of the activity in the Holocene from the existence of the reverse-inclined terrace II at Umaji.Judged from distribution, the F3 fault is corresponding to "the Kameoka fault in the foot of a mountain" described by Okada&Togo ed. (2000). There is no evidence of the F3 faulting during the late Quaternary.
5 0 0 0 韓国南東部の活断層系における大地震再来時間の評価
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫 JO 華龍 金 性均 慶 在福 全 明純 大倉 敬宏 久家 慶子 中西 一郎 入月 俊明 秋元 和実 山路 敦 鈴木 康弘 渡辺 満久 岡田 篤正 KIM Sung-kyun JUN Myang-soon JO Wha-ryong KYUNG Jai-bok
- 出版者
- 京都大学
- 雑誌
- 国際学術研究
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 1994
韓国南東部の梁山断層は,ほぼ北北東-南南西方向に約200kmにわたって走り,顕著な破砕帯を伴っている.この断層系において活断層変位地形を野外調査し,その主断層についてトレンチ掘削を実施した.この断層は河成段丘面群とその構成層を変位させ,東側の相対的隆起を伴う右横ずれの活断層であることを確認した(岡田ほか,1994).蔚山郡彦陽南方では,大規模な宅地開発が進められているので,その用地を利用して,主断層に伴われる地殻運動やそれ並行すると推定した副断層について多くのトレンチ調査を行った。こうした調査から,次のような事柄が判明した.彦陽南方の台地(高位面)は北東流していたかつての酌川川が形成した扇状地であり,初生的には北東へ傾いていたはずであるが,トレンチ地点付近では西方へ逆傾斜している.掘削調査の結果,高位面を構成する礫層が撓曲変形を受けていることが判明した.この高位面の撓曲による上下変位量は約5mである.いくつかの断層は認められたが,地表面まで切断するものは見当たらなかった.梁山断層の平均変位速度や高位段丘の形成時期を解明する必要があるので,梁山断層が通過する彦陽地域から太和江沿いに河成段丘面を追跡し,海成段丘面との関係を調べ,段丘面編年に関する資料を得るように努めた.それらの結果は,次のように要約される.河成段丘面はfH面群(fH1面・fH2面)・fH面群(fH1面・fM2面)・fL面群(fL1面〜fL3面)に,海成段丘面はm1面〜m3面に区分できる.海成段丘の旧汀線高度は,それぞれ53.3m・18.7m・3.4mである.fH面群やfM面群には赤色風化殻が形成されており,とくにfH面群で顕著である.fL面群の構成層は新鮮でほとんど風化していない.各河成段丘面は滑らかに蔚山湾周辺まで連続する.蔚山湾周辺では,fH2面は+10mの位置へ,fH1面は数mの位置へと連続してゆく.fL1面は下流部で沖積面下に埋没し,蔚山湾周辺での推定高度は-10mである.こうした資料からみて,fM1面が最終間氷期直前の氷期に,m2面が最終間氷期に形成された可能性が高い.fH面群はそれ以前の海面低下期に,m1面は最終間氷期以前の高海面期に形成されたと推定できる.南北〜北北西-南南東走向の蔚山断層系(延長約40km)は慶州市付近で梁山断層系に会合するが,この中央部に沿っても活断層変位地形の存在と,段丘堆積物を変位させる断層露頭が確認された.この特徴や関連現象について調べ,次のような事柄が判明した.蔚山断層系の断層線は著しく弯曲している.断層露頭表現や地形面の変形状態とから考えると,この断層の活動様式は典型的な逆断層である.第四紀後期に形成された地形面や堆積物が明瞭に変位を受けているので,蔚山断層は明らかに活断層である.この断層は高位段丘面を15m,中位段丘面を5m,上下方向へ変位させており,累積的な変位が認められる.断層崖や段丘面の変位方向からみて,東側の山地域が少なくとも第四紀の中ごろから継続的に隆起している.蔚山断層に沿って,明瞭な断層露頭が2ヶ所で観察された.末方里集落東方にある寺谷池北岸では,破砕した花崗岩が地形面を構成する礫層に,走向:ほぼ南北で,傾斜:25-30°Eの衝上面をもって接している.露頭上部では,上盤の花崗岩を被覆する礫層と砂礫層・腐植質層が急斜・逆転している.数本の断層が伴われ,幅数10cmの断層帯となっている.開谷里集落北東方の淵安川河床でも,やや風化した礫層の上に花崗岩が衝上している.末方里集落東方では,中位面を構成するシルト質層が液状化作用を受けて変形し,堆積直後の大地震発生を示唆する.その再来時間については,堆積物や地形面の年代解明を現在行っており,それらの結果を待って評価したい.こうした南北方向の逆断層性活断層の存在は,当域もほぼ東西方向の広域応力場に置かれていることを示唆する.これは北北東-南南西方向の梁山断層系が右ずれを示すこととも符号し,同じ応力場にあることを意味する.また,浦項市付近には,海成中新統が分布していることから,中新世以降の梁山断層の運動像を解明するために,地質調査を実施した.
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫 山田 聡治
- 出版者
- 独立行政法人防災科学技術研究所
- 雑誌
- 防災科学技術研究所研究資料 (ISSN:0917057X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.166, pp.161-175, 1995-03-31
The temporal variation of the number of LF and VLF noises has been compared with the occurrence of near shallow earthquakes. The results have been described by Oike et al.(1992), Oike and Murakami(1993) and Oike et al.(1993). In the case of 70 per cent of large earthquakes with magnitude larger than or equal to 6.0 anomalous increase of LF noises is observed within one day before the main shock whose epicentres are located in the land or shallow sea region. Similar phenomena are found in the case of near shallow earthquakes with magnitude larger than or equal to 5.0. Also inthe case of the largest earthquake (M7.8) during the observation a similar increase of LF and VLF noises as above mentioned was recorded. New observation system has been developed to record the wave forms of such phenomena and wave forms of co-seismic radiations from hypo-centers of large earthquakes. We have developed observation systems of electromagnetic radiations (EMR) related with the occurrence of earthquakes. Observing EMR at many and various observation points is important to detect EMR related with earthquakes. It is also important to observe them in low and wide frequency ranges for understanding the characteristics of the waves. We chose the ball antenna as a sensor which has sensitivity in low and wide frequency range (Ogawa et al., 1966). It is difficult to cover all frequency ranges by only one recorder, so we divided signals into several frequency bands and designed the most suitable filter and recording system for each band. We have developed handy observation system for EMR in the frequency range from 80Hz to 20kHz. Using this system, we can easily record EMR at any points and at any time. For example, going to the region where earthquake swarm is occurring, we can record EMR phenomena in the hypo-central region. Observation system for basic stations can record EMR in frequency range from DC to 20kHz broader than the handy system. By this system, we can get and make detailed analysis of records of EMR. By these two systems, we can expect to discuss EMR phenomena related with earthquakes. Such phenomena are possible to be caused by various mechanisms. It is also important to observe and analyze EMR from lightnings, because there is a possibility of the physical relationship between earthquakes and lightnings (Oike et al, 1993). During the observation using the developed recording systems the large earthquake of magnitude 7.8 occurred in the southwestern off Hokkaido region. Before and after the earthquake the anomalous increase of the number of LF and ELF noises were observed by the usual system and coseismic anomalous signals were recorded by the newly developed handy recording system.
4 0 0 0 OA 梁山断層 (韓国東南部) 中央部の活断層地形とトレンチ調査
- 著者
- 岡田 篤正 渡辺 満久 佐藤 比呂志 全 明純 曹 華龍 金 性均 田 正秀 池 憲哲 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 東京地学協会
- 雑誌
- 地学雑誌 (ISSN:0022135X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.103, no.2, pp.111-126, 1994-04-25 (Released:2010-10-13)
- 参考文献数
- 51
- 被引用文献数
- 12 39
Many distinct lineaments have been recognized by Landsat images in Korean Peninsula. The Yangsan fault system situated in the southeastern part of Korea is especially linear, continuously traceable for a long distance (about 200km), and particularly remarkable among these lineaments. The topographic expression of the Yangsan fault system is derived from the straightly stretching fault valley with wide shattered zones in the direction of NNE-SSW. This fault system extends for about 200km from the mouth of the Nagdong River west of Busan in the south to Yeondong in the north, and geologically separates Korean Peninsula from the Japan Sea. The amount of horizontal displacement may reach 30km. It is recognized as one of the most important faults in Korean Peninsula.From the interpretations of aerial photographs, and field surveys along the central part of the Yangsan fault system, the main results are summarized as follows:1. The Yangsan fault system has repeatedly moved in the late Quaternary. The lower to higher river terrace surfaces on this system show cumulative vertical offsets.2. The vertical component is upthrown on the east side from considering the terrace offset and the distribution of the mountainous lands. This vertical movement is reverse to the topographical situation on the meso-scale.3. The fault trace is extremely straight. The fault plane is almost vertical. The shatteredzone exceeds tens of meters in width with a remarkable fault gouge.4. The longer axis of flat clasts within the gravel observed in excavated the exploratory trench showed the re-arrangement along the fault. The predominantly right-lateral movements were recognized as the elongation of clayey parts and breccias in the fault gouge.5. From these characteristics, the Yangsan fault was clarified to be active with predominantly right-lateral movement. Estimated ages of terraces and its deposits give average rates of vertical and right slip on the Yangsan fault system at about 0.02-0.03mm/y, and at least 0.05-0.1mm/y, respectively.6. The fault topography is not found on the lower and lowest terraces. As the surface of the terrace has widely been cultivated as paddy fields for long historical time, lower fault scarplets less than a few meters high might have been modified or destroyed by the human actions. Therefore, we cannot mention the existence of the younger movement on the lower and lowest terraces.
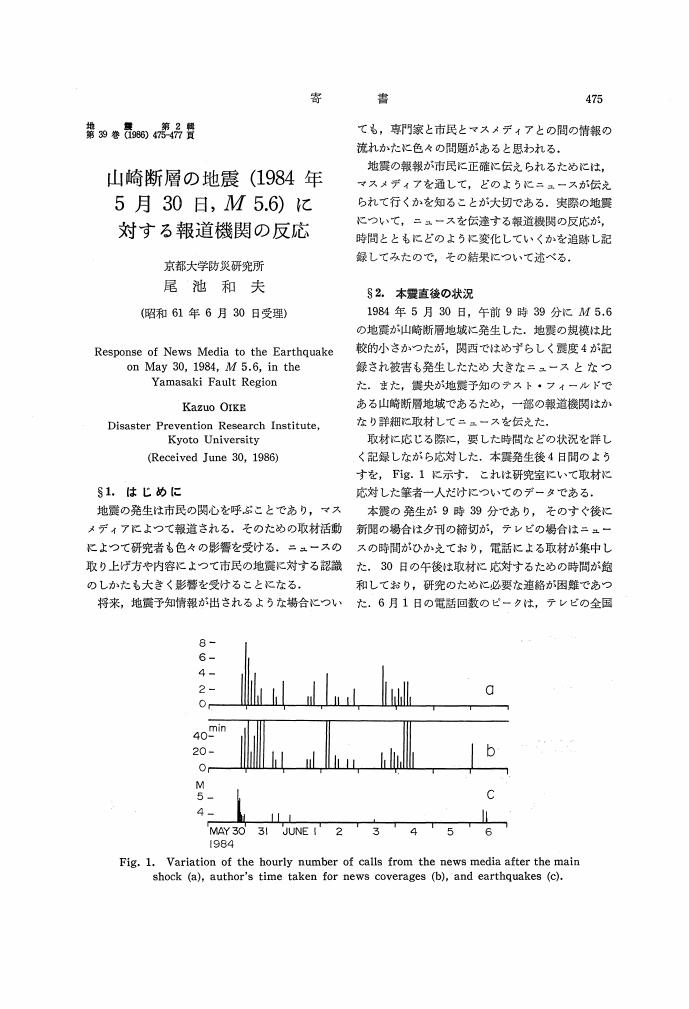
2 0 0 0 OA 山崎断層の地震 (1984年5月30日, M5.6) に対する報道機関の反応
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本地震学会
- 雑誌
- 地震 第2輯 (ISSN:00371114)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.475-477, 1986-09-25 (Released:2010-03-11)
2 0 0 0 2038年南海トラフの巨大地震
2 0 0 0 OA 1968年11月8日焼岳に発生した群発地震の発震機構について
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 京都大学防災研究所
- 雑誌
- 京都大学防災研究所年報. A = Disaster Prevention Research Institute Annuals. A (ISSN:0386412X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.A, pp.133-140, 1970-03-01
The mechanism of earthquake swarm that occurred at Mt. Yakedake on November 8, 1968, have been studied. The swarm began at Olh3Om and terminated at 14h51m. 43 shocks wererecorded at Kamitakara by the vertical component seismograph for the observation of micro-earthquakes. The frequency distribution of the P-IS interval times of the swarm corresponds toone of four peaks in that distribution which were observed at the station during four monthsbefore the occurrence of the earthquake swarm.The foci of these shocks have been determined from the P-IS times observed at the near micro-earthquake observation stations. They are confined within a small volume whose dimensionis about 500 meters.The time variation of the S/P which means the ratio of the maximum amplitudes of P and Swaves have been investigated. The push-pull distributions of the initial P motions have beenalso studied. The results show that the focal mechanism changes in relation to the activityof the earthquake swarm and seems to approach the stationary state at the end of the swarm.It is supposed that the occurrence of the main shocks disturbed the stress field around theirfoci and gave the great influences upon the mechanism of the smaller shocks.This earthquake swarm is separated into four sequences. In the first sequence the large shockof M=~3.4 occurred in isolation. The main shock of M=3.3 and many aftershocks took placein the second sequence, the main shock of M =03.1 with some foreshocks and aftershocks occurredin the third one and the swarm of some smaller shocks occurred in the fourth one. This variationof the characteristics of the activity of each sequence seems to be related to the development ofthe fractures in the focal region.
2 0 0 0 OA 和歌山地方の地殻構造と微小地震の発震機構
- 著者
- 三雲 健 大塚 道男 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本地震学会
- 雑誌
- 地震 第2輯 (ISSN:00371114)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, no.3, pp.213-225, 1970-09-28 (Released:2010-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The focal mechanism of 20 microearthquakes in the Wakayama region have been determined from the seismograms recorded at ten temporary stations and eight routine network stations covering the region.The hypocenters of the earthquakes have been determined for five different crustal models (with a continuously varied velocity profile), to estimate the accuracy of their location and the emergent angle of seismic rays at the focus. The radiation pattern of P wave first motions for the 15 shocks, which was corrected for an appropriate crustal structure, can be interpreted by the double-couple type mechanism with dipping nodal planes.The average of the maximum pressure axes is oriented nearly horizontally along the N70°W-S70°E direction, while the axes of the maximum tension show a steep dip in many cases. If a slip dislocation is assumed to be a likely model of the earthquakes, the source would be thrust faulting with a predominant component of dip slip. The other five earthquakes shows, however, the radiation pattern inconsistent with the double-couple type mechanism.
2 0 0 0 OA 中国のダム誘発地震について
- 著者
- 石川 有三 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本地震学会
- 雑誌
- 地震 第2輯 (ISSN:00371114)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.2, pp.171-181, 1982-06-25 (Released:2010-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Ten reservoir induced earthquakes were investigated. The relation between the dam height and the maximum magnitude of the induced earthquake was found. We show that there are the magnitude limit of earthquake related with the dam height. The Shenwo earthquake, this was only one exception of this relation, wasn't far from the 1975 Haicheng earthquake. It occurred only 43 days before the Haicheng earthquake. We think the Shenwo earthquake occurred in the precursory period of the Haicheng earthquake. So we concluded that it occurred under the special tectonic condition just before the large earthquake.Fault plane solutions for reservoir induced earthquakes were also compared with those for natural ones. We got the result that the directions of P-axis and T-axis for induced earthquakes were not always same to those for natural ones. So, we concluded that induced earthquakes occurred in the faults which were weakened by the permeated water rather than in the faults which were easily dislocated by the tectonic force. Large aftershocks of the Xinfengjiang earthquake were investigated and we showed the examples of the shock induced by loading and unloading.The b-values for the aftershocks of induced earthquakes were calculated, but we got only one b-value for natural one which could be compared to induced one and there was no significant difference between them.
- 著者
- 趙 志新 松村 一男 尾池 和夫 石川 有三
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本地震学会
- 雑誌
- 地震 第2輯 (ISSN:00371114)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.3, pp.383-396, 1987-09-25 (Released:2010-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 4 4
Mutual relations of seismicity in the long period in various regions from North China to Japan trench in East Asia have been analyzed. Time series of events were analyzed in various regions in North China, Korean Peninsula and Japan Island.The seismicity of each region was high in the period from 1550 to 1700. Then quiet period had been lasting until 1900. From 1900 the active period began again and have continued up to the present.Impulsive activities were found in the western part of North China and Japan Islalds in a short time range around 1830 during the quiet period. It seems that short period variations superpose on the long period variation. These short period variations in two regions also correlated to each other.Synchronous variations of seismicity in these regions are implicated in the formation of earthquake generating stress fields from North China to Japan trench under the common tectonic conditions. The release and the accumulation of stresses correspond to the active and quiet period of seismicity, respectively.Correlations among seismicities and stress fields from North China to Japan trench suggest that there is a transmission of the tectonic force from the subduction of the pacific plate along the Japan trench to North China through Korean Peninsula.
1 0 0 0 OA 中国の地震予知
はじめに 古来、中国には大地震は政治に対する天の警告である、という考えがあって、地震についての記載が非常に多く残されている。これらの資料はよく整理されていて、今、地震予報のための基礎となっている。現在の中国でも、大地震は政治を動かし、農業や工業に重大な影響を与えている。 私は、一九七四年七月、中国科学技術協会の招きで、東京大学の浅田敏教授、名古屋大学の志知竜一助教授とともに、外国人の専門家としては、おそらく初めて、中国の地震予報の仕事を直接見ることができた。その仕事の現場で、詳しく資料を見、実際に地震予報を出していることを知った時、私たち三人は、目を見張る思いだった。一九七五年二月、日本の地震学会は、海城地震の予報と予防に成功した中国の専門家たちを招き、その成果を講演してもらった。その時、三週間の日程のほとんどを、顧功叙先生を団長とする六名の中国地震考察団のメンバーと、私は寝食をともにしながら世話役としてつきそい、いろいろのことについて話し合った。一九七七年五月一六日から三週間、日本の地震学会は、中国科学院の招きを受けて、東北大学の鈴木次郎教授を団長とする八人の代表団を中国に派遣した。私は、その団員の一人として参加し、大陸では現在もっとも地殻活動の激しい雲南省へ視察旅行をすることができた。 (中略) これらの日中の地震関係者の交流を通じて、得たものは大層多く、その内容は貴重である。中国の専門家たちによって整理されたデータは、日本での地震予知・予報・予防の仕事にきわめて重要な情報を提供してくれる。彼らの大地震予知・予報・予防の経験は、これからそれを体験しょうとする日本にとって重要である。この本では、中国での成果と経験を、著者が自分自身の目でデータを確認し、直接話を聞き、あるいは現場を見たことを中心にまとめ、わかりやすく解説して、日本での地震予知と予防の仕事に役立てたいと思う。 地震の専門家にも、また一般の読者にも、大地震予報の可能性とその効果を、また地震予報にとって、専門家と大衆と行政組織との結びつきがいかにたいせつであるかということを、実例を通じて理解していただきたいと思っている。
1 0 0 0 OA 東日本の巨大地震に学ぶ(1) プレート収束域にできた日本列島
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本原子力学会
- 雑誌
- 日本原子力学会誌ATOMOΣ (ISSN:18822606)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.10, pp.675-677, 2011 (Released:2019-09-06)
福島第一原子力発電所1号機の設置許可が出て,海抜35mの断崖が10mまで削られ,GEに引き渡されて発電所の建設工事が開始された1967年の頃,地球科学では,プレートテクトニクスの仮説が登場して発展し始めた時であった。 今,仮説ではなく,実測しながら見ているプレート運動のことを,できるだけ普通の言葉で解説したい。固体地球の運動の中で,2011年東北地方太平洋沖地震の発生を位置づけ,この巨大地震の発生の仕組みと,日本列島の今後の地震活動を,5回の連載で解説したい。
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫 村上 寛史
- 出版者
- 独立行政法人防災科学技術研究所
- 雑誌
- 防災科学技術研究所研究資料 (ISSN:0917057X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.157, pp.221-251, 1993-03-29
Continuous observations of variation of the number of LF and VLF electromagnetic noises have been done at the Uji station in Kyoto Prefecture. LF noise is observed by CRF-1 type radio receiver whose frequency is fixed at 163kHz and VLF noise is observed by ball antenna with band-pass filter from 1 to 10kHz. The temporal variation of the number of LF and VLF noises has been compared with the occurrence of near shallow earthquakes. In the case of 70 per cent of large earthquakes with magnitude larger than or equal to 6.0 anomalous increase of LF noises is observed within one day before the main shock whose epicentres are located in the land or shallow sea region. Similar phenomena are found in the case of near shallow earthquakes with magnitude larger than or equal to 5.0. Present study indicates the possibility of the existence of certain kinds of physical relationship between the occurrence of shallow earthquakes and LF and VLF electromagnetic noises.
1 0 0 0 IR 地震学と統計学 (統計数理研究所 研究活動 (研究会報告 大学教育における統計学))
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 統計数理研究所
- 雑誌
- 統計数理 = Proceedings of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics (ISSN:09126112)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.2, pp.253-257, 1993-12
1 0 0 0 OA 朝鮮半島および中国大陸における地震発生の季節性
- 著者
- 松村 一男 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 京都大学防災研究所
- 雑誌
- 京都大学防災研究所年報. B = Disaster Prevention Research Institute Annuals. B (ISSN:0386412X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.B-1, pp.185-192, 1985-04-01
1 0 0 0 OA 降雨と地震発生との関係について
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 京都大学防災研究所
- 雑誌
- 京都大学防災研究所年報. B = Disaster Prevention Research Institute Annuals. B (ISSN:0386412X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.B-1, pp.35-45, 1977-04-01
1 0 0 0 OA 地震学からみた中央構造線 : 中央構造線の形成過程
- 著者
- 塩野 清治 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 日本地質学会
- 雑誌
- 日本地質学会学術大会講演要旨
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.85, pp.23-24, 1978-04-01
1 0 0 0 OA 鳥取微小地震観測所の震源表について
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本地震学会
- 雑誌
- 地震 第2輯 (ISSN:00371114)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.3, pp.331-346, 1975-10-10 (Released:2010-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
Five stations of the Tottori Microearthquake Observatory have supplied an amount of records of microearthquakes since June, 1965. They are very useful to investigate the characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution of microearthquakes. Using data from three stations MZT, OYT and IZT, a seismological bulletin has been compiled. It contains P, P-S and P-F times and directions of initial motions at three stations, the coordinates of foci calculated from data of three stations and magnitude of each shock determined from total duration (P-F time).From June, 1965 to December, 1973, 7346 earthquake foci have been determined. Their epicenters have been plotted on seismicity maps. One of significant results from them is that the close relation between active faults and alignments of epicenters has been recognized.Computed results of epicenters from data of the three stations have good accuracy comparing with those from five stations. Errors of hypocenters near to the network are less than 2km. Those of distant foci whose P-S times are larger than 10 seconds are less than 10km. Because of the important purpose to know the temporal distribution of microearthquakes, almost all data containing some reading values which do not have so good accuracy have been used for calculation.Frequency distribution of magnitudes shows the normal activity in this region. It also shows that distant shocks whose magnitude are larger than 2.0 and epicentral distances are about 150km, are detected by this network of three stations. Hypocenters whose magnitudes are larger than 1.0 have been detected in the near region around the network.
1 0 0 0 OA 電卓を利用した積算記録計
- 著者
- 尾池 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本地震学会
- 雑誌
- 地震 第2輯 (ISSN:00371114)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.459-461, 1985-09-25 (Released:2010-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 1