- 著者
- Takahiro Yamauchi Yasuo Okumura Koichi Nagashima Ryuta Watanabe Yuki Saito Katsuaki Yokoyama Naoya Matsumoto Katsumi Miyauchi Sakiko Miyazaki Hidemori Hayashi Yuya Matsue Yuji Nishizaki Shuko Nojiri Tohru Minamino Hiroyuki Daida
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0318, (Released:2023-08-09)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: The HELT-E2S2score, which assigns 1 point to Hypertension, Elderly aged 75–84 years, Low body mass index <18.5 kg/m2, and Type of atrial fibrillation (AF: persistent/permanent), and 2 points to Extreme Elderly aged ≥85 years and previous Stroke, has been proposed as a new risk stratification for strokes in Japanese AF patients, but has not yet undergone external validation.Methods and Results: We evaluated the prognostic performance of the HELT-E2S2score for stroke risk stratification using 2 large-scale registries in Japanese AF patients (n=7,020). During 23,241 person-years of follow-up (mean follow-up 1,208±450 days), 287 ischemic stroke events occurred. The C-statistic using the HELT-E2S2score was 0.661 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.629–0.692), which was numerically higher than with the CHADS2score (0.644, 95% CI 0.613–0.675; P=0.15 vs. HELT-E2S2) or CHA2DS2-VASc score (0.650, 95% CI, 0.619–0.680; P=0.37 vs. HELT-E2S2). In the SAKURA AF Registry, the C-statistic of the HELT-E2S2score was consistently higher than the CHADS2and CHA2DS2-VASc scores across all 3 types of facilities comprising university hospitals, general hospitals, and clinics. However, in the RAFFINE Study, its superiority was only observed in general hospitals.Conclusions: The HELT-E2S2score demonstrated potential value for risk stratification, particularly in a super-aged society such as Japan. However, its superiority over the CHADS2or CHA2DS2-VASc scores may vary across different hospital settings.
- 著者
- Masayoshi Suda Goro Katsuumi Tamar Tchkonia James L. Kirkland Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0657, (Released:2023-10-26)
- 参考文献数
- 122
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Aging is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and accumulating evidence indicates that biological aging has a significant effect on the onset and progression of CVDs. In recent years, therapies targeting senescent cells (senotherapies), particularly senolytics that selectively eliminate senescent cells, have been developed and show promise for treating geriatric syndromes and age-associated diseases, including CVDs. In 2 pilot studies published in 2019 the senolytic combination, dasatinib plus quercetin, improved physical function in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and eliminated senescent cells from adipose tissue in patients with diabetic kidney disease. More than 30 clinical trials using senolytics are currently underway or planned. In preclinical CVD models, senolytics appear to improve heart failure, ischemic heart disease, valvular heart disease, atherosclerosis, aortic aneurysm, vascular dysfunction, dialysis arteriovenous fistula patency, and pre-eclampsia. Because senotherapies are completely different strategies from existing treatment paradigms, they might alleviate diseases for which there are no current effective treatments or they could be used in addition to current therapies to enhance efficacy. Moreover, senotherapies might delay, prevent, alleviate or treat multiple diseases in the elderly and reduce polypharmacy, because senotherapies target fundamental aging mechanisms. We comprehensively summarize the preclinical evidence about senotherapies for CVDs and discuss future prospects for their clinical application.
- 著者
- Toshiyuki Nagai Takayuki Inomata Takashi Kohno Takuma Sato Atsushi Tada Toru Kubo Kazufumi Nakamura Noriko Oyama-Manabe Yoshihiko Ikeda Takeo Fujino Yasuhide Asaumi Takahiro Okumura Toshiyuki Yano Kazuko Tajiri Hiroyuki Matsuura Yuichi Baba Haruki Sunami Shingo Tsujinaga Yasutoshi Ota Keiko Ohta-Ogo Yusuke Ishikawa Hideo Matama Nobutaka Nagano Kimi Sato Kazushi Yasuda Yasushi Sakata Koichiro Kuwahara Tohru Minamino Minoru Ono Toshihisa Anzai on behalf of the Japanese Circulation Society Joint Working Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0696, (Released:2023-03-10)
- 被引用文献数
- 17
- 著者
- Yuji Okura Kazuyuki Ozaki Hiroshi Tanaka Tatsuya Takenouchi Nobuaki Sato Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-19-0426, (Released:2019-09-18)
- 参考文献数
- 98
- 被引用文献数
- 10 10
Onco-cardiology, a new academic field, aims to improve the quality of life and prognosis of cancer patients and survivors with cardiovascular diseases (CVD). With the aging of the population, an epidemic of cancer with CVD is emerging in developed countries. Cancer and CVD share risk factors, pathophysiology, treatments, and preventive and rehabilitative measures. A multidisciplinary team-based approach is needed to support cancer treatment to maximize its effectiveness and minimize its cardiotoxic potential. Basic and clinical onco-cardiology are already being practiced harmoniously. However, systematization in academia and clinical practice and accumulation of evidence have just started. In this review, we present the epidemiology, common risk factors between cancer and CVD, future epidemic of CVD in patients with cancer, and the necessity for an onco-cardiological approach to managing the burden of CVD in cancer patients and survivors.
4 0 0 0 OA Effects of Phase II Cardiac Rehabilitation on Physical Function and Anxiety Levels in Frail Patients
- 著者
- Akio Honzawa Miho Nishitani-Yokoyama Kazunori Shimada Mitsuhiro Kunimoto Tomomi Matsubara Rie Matsumori Hiroki Kasuya Kei Fujiwara Mayumi Doi Kana Takagi-Kawahara Abidan Abulimiti Jianying Xu Akie Shimada Taira Yamamoto Atsushi Amano Tohru Asai Hiroyuki Daida Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-22-0008, (Released:2022-06-08)
- 参考文献数
- 32
Background: Frailty is an important prognostic factor in patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and patients with CVD have a high rate of concurrent psycho-emotional stress, as well as depressive mood and anxiety symptoms. Despite this, few reports have examined the effects of the efficacy of Phase II cardiac rehabilitation (CR) in frail patients, including improvements in anxiety levels.Methods and Results: In all, 137 patients (mean [±SD] age 65.8±13.0 years; 71% male) who participated in Phase II CR and were assessed after CR completion were included in this study. Patients were evaluated using the Kihon Checklist (KCL) form at the beginning of CR and were divided into the 3 groups according to KCL scores: frail (n=34, 25%), pre-frail (n=40, 29%), and non-frail (n=63, 46%). Physical function and anxiety levels were compared among the 3 groups. The pre-frail and frail groups had significantly higher state anxiety and trait anxiety than the non-frail group (P<0.01). At the end of Phase II CR, all 3 groups showed significant improvements in the 6-min walking distance (P<0.05). State anxiety improved significantly in the non-frail and pre-frail groups, whereas trait anxiety only improved in the non-frail group.Conclusions: Physical function was improved in frail patients who participated in Phase II CR. However, there was no significant improvement in their level of anxiety.
- 著者
- Yuji Okura Kazuyuki Ozaki Hiroshi Tanaka Tatsuya Takenouchi Nobuaki Sato Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.11, pp.2191-2202, 2019-10-25 (Released:2019-10-25)
- 参考文献数
- 98
- 被引用文献数
- 5 10
Onco-cardiology, a new academic field, aims to improve the quality of life and prognosis of cancer patients and survivors with cardiovascular diseases (CVD). With the aging of the population, an epidemic of cancer with CVD is emerging in developed countries. Cancer and CVD share risk factors, pathophysiology, treatments, and preventive and rehabilitative measures. A multidisciplinary team-based approach is needed to support cancer treatment to maximize its effectiveness and minimize its cardiotoxic potential. Basic and clinical onco-cardiology are already being practiced harmoniously. However, systematization in academia and clinical practice and accumulation of evidence have just started. In this review, we present the epidemiology, common risk factors between cancer and CVD, future epidemic of CVD in patients with cancer, and the necessity for an onco-cardiological approach to managing the burden of CVD in cancer patients and survivors.
- 著者
- Tohru Minamino Miki Kinoshita Yusuke V. Morimoto Keiichi Namba
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e190046, (Released:2022-11-19)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
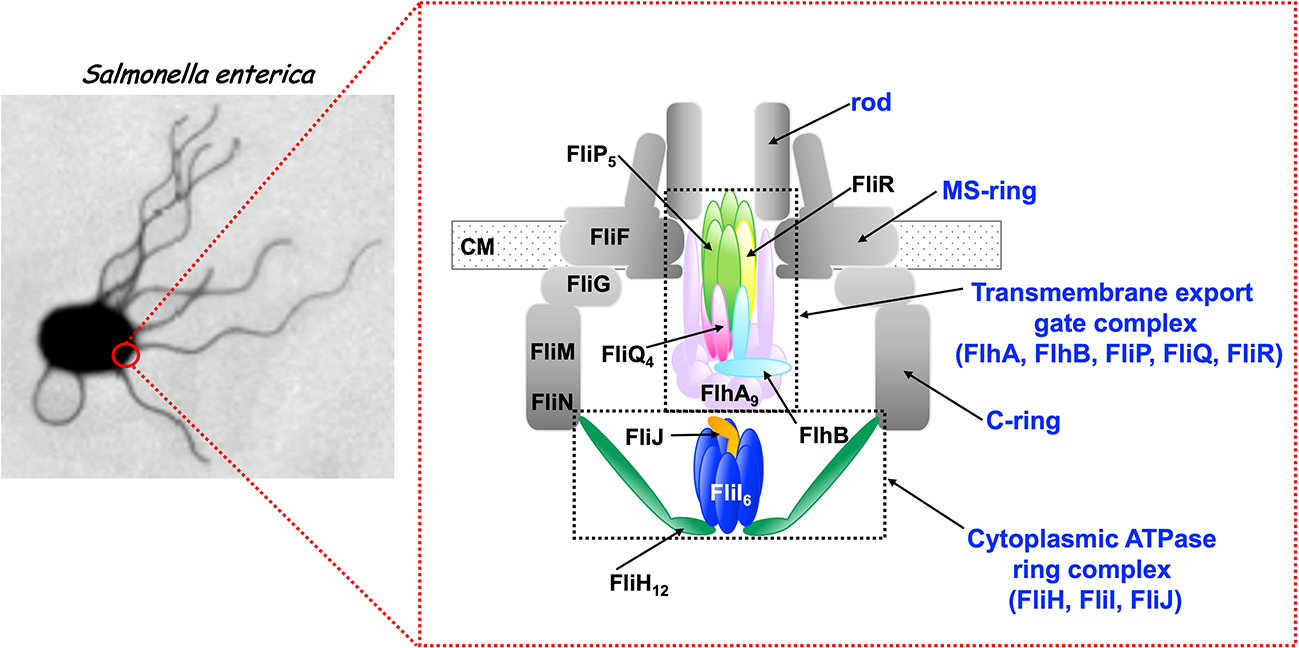
Bacteria employ the flagellar type III secretion system (fT3SS) to construct flagellum, which acts as a supramolecular motility machine. The fT3SS of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is composed of a transmembrane export gate complex and a cytoplasmic ATPase ring complex. The transmembrane export gate complex is fueled by proton motive force across the cytoplasmic membrane and is divided into four distinct functional parts: a dual-fuel export engine; a polypeptide channel; a membrane voltage sensor; and a docking platform. ATP hydrolysis by the cytoplasmic ATPase complex converts the export gate complex into a highly efficient proton (H+)/ protein antiporter that couples inward-directed H+ flow with outward-directed protein export. When the ATPase ring complex does not work well in a given environment, the export gate complex will remain inactive. However, when the electric potential difference, which is defined as membrane voltage, rises above a certain threshold value, the export gate complex becomes an active H+/protein antiporter to a considerable degree, suggesting that the export gate complex has a voltage-gated activation mechanism. Furthermore, the export gate complex also has a sodium ion (Na+) channel to couple Na+ influx with flagellar protein export. In this article, we review our current understanding of the activation mechanism of the dual-fuel protein export engine of the fT3SS. This review article is an extended version of a Japanese article, Membrane voltage-dependent activation of the transmembrane export gate complex in the bacterial flagellar type III secretion system, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 62, p165–169 (2022).
2 0 0 0 OA Frontiers of microbial movement research
- 著者
- Tohru Minamino Daisuke Nakane Shuichi Nakamura Hana Kiyama Yusuke V. Morimoto Makoto Miyata
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.3, pp.e200033, 2023 (Released:2023-09-15)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 著者
- Tomohiro Kaneko Sakiko Miyazaki Takuma Koike Azusa Murata Ryoko Morimoto Kuniaki Hirose Kazuhisa Takamura Daisuke Endo Atsushi Amano Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.8176-21, (Released:2021-10-19)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Atypical Shone's complex is a rare congenital anomaly involving a left-sided obstructive lesion of two or three cardiovascular levels. A 70-year-old man with dyspnea on exertion was diagnosed with severe aortic stenosis (AS) with a bicuspid valve, complicated by severe aortic coarctation (CoA) and a double-orifice mitral valve. He underwent surgery for AS and CoA in one session. It is important to search for complicated malformations, even in cases of bicuspid aortic valve found in old age.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Terashima Akihiro Kawamoto Yusuke V. Morimoto Katsumi Imada Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.14, pp.191-198, 2017 (Released:2017-12-19)
- 参考文献数
- 57
- 被引用文献数
- 1 43
The bacterial flagellum is a supramolecular motility machine consisting of the basal body as a rotary motor, the hook as a universal joint, and the filament as a helical propeller. Intact structures of the bacterial flagella have been observed for different bacterial species by electron cryotomography and subtomogram averaging. The core structures of the basal body consisting of the C ring, the MS ring, the rod and the protein export apparatus, and their organization are well conserved, but novel and divergent structures have also been visualized to surround the conserved structure of the basal body. This suggests that the flagellar motors have adapted to function in various environments where bacteria live and survive. In this review, we will summarize our current findings on the divergent structures of the bacterial flagellar motor.
- 著者
- Hiroshi Watanabe Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.16, pp.2285-2286, 2018-08-15 (Released:2018-08-15)
- 参考文献数
- 8
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
- 著者
- Tohru Minamino Miki Kinoshita Yusuke V. Morimoto Keiichi Namba
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.e190046, 2022 (Released:2022-12-07)
- 参考文献数
- 83
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Bacteria employ the flagellar type III secretion system (fT3SS) to construct flagellum, which acts as a supramolecular motility machine. The fT3SS of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is composed of a transmembrane export gate complex and a cytoplasmic ATPase ring complex. The transmembrane export gate complex is fueled by proton motive force across the cytoplasmic membrane and is divided into four distinct functional parts: a dual-fuel export engine; a polypeptide channel; a membrane voltage sensor; and a docking platform. ATP hydrolysis by the cytoplasmic ATPase complex converts the export gate complex into a highly efficient proton (H+)/protein antiporter that couples inward-directed H+ flow with outward-directed protein export. When the ATPase ring complex does not work well in a given environment, the export gate complex will remain inactive. However, when the electric potential difference, which is defined as membrane voltage, rises above a certain threshold value, the export gate complex becomes an active H+/protein antiporter to a considerable degree, suggesting that the export gate complex has a voltage-gated activation mechanism. Furthermore, the export gate complex also has a sodium ion (Na+) channel to couple Na+ influx with flagellar protein export. In this article, we review our current understanding of the activation mechanism of the dual-fuel protein export engine of the fT3SS. This review article is an extended version of a Japanese article, Membrane voltage-dependent activation of the transmembrane export gate complex in the bacterial flagellar type III secretion system, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 62, p165–169 (2022).
1 0 0 0 OA Effects of Phase II Cardiac Rehabilitation on Physical Function and Anxiety Levels in Frail Patients
- 著者
- Akio Honzawa Miho Nishitani-Yokoyama Kazunori Shimada Mitsuhiro Kunimoto Tomomi Matsubara Rie Matsumori Hiroki Kasuya Kei Fujiwara Mayumi Doi Kana Takagi-Kawahara Abidan Abulimiti Jianying Xu Akie Shimada Taira Yamamoto Atsushi Amano Tohru Asai Hiroyuki Daida Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.7, pp.308-314, 2022-07-08 (Released:2022-07-08)
- 参考文献数
- 32
Background: Frailty is an important prognostic factor in patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and patients with CVD have a high rate of concurrent psycho-emotional stress, as well as depressive mood and anxiety symptoms. Despite this, few reports have examined the effects of the efficacy of Phase II cardiac rehabilitation (CR) in frail patients, including improvements in anxiety levels.Methods and Results: In all, 137 patients (mean [±SD] age 65.8±13.0 years; 71% male) who participated in Phase II CR and were assessed after CR completion were included in this study. Patients were evaluated using the Kihon Checklist (KCL) form at the beginning of CR and were divided into the 3 groups according to KCL scores: frail (n=34, 25%), pre-frail (n=40, 29%), and non-frail (n=63, 46%). Physical function and anxiety levels were compared among the 3 groups. The pre-frail and frail groups had significantly higher state anxiety and trait anxiety than the non-frail group (P<0.01). At the end of Phase II CR, all 3 groups showed significant improvements in the 6-min walking distance (P<0.05). State anxiety improved significantly in the non-frail and pre-frail groups, whereas trait anxiety only improved in the non-frail group.Conclusions: Physical function was improved in frail patients who participated in Phase II CR. However, there was no significant improvement in their level of anxiety.
- 著者
- Tsugumi Takayama Takuya Ozawa Akiko Sanada Tohru Watanabe Masahiro Ito Satoru Hirono Yoshifusa Aizawa Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.6, pp.823-827, 2018-03-15 (Released:2018-03-15)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
A 33-year-old man with severe aortic regurgitation underwent initial aortic valve replacement (AVR). During the 2 years after AVR, 3 reoperations for prosthetic valve detachment were required. During hospitalization, he had no typical clinical findings, with the exception of a persistent inflammatory reaction; a pseudo-aneurysm around the Bentall graft developed 27 days after the 4th operation. This unique clinical course suggested the possibility of Behçet's disease. In the 8 years of follow-up after the administration of prednisolone, the pseudo-aneurysm did not become enlarged and the detachment of the prosthetic valve was not observed. We herein present a case of cardiovascular Behçet's disease, with a review of the literature.
1 0 0 0 OA Metabolomic Analysis in Heart Failure
- 著者
- Ryutaro Ikegami Ippei Shimizu Yohko Yoshida Tohru Minamino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.1, pp.10-16, 2017-12-25 (Released:2017-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 71
- 被引用文献数
- 30
It is thought that at least 6,500 low-molecular-weight metabolites exist in humans, and these metabolites have various important roles in biological systems in addition to proteins and genes. Comprehensive assessment of endogenous metabolites is called metabolomics, and recent advances in this field have enabled us to understand the critical role of previously unknown metabolites or metabolic pathways in the cardiovascular system. In this review, we will focus on heart failure and how metabolomic analysis has contributed to improving our understanding of the pathogenesis of this critical condition.
- 著者
- David J. Castillo Shuichi Nakamura Yusuke V. Morimoto Yong-Suk Che Nobunori Kami-ike Seishi Kudo Tohru Minamino Keiichi Namba
- 出版者
- 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- BIOPHYSICS (ISSN:13492942)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, pp.173-181, 2013 (Released:2013-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 4 34
The bacterial flagellar motor is made of a rotor and stators. In Salmonella it is thought that about a dozen MotA/B complexes are anchored to the peptidoglycan layer around the motor through the C-terminal peptidoglycan-binding domain of MotB to become active stators as well as proton channels. MotB consists of 309 residues, forming a single transmembrane helix (30-50), a stalk (51-100) and a C-terminal peptidoglycan-binding domain (101-309). Although the stalk is dispensable for torque generation by the motor, it is required for efficient motor performance. Residues 51 to 72 prevent premature proton leakage through the proton channel prior to stator assembly into the motor. However, the role of residues 72-100 remains unknown. Here, we analyzed the torque-speed relationship of the MotB(Δ72-100) motor. At a low speed near stall, this mutant motor produced torque at the wild-type level. Unlike the wild-type motor, however, torque dropped off drastically by slight decrease in external load and then showed a slow exponential decay over a wide range of load by its further reduction. Since it is known that the stator is a mechanosensor and that the number of active stators changes in a load-dependent manner, we interpreted this unusual torque-speed relationship as anomaly in load-dependent control of the number of active stators. The results suggest that residues 72-100 of MotB is required for proper load-dependent control of the number of active stators around the rotor.