5 0 0 0 OA 過渡的に生じる中間体ヌクレオソームにおけるヒストンテール動態の解析
- 著者
- 亀田 健 粟津 暁紀 冨樫 祐一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.5, pp.288-290, 2020 (Released:2020-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 1
5 0 0 0 OA 単一分子蛍光分光で見える光合成アンテナ系の揺らぐエネルギー移動経路
- 著者
- 柴田 穣
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.023-026, 2021 (Released:2021-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 1
5 0 0 0 OA 繊毛ダイニン軽鎖と重鎖微小管結合部位の複合体構造―見えてきた軽鎖LC1の役割―
- 著者
- 八木 俊樹 戸田 暁之 市川 宗厳 栗栖 源嗣
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.020-022, 2021 (Released:2021-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 被引用文献数
- 1
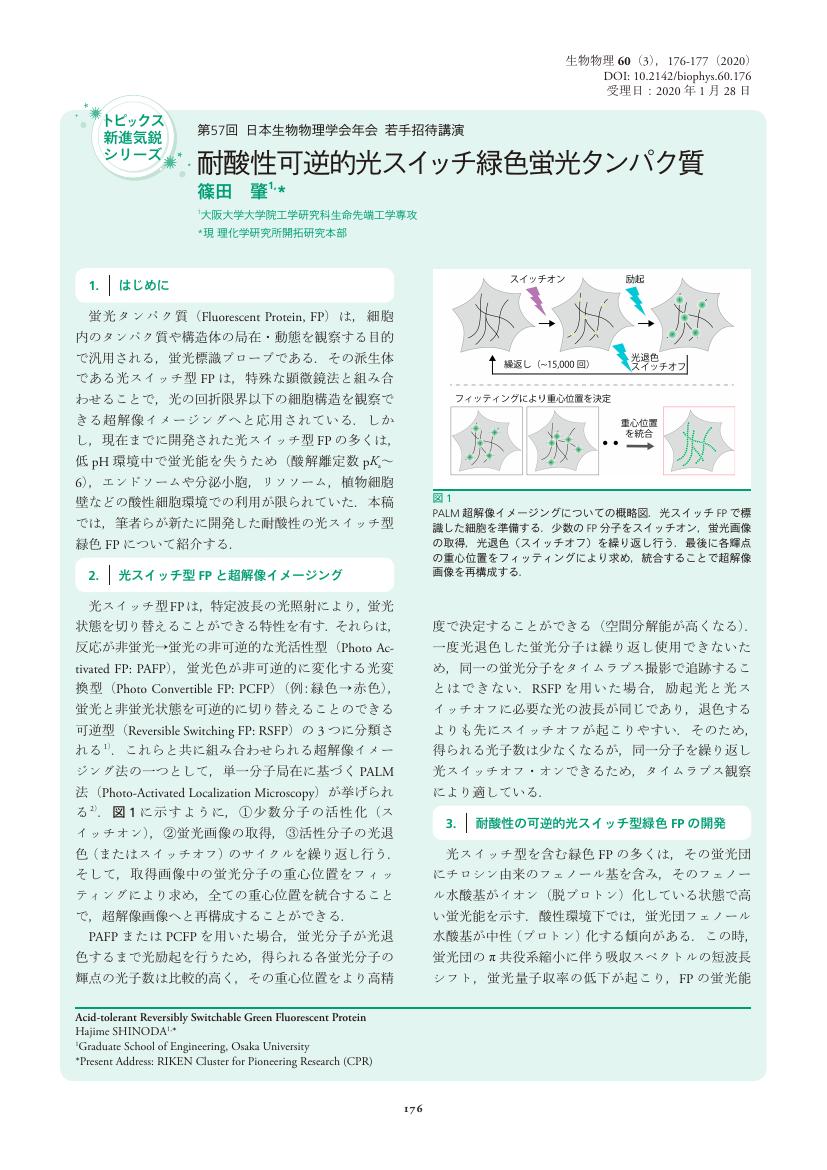
5 0 0 0 OA 耐酸性可逆的光スイッチ緑色蛍光タンパク質
- 著者
- 篠田 肇
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.3, pp.176-177, 2020 (Released:2020-05-27)
- 参考文献数
- 5
5 0 0 0 OA 書評3
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.6, pp.340, 2013 (Released:2013-11-25)
5 0 0 0 OA S3B01生物としてのゼータ関数-ピタゴラスからリーマン予想まで
- 著者
- 黒川 信重
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.1, 2001-09-10
5 0 0 0 OA タンパク質-化合物複合体情報を用いたバーチャルスクリーニング手法
- 著者
- 千見寺 浄慈
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.4, pp.221-223, 2016 (Released:2016-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 6
5 0 0 0 OA 越境するのか? されるのか? 4次元ポケットを介した創造
- 著者
- 根本 航 内古閑 伸之
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.2, pp.110-111, 2012 (Released:2012-03-30)
- 参考文献数
- 5
4 0 0 0 OA 細胞のばらつきはノイズではなく情報である
- 著者
- 和田 卓巳 廣中 謙一 黒田 真也
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.5, pp.288-292, 2021 (Released:2021-09-28)
- 参考文献数
- 16
Organisms can adapt to the environment robustly despite large heterogeneity of cellular response. Heterogeneity of cellular responses has been regarded as noise, which reduces accurate information transmission. The heterogeneity consists of intracellular variation caused by stochasticity of biochemical reactions, and intercellular variation caused by differences in amounts of molecules (cell-to-cell variability). We found that intercellular variation increases gradualness of the multi-cellular dose-response (response diversity effect), resulting in increase of accuracy of information transmission. This “response diversity effect” is a novel mechanism that enables multi-cellular organisms to utilize cell-to-cell variability as information not noise.
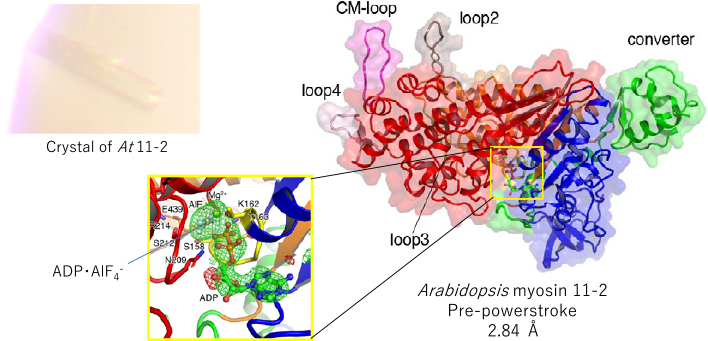
4 0 0 0 OA 生物界最速のミオシンの構造-機能相関
- 著者
- 伊藤 光二 原口 武士 玉那覇 正典 鈴木 花野 村田 武士
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.2, pp.91-96, 2023 (Released:2023-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 20
生物界最速ミオシンが淡水産藻類シャジクモに存在することが予見されていたが,その実体は不明であった.最近,私達はそのクローニングに成功し,さらに,最速のミオシンクラスであるミオシン11の高解像度結晶構造解析に世界で初めて成功し,最速ミオシンの秘密はアクチンとの結合領域にあることを明らかにした.
4 0 0 0 OA 微小管の破壊と修復:分子モーターによる微小管の新陳代謝
- 著者
- 井上 大介
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.24-27, 2022 (Released:2022-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 16
これまで,微小管のダイナミクスは,その末端でのみ生じると考えられてきたが,最近,格子中心部でも発生することが明らかとなってきた.本稿では,微小管格子内ダイナミクスに関する最近の研究について解説し,その中で,筆者らの生体分子モーターによる微小管格子内ダイナミクスの促進に関する研究について紹介する.
4 0 0 0 OA 蛍光および化学発光タンパク質の様々な応用
- 著者
- 永井 健治 松田 知己
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.6, pp.305-310, 2015 (Released:2015-11-28)
- 参考文献数
- 30
After the gene cloning and development of GFP color variants about 20 years ago, fluorescent and luminescent proteins have become indispensable tools for biological research. Their genetically encodablity and light-emitting property has revolutionized our research ability by allowing the visualization of variety of living specimen ranging from biochemical events, proteins, cells, and organisms. Detailed understanding of the physicochemical mechanisms responsible for light generation has helped drive performance improvements and application development. Here we will cover basics of light-emitting proteins, as well as the use of them for bioimaging and biomanipulation.
4 0 0 0 OA TRPV4チャネルと機械刺激受容
- 著者
- 鈴木 誠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.5, pp.268-271, 2005 (Released:2005-09-26)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 著者
- 西坂 崇之
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.4, pp.155, 2010 (Released:2010-07-25)
4 0 0 0 OA 胃の中が強い酸性になる仕組み
- 著者
- 阿部 一啓
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.2, pp.073-078, 2019 (Released:2019-03-26)
- 参考文献数
- 18
When we have food intake, pH of the stomach reaches around 1. This highly acidic environment is indispensable for the digestion. Gastric proton pump, H+,K+-ATPase is a membrane protein responsible for the gastric acid secretion. Its crystal structures now reveal how this proton pump extrudes H+ even into the pH 1 environment of the stomach.
4 0 0 0 OA 複眼のタイルパターンを決める幾何学機構
- 著者
- 佐藤 純
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.6, pp.334-337, 2022 (Released:2023-01-25)
- 参考文献数
- 7
複眼の六角形タイル構造は物理的に安定と言われ,細胞形態が物理的制約に従って決められているという考えと合致する.しかし,ある種の変異体においては物理的に不安定な四角形タイルに変化する.ハエの複眼が六角形および四角形タイルを示す機構を解明することにより,細胞形態を幾何学的に制御するメカニズムを明らかにした.
4 0 0 0 OA モータータンパク質でつくる光造形可能な人工筋肉:分子設計からマイクロデバイスまで
- 著者
- 平塚 祐一 新田 高洋
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.2, pp.137-139, 2022 (Released:2022-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 6
筋肉は分子レベルから階層的に組み上げられた精巧な分子システムである.我々は工学的なアプローチで筋肉の人工合成(人工筋肉)とメカニズムの解明を目指している.本稿では,遺伝子工学的に改変したモータータンパク質を用いて,光照射した特定の部位に人工筋肉を自発的に形成させる手法と,その応用例について解説する.
- 著者
- 宮崎 亮次 森 博幸 秋山 芳展
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.036-039, 2021 (Released:2021-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 8
4 0 0 0 OA 液液相分離が駆動する細胞内オルガネラ
- 著者
- 下林 俊典 大崎 雄樹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.5, pp.267-271, 2020 (Released:2020-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Recently, there is growing evidence in the field of cell biology that membrane-less organelles or condensates are formed by liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS), as well as some types of membrane-bound organelles like lipid rafts and lipid droplets. Biophysical analyses are powerful and indispensable to elucidate those structures, dynamics and (dys)functions. Here, we combine in vivo intracellular imaging with in vitro synthetic biology and soft-matter physics, to show a new avenue for understanding the biophysics of LLPS-driven organelles. In this review, we particularly discuss macro-to-micro phase separation in lipid rafts and liquid-liquid crystal phase transition in lipid droplets.
4 0 0 0 OA 「今のめり込み術」のマルチ効能
- 著者
- 永井 健治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.2, pp.075, 2014 (Released:2014-03-28)