6 0 0 0 OA 天然にないものの生物物理学
- 著者
- 瀧ノ上 正浩
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.5, pp.263, 2020 (Released:2020-09-30)
6 0 0 0 OA 軸索の走化性から神経回路形成に至る配線原理
- 著者
- 本田 直樹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.3, pp.141-143, 2019 (Released:2019-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 10
6 0 0 0 OA 天然変性タンパク質とは何か?
- 著者
- 西川 建
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.49, no.1, pp.004-010, 2009 (Released:2009-01-25)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
Proteins with wholly or partly denatured structure in vivo are called intrinsically disordered or natively unfolded proteins (NUPs). Functional importance of NUPs has been revealed by NMR studies as first reviewed by P. Wright in 1999. Since then, computational analyses on NUPs have also been intensively carried out to predict that about one third of eukaryotic proteins are occupied by NUPs. I will start my overview with a question why it was historically so late to find out NUPs as one of important subjects of protein science, and then move on to several issues such as, whether NUPs are really specific to eukaryotes or not, what means a particularly higher fraction of NUPs existing in the cell nucleus, what is the evolutionary implications of NUPs and so on. The contents will be described from rather a personal point of view.
6 0 0 0 OA 言葉を取り戻せ
- 著者
- 林 重彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.2, pp.071-071, 2017 (Released:2017-03-30)
6 0 0 0 OA 教師付き学習法によるメタボローム規模での多段階代謝経路予測
- 著者
- 小寺 正明 五斗 進
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.3, pp.160-163, 2015 (Released:2015-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 10
6 0 0 0 OA 「目の肥えた」野次馬
- 著者
- 亘 弘
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.5, 1992-09-25
5 0 0 0 OA 代謝漏出による微生物の共存共栄戦略
- 著者
- 山岸 純平 斉藤 稔 金子 邦彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.6, pp.400-403, 2021 (Released:2021-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 8
5 0 0 0 OA カプサイシン受容体:熱・プロトンで活性化されるイオンチャネル
- 著者
- 富永 真琴 Michael J. CATERINA Tobias A. ROSEN David JULIUS
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.159-164, 1999-05-25 (Released:2000-04-12)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Capsaicin, the main pungent ingredient in 'hot' chili peppers, elicits burning pain by activating specific (vanilloid) receptors on sensory nerve endings. We have isolated a functional cDNA encoding a capsaicin receptor from sensory neurons using an expression cloning strategy. The cloned vanilloid receptor (VR1) is a nonselective cation channel with six transmembrane domains that is structurally related to a member of the TRP family. VR1 is also activated by increases in temperature in the nonoxious range (>43 °C. We also find that protons decrease the temperature threshold for VR1 activation such that even moderately acidic conditions (pH
5 0 0 0 OA 人体表面からの極微弱生物フォトン発光と脳波の同時計測
- 著者
- 宇佐 史 稲場 文男
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.5, pp.259-262, 1990-09-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 13
5 0 0 0 OA 昆虫の飛行メカニズム(流体力学的視点から)
- 著者
- 河内 啓二
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.5, pp.279-284, 1999-09-25 (Released:2000-04-12)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 4 7
Flight mechanism of insect is different from that of our familiar system of aircraft, machinery, or bird. Recent studies quantitatively indicated that many features of insect flight mechanism, such as thin airfoil, high beating frequency, or continuous beating motion, well conform to the fluiddynamic condition given to the insect.
- 著者
- 菊池 誠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.6, pp.360-364, 2022 (Released:2023-01-25)
- 参考文献数
- 9
生命は進化の過程で機能に加えて変異に対する頑健性を獲得した.この過程を数理モデルで理解するために,進化シミュレーションと比較する対照群をマルチカノニカル法で構築する手法を提案する.遺伝子制御ネットワークで計算を行い,進化が頑健性を増強させることと進化では双安定性の出現が遅れることを定量的に示した.
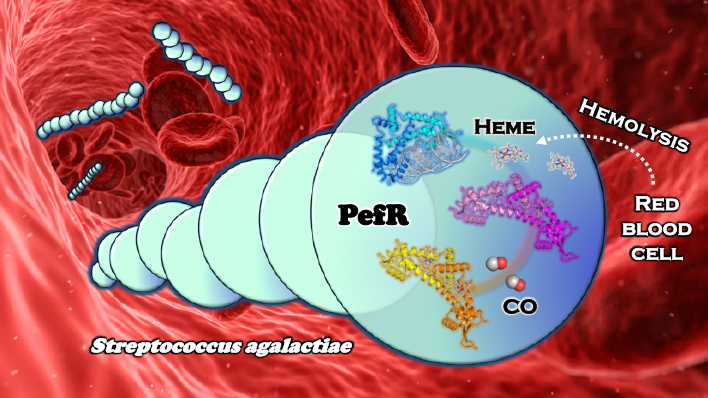
5 0 0 0 OA 病原菌の生存戦略:ヘム濃度センサータンパク質PefRの作動メカニズム
- 著者
- 澤井 仁美
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.2, pp.102-103, 2023 (Released:2023-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 5
動物の血液に感染し「ヘム鉄」を栄養として生きている病原菌は,どのようにしてその濃度を感知し,摂りすぎによる毒性を回避しているのだろうか?ヘム濃度センサータンパク質PefRの作動メカニズムから,その謎に迫る.
5 0 0 0 OA 遺伝暗号リプログラミング技術
- 著者
- 小嶋 達矢 林 勇樹 菅 裕明
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.1, pp.004-009, 2012 (Released:2012-01-31)
- 参考文献数
- 25
Genetic code reprogramming enables us to assign nonproteinogenic amino acids to codons in place of proteinogenic amino acids according to the genetic code, which allows us to express desired nonstandard peptides using an in vitro translation system. Here, we discuss FIT (Flexible In vitro Translation) system, which is a method that facilitates genetic code reprogramming by employing flexizymes. Furthermore, we also report a method called RaPID (Random non-standard Peptide Integrated Discovery) system, which is an integration of FIT system with an in-vitro mRNA display. RaPID system allows us to select peptides with high binding affinities from highly diverse nonstandard peptide libraries and is quickly becoming a valuable new tool for drug discovery.
5 0 0 0 OA 磁気を感じる生物
- 著者
- 前田 豊 溝田 学
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.4, pp.209-214, 1984-07-25 (Released:2009-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 28
5 0 0 0 OA キネシン型分子モーターの構造変化と動作機構
- 著者
- 仁田 亮
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.3, pp.133-139, 2014 (Released:2014-05-27)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Molecular motor kinesins move processively along microtubules by using energy derived from ATP hydrolysis. Almost all of the intermediate structures of this ATPase reaction cycle have been solved for the monomeric kinesin KIF1A. Based on this structural information, we present here the common atomic mechanisms of kinesin motility, which can be applied not only to the monomeric kinesins but also to the dimeric kinesins. Structural studies have suggested that kinesins accomplish their mission by utilizing the evolutionary conserved strategy among the various ATPases/GTPases/kinases in which they use the energy from the ATP/GTP hydrolysis to attach/detach to/from their effectors.
5 0 0 0 OA 耳のずれたフクロウ:聴覚空間認識の脳内機構
- 著者
- 藤田 一郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.3, pp.147-153, 1992-05-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Barn owls localize sound most accurately among all animals. Studies on the brain mechanisms of their sound localization represent a case where many important questions in sensory physiology can be addressed in a straightforward way. This article will review our current understanding of how neurons in the owl's auditory system create their selectivity to position of sounds.
5 0 0 0 OA ヒトゲノムDNAの不規則で柔軟な収納原理
- 著者
- 前島 一博 城地 保昌 西野 吉則 高田 英昭 鎌田 福美 日原 さえら
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.1, pp.004-010, 2013 (Released:2013-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 29
How is 2-m-long genomic DNA organized into a mitotic chromosome or nucleus? The nucleosome fiber has long been assumed to be folded into a 30-nm chromatin fiber, and further helically folded larger fiber. However, when we observed frozen hydrated human mitotic cells using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), no higher-order structures including 30-nm chromatin fibers were found. To further investigate the bulk structure of mitotic chromosomes, we performed small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at SPring-8. No structural feature larger than 11 nm was detected, even on a chromosome-diameter scale (~1 μm). We also found a similar scattering pattern in interphase nuclei of HeLa cells in the range up to ~275 nm. Our findings suggest a common structural feature in interphase and mitotic chromatins: compact and irregular folding of nucleosome fibers occurs without a 30-nm chromatin structure.
5 0 0 0 OA ナメクジの記憶メカニズム―逆行性健忘による解析―
- 著者
- 関口 達彦 山田 淳 鈴木 晴彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.5, pp.26-31, 1991-09-25 (Released:2009-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 30
5 0 0 0 OA 微生物ロドプシンの多様性と可能性
- 著者
- 須藤 雄気 小島 慧一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.4, pp.209-214, 2020 (Released:2020-07-29)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
One of the major topics in biophysics and physicobiology is to understand and utilize biological functions using various techniques. Rhodopsin is a photoreactive membrane-embedded protein that uses a retinal pigment (vitamin-A aldehyde) as a chromophore. By taking advantages of its photoreactivity, structure-function relationship of rhodopsins has been widely investigated with a variety of methods. Of note, recent rhodopsin research provided unexpected information regarding (i) wide distribution in various organisms, (ii) rich functional diversity and (iii) great potential for optogenetics. Here we review these three topics with future directions.
5 0 0 0 OA 若手の会だより ~女子学生中心の企画を催して~
- 著者
- 黒川 南
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.130-131, 2021 (Released:2021-03-25)