1 0 0 0 OA 日本酒濃縮入浴剤の効果
- 著者
- 前田 真治 杉田 淳 齋藤 雅人 萩原 摩里 池本 毅
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.3, pp.179-186, 2006 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 7
日本酒濃縮物 (日本酒濃縮入浴剤) 添加温水が人体にどのような影響をもたらし、有用な作用があるかをみるために、健常成人を対象に日本酒濃縮物添加温水、またその特異成分であるα-エチルグルコシド添加温水、水道水温水とを比較検討した。その結果、血圧・脈拍は3者間で差がなく心肺への負担は水道水温水と同じであった。前額部の表面皮膚温で日本酒濃縮物添加温水が他2者に比して出浴後緩徐な低下であり、保温効果が示唆された。深部体温計の経過から日本酒濃縮物添加温水が、熱吸収効率の高い要因としてα-エチルグルコシドの関与が考えられた。皮膚血流量増加も加味した結果から、日本酒濃縮物添加温水は、温水中の熱が身体内に入りやすく、かつ出にくい環境を作り出すと考えられる。その要素として、α-エチルグルコシド以外の溶存物質が関与することで、より強い熱運搬作用と保温作用をもつと結論した。皮膚水分量の測定から、温水中に入っている部分では、出浴後早期の潤いはあるが、早期に以前の状態に戻ることがわかった。温水中に入っていない顔面は、皮膚の角層水分量が日本酒濃縮物添加温水の方が良好であり、保湿量が増加していることが認められた。
1 0 0 0 OA Differential hypotermia による悪性脳腫瘍治療の試み
- 著者
- 西本 詮
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.9-13, 1982 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 15
1 0 0 0 OA 皮膚に有用な温泉水成分を探る
- 著者
- 井上 紳太郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.1, pp.12-13, 2003 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 2
1 0 0 0 OA 質問紙調査に基づく、妊婦の入浴習慣と妊娠経過への影響
- 著者
- 中山 毅
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.3, pp.250-256, 2014-05-30 (Released:2014-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
入浴習慣は国や文化により大きく異なるが、一方で時代による変遷もあり、近年ではシャワー浴が普及する等の変化が現れている。そこで、現代の妊婦の入浴習慣について調査すると同時に、妊娠経過に及ぼす影響につき検討した。 2011年4月1日より2012年2月29日までに当院で出産をし、1ヶ月健診をおこなった褥婦204名を対象とし、無記名アンケートを実施した。アンケートは、入浴習慣、温泉浴に関する多肢選択法および自由記入法からなる。これらの結果と、妊娠経過中に起こったイベントにつき、後方視的に関連性を検討した。 204名の妊婦の内訳は、初産婦が99名、1経産が76名、2経産以上が29名であった。産科合併症としては、切迫流産が12名、切迫早産が35名、早産が15例、妊娠高血圧症候群が7名、微弱陣痛が10名、前期破水が26名に認めた。一方で妊娠中の入浴習慣については、全例毎日入浴習慣があったが、内訳として、毎日シャワー浴を行う妊婦(シャワー浴群)が38名(19%)、週に1~3回の湯浴が45名(22%)、週4日以上の湯浴を行う妊婦(湯浴群)が121名(59%)であった。産科合併症を比較したところ、湯浴群において、妊娠高血圧症候群の頻度が高く、一方で微弱陣痛に関しては、シャワー浴群の方が多い傾向にあった。 さらに、入浴習慣が外陰部の保清に影響するか、また細菌性腟症の原因や助長因子となるかについては、科学的根拠が乏しいが、本検討より湯浴を日常とする生活習慣が、腟内細菌叢やpHに影響を及ぼす可能性が示唆された。
1 0 0 0 OA 別府温泉と地震
- 著者
- 由佐 悠紀
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.6-7, 1997 (Released:2010-04-30)
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉地の医療機関のこれから
- 著者
- 小笠原 真澄
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.2, pp.95-96, 2016-05-31 (Released:2016-07-04)
1 0 0 0 OA 関節リウマチの発症 : 遺伝要因と環境要因
- 著者
- 山本 一彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.1, pp.20-21, 2013-11-29 (Released:2014-03-14)
- 参考文献数
- 5
1 0 0 0 OA 灸刺激が仙骨部の血流量に及ぼす影響について
- 著者
- 松本 毅 木村 友昭 形井 秀一 波多野 義郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.2, pp.96-101, 2005 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 15
The purpose of this study was to determine if Moxibustion stimulus influence on the circulation in the sacral area.In the first phase of this study, the influence of indirect Moxibustion stimulus (using‹SEN-NEN-KYU›) on the amount of blood flowing to the sacrum was investigated using laser Doppler Perfusion Imager PeriScan PIM II.Significant increase in the amount of blood flow in radial directions were observed around the area where Moxibustion was applied. Immediately after the stimulus, significant differences in the amount of blood flow were observed within 2.5cm to the right and left and 1.5cm above and below the stimulated spot.With increasing time after the Moxibustion stimulus, the amount of blood flow gradually decreased concentrically returning to the original state over time. However, the amount of blood flow at the Moxibustion spot was significantly higher than the original state 32 minutes and 52 seconds after the Moxibustion treatment.Increased blood flows to pressure ulcers area induced by Moxibustion stimulus are considered to restrict or arrest the progress of pressure ulcers (according to Stage I of the International Association for Enterostomal Therapy (IAET) classification) on in-home care.
1 0 0 0 OA 慢性関節リウマチに対する冷泉浴の効果
- 著者
- 吉田 史郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.4, pp.171-180, 1989 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 23
慢性関節リウマチ (RA) に対する温泉浴の効果はよく知られているが、冷泉浴については研究がない。そこで九重、寒の地獄泉 (単純硫化水素泉、泉温13℃) 入浴のRAに対する影響を別府堀田泉浴 (単純硫化水素泉、泉温40℃) 入浴の場合と比較観察した。握力、ランスバリー活動指数、日常生活動作点数はいずれも3週間の連浴 (1日2回入浴) によって、両泉とも改善をみたが、有意差は冷泉浴の場合にのみ認められた. したがってRAに対する効果はむしろ冷泉浴の方が勝っていると思われた。血中コルチゾール、尿中17-OHCS、尿中17-KS値は3週間の連浴中、両泉とも有意の変動を示さなかった。したがって作用機序として副腎皮質刺激作用は考え難かった。一方血中ノルアドレナリンは入浴直後一過性に有意に増加したが、特に冷泉浴で著明であった。しかも増加の程度は冷泉浴の時間と相関し、それが長くなるほど大となった。尿中ノルアドレナリン排泄量も冷泉浴連浴によって次第に増加し、3週後には有意差となったが、なお正常範囲内であった。アドレナリンに関しては血中、尿中とも有意の変動を示さなかった。以上よりノルアドレナリン増加によって示唆される交感神経刺激がRAに対する冷泉浴効果の機序の一つである可能性が考えられた。
1 0 0 0 OA 時計遺伝子Bmal1と生体リズム研究の現在
- 著者
- 池田 正明
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.1, pp.5-5, 2016-02-27 (Released:2016-03-31)
1 0 0 0 OA 伊豆半島の温泉の特徴と医学的考察
- 著者
- 矢野 一行
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.3, pp.176-190, 2016-10-31 (Released:2017-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 29
温泉医学の先進国であるドイツを中心としたヨーロッパ諸国では科学的根拠に基づいた温泉治療が専門医を配置した温泉病院や医療施設で広く行われている.一方,世界でも類をみない温泉大国のわが国では,温泉は湯治や,観光,レジャーなどによる“気分”的利用が中心をなし,温泉を科学的に究明し,近代医療の相補療法(Complementary Medicine)として活用し,国民の健康に役立てようとする総合的な取り組みはなされていない. 限られた小面積の伊豆半島には,海底火山,陸上複成火山,そして単成火山,それぞれの時代の地層がモザイク的に分布し,それらの地層にはさまざまな泉質の温泉が散在している.このような場所は世界でも珍しく,温泉の本質を科学的に究明するには最適な場所と考えられる.そこで,これらの温泉地を訪れ入手した情報を基にそれぞれの温泉の特性を明らかにし,今後の温泉研究の方向性を示すことを目標とした. 今回調べた伊豆半島の温泉は,弱アルカリ性かアルカリ性の硫酸塩泉,塩化物泉,単純温泉の3種類であり,非火山性温泉には珍しく,殆どが高温泉である.西伊豆・中伊豆の古い地層の硫酸塩泉の起源は海底火山によるグリーンタフ(Green tuff)岩石中の硬石膏によるもので,基本成分である硫酸イオンの濃度は非常に高く,高い薬理効果が期待される.また,塩化物泉には,東伊豆の地下深部のマグマの熱源による海洋水の熱水対流系で形成された温泉と,南伊豆の地下深部の熱水に地表付近で海洋水が混入した高張性温泉がある.単純温泉は,古い地層の西伊豆・中伊豆では硫酸塩泉の性質,東伊豆では硫酸塩泉と塩化物泉の性質,南伊豆では硫酸イオンの量は少ないが,相対的に炭酸水素イオンや炭酸イオンなどの割合が増え,それぞれ特徴のある性質の温泉になっている. 伊豆半島のこれらの温泉を活用し,温泉医学の確立を目指すには,下記の研究課題の解明が待たれる.(1)特徴ある温泉の源泉と浴槽の温泉水の物理化学成分の直接比較:温泉水の地上に湧出直後から浴槽に至るまでの間に変化した物理化学的性質を検討する.(2)飲泉可能な温泉水に含まれているミネラル成分の定量分析:特に,抗酸化酵素に含まれているミネラル類と日常生活で不足しがちなミネラルを中心に検討する.(3)実験動物やiPS細胞などによる硫酸塩泉の薬理効果の指標の作成:硫酸塩泉のそれぞれ陽イオンと陰イオンの組み合わせによる薬理効果を動物や細胞等を用いた客観的指標で評価する.(4)高張性塩化物泉の浴用によるセシウム137とストロンチウム90のデトックス効果の検討:福島第一原発事故や廃炉関連の仕事で被曝した人が,これらの放射性元素の同族元素を多く含む温泉に入浴することによって,放射線被曝を軽減できるかどうかを検討する.(5)単純温泉の浴用による医療被曝障害の予防効果の検討:わが国は放射線診断や放射線治療による医療被曝障害が非常に高い国であるので,入浴によってこの被曝障害を予防・軽減できるかどうかを検討する.
1 0 0 0 OA 入浴と水電解質代謝
- 著者
- 北村 勇 柴田 俊郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694240)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.22, no.2, pp.97-119, 1958-09-25 (Released:2010-08-06)
The problem of water and electrolyte metabolism, an essential regulation in the living body of its internal environment, has been investigated by many researchers. In this paper, we have summarized our study concerned with the effects of thermal bath (plain water or hot spring) on the water and electrolyte metabolism. Also, some related changes in circulatory and endocrine systems were considered.Twelve young men were selected and series of comparative study before and after each bathing for 10 minutes duration at temperature of 40 to 43°C have been performed.I Water and electrolyte metabolism(1) Immediately after the bathing no change was observed in the total body water. The extracellular fluid and the plasma volume increased; hematocrit values were lowered, while the total blood water as well as the plasma water was both increased and the water content of blood corpuscles was decreased. This result was inferred to a replacement of body water from inside to outside of the cells.(2) The minute volume of urine voided immediately after the bathing showed a transient increase, whereas it was decreased after the period of bath and also less than the pre-bathing stage.(3) Plasma Na was lowered after the bathing, while K and Cl remained unchanged. Na content of blood corpuscles showed a rise and K was lowered. The same tendency has also been observed in the skeletal muscle.(4) Reabsorption of Na as well as excretion of K in the urine was slightly increased after the bathing.(5) There was a loss of electrolytes into sweat.(6) The permeability of Na24 across the capillary wall was increased during and immediately after the bathing.II Changes in circulatory and endocrine systems related with water and electrolyte metabolismAmong many changes induced by thermal bathing which may cause alteration in circulatory and endocrine systems, a rise of body temperature and an induced hyperfunction of adrenal glands were considered to play a major role in the whole processes.
1 0 0 0 OA 高濃度塩類泉 (Na, Ca, Mg塩化物, 硫酸塩) 入浴の深部体温と循環動態への効果
- 著者
- 堀切 豊 下堂園 恵 王 小軍 須藤 和彦 林 菊若 田中 信行 小原 該一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.4, pp.181-186, 2000 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 12
The effects of high concentration mineral water bating (31.16g/kg, mainly composed of Na, Ca, Mg chloride and sulfate) were studied in 13 healthy men (44.9±16.3y.o.). The subjects took 41°C, 10min bathing and kept warmth by a blanket for 30min. Blood pressure (BP), Heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), total peripheral resistance (TPR) and sublingual temperature by electric thermista as deep body temperature were measured during and after bathing. Skin blood flow by LASER doppler flow meter and venous partial gas pressure and pH were also measured.Sublingual and forehead temperature was increased significantly by +1.4°C after 10min bathing and +0.9°C increase continued even after 30min. Diastolic BP and TPR were significantly decreased, and HR and CO were significantly increased by +20bpm and +2.7l/min, respectively. Significant increase of skin blood flow was also demonstrated. Significant increase of venous pO2 (+20 Torr) and decrease of pCO2 (-8.0 Torr) suggested the improvement of peripheral oxidative metabolism due to increased CO.High concentration mineral water bathing was highly effective than simple water bathing probably due to the thick coating effect by binding concentrated minerals with skin furface protein.
1 0 0 0 OA 入浴介助を必要とする高齢者の背景因子
- 著者
- 早坂 信哉 石川 鎮清 岡山 雅信 梶井 英治 中村 好一 小栗 重統 岡山 明 柳川 洋
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.4, pp.173-181, 2001 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 15
To determine the background of aged people who need bathing assistance, we analyzed data of the Survey on Demand for Health and Welfare Services of Japan as of 1997. The survey covered 21, 723 persons aged 65 years or older, and 1, 193 caregivers who provide care to persons 65 years or older throughout Japan. The main parameters were aged people's sex, age, marital status, health condition, degree of bed rest, and needs of care in daily life; relation between caregivers and aged people; life with care giver; job; family composition; use of home care services; demand for home care services; caregivers' sex, age, health condition, and employment status; and demand for home care services. Subjects were divided into three groups, those who need bathing assistance, those who do not need bathing assistance, and those who do not need care in daily life, and the rate was shown for each item. The results indicated that the rate of those who need bathing assistance was higher among (1) aged people who were older, have poor health, and are in bed alweys or almost alweys, (2) aged people who needed care in daily life, used home care service, and required home care service, and (3) aged people whose caregivers required home care services.Aged people who need bathing assistance are subject to frequent bathing accidents, so we need to pay attention to safe bathing service.
1 0 0 0 OA 湯田温泉ニ就テ
- 著者
- 北村 大藏 添田 漸
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694240)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.7, no.4, pp.257-264, 1942-04-25 (Released:2010-08-06)
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉の効果をいかに測るか
- 著者
- 名郷 直樹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.1, pp.25a-26, 2007 (Released:2010-04-30)
1 0 0 0 OA 慢性関節リウマチにおける局所極低温療法と積極的運動療法の効果
- 著者
- 石原 義恕 藤田 朝雄 小林 邦雄 大土井 淑郎 斎藤 幾久次郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3-4, pp.119-130, 1983 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 10
In order to compare the result of local cryo-therapy on rheumatoid arthritis against the conventional local heat application a comparative clinical study was performed.Twenty rheumatoid patients with bilateral knee joint involvement were selected cryo-therapy was given for five minutes with cryogenic air generator (Nihonsanso-L-10) at-100°C on below in eleven patients, whereas local heat was applied with hot packs for 15 minutes at 70-80°C in nine patients.All the patient underwent a daily active exercise schedule after the local treatment, these treatment were given for three months continuously and the result were evaluated. For the evaluation, twelve items were selected including, range of motion, muscle strength, walking capacity, roentgengram and etc.The patients were evaluated before the treatment, 1.5 months after the treatment and at the end of the treatment.The result: both groups showed some improvement in general, but there was no significant difference between them, muscle stiffness and joint pain seemed to be slightly between after the cryo-therapy compared to the local heat application, however post-treatment x-ray showed some progression of joint destruction in the former. The result suggest that local cryo-therapy has a certain place in rheumatoid treatment although not significantly better than the conventional local heat application, if it is applied under due care.
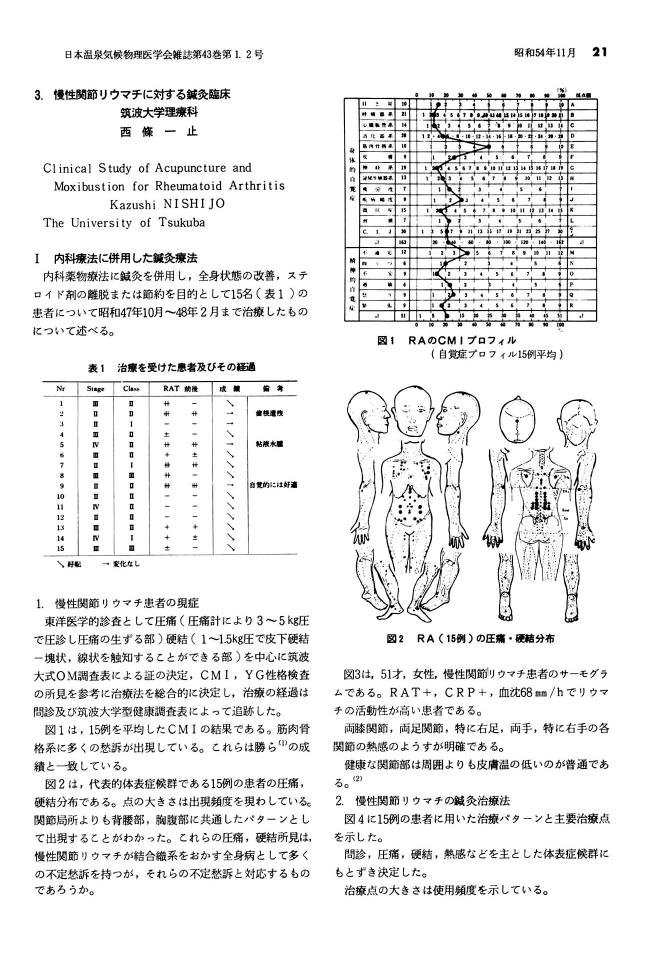
1 0 0 0 OA 慢性関節リウマチに対する鍼灸臨床
- 著者
- 西條 一止
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.1-2, pp.21-28,39, 1979 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 6
1 0 0 0 OA 「水中運動療法の歴史的概観」
- 著者
- 清水 富弘
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.72, no.4, pp.274-275, 2009 (Released:2013-05-21)
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉の分析法
- 著者
- 滝沢 英夫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.1, pp.13-14, 2010 (Released:2013-09-05)