1 0 0 0 OA ドラッグデリバリーシステム技術を使うためのメディシナルケミストと製剤研究者の協働と戦略
- 著者
- 真野 高司
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.133, no.1, pp.67-72, 2013-01-01 (Released:2013-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 6
In order to successfully apply drug delivery systems (DDS) to new chemical entities (NCEs), collaboration between medicinal chemists and formulation scientists is critical for efficient drug discovery. Formulation scientists have to use ‘language’ that medicinal chemists understand to help promote mutual understanding, and medicinal chemists and formulation scientists have to set up strategies to use suitable DDS technologies at the discovery phase of the programmes to ensure successful transfer into the development phase. In this review, strategies of solubilisation formulation for oral delivery, inhalation delivery, nasal delivery and bioconjugation are all discussed. For example, for oral drug delivery, multiple initiatives can be proposed to improve the process to select an optimal delivery option for an NCE. From a technical perspective, formulation scientists have to explain the scope and limitations of formulations as some DDS technologies might be applicable only to limited chemical spaces. Other limitations could be the administered dose and, cost, time and resources for formulation development and manufacturing. Since DDS selection is best placed as part of lead-optimisation, formulation scientists need to be involved in discovery projects at lead selection and optimisation stages. The key to success in their collaboration is to facilitate communication between these two areas of expertise at both a strategic and scientific level. Also, it would be beneficial for medicinal chemists and formulation scientists to set common goals to improve the process of collaboration and build long term partnerships to improve DDS.
1 0 0 0 OA 高等植物より得られる抗腫瘍活性物質の研究
- 著者
- 糸川 秀治 竹谷 孝一 一柳 幸生 森田 博史
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.119, no.8, pp.529-583, 1999-08-01 (Released:2008-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 149
- 被引用文献数
- 2 10
A lot of anticancer agents have been isolated from natural sources, especially from microorganisms and plants. However, there is no special type of compounds for cancer therapy. Various types of substances are effective for various types of cancers and tumors : for instance, alka1oids, lignans, terpenes and steroids, etc. In this report, the authors will describe especially about higher plants.
- 著者
- 平川 善行 原田 清
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.103, no.6, pp.690-695, 1983-06-25 (Released:2008-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 5
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
In the previous paper, a new technique for particle size reduction of oxolinic acid (OA), a slightly soluble model drug having an acidic group in a molecule, by the crystallization through the neutralization of its alkaline solution in the presence of certain surfactant or polymer was described. The wet sieving method by the use of polycarbonate membrane filter for the evaluation of size reduction effect was also described. Various factors affecting the size reduction of OA were investigated in this paper. The results obtained were as follows ; manners of participation in various factors affecting the size reduction varied with OA concentration at crystallization, and in the case of 5 w/v% OA concentration, the influences of addition rate of hydrochloric acid solution, stirring rate, reaction temperature and concentration of hydrochloric acid were relatively low. Size reduction effects of various surfactants and polymers were investigated. All of them were effective, though differences were recognized in the extent of size reduction. It has been found that the establishment of optimal conditions to obtain the finest particles is enabled and moreover, there is a possibility to prepare the particle that have an optional particle size by regulating the various factors.
- 著者
- 平川 善行 原田 清
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.102, no.10, pp.951-959, 1982-10-25 (Released:2008-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 26
When slightly soluble medicinal crystals are administered orally, their particle size is one of the important factors affecting the bioavailability. Therefore, it was attempted to develop a new technique of particle size reduction, in which the addition of surfactants or polymers at crystallization was examined. In order to evaluate the size reduction effect for oxolinic acid (OA), the wet sieving method was studied by the use of the polycarbonate memblane filter. This method consists of the following procedures : 1) sonication of suspension more than 10 min, 2) suction filtration of suspension after dilution, 3) measurement of the weight of the residue on each filter by the determination of OA, 4) plots of the cumulative weight of residues on a log-probability paper, followed by calculation of apparent geometric mean diameter on weight basis, 5) regulation of the volume of filtrate according to the particle size of microcrystallines. It was found that the new method studied enabled to evaluate the size reduction effect easily and accurately.
1 0 0 0 OA 医薬品粉体の基礎的特性についての評価法 : 粒子径の測定(セミナー)
- 著者
- 小口 敏夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.4, pp.315-320, 2008-04-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 著者
- 鴻池 敏郎
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.203-207, 2002-03-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 4
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA より効率的により良い塩形を選択するために(B・物理系薬学)
- 著者
- 石原 比呂之
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.12, pp.1266-1267, 2006-12-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 2
1 0 0 0 OA BSE,その後 : ウシ由来の医薬品原料(話題)
- 著者
- 杉村 直幸
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.12, pp.1173-1177, 2002-12-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA PDE4阻害薬KW-4490の実用的合成プロセス(JSPC優秀賞,最前線)
- 著者
- 柳沢 新
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.2, pp.133-137, 2009-02-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 9
1 0 0 0 OA 動注用アイエーコール
- 著者
- 乾 勝
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.70-71, 2010-01-01 (Released:2018-08-23)
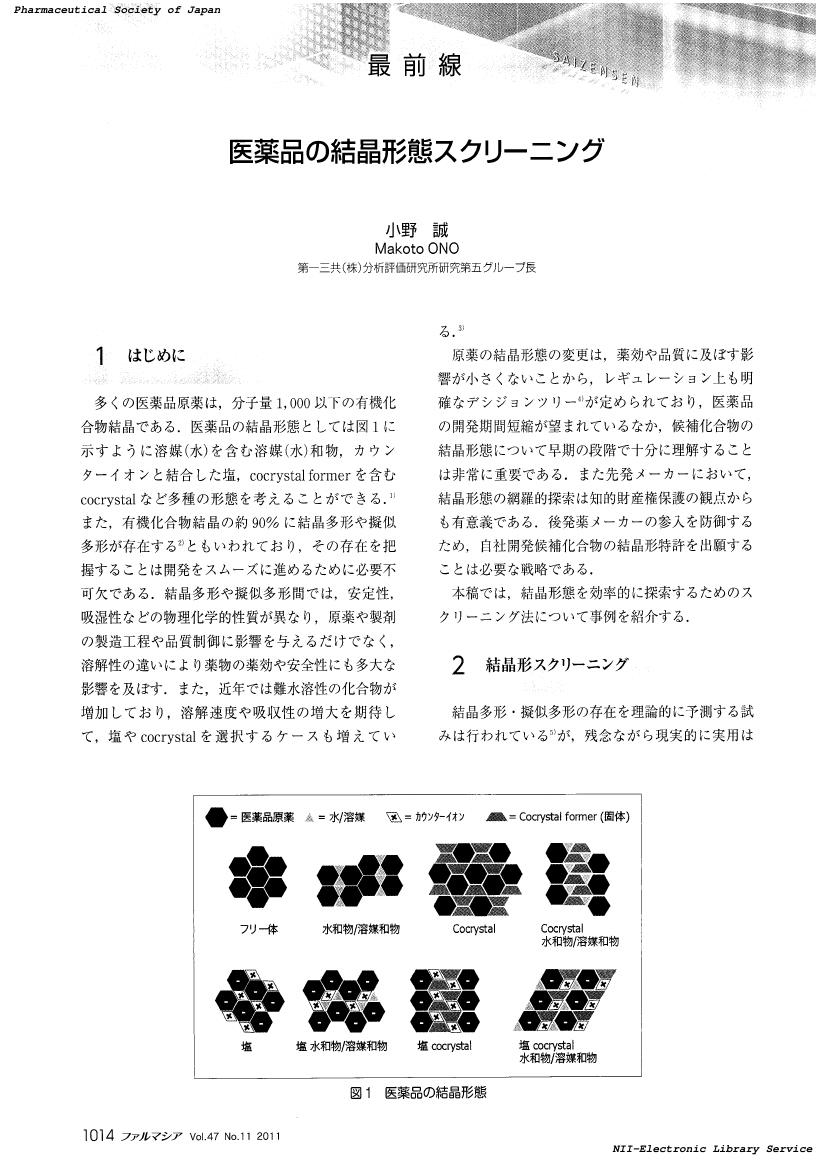
1 0 0 0 OA 医薬品の結晶形態スクリーニング
- 著者
- 小野 誠
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.11, pp.1014-1018, 2011-11-01 (Released:2018-08-23)
1 0 0 0 OA 医薬品研究におけるクリスタルエンジニアリングの重要性
- 著者
- 髙田 則幸 滝山 博志 中上 博秋 山本 恵司 池田 幸弘
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.11, pp.1005-1011, 2011-11-01 (Released:2018-08-23)
1 0 0 0 OA 医薬品開発における開発形態の最適化
- 著者
- 小嶌 隆史 池田 幸弘
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.5, pp.387-391, 2016 (Released:2016-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 12
近年の医薬品開発においては,様々な機能を持った製剤が展開されている.経口製剤だけを取り上げても,腸溶性製剤,可溶化製剤,持続吸収型徐放製剤,舌下錠,口腔内崩壊錠等,多種存在する.一方,治験初期では,原薬を出品後,治験サイトで溶解,懸濁あるいはカプセル充填して投薬されるなど,簡易な製剤で開発される場合もある.いずれの製剤においても,多くの場合,使用される原薬形態は結晶性の粉末である.結晶は非晶質と比較して物理的・化学的に安定であり,原薬および製剤の品質保持において優位であるだけでなく,製造における堅牢性確保の点からもメリットは多い.これに対し,溶解性の改善などを目的とした非晶質製剤として開発する場合には,品質や製造性の担保のための工夫がなされている.すなわち,高品質な医薬品を安定的に患者さんに届けることを使命とする製薬企業において,医薬品開発を俯瞰的に捉えた開発形態の選定は重要な項目である.過去には,不十分な開発形態の選定が原因による特許訴訟や製造中止の事例が報告されている.企業経営の問題にとどまらず,患者さんや広く社会に及ぼす影響も大きいことから,製薬企業には適切な開発形態の選定が求められている.本稿では,医薬品開発における開発形態選定の現状に加え,物性・原薬製造工程・製剤化工程研究を交えた新たな展開について紹介する.
- 著者
- 中塚 隆 金子 彰
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.219-223, 2002-03-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 著者
- 佐野 隆宏
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.224-228, 2002-03-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 10
1 0 0 0 OA プロスタノイドの微量分析法
- 著者
- 横田 一成 宮崎 浩
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, no.12, pp.1261-1268, 1987-12-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
1 0 0 0 OA プロスタノイドの医薬品への製剤化 : 現状と将来
- 著者
- 上釜 兼人 平山 文俊
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, no.12, pp.1237-1242, 1987-12-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
1 0 0 0 OA ヘパリン不純物問題とその対応(話題)
- 著者
- 川崎 ナナ
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.12, pp.1167-1171, 2008-12-01 (Released:2018-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 10
1 0 0 0 OA 品質規格と有効期間の設定
- 著者
- 伊藤 亮一
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.5, pp.450-454, 2017 (Released:2017-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 3
製剤の品質規格に関しては、通常の規格及び試験方法は、ICHQ6Aに基づき、またRTRTは、ICHQ8(R2)において、規定される。有効期間の設定に関しては、ICHQ1Eで規定されている統計学的手法に基づき、「長期保存試験結果から外挿する場合」及び「共分散分析を用いた場合」の設定方法に関して、解説した。また規格及び試験方法・有効期間の変更に関しては、類縁物質のHPLC法(アイソクラティク法)からHPLC法(グラジエント法)へ変更される場合の要求条件及び有効期間の24箇月から36箇月への変更事例を解説した。
1 0 0 0 OA 原薬製造工程におけるQuality by Designの実践
- 著者
- 村瀬 辰史
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- ファルマシア (ISSN:00148601)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.5, pp.420-424, 2017 (Released:2017-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 6
医薬品は健康維持に重要な役割を果たす一方で,その品質不良は生命に悪影響を及ぼす可能性がある.そのため,医薬品・原薬の品質管理では,試験による品質の確認だけでなく,深い理解を伴った頑健な製造工程によって,高品質の製品を間違いなく製造すること,すなわち「品質を製造工程で造り込む」Quality by Design(QbD)が重要視されている.本稿では,工程の頑健性を示す方法論の1つとして統計手法に着目し,その活用に向けた環境作りと,当社開発プロジェクトでの実践例について紹介する.