- 著者
- 鈴木 伸治 篠原 孝明 三田 勝己 赤滝 久美 渡壁 誠
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.12, 1999-12-18
- 著者
- 八幡 徹太郎 染矢 富士子 立野 勝彦
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine = 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- The Japanese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine = リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.10, pp.696-701, 2005-10-18
金沢大学医薬保健研究域保健学系
- 著者
- 寺本 洋一 馬場 尊 才藤 栄一 太田 喜久夫
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.3, 2003-03-18
健常成人8人(平均35.6歳)を対象に,息こらえによる酸素分圧の低下が酸素飽和度に反映されるかを検証した.実測値の測定は最大吸気から約1,2,3l/呼気し息こらえを開始し,パルスオキシメーターにて安静時,20,40,60秒後,最低の酸素飽和度を測定,息止め時間も記録した.理論値の測定は,Borenの残気量予測式等を用い,肺胞内空気の酸素消費に着目し算出した.実測値と理論値の比較で最高(R=0.85)の相関を認めた.実測値と予測値には10〜20秒のタイムラグがあり,約10〜20秒後の実測値において,予測値とほぼ同値の酸素飽和度が認められた.肺胞壁内毛細血管から上肢末梢血管まで血液が循環するのに必要な時間を考慮する必要があった.予測値と20秒後の実測値の相関をみると最高R=0.81の相関を認めた.各症例の酸素飽和度低下度と各パラメーターとの相関では高年齢,肥満,低肺活量,低活動性,smoking index高値の症例において酸素飽和度低下の傾向が著しいことが示唆された.
1 0 0 0 OA 筋出力特性に注目した新しい筋力評価の試み
- 著者
- 宮下 智
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.4, pp.223-229, 1998-04-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
従来,筋力評価に関する研究は等速性筋力測定装置を用い,ピークトルク値を比較検討することが多かった.しかし,筋力の強い者が必ずしも怪我に強いとは言いきれない側面が近年指摘され,測定項目や方法についての問題提起がなされている.そこで本研究は膝関節屈曲伸展運動時,ピークトルクを発生する時の関節角度と角速度の関係に注目し,最大筋力を発揮する際の過程を探った.対象は現役スポーツ選手,男子10名(26.7±3.9歳),女子18名(20.1±2.8歳).その結果,ピークトルクを発揮する時は,男女に関係なく,関節角度と角速度の有意な相関関係の上に筋出力されることがわかった.このことはピークトルクがどの関節角度で,どの角速度上で発揮されているかを明らかにするものであり,この結果から具体的な運動処方につなげることができる新しい筋出力特性の評価法であると結論した.
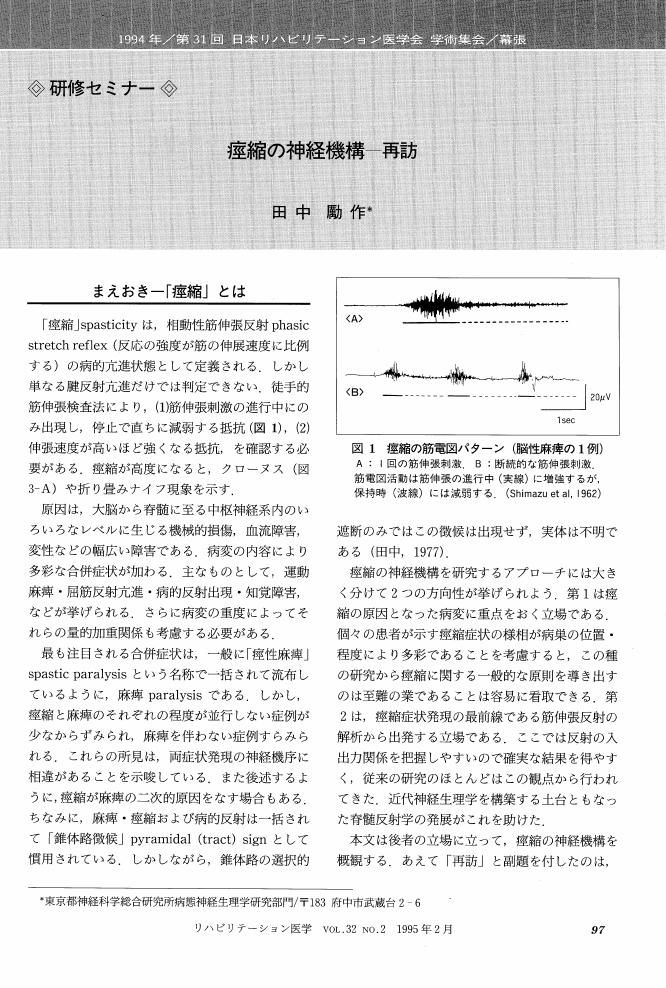
1 0 0 0 OA 痙縮の神経機構 再訪
- 著者
- 田中 勵作
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.2, pp.97-105, 1995-02-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 10 4
- 著者
- 園田 茂 才藤 栄一 道免 和久 千野 直一 木村 彰男
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.4, pp.273-278, 1993-04-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 5 2
脳血管障害において,機能障害評価は必須である.しかし既存の評価法は十分とは言い難かった.そこでわれわれはBuffalo symposiumの勧告に準じて機能障害評価法Stroke Impairment Assessment Set (SIAS)を作成した.SIASは運動,腱反射,筋緊張,感覚,可動域,疼痛,体幹,高次脳,健側機能評価を含んでいる.このSIASを用いて発症4週以内の脳血管障害患者66名を評価し,クラスター分析にて群分けを行った.SIASの得点分布は弛緩性完全麻痺を示す得点以外はほぼ均等であった.またクラスター分析にて全般低下群,健側機能良好群など予後予測に有用と思われる4群に分けられた.以上よりSIASは簡便で有用な機能障害評価表と考えられた.
1 0 0 0 OA 成人脳性麻痺の臨床像 ―痙性と筋力の影響―
- 著者
- 丸石 正治 黒瀬 靖郎 片山 昭太郎
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.8, pp.564-572, 2005 (Released:2006-09-22)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disorder that results from a nonprogressive brain lesion that occurs during prenatal or perinatal development. As motor function in patients with CP changes with brain development, it may be more suitable to make a quantitative evaluation during adulthood than childhood. But until now there has been little information available about adult CP. In this review, we investigate the clinical characteristics and ADL scores in adult CP patients from our series of clinical experience. From our previous study that assessed the clinical characteristics of adult CP using uniform scale, a population of adult CP patients showed markedly increased muscle tone and moderate muscle weakness. These two factors did not correlate with each other, and were independently responsible for worse ADL scores. Decreased functional ability and secondary muscloskeletal problems such as cervical spondylosis are common in adult CP patients. We therefore added a review of them such reports from the literatures.
1 0 0 0 OA 腰椎の特徴と腰背筋の筋力増強
- 著者
- 大井 淑雄
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.1, pp.15-17, 1993-01-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 脳機能局在
- 著者
- 後藤 昇 後藤 潤
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.4, pp.296-302, 2001-04-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 2 4
The functional localization of the cerebrum is described from the anatomical point of view. In the central nervous system, neurons or nerve fibers with the same function gather to form gray matters or nerve fiber bundles. This article briefly describes and discusses about morphology of the telencephalon, structures of the cerebral cortex and functional localization of the cerebral cortex. On the surface of the telencephalon, there are many sulci and gyri. Several sulci such as the central, lateral, parietooccipital, etc. subdivide the pallium into five lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal and insular. The insula is covered by the operculi frontale, frontoparietale et temporale. Under the microscopic observation of cerebral corteces, they consist of six cortical layers which vary from part to part. Since Brodmann (1909) divided the cortical areas into 52, we can explain cerebral areas properly for example, Brodmann's cytoarchitectonic areas 4, 3-1-2, 17, 41, 44, etc. Regarding cerebral functional localizations, Broca (1861) proposed first a theory of cerebral functional localization on motor speech after examining a patient with motor aphasia. Penfield and Rasmussen (1950) published a monograph entitled “The cerebral cortex of man: A clinical study of localization of function”. They studied cerebral functions at various parts using many patients with brain damages prior to surgical treatments. Their study have covered sensorimotor representation of the body, head and eye movement, representation of autonomic system, vocalization and arrest of speech, secondary sensory and motor representation, vision, hearing and equilibration, memory, sensory perception, etc. This review article plays up several important points of past researches on human beings.
1 0 0 0 OA 脳機能局在
- 著者
- 後藤 昇 後藤 潤
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.4, pp.296-302, 2001-04-18
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The functional localization of the cerebrum is described from the anatomical point of view. In the central nervous system, neurons or nerve fibers with the same function gather to form gray matters or nerve fiber bundles. This article briefly describes and discusses about morphology of the telencephalon, structures of the cerebral cortex and functional localization of the cerebral cortex. On the surface of the telencephalon, there are many sulci and gyri.Several sulci such as the central,lateral,parietooccipital, etc. subdivide the pallium into five lobes:frontale, parietal, occipital, temporal and insular The insula is covered by the operculi frontale, frontoparietale et temporale. Under the microscopic observation of cerebral corteces, they consist of six cortical layers which vary from part to part.Since Brodmann (1909) divided the cortical areas into 52, we can explain cerebral areas properly for example, Brodmanns cytoarchitectonic areas 4, 3-1-2, 17, 41, 44, etc. Regarding cerebral functional localizations, Broca (1861) proposed first a theory of cerebral functional localization on motor speech after examining a patient with motor aphasia.Penfield and Rasmussen (1950) published a monograph entitled "The cerebral cortex of man:A clinical study of localization of function". They studied cerebral functions at various parts using many patients with brain damages prior to surgical treatments. Their study have covered sensorimotor representation of the body,head and eye movement, representation of autonomic system, vocalization and arrest of speech, secondary sensory and motor representation, vision, hearing and equilibration,memory, sensory perception, etc. This review article plays up several important points of past researches on human beings.
1 0 0 0 OA 患者の自己決定権
- 著者
- 加藤 一郎
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.1, pp.21-27, 1990-01-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 神経心理学的テスト
- 著者
- 山下 光 山鳥 重
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.9, pp.651-658, 1994-09-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
- 著者
- 三好 正堂
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテ-ション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.8, pp.p635-637, 1991-08
1 0 0 0 OA 認知運動療法と運動学習
- 著者
- 塚本 芳久 山田 真澄
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.5, pp.345-351, 1998-05-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 24
1 0 0 0 3-5-11 肩関節に対する初動負荷トレーニングの効果について(脳卒中・上肢治療(1),口演,一般演題,リハビリテーション医学の進歩と実践,第43回日本リハビリテーション医学会学術集会)
- 著者
- 楠元 恵一 尾花 正義
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, 2006-05-18
1 0 0 0 辺地のリハビリテーション
- 著者
- 水野 祥太郎 河邨 文一郎 花田 ミキ
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, no.4, pp.292-297, 1972-10-18
- 著者
- 小坂 健二 中村 隆一
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.2, pp.93-100, 1983
筋電図反応時間(EMG-RT)は肢位変化によって変化することが知られている.例えば上腕三頭筋のEMG-RTは,促通肢位で短縮する.このEMG-RTの肢位依存性は,小脳障害患者で消失するがPNFによって一時的に回復する.このPNFの効果の神経機序を検討するために,サルの大脳皮質運動野刺激によって惹起されるEMGの潜時の肢位依存性について検討し,小脳核の破壊前と破壊後の肢位依存性の変化を比較検討した.さらに破壊後,皮質反復刺激を行なった.<br>皮質上肢運動野の連続電気刺激によるEMGの潜時は,肩のretraction肢位と比較するprotraction肢位で短縮した.この潜時の肢位依存性は,小脳核破壊によって消失した.試行間隔を短縮し,皮質刺激を反復すると,消失した肢位依存性は回復した.これらの神経機序については次のように考えられる.潜時の肢位依存性は,肢位変化による運動感覚入力が皮質運動野の興奮性を変化させた結果の現象である.小脳はこの運動感覚の入力系と運動の出力系に対してmodulatorとして作用しており,その破壊によって肢位依存性は消失する.この肢位依存性の回復には,試行間隔を短縮して皮質刺激を反復することでおこる上位中枢への運動感覚情報のより強力な入力が有効である.<br>このことからPNF治療には,最大抵抗下における随意運動の反復によって上位中枢への運動感覚入力を強化させることが重要である.
1 0 0 0 肩運動の筋電図学的研究
- 著者
- 菅原 黎明
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.11, no.1, pp.41-53, 1974
- 被引用文献数
- 2 12
肩運動は大きな運動域をもつが,これは肩関節と肩甲骨と鎖骨の総合された動きによりもたらされる.古来より肩運動に関与するrotator cuff musclesを始め多くの関与筋群の活動動態は検索されて来た.しかしながら肩運動は多様にして複雑なために今まで十分な解明はなされていない.この様な観点に立脚してrotator cuff musclesを始め肩運動に関与する筋群の活動動態を筋電図を用いて分析した.<br>健康男子9名の利き肩を用い,主として立位における前方挙上,後方挙上,外方挙上,内方挙上,外旋および内旋の各運動を行なわせた.被検筋は棘上筋,棘下筋,肩甲下筋,小円筋,大円筋,三角筋各部,大胸筋鎖骨部および胸骨部,小胸筋,上腕二頭筋長頭および短頭,上腕三頭筋長頭,広背筋,烏口腕筋,僧帽筋各部,大および小菱形筋,前鋸筋および肩甲挙筋の各筋である.電極はpolyurethane coatingしてある直径0.07mm.の銅線をfine wire electrodeとして用いた.8チャンネル筋電計を用い,得られた筋電図と関節運動は2現象同時撮影装置により16mm.映画フィルム上に同時記録した.このフィルムはFilm motion analyzerを用いて定性分析された.<br>結果<br>1) rotator cuff musclesはすべての筋が常時moverあるいはsynergistとして関与するのではなく関節運動の方向によりそれぞれ特定の筋群が適時作動すると思われる.<br>2) 三角筋鎖骨部,大胸筋,広背筋,烏口腕筋においては内旋作用は認められなかった.また肩甲下筋は特別な負荷を加えない内旋時において唯一の活動筋である.<br>3) 棘下筋と小円筋は外旋時に重要な機能を有するが,三角筋肩甲棘部にはこの作用は認められなかった.<br>4) 小円筋と棘下筋との間には若干の機能的な差異がある.すなわち小円筋は外方挙上の後半と内方挙上時に関与するが,棘下筋は外方挙上に関与するが内方挙上時には関与しなかった.<br>5) 大円筋と広背筋との間には若干の機能的な差異がある.すなわち大円筋は後方挙上と内方挙上時に働くが広背筋は前方挙上,後方挙上,外方挙上,内方挙上時に働く.<br>6) 関与筋群の活動動態に若干の経時的差異を認めた.
1 0 0 0 OA リハビリテーションと歩行分析
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.10, no.4, pp.247-270, 1973-10-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
1 0 0 0 OA 手の機能解剖
- 著者
- 室田 景久
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.4, pp.257-261, 1992-04-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 被引用文献数
- 2 1