- 著者
- 高橋 正三 武川 恒 高橋 孝志 土井 隆行
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.3, pp.501-503, 1988-08-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 11 11
ワモンゴキブリの性フェロモンの一つペリプラノンA (PA) とそのエピマー (EPA) を使って, Periplaneta 属, Blatta 属6種の雄に対する性フェロモン活性を実験室内で生物検定した. PAのワモンゴキブリに対するフェロモン活性はペリプラノンB (PB) の約1/1000で, EPAの活性はPAの約1/1000であった. PA, EPAおよびPAとPBの混合物はワモンゴキブリ以外にヤマトゴキブリ, トビイロゴキブリ, コワモンゴキブリ, トウヨウゴキブリの雄にもフェロモン活性があった.
1 0 0 0 OA 病害防除における抵抗性誘導剤の可能性
- 著者
- 沢田 治子
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.4, pp.326-329, 2009-11-25 (Released:2013-12-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 2 3
1 0 0 0 OA 殺菌剤メパニピリムの開発
- 著者
- 林 茂 前野 真一郎 木本 隆啓 永田 俊浩
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.22, no.2, pp.165-175, 1997-05-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
- 参考文献数
- 49
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Katsuta Michikazu Nomura Takeo Wakita Hidenori Daido Yumi Kobayashi Atsuko Kawahara Shinichi Banba
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.2, pp.120-128, 2019-05-20 (Released:2019-05-20)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 32 49
Broflanilide (1), discovered by Mitsui Chemicals Agro, Inc., has a unique chemical structure characterized as a meta-diamide and exhibits high activity against various pests, including Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, and Thysanopteran pests. Because broflanilide has a novel mode of action, the Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) categorized it as a member of a new group: Group 30. The meta-diamide structure was generated via drastic structural modification of a lead compound, flubendiamide (2), and the subsequent structural optimization of meta-diamides on each of its three benzene rings led to the discovery of broflanilide. In the present study, the details of the generation of meta-diamides from the lead compound and the structural optimization of meta-diamides are described.
1 0 0 0 OA 第8回カリフォルニア農薬残留ワークショップ
- 著者
- 斎藤 勲
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.22, no.1, pp.52-54, 1997-02-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
1 0 0 0 OA 新規水稲用除草剤ペノキススラムDASH-001SCの開発とその特性について
- 著者
- 白石 郁雄
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.3, pp.265-268, 2005-08-20 (Released:2014-06-08)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
- 著者
- Yingchen Li Lin Liu Jun Yang Qing Yang
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.43-52, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 4 17
Chitin deacetylase (CDA) is a key enzyme involved in the modification of chitin and plays critical roles in molting and pupation, which catalyzes the removal of acetyl groups from N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitin to form chitosan and release acetic acid. Defects in the CDA genes or their expression may lead to stunted insect development and even death. Therefore, CDA can be used as a potential pest control target. However, there are no effective pesticides known to target CDA. Although there has been some exciting research progress on bacterial or fungal CDAs, insect CDA characteristics are less understood. This review summarizes the current understanding of insect CDAs, especially very recent advances in our understanding of crystal structures and the catalytic mechanism. Progress in developing small-molecule CDA inhibitors is also summarized. We hope the information included in this review will help facilitate new pesticide development through a novel action mode, such as targeting CDA.
1 0 0 0 OA 殺ダニ剤エトキサゾールの開発
- 著者
- 鈴木 純二 石田 達也 渋谷 一郎 戸田 和哉
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.26, no.2, pp.215-223, 2001-05-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 24 25
- 著者
- Mei-Yin Chien Chih-Min Yang Chao-Hsiang Chen
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.1, pp.30-34, 2022-02-20 (Released:2022-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Over ten-year routine inspection results on organochlorine pesticide (OCP) residue were summarized, OCPs residues, including BHC isomers (α, β, γ, and δ-BHC), DDT analogs (p,p′-DDD, p,p′-DDE, o,p′-DDT, and p,p′-DDT), and pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) and its metabolites (pentachloroaniline and methyl pentachlorophenyl sulfide (MPCPS)), in 1,665 samples for 37 types of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) using the QuEChERS method coupled with the GC-ECD. Based on the maximal residue levels for OCPs set by Asian pharmacopeias, PCNB contamination in Ginseng radix as well as the total DDT and PCNB contamination in Panacis quinquefolii radix are of concern. OCP residues in different parts of Panax ginseng were also compared. The total BHC residue in leaf and fibrous root, as well as the total DDT and PCNB residue in all parts, exceeded MRL of 0.1 mg/kg. Overall, this study provided meaningful results about OCP residue in CHM for pharmaceutical industries and consumers.
1 0 0 0 OA キュウリうどんこ病菌に及ぼすレシチンの影響
- 著者
- 本間 保男 高橋 広治 水野 宏 見里 朝正
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.1, pp.33-40, 1977-02-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
- 参考文献数
- 8
- 被引用文献数
- 1
キュウリうどんこ病菌 Sphaerotheca fuliginea を供試し, 本菌の生育過程に及ぼす大豆レシチンの影響を検討した. キュウリ子葉裏面に大豆レシチン2000ppmを処理し, うどんこ病菌分生胞子を接種し, 分生胞子の発芽, 菌糸の伸長, 分生子梗, 分生胞子の形成を経時的に走査電顕により観察した. 分生胞子の発芽には著しい抑制はみられなかったが, 無処理区に比し, 発芽管がやや太く, 短くなり, 菌糸の伸長が遅くなる傾向がみられた. もっとも顕著な影響は, 処理区の接種3日目以降の菌糸先端部に現われた. すなわち, 伸長した菌糸の先端部周縁に薄膜が見られ, うなぎ尾状を呈し, 日数の経過とともに膜の部分が拡大することであった. また無処理区に比し, 分生子梗, 分生胞子の形成が遅れ, 数も少なく, とくに分生胞子が分生子鎖から離脱せずに, そのままたれ下がり, 全体的にゼンマイ状を呈するものがみられた.
- 著者
- 永山 敏廣 真木 俊夫 観 公子 飯田 真美 田村 行弘 二島 太一郎
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.14, no.1, pp.39-45, 1989-02-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 5 5
日本茶の茶葉中に検出された有機リン系農薬は, 茶の種類や生産地により特徴が見られた. また, 多種の農薬が同一の茶葉に残留し, とくに, MEP, EPNおよびイソキサチオンの検出率が高かった. さらに, CVP, イソキサチオンおよびプロチオホスは, 1ppmを超えて残留した茶葉が見られた. これら残留量の多かった農薬のうち, イソキサチオンおよびプロチオホスは茶湯中への浸出率が低く, 飲用上とくに問題はないと考えられる. しかし, CVPは3ppmを超えて残留した茶葉があり, 浸出率も高かった.今回の調査では, 茶葉中の有機リン系農薬の残留量は全般的には微量であり, 食品衛生上とくに問題があるとは考えられない. しかし, 登録保留基準値を超える農薬の残留するものが1検体とはいえ見いだされており, また, 同一の茶葉に多種の農薬が同時に残留していたことから, 今後生産者は農薬散布に当たり, その使用時期や使用方法などに十分配慮して, 茶葉中残留農薬量を極力減らし, 消費者の安全を図らなければならないと考える.
1 0 0 0 ストリゴラクトンの構造多様性と植物界における分布
- 著者
- 米山 弘一 謝 肖男 米山 香織 竹内 安智
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of pesticide science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.4, pp.302-305, 2009-11-20
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
被子植物の約1%(3000-4500種)は他の植物に寄生する寄生植物である。寄生植物のなかでも、農業生産に大きな被害を与えているのがハマウツボ科の根寄生雑草ストライガとオロバンキである。ストライガは光合成機能を有する半寄生性で、主にソルガム、トウモロコシ、サトウキビ、イネなどイネ科植物に寄生する。オロバンキは光合成機能を失った全寄生性で、主にトマト、ニンジン、タバコ、アブラナなどの双子葉植物に寄生する。これらの根寄生雑草は、巧妙な生存戦略によってその生息範囲を拡大している。それは、(1)大量の種子を生産し、(2)種子の寿命が長く、(3)種子発芽が宿主由来の化学物質によって誘導されることである。すなわち、根寄生雑草の種子は、宿主の根から分泌される発芽刺激物質にさらされて初めて発芽する。この発芽刺激物質には少なくとも3種類の化合物群、すなわち、ソルガムのジヒドロソルゴレオン、ヒマワリのセスキテルペンラクトン、そしてストリゴラクトン(SL)、が知られているが、最も多くの植物種が生産・分泌している発芽刺激物質がSLである。本稿では、SLの構造多様性と植物界における分布について解説する。
1 0 0 0 除草剤ピラフルフェンエチルの開発
- 著者
- 三浦 友三 馬渕 勉 東村 稔 天沼 利宏
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of pesticide science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.2, pp.219-240, 2003-05
ピラフルフェンエチル(pyraflufen-ethyl)は日本農薬(株)によって創製され、実用化されたプロトポルフィリノーゲン酸化酵素(Protox)阻害型除草剤である。本化合物はコムギに対して高い安全性を示すと共に広範囲の広葉雑草に対して10g a.i./ha前後の低薬量で極めて高い除草活性を示す。特にコムギ栽培における難防除雑草の一つであるヤエムグラ(Galium aparine)に卓効を示す。ピラフルフェンエチルは日本ではムギ用除草剤として、エコパートフロアブルの商品名で1999年に農薬登録の許可を得て販売を開始した。また同時に果樹園の下草防除や非農耕地の非選択性除草剤として、グリホサートトリメシウム塩との混合剤であるサンダーボルトの販売も開始した。さらに、2001年バレイショ枯凋剤として、デシカン乳剤の販売を開始した。これらは海外においても14か国で登録・上市され、数か国で開発途上にある。本稿では、ピラフルフェンエチルの創出の経緯、工業的製造法、構造活性相関、除草活性、作用機構、各種毒性試験結果について概要を述べる。
- 著者
- Toshifumi Nakao Miyuki Kawashima Shinichi Banba
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.D19-017, (Released:2019-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 5 9
The peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae, is a serious crop pest that has developed imidacloprid resistance, mainly through overexpression of CYP6CY3. Here, we established a metabolic assay using Drosophila S2 cells that stably expressed CYP6CY3. We found that CYP6CY3 showed metabolic activity against imidacloprid, as well as acetamiprid, clothianidin, and thiacloprid, but had no activity against dinotefuran. Our study suggested that stable gene expression in Drosophila S2 cells is useful for examining which insecticide is metabolized by P450 monooxygenases.
1 0 0 0 内分泌撹乱作用問題に対するアカデミアの取組み
- 著者
- 宮本 純之
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- 日本農薬学会誌(Journal of Pesticide Science) (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.1, pp.110-113, 1999
1 0 0 0 混合生薬抽出物液剤の毒性試験の概要
- 著者
- 株式会社アルム開発本部
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- 日本農薬学会誌(Journal of Pesticide Science) (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.3, pp.S253-S254, 1992
OKY-500の安全性を評価するため, 各種毒性試験を実施したところ, 本剤はきわめて安全性の高い薬剤であることが示された.<br>OKY-500のラットおよびマウスにおける急性毒性は普通薬に相当した.<br>眼粘膜一次刺激性, 皮膚一次刺激性, および皮膚感作性は陰性であった.<br>変異原性は, 枯草菌を用いたDNA修復試験, 細菌を用いる復帰変異試験および染色体異常試験のいずれにおいても陰性であった.<br>アルムグリーン (試験名OKY-500) は, 平成3年5月に芝用植物成長調整剤として登録を取得した.<br>本剤は日本薬局方第11版の生薬より構成されており, 人畜無害で魚毒性もまったく見られなかった. さらに急性毒性や眼粘膜一次刺激性試験などについても完全に無毒であることが証明された. さらに, 本剤はゴルフ場周辺の樹木に対し何ら影響を与えず, かつ芝の根の生長を促進する効果を示した.<br>このように本剤は漢方薬独特の効能・効果と総合作用を示して, 結果的に病気にかかりにくい芝生を育成するゴルフ場芝生管理用の漢方農薬 (植物成長調整剤) である.
- 著者
- Li Min-Yi Zhang Jing Feng Gang Satyanandamurty Tirumani Wu Jun
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- 日本農薬学会誌(Journal of Pesticide Science) (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1, pp.22-26, 2011
- 被引用文献数
- 10
熱帯地域において,Brontispa longissima(Gestro)はヤシの木に重大な被害をもたらす害虫である。我々は,熱帯マングローブの潜在的殺虫剤リード化合物探索研究において,インドマングローブXylocarpus moluccensisの種子からΔ8,14二重結合をもつメキシカノライドであるカヤシンと2'S-メチルブタノイルプロセラノリドを単離した。これらの化合物の構造は文献データと比較して同定した。50μg/mlの濃度では,カヤシンはB. longissimaの2齢から5齢幼虫に対して強い殺虫効果を示し,2'S-メチルブタノイルプロセラノリドは5齢幼虫に対して顕著な殺虫効果を示した。B. longissimaの5齢幼虫に対する24時間と48時間暴露のLC50(半数致死濃度)は,カヤシンは7.27と3.39μg/ml,2'S-メチルブタノイルプロセラノリドは10.57と4.03μg/mlであった。2種の化合物のB. longissimaの5齢幼虫に対する殺虫活性は,アザジラクチンとトオセンダニンよりも強く,ロテノンと同程度であった。しかし,Prodenia litura(Fabricius)の3齢幼虫に対しては,これらの化合物は中程度の摂食阻害活性しか示さなかった。以上の結果は,カヤシンと2'S-メチルブタノイルプロセラノリドは,B. longissimaの幼虫に対して選択的な殺虫活性を持っていることを示唆しており,B. longissima防除用の有力な殺虫剤候補になると思われる。
1 0 0 0 OA コガネムシ類幼虫に特異的な Bacillus thuringiensis
- 著者
- 堀 秀隆 佐藤 令一 大庭 道夫
- 出版者
- 日本農薬学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.1, pp.99-107, 1995-02-20 (Released:2010-08-05)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
- 著者
- Atsushi Ishihara
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.4, pp.382-392, 2021-11-20 (Released:2021-11-20)
- 参考文献数
- 79
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Plants synthesize and accumulate a wide variety of compounds called secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites serve as chemical barriers to protect plants from pathogens and herbivores. Antimicrobial secondary metabolites are accumulated to prevent pathogen infection. These metabolites are classified into phytoalexins (induced in response to pathogen attack) and phytoanticipins (present prior to pathogen infection). The antimicrobial compounds in the grass family (Poaceae) were studied from the viewpoint of evolution. The studies were performed at three hierarchies, families, genera, and species and include the following: 1) the distribution of benzoxazinoids (Bxs) in the grass family, 2) evolutionary replacement of phytoanticipins from Bxs to hydroxycinnamic acid amide dimers in the genus Hordeum, and 3) chemodiversity of flavonoid and diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. These studies demonstrated dynamic changes in secondary metabolism during evolution, indicating the adaptation of plants to their environment by repeating scrap-and-build cycles.
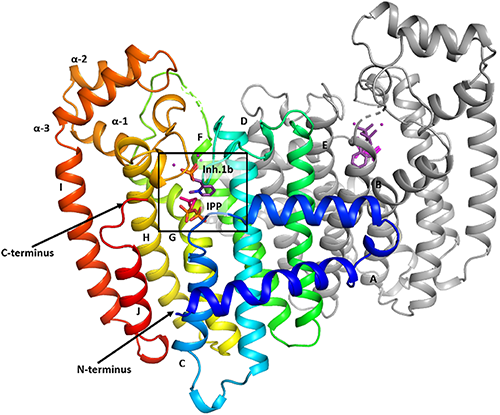
- 著者
- Marie-Ève Picard Michel Cusson Stephanie E. Sen Rong Shi
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.7-15, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Reducing the use of broad-spectrum insecticides is one of the many challenges currently faced by insect pest management practitioners. For this reason, efforts are being made to develop environmentally benign pest-control products through bio-rational approaches that aim at disrupting physiological processes unique to specific groups of pests. Perturbation of hormonal regulation of insect development and reproduction is one such strategy. It has long been hypothesized that some enzymes in the juvenile hormone biosynthetic pathway of moths, butterflies and caterpillars (order Lepidoptera) display unique structural features that could be targeted for the development of Lepidoptera-specific insecticides, a promising avenue given the numerous agricultural and forest pests belonging to this order. Farnesyl diphosphate synthase, FPPS, is one such enzyme, with recent work suggesting that it has structural characteristics that may enable its selective inhibition. This review synthesizes current knowledge on FPPS and summarizes recent advances in its use as a target for insecticide development.