2 0 0 0 森林浴効果の生理・心理学的研究
- 著者
- 近藤 照彦 武田 淳史 武田 信彬 下村 洋之助 谷田貝 光克 小林 功
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.2, pp.131-138, 2008-02-01
- 被引用文献数
- 3 2
We performed a physio-psychological research on the mental, physical relaxation and health-keeping effect of <i>Shinrin-yoku</i> (forest walking) in Kawaba village. Eleven male and 8 female healthy elderly residents in Kawaba village, whose average age was 74.0±3.5 years old for male and 74.9±2.9 years old for females volunteered for this experiment. All members walked for one hour in the Kawaba Forest on August 17 under cloudy skies, 30-32°C temperature, 58-60% humidity, and, 0-2m/sec wind condition and walked again for another one hour in a non-forest rural agricultural area on August 21 under almost the same weather conditions. Phytoncides in the air, Profile of Mood State (POMS) test, blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), fasting levels of serum natural killer cell activity (NK), plasma catecholamine (adrenaline, noradrenalin and dopamine), plasma cortisol, and serum adiponectin were measured before and after walking. Phytoncides were detected in the forest and non-forest, all members showed a decrease of POMS total scale, BP, adrenalin and serum cortisol. Six (3 male and 3 female subjects) of them expressed an increase of serum NK cell activity after the forest-walking. One female showed a high serum NK cell activity after both forest and non-forest rural walking.<br>Our experiment on the forest-walking in Kawaba village indicated that its relaxation and health-keeping effects, probably due to walking in the fresh forest air.
2 0 0 0 OA 部分浴である足浴および手浴の体温応答
- 著者
- 美和 千尋 島崎 博也 出口 晃 前田 一範 水谷 真康 川村 陽一 森 康則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.2, pp.106-111, 2016-05-31 (Released:2016-07-04)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 1
部分浴は体に一部を入浴する方法で,足浴と手浴がよく用いられている.部分浴は温められた部分の大きさにより温熱効果が異なると思われるが,その詳細は明らかとなっていない.そこで,この論文では,足浴と手浴における体温応答がどのように異なるのかを検討する.若年健常者10名(平均年齢23.2±1.3歳)の被験者を対象とし,座位にて安静5分間,足浴として一側と両側の下腿部を,手浴として一側と両側の前腕部を42°Cの湯に15分間浸け,さらに終了後5分間安静を行った.測定項目は鼓膜温,皮膚血流量,発汗量と主観的変化として温熱感と快適感を申告させた.鼓膜温についてはサーミスターにより外耳道の皮膚温を,皮膚血流量として右側の上腕部(非浸水部)をレーザードップラー血流計で,発汗量として右側の上腕部(非浸水部)をカプセル換気法で測定した.両側の足浴と手浴時の鼓膜温は,有意に上昇し,最大上昇温度は入浴しないときに比べ,有意に上昇した.皮膚血流量と発汗量は,全ての負荷条件で有意な増加は認められなかった.温熱感と快適感は全ての入浴負荷で,入浴しないときに比べ,有意に,「暑い」,「快適である」と申告した.温熱感においては両側の足浴,手浴で一側と比べて,「暑い」と申告した.これらの体温応答の変化は,同一身体部位においては温める表面積の大きさに依存し,異なる身体部位では,様々な要因により異なることが示唆された.
2 0 0 0 OA 気圧と虫垂炎
- 著者
- 福田 稔 安保 徹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.4, pp.236-242, 1996 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 13
Since the incidence of acute appendicitis seems to vary depending on weather (e. g., the perforation increases under a high atmospheric pressure), we investigated the underlying mechanism.We classified 112 patients who underwent appendectomy into three groups according to the atmospheric pressure at the time of onset. We found that gangrenous cases (high infiltration of granulocytes) occur more frequently at high atmospheric pressures while catarrhal cases (no infiltration of granulocytes) occurred more frequently at low atmospheric pressures. The physiological variations of granuocytes and lymphocytes in the blood with respect to the atmospheric pressure were then examined in a healthy volunteer. Granulocytosis increases under a high pressure due to the sympathetic activity, whereas lymphocytosis increases under a low pressure due to the parasympathetic activity. Results obtained from gangrenous cases showed much granulocytosis in the blood as well as appendix while catarrhal cases showed much lymphocytosis in the blood and appendix. This seems to imply that granulocytosis induced by the increase in sympathetics activity might be closely related to the onset of gangrenous appendicitis. Even in gangrenous cases, bacteria were not found around the granulocytes in the appendix or in the cytoplasma of granulocytes as observed in electron microscopy. These results may be extremely useful in exploring the etiology of suppurative diseases which are caused without apparent bacterial infections.
2 0 0 0 OA 炭酸泉の医学的効果
- 著者
- 前田 眞治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.75, no.1, pp.24-26, 2011-11-24 (Released:2013-10-18)
- 参考文献数
- 2
2 0 0 0 OA ラットin vivo肉離れ損傷モデルの作製とそれに及ぼす鍼通電刺激の効果について
- 著者
- 吉田 行宏 林 知也 矢野 忠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.73, no.3, pp.177-190, 2010 (Released:2013-09-05)
- 参考文献数
- 40
Aim The study aimed to develop an appropriate in vivo rat model of muscle strain to investigate whether electroacupuncture is useful for improving muscle strain.Methods An in vivo muscle strain model was developed with Wistar rats by the eccentric contraction (EC) evoked by pulling their hind limb with a stainless-steel wire that was connected to a weight; the EC was given under anesthesia during tetanic contraction in their gastrocnemius evoking by electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve. Development of muscle strain was evaluated by comparing the muscle tension induced by the twitch of the gastrocnemius, pain thresholds measured using the Randall-Selitto test, and the serum creatine kinase (CK) activity between the following three experimental groups : EC×1 group, EC was temporarily evoked to their hind limb only once (n=10); EC×5 group, EC was temporarily evoked to their hind limb five times consecutively (n=6); and control group, EC was not evoked to their hind limb (n=6). After confirming the absence of a significant difference in the parameters between the two EC conditions, the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) was evaluated using the model of one-time EC (EA group n=10). At 12 hours after EC, EA was carried out at a frequency of 50 Hz and an intensity of 0.5 mA for 15 min; this stimulation was given for six consecutive days.Results Muscle tension, pain thresholds, and the CK activity showed no remarkable changes in the control group during the experimental period. A significant decrease in the muscle tension was observed after EC in the EC×1 and EC×5 groups, and the decrease sustained until 48 and 24 hours after EC, respectively. Pain thresholds in the EC×1 and EC×5 groups were significantly lower than those in the control group at each of the time periods studied after EC, and were sustained at least until 120 hours after EC. The CK activity increased in the EC×1 and the EC×5 groups at 30 minutes after EC. Recovery in muscle tension after EC was faster in the EA group than in the EC×1 group. Pain thresholds also showed faster recovery in the EA group than in the EC×1 group, indicating statistically significant differences at 72, 96, and 120 hours after EC.Discussion The in vivo rat model, which was developed in the present study, was considered to be an appropriate model of muscle strain because it clearly showed a decrease in the muscle tension and pain thresholds, and an elevation in the CK activity. EA was considered to be capable of accelerating the recovery of muscle strain as it was found to improve muscle tension and pain thresholds in the model.
2 0 0 0 慢性関節リウマチに対する高濃度炭酸ガス浴の効果
- 著者
- 前田 真治 山北 秀香 佐々木 麗 田中 裕美子 後出 秀聡 木村 広 井上 市郎
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.4, pp.187-194, 1998-08-01
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 1
慢性関節リウマチ (RA) 患者を対象に組織循環改善作用と新陳代謝亢進による疼痛の軽減を目的に90%以上になる高濃度炭酸ガス浴装置を用い効果を調べた。<br>気体としての炭酸ガス浴は更衣動作の障害されているRA患者にとって, 衣服のまま入浴できる画期的な入浴法である。血圧・脈拍の大きな変化なく, 循環機能の影響の少ない入浴法と考えられた。表面皮膚温も前値に比べ入浴後期に1℃以上の上昇がみられ, 局所の血液循環の改善が示唆され, 老廃物・疼痛物質などの除去・新陳代謝改善の効果が期待できると考えられた。ADL得点 (平均67→75/96), Visual Analogue Pain Scale (5.3→2.7/10), Face Scale (9.4→5.4/20), AIMS変法 (身体的要素28.5→30.1, 社会的25.2→27.3, 精神的26.2→29.9/36) と入浴前に比べ有意に改善しており, 高濃度炭酸ガス浴がRA患者のADL・QOLの改善に効果があると思われた。
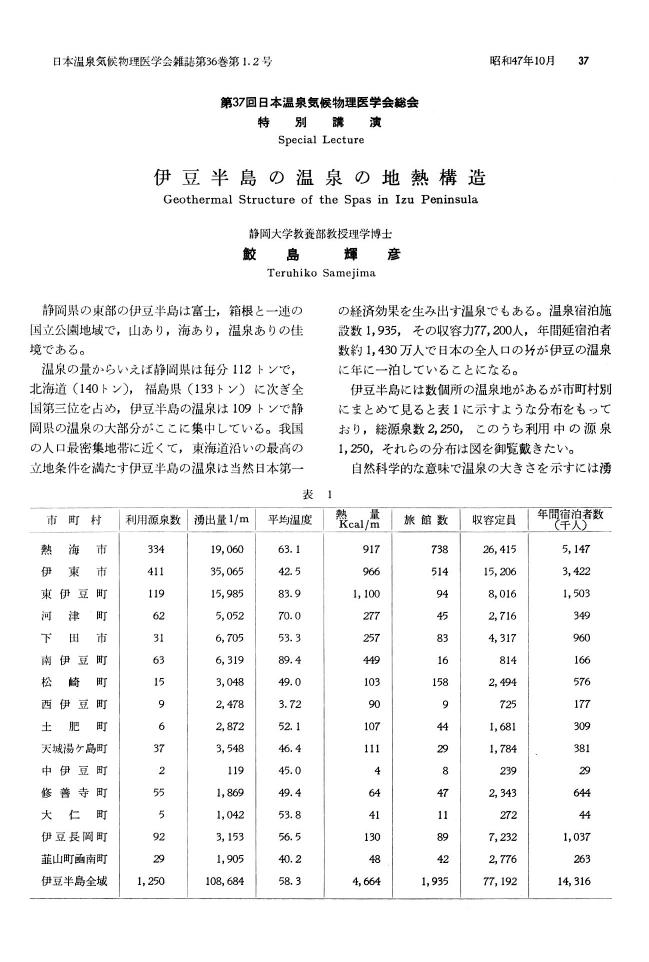
2 0 0 0 OA 伊豆半島の温泉の地熱構造
- 著者
- 鮫島 輝彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1-2, pp.37-39, 1972 (Released:2010-08-06)
2 0 0 0 ラットのアキレス腱修復に与える鍼通電刺激の効果
- 著者
- 大井 優紀 井上 基浩 中島 美和 糸井 恵 北小路 博司
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.75, no.2, pp.112-123, 2012-02-29
目的:鍼通電刺激の腱修復能に及ぼす影響について調査する目的で、アキレス腱断裂モデルラットを用いて、組織学的、および力学的に検討した。<br>方法:Wistar系ラット(雄性、12週齢)60匹を用いて、アキレス腱断裂モデルを作成し、無作為に鍼通電刺激群(EA群)と無処置群(Control群)の 2群に分けた。EA 群は、軽度麻酔拘束下にアキレス腱断裂部の内外側に先端部が腱断裂部に接触するようにそれぞれ鍼を刺入し、内側部を陰極、外側部を陽極として間欠的直流鍼通電刺激(刺激条件:刺激幅 5 ms、刺激頻度 50 Hz、刺激強度 20 μA、刺激時間 20分間)をモデル作成日の翌日から各評価日まで連日行った。Control群は麻酔拘束処置のみ行った。評価として、モデル作成後 7日と 10日に修復腱を採取し、設定した関心領域内の全細胞数(HE染色)、TGF-<i>β</i>1、および b-FGF の陽性細胞数(免疫組織化学染色)の計測とそれぞれの染色による組織像の観察を行った。また、モデル作成後 10日には、引張試験による修復腱の最大破断強度を測定した。<br>結果:HE染色では、各評価日とも群間に有意差を認め、EA群で明らかな細胞数の増加を認めた(7日:p<0.05、10日:p<0.001)。免疫染色においては、TGF-<i>β</i>1、b-FGFともにモデル作成後7日のEA群で最も強い発現を認め、他との間に有意差を認めた[(TGF-<i>β</i>1:7日 EA群vs. 10日 EA群:p<0.001、vs. 7日 Control群:p<0.0001、vs. 10日 Control群:p<0.0001)(b-FGF:7日 EA群vs. 10日 EA群:p<0.001、vs. 7日 Control群:p<0.0001、vs. 10日 Control群:p<0.0001)]。モデル作成後 10日における修復腱の最大破断強度は EA群で有意に高い値を示した(pp<0.01)。<br>考察・結語:アキレス腱断裂後早期の検討において、EA群では細胞数の増加と成長因子の発現量増加、さらに腱強度の増大を認めた。これらの結果から、直流鍼通電刺激は腱修復部における細胞増殖と成長因子の発現に有益に作用し、修復腱の力学的強度を高めることが示唆され、腱修復能に促進的に作用する有用な方法となる可能性が考えられた。
- 著者
- 堀 進悟 鈴木 昌 伊香賀 俊治
- 出版者
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.1, pp.14-16, 2013-11
2 0 0 0 OA 季節と疾病
- 著者
- 籾山 政子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.1-2, pp.15-17, 1965-11-25 (Released:2010-08-06)
2 0 0 0 OA 単純泉における温泉療法による脱ストレス作用と免疫機能の変化
- 著者
- 大塚 吉則 中谷 純 及川 隆司
- 出版者
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, no.3, pp.121-127, 2002-05-01
It is reported that changes in immunological system are one of the underlining mechanisms of balneotherapy effects. Since there is no study concerning the mechanisms how balneotherapy with a simple thermals works, we tried to examine both the changes of immunological functions and stress relieving effect of balneotherapy. Fourteen inpatients (mean age 63 years) suffering from such as cerebrovascular diseases participated in the present study. Before and after 6-week balneotherapy, lymphocyte subset counts, levels of cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, IF-γ etc.) were determined and lymphocyte blastogenetic tests were also performed . In addition, stress barometers (urinary 17-ketosteroidsulfate (17KSS) / 17hydroxycorticosteroid (17OHCS)) were measured. As a result, no significant changes in cytokine levels were observed. Percentage of T cell count decreased and that of B cell increased. Percentage of suppressor T cell count decreased and that of helper and killer T cell tended to increase (not significant). Lymphocyte blastogenetic tests by ConA and PWM showed enhanced responses and urinary 17KSS / 170HCS levels increased after balneotherapy. From these findings, it is suggested that 6-week balneotherapy with a simple thermals has a potential of augmenting immunological functions and also possesses stress relieving effect.
- 著者
- 百合 邦子 坂口 俊二 鍋田 理恵 久下 浩史 若山 育郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.3, pp.237-249, 2014-05-30 (Released:2014-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
目的:本研究では、若年女性の冷え症に対する温筒灸治療の効果を、膝陽関(GB33)穴と三陰交(SP6)穴との比較試験で検討した。方法:対象は女子大学生13名(平均年齢20.7±1.3歳)とした。対象者を坂口らの判別分析による判定法に身長を考慮し、膝陽関群(6名)と三陰交群(7名)とに割り付けた。1週間の前観察期間を経て、介入期間には各経穴について温筒灸(長安NEO、山正)1~2壮を週2回で4週間行った。介入期間終了後2週間を追跡期間とした。評価には冷えを含む14症状の6件法と冷えの程度をVisual Analogue Scale (VAS)で回答する独自の評価票(冷え日記)を用いた。結果:13名中3名は前観察期間終了後に脱落し、解析対象は両群とも5名となった。2群間で年齢、身長、体重、BMI、VAS、愁訴得点などの初期値に有意差はみられなかった。VASおよび愁訴得点は、何れも群間と試験期間との間に交互作用はみられなかった。群別では、両群ともVASは前観察期間に比して介入期間、追跡期間とも有意な変化はみられなかった。愁訴得点については、両群とも介入開始より漸次減少したが、膝陽関群で介入期間3・4週目、三陰交群では介入期間4週目と追跡2週目で前観察期間と比して有意に減少した。また、愁訴得点を項目別に検討すると、膝陽関群には肩こり、口の乾きに、三陰交群には肩こり、口の乾き、イライラで有意差がみられた。具体的には、膝陽関群では肩こりは追跡期間1・2週目で有意に減少し、口の乾きは介入期間3・4週目で有意に減少した。一方、三陰交群では、肩こりは介入期間2・4週目、追跡期間1・2週目で有意に減少し、口の乾きは介入期間4週目、追跡期間2週目において、イライラは介入期間1・2・4週目に有意な減少を示した。結語:若年女性の冷え症に対する温筒灸治療は、膝陽関穴、三陰交穴ともに外気温が低下しても冷え症を悪化させることなく、随伴愁訴を改善させることが示唆された。
1 0 0 0 OA 森林浴が生体に及ぼす生理学的効果の研究
- 著者
- 近藤 照彦 武田 淳史 小林 功 谷田貝 光克
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.3, pp.169-177, 2011 (Released:2012-12-07)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1
森林浴は、リラクセーションならびに心身の健康をもたらすとされる。我々は高齢者を対象として、森林浴が生体に及ぼす生理学的効果について検討した。被験者は、2008年から2010年の3回の森林浴測定に参加した高齢者男性24名(65.5±2.5歳)および女性24名(65.0±3.0歳)である。森林浴測定は、8月第3週水曜日の日程で2時間行った。測定時の天候は晴れ、気温30℃から32℃、湿度58%から60%、風速0m/secから2m/secであった。森林浴および非森林浴の測定は、被験者を3グループに分けた。1つのグループは、防臭マスクによる嗅覚遮断男性8名および女性8名、アイマスクによる視覚遮断男性8名および女性8名、コントロール男性8名および女性8名(非遮断)である。非森林浴は、同一被験者による室内環境において日を変えて同一条件下で測定した。フィトンチッド濃度は、ガスクロマトグラフィー質量分析法を用いた。測定項目は、森林浴ならびに非森林浴前後の気象データ、心拍数、血圧、カテコールアミン3分画、コルチゾールおよびNK細胞活性について調べた。本研究における森林浴測定地点から樹木由来のフィトンチッドが3種類検出された。男性の森林浴および非森林浴における平均心拍数は、89bpmおよび85bpmであった。女性の森林浴および非森林浴における平均心拍数は、86bpmおよび85bmpであった。森林浴前後の男女収縮期血圧は、嗅覚遮断およびコントロールにおいてそれぞれ有意に低下した。森林浴前後の男性拡張期血圧は、嗅覚遮断およびコントロールにおいてそれぞれ有意に低下した。森林浴前後の男女アドレナリンは、嗅覚遮断およびコントロールにおいてそれぞれ有意に低下した。森林浴前後のノルアドリナリンは、男性のコントロール、女性の嗅覚遮断およびコントロールにおいてそれぞれ有意に低下した。同様に、男女のコルチゾールは、嗅覚遮断およびコントロールにおいて有意に低下した。森林浴前後の男女NK細胞活性は、有意差を認めなかった。非森林浴前後における血圧、カテコールアミン、コルチゾールおよびNK細胞活性は、男女とも有意差を認めなかった。 森林浴は、フィトンチッドや緑の森林環境が生体に対してリラックス効果を及ぼすことが指摘されている。今回、高齢男性および女性を対象とした検討から、視覚遮断群で有意差は認めた測定項目はなかった。有意差を認めた測定項目は、嗅覚遮断およびコントロールの両群であった。森林浴の生体に対する効果は、フィトンチッドも含めた生体五感に関わる複合的要素の生理学的効果が短時間に存在する可能性が示唆された。 香りや視覚の量的、質的データと生理・心理的応答との関連性の調査結果の蓄積が今後の課題である。
- 著者
- 渡邊 弘美 頼住 孝二
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.2, pp.96-100, 1997 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 10
We studied the effects of bathing in warm water on cerebral blood flow (CBF). Seven healthy male volunteers were subjected to experiments. The subjects were bathed in warm water at 39°C for 20 minutes in a sitting position immersed up to the neck. Each subject received two CBF examinations: one under normal conditions and the other after taking a bath mentioned above. There was an interval of at least seven days between the two examinations. To measure CBF, we used the Patlak plot method with technetium-99m ethyl cysteinate dimer (99m-Tc ECD). To examine CBF after bathing, 99m-Tc ECD was injected within 10 minutes after bathing. Brain perfusion index (BPI) and regional CBF (rCBF) were used as indexes for evaluating CBF. The body temperature, pulse, blood pressure, arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide pressure, and hematocrit were also measured. Wilcoxon's signed rank test was used for statistical analyses. The following were observed:1) BPI increased significantly after bathing (p<0.05).2) rCBF in the cerebral cortex, particularly in the frontal lobe, tended to increase after bathing (p<0.05). No definite changes were observed in the cerebellar cortex, caudate nucleus, or thalamus.3) The body temperature and pulse increased significantly after bathing. No definite changes were observed in blood pressure, arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide pressure, or hematocrit. From the above, we conclude that bathing in warm water causes the cerebral blood flow to increase in healthy subjects.
1 0 0 0 OA 入浴介護に関連した体調不良・事故発生と入浴前血圧,体温との関連:症例対照研究
- 著者
- 早坂 信哉 原岡 智子 尾島 俊之
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2294, (Released:2016-02-22)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 2
【背景・目的】介護保険によって入浴サービスが提供されているが,現在,高齢者にとって安全な入浴が可能か否かの具体的な判断基準・指針がなく,介護現場の入浴担当者は判断に困難を感じている.特に入浴前の体調確認は主に血圧測定,体温測定によって実施されていることから,本研究は,入浴前の血圧や体温と,入浴に関連した体調不良や事故の発生との関連について明らかにすることを目的とした.【方法】1.研究デザイン:症例対照研究(前向き調査による症例登録方式).2.調査対象:訪問入浴事業所として登録がある2,330か所の全事業所.3.調査方法:症例は入浴に関連した体調不良・事故の症例(以下,異常例と言う).対照は各事業所2例無作為抽出.調査期間は2012年6月~2013年5月までの1年間.4.解析方法:年齢,性別,障害高齢者の日常生活自立度(寝たきり度),要介護度,modified Rankin Scale,意識レベル,認知症高齢者の日常生活自立度,入浴前の血圧,入浴前の体温を単純比較した.その後,ロジスティック回帰分析を用いて,すべての体調不良・事故発生及び発熱,血圧上昇・低下を除いた体調不良・事故発生を目的変数に,その他の測定項目を説明変数とした単変量・多変量解析を実施した.【結果】異常例596件,対照1,511件を解析した.単純比較では異常例で体温が高かった.発熱,血圧上昇・低下を除いた体調不良・事故発生での多変量解析では,収縮期血圧は160~179mmHgでオッズ比(95%信頼区間)3.63(1.39-9.50),拡張期血圧は100~109mmHgで同14.71(1.31-165.77),体温は37.5~37.9°Cで同16.47(3.30-82.40),38.0°C以上で同6.57(1.40-30.81)と有意な関連があった.【結論】高齢者における160/100mmHg以上の血圧,37.5°C以上の体温は入浴関連の体調不良・事故の危険因子である可能性がある.
1 0 0 0 OA 温泉入浴習慣の効果と有害事象
- 著者
- 前田 豊樹 三森 功士 牧野 直樹 堀内 孝彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.2, pp.41-47, 2019-05-31 (Released:2019-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 22
これまで温泉治療が様々な疾患に療養効果があることは示されてきたが,一般的にどのような疾病に予防効果があるのかは示されていない.また,温泉入浴の禁忌症は示されているものの,某かの疾病の発症を促進する可能性についても知られていない.このような状況を踏まえて,筆者らは,平成24年度から3カ年間,65歳以上の高齢別府市民2万人を対象に,温泉の利用歴と各種疾患の既往歴に関するアンケート調査を実施し,その解析結果を先頃論文報告した.結果は,性別によって分かれており,温泉入浴が,男性においては,心血管疾患の予防に寄与し,女性では,高血圧に予防的に働くが,膠原病などの発症には促進的に働く可能性などが示唆された.このように,温泉は必ずしもすべての疾患の予防に働くわけではなく,一部促進する場合もあり得ることが伺えた.この疫学調査から伺える予防的効果には,温泉の効能としては期待されてこなかったものやこれまで示されてきた効能に反するものが含まれている.本編では,様々な疾患に対する温泉の予防効果と治療効果のずれという観点から,アンケートによる疫学調査をレビューする形で紹介したい.
1 0 0 0 OA 中国の針麻酔と針治療および湯液療法
- 著者
- 大島 良雄
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.1-2, pp.4-7, 1973 (Released:2010-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 9
1 0 0 0 OA フランスのスパセラピーとマッサージ
- 著者
- 殿山 希 ジュアンド 康子 成島 朋美
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.76, no.2, pp.137-146, 2013-02-28 (Released:2013-10-23)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 被引用文献数
- 1
2012年3月19∼28日、フランスに滞在して現地でスパセラピーを視察する機会を得た。 SPAセラピーとは、「水による健康法」の意味で、温泉水を用いる温泉療法le thermalisme、海水を用いる海洋療法la thalassothérapie、水を用いる水治療法la balnéothérapieを指し、フランス自然療法のひとつである。 フランスには、89ヵ所の温泉地がある。18日間(日曜を除く3週間)の温泉地滞在での温泉水を用いた治療である温泉療法に国の健康保険が適応となる。一方、海洋療法は、現在はリラクセーションとして扱われている。 温泉療法と海洋療法では、ジェットバス入浴、シャワーマッサージ(シャワー圧注)、マッサージ、プールでの運動法、泥療法(泥パックとラッピング)など同様の施術を行うが、使用している水(温泉水·海水)、目的(病気の治療·ウェルビーイング)、対象(患者·一般健康者)、施術を行う者(医療マッサージの免許を持つ人·エステティシャンや水治療法士)が異なる。また、温泉療法センターにおいても、治療部門とリラクセーションスパでは、同様の違いがあった。 フランスでは、マッサージとは医療マッサージを指し、masseur-kinésithérapeuteの国家資格を持つ人が行い、国の健康保険の適応となる。病院や温泉療法センターで働き、また、開業権も持つ。 一方、ウェルビーイングを目的とした施術は法的規制を受けず、医療的目的で行われるmassageとは区別されており、エステティシャンの資格を持つ人が主に行っていた。
1 0 0 0 OA 冷え感を有する健康人におけるカイロ加温の部位別検討試験
- 著者
- 嶋 良仁 渡邉 あかね 井上 暢人 國友 栄治 丸山 哲也
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.3, pp.105-112, 2020-10-31 (Released:2021-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 9
【目的】「冷え」は正常な体温であるにもかかわらず,手または足が冷えている状態である.疾病の有無に関係なく,高齢者を中心に多くの人がこの「冷え」に悩まされている. 冷えを和らげる方法のひとつに使い捨てカイロで手を温めることがあるが,この方法では手が塞がり日常の作業を妨げる.そこで,カイロで上肢の別の部分を加熱することで,手の冷えを緩和できるかどうかを調査した. 【方法】インフォームド・コンセントの後,脈管異常の指摘がこれまでない冷えを自覚する30名に頸部,肘,手首の加温の検討を行った.18名はそれぞれ1週間のインターバルをあけて3ヶ所を指定された順に1週間ずつカイロで加温を行った.残りの参加者は,カイロ固定用ホルダーの影響を観るためにホルダーだけを装着した.すべての参加者は,10cmのvisual analog scaleによる手の冷え評価を連日記録させた. 同様にカイロやホルダー装着が日常作業に差し障ったかを連日評価させた.1週間の加温の治療効果を観るために,カイロまたはホルダーのみを使用した期間終了翌日に,サーモグラフィーとlaser speckle contrast analysis(LASCA)を使用して,24℃20分間の室温順応後に両手の表面温度と血流を計測した. 【結果】頸部と肘部のカイロ加温中に冷えVASの有意な低下が観察された.日常への差し障り度評価は3ヶ所間で差がなかった.手の表面温度・血流はカイロ(あるいはホルダーのみ)の使用で上昇は観察されなかった. 【結語】手を温めなくても手の冷えを改善できることと,加温部位によってその効果が異なることが判明した.この研究は,「冷え」を改善する新しい方法につながると考えられる.サーモグラフィー等の客観的評価は,外気温等の測定条件の影響が非常に大きく,評価方法の検討が必要と考えられた.
1 0 0 0 OA 低周波鍼通電療法の臨床的研究 筋刺激 (筋パルス) と神経刺激 (神経パルス) の検討
- 著者
- 坂井 友実 安野 富美子 田和 宗徳 矢野 忠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本温泉気候物理医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.2, pp.87-108, 2004 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 55
- 被引用文献数
- 2
We investigated the difference between muscle-EAT and nerve-EAT basically and clinically. A basic study was performed on healthy adult males. The skin blood flow, deep-tissue temperature, deep hemodynamics, heart rate, and deep-pain threshold were adopted as indexes, and they were compared for a total of three groups: the muscle stimulation-EA group, nerve stimulation-EA group and control group (no stimulation). An acupuncture needle was inserted into the gastrocnemius muscle for muscle stimulation-EA and another needle into the tibial nerve in the femoral region for nerve stimulation-EA. Electric current was then applied at 1Hz for 15 minutes after the flexibility of the foot joint was conformed. Each index was measured after it became stable and was recorded from 10 minutes before starting stimulation until 20 minutes after ending stimulation.A clinical study was performed on 41 patients with cervical radiculopathy. Muscle-EAT was applied to the patients as the first choice. Cases graded five points or less in pain score (10-point method) after one month were included in the muscle-EAT group. Cases graded six points or more were subjected to nerve-EAT and were included in the nerve-EAT group. The therapeutic results in these two groups were examined for a period of three months at intervals of one month based on the pain score and the evaluation criteria for the results of treatment of cervical radiculopathy.As a result, we found that the skin blood flow significantly increased on the stimulated side in both the muscle stimulation-EA and nerve stimulation-EA group. The increase was greater in the nerve stimulation group than in the muscle stimulation group. The deep-tissue temperature rose significantly on the stimulated side in the nerve stimulation-EA group. Regarding the deep hemodynamics, deoxy Hb decreased significantly in the nerve stimulation-EA group. No difference was found in heart rate between the two groups. The deep-pain threshold was significantly raised by nerve stimulation.Patients with cervical radiculopathy who did not respond to continuous muscle-EAT for one month were subjected to nerve-EAT. After three months (two months after changing to nerve-EAT), similar improvements were found in both groups. Significant improvement of paresthesia was obtained with nerve-EAT.These results suggested that the nerve-EAT influences the peripheral circulation and the deep pain threshold more effectively, enhancing the clinical efficacy.