- 著者
- Rabab A. Husseini Naoko Abe Tomoaki Hara Hiroshi Abe Kentaro Kogure
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.2, pp.301-308, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 7
mRNA vaccines have attracted considerable attention as a result of the 2019 coronavirus pandemic; however, challenges remain regarding use of mRNA vaccines, including insufficient delivery owing to the high molecular weights and high negative charges associated with mRNA. These characteristics of mRNA vaccines impair intracellular uptake and subsequent protein translation. In the current study, we prepared a minimal mRNA vaccine encoding a tumor associated antigen human gp10025–33 peptide (KVPRNQDWL), as a potential treatment for melanoma. Minimal mRNA vaccines have recently shown promise at improving the translational process, and can be prepared via a simple production method. Moreover, we previously reported the successful use of iontophoresis (IP) technology in the delivery of hydrophilic macromolecules into skin layers, as well as intracellular delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA). We hypothesized that combining IP technology with a newly synthesized minimal mRNA vaccine can improve both transdermal and intracellular delivery of mRNA. Following IP-induced delivery of a mRNA vaccine, an immune response is elicited resulting in activation of skin resident immune cells. As expected, combining both technologies led to potent stimulation of the immune system, which was observed via potent tumor inhibition in mice bearing melanoma. Additionally, there was an elevation in mRNA expression levels of various cytokines, mainly interferon (IFN)-γ, as well as infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in the tumor tissue, which are responsible for tumor clearance. This is the first report demonstrating the application of IP for delivery of a minimal mRNA vaccine as a potential melanoma therapeutic.
- 著者
- Fumie Mitani Ryosuke Hayasaka Akiyoshi Hirayama Chitose Oneyama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.10, pp.1572-1580, 2022-10-01 (Released:2022-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) originating from intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) formed within multivesicular bodies (MVBs), often referred to as small EV (sEV) or exosomes, are aberrantly produced by cancer cells and regulate the tumor microenvironment. The tyrosine kinase c-Src is upregulated in a wide variety of human cancers and is involved in promoting sEV secretion, suggesting its role in malignant progression. In this study, we found that activated Src liberated synaptosomal-associated protein 23 (SNAP23), a SNARE molecule, from lipid rafts to non-rafts on cellular membrane. We also demonstrated that SNAP23 localized in non-rafts induced cholesterol downregulation and ILV formation, resulting in the upregulation of sEV production in c-Src-transformed cells. Furthermore, the contribution of the SNAP23-cholesterol axis on sEV upregulation was confirmed in pancreatic cancer cells. High SNAP23 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. These findings suggest a unique mechanism for the upregulation of sEV production via SNAP23-mediated cholesterol downregulation in Src-activated cancer cells.
- 著者
- Zhaoyu Xing Wanma Pan Jing Zhang Xianlin Xu Xuemei Zhang Xiaozhou He Min Fan
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.5, pp.610-615, 2017-05-01 (Released:2017-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 13 22
The current research was designed to study the role of hydrogen in renal fibrosis and the renal epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1). Hydrogen rich water (HW) was used to treat animal and cell models. Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) was performed on Balb/c mice to create a model of renal fibrosis. Human kidney proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2 cells) were treated with TGF-β1 for 36 h to induce EMT. Serum creatinine (Scr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were measured to test renal function, in addition, kidney histology and immunohistochemical staining of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) positive cells was performed to examine the morphological changes. The treatment with UUO induced a robust fibrosis of renal interstitium, shrink of glomerulus and partial fracture of basement membrane. Renal function was also impaired in the experimental group with UUO, with an increase of Scr and BUN in serum. After that, Western-blot was performed to examine the expression of α-SMA, fibronectin, E-cadherin, Smad2 and Sirtuin-1 (Sirt1). The treatment with HW attenuated the development of fibrosis and deterioration of renal function in UUO model. In HK-2 cells, the pretreatment of HW abolished EMT induced by TGF-β1. The down-regulation the expression of Sirt1 induced by TGF-β1 which was dampened by the treatment with HW. Sirtinol, a Sirt1 inhibitor, reversed the effect of HW on EMT induced by TGF-β1. HW can inhibit the development of fibrosis in kidney and prevents HK-2 cells from undergoing EMT which is mediated through Sirt1, a downstream molecule of TGF-β1.
- 著者
- Kentaro Nakanishi Keiichi Hiramoto Kazuya Ooi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.6, pp.884-887, 2021-06-01 (Released:2021-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Several studies have been conducted to investigate the anti-cancer effects of vitamin C (VC). However, the effect of high-dose VC administration on tumor angiogenesis remains unclear. Focusing on our high-dose VC, our study investigated the effect of high-dose VC (4 g/kg) on vascular endothelial growth in mice with xenografts of a rectal cancer cell line referred to as Colon 26. Male mice harboring Colon 26 tumors were established, and high-dose VC solution was orally administered once daily for 14 d. On the final day of the study, the lower limb tumor tissues and serum samples were collected and analyzed for the expression of tumor angiogenesis related proteins as well as the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Oral VC administration decreased tumor volumes and increased p53 and endostatin levels. In addition, plasma and in tumor part ROS levels and tissue hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) were reduced by VC administration. In addition, the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGFD) were decreased by VC administration. These results suggest that VC exerts its anti-cancer effects by suppressing angiogenesis.
- 著者
- Mayumi Nakanishi-Matsui Naomi Matsumoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.10, pp.1426-1431, 2022-10-01 (Released:2022-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 54
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) shares its structure and rotational catalysis with F-type ATPase (F-ATPase, ATP synthase). However, unlike subunits of F-ATPase, those of V-ATPase have tissue- and/or organelle-specific isoforms. Structural diversity of V-ATPase generated by different combinations of subunit isoforms enables it to play diverse physiological roles in mammalian cells. Among these various roles, this review focuses on the functions of lysosome-specific V-ATPase in bone resorption by osteoclasts. Lysosomes remain in the cytoplasm in most cell types, but in osteoclasts, secretory lysosomes move toward and fuse with the plasma membrane to secrete lysosomal enzymes, which is essential for bone resorption. Through this process, lysosomal V-ATPase harboring the a3 isoform of the a subunit is relocated to the plasma membrane, where it transports protons from the cytosol to the cell exterior to generate the acidic extracellular conditions required for secreted lysosomal enzymes. In addition to this role as a proton pump, we recently found that the lysosomal a3 subunit of V-ATPase is essential for anterograde trafficking of secretory lysosomes. Specifically, a3 interacts with Rab7, a member of the Rab guanosine 5ʹ-triphosphatase (GTPase) family that regulates organelle trafficking, and recruits it to the lysosomal membrane. These findings revealed the multifunctionality of lysosomal V-ATPase in osteoclasts; V-ATPase is responsible not only for the formation of the acidic environment by transporting protons, but also for intracellular trafficking of secretory lysosomes by recruiting organelle trafficking factors. Herein, we summarize the molecular mechanism underlying secretory lysosome trafficking in osteoclasts, and discuss the possible regulatory role of V-ATPase in organelle trafficking.
- 著者
- Yugo Takagi Shun Nishikado Jumpei Omi Junken Aoki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.8, pp.1008-1021, 2022-08-01 (Released:2022-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 145
- 被引用文献数
- 5
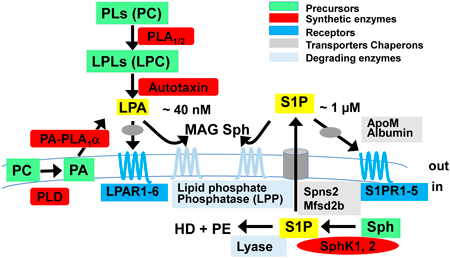
Lysophospholipids are phospholipids with only one fatty acid. During the past two decades, it has become apparent that lysophospholipids are not merely degradation products but have various physiological and pathological functions in vivo via G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-type receptors. These include lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), lysophosphatidylinositol/lysophosphatidylglucose (LPI/LPtdGlc), and lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS). This review focuses on identifying the functions of the receptors, enzymes, transporters, and carrier proteins required for these four lysophospholipids to function as lipid mediators. We also note that many of advances in this field have been made by Japanese pharmaceutical scientists.
- 著者
- Yuki Koshino Hiroaki Tanaka Takakiyo Tatsumichi Yuuri Houchi Jun Nishimura Shinji Kosaka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.10, pp.1482-1488, 2022-10-01 (Released:2022-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1
This study aimed to evaluate the effects on the medical economy of the use of tracing reports by pharmacy-based pharmacists for pharmaceutical interventions, including to reduce leftover medicines. These effects were estimated by analyzing 267 tracing reports issued by pharmacy pharmacists over a period of 1 year, 2020–2021. We estimate that these interventions created cost savings of USD108170.02/year (USD104800 via pharmaceutical interventions, USD3370.02 via interventions to reduce leftover medicines). The cost savings from pharmaceutical interventions prompted by patient follow-up was estimated to be USD47650. The medical economic effect per tracing report was estimated to be USD392.51 from pharmaceutical interventions, USD12.62 from reducing leftover medicines, and USD445.33 from pharmaceutical intervention prompted by patient follow-up. Overall, therefore, pharmaceutical interventions by pharmacy pharmacists using tracing reports, including those designed to reduce leftover medicines, may benefit the medical economy.
- 著者
- Masamitsu Maekawa Keitaro Miyoshi Aya Narita Toshihiro Sato Yu Sato Masaki Kumondai Masafumi Kikuchi Katsumi Higaki Torayuki Okuyama Yoshikatsu Eto Hiroshi Sakamaki Nariyasu Mano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1259-1268, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 65
- 被引用文献数
- 3
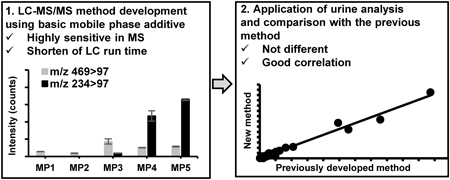
As Niemann–Pick disease type C (NPC) is difficult to diagnose owing to its various clinical symptoms; biomarker tests have been developed. Previously, we revealed urinary sulfated cholesterol metabolites as noninvasive biomarkers for NPC. However, LC/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) requires long separation time and large urine volumes. Recently, a basic mobile phase was reported to increase the MS intensity. Thus, we developed a highly sensitive and rapid LC/MS/MS method for analyzing urinary cholesterol metabolites using a basic mobile phase additive. 3β-Sulfooxy-7β-N-acetylglucosaminyl-5-cholenic acid, its glycine and taurine conjugates, 3β-sulfooxy-7β-hydroxy-5-cholenic acid, and 7-oxo form were measured, with selected reaction monitoring in negative ion mode. Oasis HLB and L-column 3 were used for column-switching LC/MS/MS and urine diluted 10-fold was employed as the sample. After trapping, gradient separation was performed using solutions containing 1% (v/v) ammonium solution. On average, a 16-fold increase in peak areas was observed compared to that obtained at pH 5.5 with the mobile phases. Although the previous method needed 60 min for separation from interference peaks, we succeeded to separate them in 7 min with optimized LC condition. Further, all compounds showed good linearity from 0.3–1000 ng/mL, with satisfactory intra- and inter-day reproducibility. The developed method was applied to the urinalysis of healthy participants and NPC patients. Overall, the concentrations of metabolites correlated with those obtained using the previous method. Therefore, we succeeded to increasing MS intensity and shorten LC running time; and the method is useful for the noninvasive diagnostic screening of patients with NPC.
- 著者
- Jong-Ho Koh Jin-Man Kim Un-Jae Chang Hyung-Joo Suh
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.26, no.1, pp.84-87, 2003 (Released:2003-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 50 77
This study was conducted to investigate the hypocholesterolemic effect of the hot-water fraction (HW) from cultured mycelia of Cordyceps sinensis in a 5 l fermenter. The composition of HW was mainly carbohydrate (83.9%) and protein (11.8%) on a dry basis, and the carbohydrate of HW consisted of glucose, mannose, galactose, and arabinose in the molecular ratio of 1.0 : 0.8 : 0.5 : 0.1, respectively. In mice fed a cholesterol-free diet and those fed a cholesterol-enriched diet, body and liver weights were not significantly different from those of the controls. The serum total cholesterol (TC) of all mice groups administered HW (150 and 300 mg/kg/d, respectively) with the cholesterol-enriched diet decreased more than in the control group. Among the mice fed the cholesterol-enriched diet, HW also increased the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol level, but decreased the very low-density lipoprotein plus low-density lipoprotein (VLDL+LDL) cholesterol level. The changes in HDL- and VLDL+LDL-cholesterol levels consequently decreased the atherogenic value. The results indicate that HW in rats administered a cholesterol-enriched diet decreased the plasma cholesterol level. The 300 mg/kg dose had a significant effect on the serum TC level.
- 著者
- Takara Ohto Manami Konishi Hiroki Tanaka Koji Onomoto Mitsutoshi Yoneyama Yuta Nakai Kota Tange Hiroki Yoshioka Hidetaka Akita
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.2, pp.299-302, 2019-02-01 (Released:2019-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 12 15
While the use of in vitro-transcribed mRNA (IVT-mRNA) in therapeutics is a rapidly expanding area, the transfection of the exogenous IVT-mRNA is accompanied by a risk of immune activation. This immunological defense mechanism suppresses cellular translation process and can reduce transfection efficiency to a considerable extent. In the present study, we investigated the in vitro effects of Integrated Stress Response Inhibitor (ISRIB), and dexamethasone, a steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, on the transfection activity of a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) that was composed of ionizable lipids and IVT-mRNA. In the case of transfection to mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells, ISRIB mainly enhanced the transfection activity at an early stage of transfection (0–6 h). In contrast, dexamethasone caused an increase in transfection activity at intermediate-late stages of transfection (4–48 h). We also investigated the in vivo effects of dexamethasone using an LNP on that the IVT-mRNA and lipid-conjugated dexamethasone (Dex-Pal) were co-loaded. The intravenous administration of the LNP successfully enhanced the protein expression in a mouse liver by up to 6.6-fold. Collectively, the co-delivery of an anti-inflammatory drug is a promising approach for enhancing transfection efficiency of IVT-mRNA.
- 著者
- Toshinori Hirai Hidefumi Kasai Masahiro Takahashi Satomi Uchida Naoko Akai Kazuhiko Hanada Toshimasa Itoh Takuya Iwamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.7, pp.948-954, 2022-07-01 (Released:2022-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
Some population pharmacokinetic models for amiodarone (AMD) did not incorporate N-desethylamiodarone (DEA) concentration. Glucocorticoids activate CYP3A4 activity, metabolizing AMD. In contrast, CYP3A4 activity may decrease under inflammation conditions. However, direct evidence for the role of glucocorticoid or inflammation on the pharmacokinetics of AMD and DEA is lacking. The pilot study aimed to address this gap using a population pharmacokinetic analysis of AMD and DEA. A retrospective cohort observational study in adult patients who underwent AMD treatment with trough concentration measurement was conducted at Tokyo Women’s Medical University, Medical Center East from June 2015 to March 2019. Both structural models of AMD and DEA applied 1-compartment models, which included significant covariates using a stepwise forward selection and backward elimination method. The eligible 81 patients (C-reactive protein level: 0.26 [interquartile range; 0.09–1.92] mg/dL) had a total of 408 trough concentrations for both AMD and DEA. The median trough concentrations were 0.49 [0.31–0.81] µg/mL for AMD and 0.43 [0.28–0.71] µg/mL for DEA during a median follow-up period of 446 [147–1059] d. Three patients received low-dose oral glucocorticoid. The final model identified that AMD clearance was 7.9 L/h, and the apparent DEA clearance was 10.3 L/h. Co-administered glucocorticoids lowered apparent DEA clearance by 35%. These results indicate that co-administered glucocorticoids may increase DEA concentrations in patients without severe inflammation.
- 著者
- Norifumi Shimizu Chiaki Hara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.8, pp.1279-1282, 2020-08-01 (Released:2020-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
Clinical studies, especially those in animal models, have provided evidence that chronic stress may play a role in the etiology of psychiatric diseases, such as depression. Because chronic stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, resulting in the excessive secretion of glucocorticoids, the chronic stimulation of glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) may be involved in the pathogenesis of depression. To further investigate the relationship between GR activation and depression, we used the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone (DEX) and the GR antagonist mifepristone to examine the effects of chronic GR stimulation on the circadian rhythms of locomotor activity and serotonergic neurotransmission in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) of rats. Chronic treatment with DEX reduced locomotor activity during the dark phase, without changing overall activity patterns. Measuring the basal release of serotonin in the BLA, using in vivo microdialysis, confirmed that chronic treatment with DEX induced serotonergic hypofunction in the BLA. The co-administration of DEX with mifepristone effectively suppressed the depressive-like symptoms caused by chronic treatment with DEX. Our results provided further evidence for a relationship between GR and depression and suggest that the pharmacological blockade of GR may increase the effectiveness of conventional pharmacotherapies used to treat depression.
- 著者
- Kazuaki Matsumoto Masaru Samura Sho Tashiro Shino Shishido Reika Saiki Wataru Takemura Kana Misawa Xiaoxi Liu Yuki Enoki Kazuaki Taguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.7, pp.824-833, 2022-07-01 (Released:2022-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 69
- 被引用文献数
- 6
The target therapeutic ranges of vancomycin, teicoplanin, and arbekacin have been determined, and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is performed in clinical practice. However, TDM is not obligatory for daptomycin, linezolid, or tedizolid. In this study, we examined whether TDM will be necessary for these 3 drugs in the future. There was no significant difference in therapeutic effects on acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection between linezolid and tedizolid by meta-analysis. Concerning the therapeutic effects on pneumonia, the rate of effectiveness after treatment with tedizolid was significantly lower than with linezolid. With respect to safety, the incidences of gastrointestinal adverse events and blood/lymphatic system disorders related to tedizolid were significantly lower than those related to linezolid. Linezolid exhibits potent therapeutic effects on pneumonia, but the appearance of adverse reactions is indicated as a problem. There was a dose-dependent decrease in the platelet count, and the target trough concentration (Ctrough) was estimated to be 4–6 or 2–7 µg/mL in accordance with the patient’s condition. The efficacy of linezolid may be obtained while minimizing the appearance of adverse reactions by performing TDM. The target therapeutic range of tedizolid cannot be achieved in immunocompromised or severe patients. Therefore, we concluded that TDM was unnecessary, considering step-down therapy with oral drugs, use in non-severe patients, and high-level safety. Concerning daptomycin, high-dose administration is necessary to achieve an area under the curve (AUC) of ≥666 as an index of efficacy. To secure its safety, Ctrough (<20 µg/mL) monitoring is important. Therefore, TDM is necessary.
- 著者
- Eui Dong Son Gyu Ho Choi Hyaekyoung Kim Byoungseok Lee Ih Seoup Chang Jae Sung Hwang
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.8, pp.1395-1399, 2007-08-01 (Released:2007-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 26 37
Alpha-ketoglutarate is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, and a rate-limiting cofactor of prolyl-4-hydroxylase. It also has a potent effect on increasing the proline pool during collagen production, but the details underlying the boosting effect on collagen production by α-ketoglutarate remain as yet unreported. To investigate the effects of α-ketoglutarate on procollagen production and wrinkle formation, we conducted experiments in cultured human dermal fibroblasts and UVB-irradiated hairless mice. Based on ELISA measurements, α-ketoglutarate (10 μM) stimulated procollagen production in fibroblasts by 25.6±4.6% compared to vehicle (dH2O)-treated control cells. Also, we demonstrated that α-ketoglutarate increased activities of prolidase, which is known to play an important role in collagen metabolism, in fibroblasts and N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-proline (Cbz-Pro), prolidase inhibitor, inhibited procollagen synthesis by α-ketoglutarate in fibroblasts. To determine the effect of topically applied α-ketoglutarate on wrinkle formation, α-ketoglutarate (1%) and vehicle (70% propylene glycol, 30% ethanol) were applied on the dorsal skin of UVB-induced hairless mice for twelve weeks. We found that α-ketoglutarate decreased wrinkle formation upon long-term topical application. These results suggest that α-ketoglutarate diminishes UVB-induced wrinkle formation by increasing collagen production, through a pathway that involves prolidase activation. Therefore, application of α-ketoglutarate may represent an effective anti-wrinkle agent for the cosmetic field.
- 著者
- 高谷 芳明 内沢 秀光 松江 一 奥崎 文一 鳴海 文昭 佐々木 甚一 石田 邦夫
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.6, pp.846-849, 1994-06-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 20 26
Squid ink, which has little commercial use and is usually discarded, was extracted using a Tris-HCl buffer (pH 6.8). The extract was fractionated using DEAE Sephacel ion-exchange chromatography and Sephacryl S-300 gel filtration to give a peptidoglycan fraction which exhibited strong antitumor activity against Meth-A fibrosarcoma in BALB/c mice following intraperitoneal administration. The fraction was composed of 7.8% peptide, 57% polysaccharide and 30% pigment. The polysaccharide component had a unique structure with equimolar ratios of GlcA, GalNAc and Fuc. Since the fraction has no direct cytotoxic effect on Meth-A cells, inhibition of tumor growth may be due to stimulation of host-mediated responses.
- 著者
- Kei Kawada Tomoaki Ishida Kohei Jobu Tsuyoshi Ohta Hitoshi Fukuda Shumpei Morisawa Tetsushi Kawazoe Naohisa Tamura Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.6, pp.720-723, 2022-06-01 (Released:2022-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Aggression is the most common adverse effect of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). This study aimed to investigate the association of aggression with AED use. The reporting odds ratio (ROR) from adverse event reports, submitted to the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database between 2004 and 2020, was used to calculate and investigate the association between AEDs and aggression. We also analyzed the association of aggression with the combined use of AEDs and the relationship between AED-associated aggression and patient characteristics. A total of 433 patients developed aggression. Significant aggression signals were detected for perampanel (crude ROR: 325.04, 95% confidence interval (CI): 118.48–752.58, p < 0.01), levetiracetam (crude ROR: 17.14, 95% CI: 10.33–26.90, p < 0.01), lacosamide (crude ROR: 16.90, 95% CI: 2.02–62.51, p < 0.01), lamotrigine (crude ROR: 15.98, 95% CI: 9.99–24.39, p < 0.01), valproate (crude ROR: 6.68, 95% CI: 4.27–10.02, p < 0.01), and carbamazepine (crude ROR: 2.47, 95% CI: 1.17–4.59, p < 0.01). The combined therapy with perampanel and levetiracetam had a significant aggression signal (adjusted ROR: 25.90, 95% CI: 1.14–59.10, p < 0.01). In addition, we found that aggression frequently occurred in patients <60 year (adjusted ROR: 2.88, 95% CI: 1.49–5.56, p < 0.01) treated with levetiracetam. These results may be useful for minimizing the risk of aggression during the treatment of AEDs.
- 著者
- Babita Shashni Shinya Ariyasu Reisa Takeda Toshihiro Suzuki Shota Shiina Kazunori Akimoto Takuto Maeda Naoyuki Aikawa Ryo Abe Tomohiro Osaki Norihiko Itoh Shin Aoki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.4, pp.487-503, 2018-04-01 (Released:2018-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 34 65
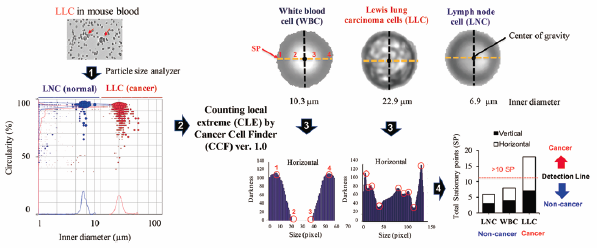
Detection of anomalous cells such as cancer cells from normal blood cells has the potential to contribute greatly to cancer diagnosis and therapy. Conventional methods for the detection of cancer cells are usually tedious and cumbersome. Herein, we report on the use of a particle size analyzer for the convenient size-based differentiation of cancer cells from normal cells. Measurements made using a particle size analyzer revealed that size parameters for cancer cells are significantly greater (e.g., inner diameter and width) than the corresponding values for normal cells (white blood cells (WBC), lymphocytes and splenocytes), with no significant difference in shape parameters (e.g., circularity and convexity). The inner diameter of many cancer cell lines is greater than 10 µm, in contrast to normal cells. For the detection of WBC having similar size to that of cancer cells, we developed a PC software “Cancer Cell Finder” that differentiates them from cancer cells based on brightness stationary points on a cell surface. Furthermore, the aforementioned method was validated for cancer cell/clusters detection in spiked mouse blood samples (a B16 melanoma mouse xenograft model) and circulating tumor cell cluster-like particles in the cat and dog (diagnosed with cancer) blood samples. These results provide insights into the possible applicability of the use of a particle size analyzer in conjunction with PC software for the convenient detection of cancer cells in experimental and clinical samples for theranostics.
2 0 0 0 OA Sialobiology of Influenza: Molecular Mechanism of Host Range Variation of Influenza Viruses
- 著者
- Yasuo Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.3, pp.399-408, 2005 (Released:2005-03-03)
- 参考文献数
- 100
- 被引用文献数
- 267 330
The gene pool of influenza A viruses in aquatic birds provides all of the genetic diversity required for human and lower animals. Host range selection of the receptor binding specificity of the influenza virus hemagglutinin occurs during maintenance of the virus in different host cells that express different receptor sialo-sugar chains. In this paper, functional roles of the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase spikes of influenza viruses are described in the relation to 1) host range of influenza viruses, 2) receptor binding specificity of human and other animal influenza viruses, 3) recognition of sialyl sugar chains by Spanish influenza virus hemagglutinin, 4) highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1, H9N2, and H7N7 avian influenza viruses and molecular mechanism of host range variation of influenza viruses, 5) role of the neuraminidase spike for the host range of influenza viruses, and 6) Development of anti-influenza drugs.
- 著者
- Yuki Sato Yoh Takekuma Takayuki Daisho Hitoshi Kashiwagi Shungo Imai Mitsuru Sugawara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.4, pp.421-428, 2022-04-01 (Released:2022-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 3
It is important to select appropriate antibiotics for infection control. Linezolid and tedizolid are newly developed and synthesized oxazolidinone antibacterial agents. It has been pointed out that there is a relationship between a high plasma concentration of the target drug and incidence of adverse effects, although it has been reported that neither linezolid nor tedizolid requires dose adjustment according to renal function. Due to the high incidence of adverse effects, both are often switched. Precise plasma concentration control by therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is desirable for reducing the adverse effects of both drugs and obtaining a better therapeutic effect. In this study, we aimed to establish a method for simultaneous quantification of linezolid and tedizolid in human plasma using LC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Sample preparation was performed by a simple operation with acetonitrile. Linezolid and tedizolid were separated by an octadecylsilyl column using a gradient elution of acetonitrile in aqueous 0.1% formic acid solution and were detected in the positive ion electrospray mode with multiple reaction monitoring. Quantification of linezolid and tedizolid ranged from 0.5 to 50 and 0.5 to 20 µg/mL, respectively. The intra-day and inter-day precision and accuracy of data were assessed and found to be acceptable. The developed method was successfully applied to measurement of the concentrations of linezolid and tedizolid. This simple method, which can simultaneously quantify both drug concentrations for daily TDM, could contribute to safer treatment of patients.
- 著者
- Yeon Sil Lee Young-Hee Kang Ju-Young Jung Sanghyun Lee Kazuo Ohuchi Kuk Hyun Shin Il-Jun Kang Jung Han Yoon Park Hyun-Kyung Shin Soon Sung Lim
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.10, pp.1968-1972, 2008-10-01 (Released:2008-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 23 59
To characterize active principles for prevention and treatment of diabetic complications, the isolation of protein glycation inhibitors from the fruiting body of Phellinus linteus was conducted in vitro using the model systems of hemoglobin-δ-gluconolactone (early stage), bovine serum albumin-methylglyoxal (middle stage), and Nα-acetyl-glycyl-lysine methyl ester-D-ribose (last stage) assays. Nine compounds were isolated from the active ethylacetate fraction of the fruiting body and identified as protocatechuic acid (1), protocatechualdehyde (2), caffeic acid (3), ellagic acid (4), hispidin (5), davallialactone (6), hypholomine B (7), interfungins A (8), and inoscavin A (9) by spectroscopic analyses. At the early stage of protein glycation, compounds 6, 8, and 9 exhibited inhibitory activity on hemoglobin A1C formation. For the middle stage, compounds 2, 6, and 9 showed a significant inhibitory effect on methylglyoxal-medicated protein modification and their IC50 values were 144.28, 213.15, and 158.66 μM, respectively. At the last stage of glycation, compound 8 was found to be a potent inhibitor of the cross-linking of proteins, which was more effective than that of aminoguanidine, a well-known inhibitor for advanced glycation end products. Consequently, compound 8 showed the most potent inhibitory effects at each stage of protein glycation. This mechanism may help to provide a protective effect against hyperglycemia-mediated protein damage.