- 著者
- Tatsuya Mizoguchi Tomonori Sugiura Yu Kawada Junki Yamamoto Masashi Yokoi Kosuke Nakasuka Kento Mori Shohei Kikuchi Tsuyoshi Ito Shuichi Kitada Toshihiko Goto Yoshihiro Seo
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0772, (Released:2023-03-21)
- 参考文献数
- 46
Background: The number of patients with heart failure (HF) has increased, and it is crucial to prevent the development of HF in patients at risk of HF. The present study aimed to risk stratify patients in Stage A and B HF based on associations between exercise-induced changes in aortic stiffness and exercise tolerance.Methods and Results: Patients in Stage A and B HF who performed a cardiopulmonary exercise test were enrolled in the study (n=106; median age 65.0 years [interquartile range 52.8–73.0 years]). Exercise tolerance was examined by the percentage of predicted peak oxygen consumption (%V̇O2peak). The ascending aortic pressure waveform was estimated non-invasively. Aortic stiffness was assessed using the augmentation index (AIx) and reflection magnitude (RM). Multivariable regression analysis showed that AIx measured both before and after exercise was significantly associated with %V̇O2peak (β=−0.221 [P=0.049] and β=−0.342 [P=0.003], respectively). When participants were divided into %V̇O2peak subgroups using a cut-off value of 60%, RM decreased immediately after exercise and remained lower 5 min after exercise in the group with preserved exercise tolerance, but recovered to baseline levels 5 min after exercise in the group with reduced exercise tolerance.Conclusions: Exercise-induced increases in aortic stiffness were associated with exercise tolerance in patients at risk of HF, suggesting that exercise-induced changes in aortic stiffness may be useful to stratify high-risk patients.
- 著者
- Shintaro Togashi Tsuyoshi Isawa Taku Honda Kenichi Furuya Kazuhiro Yamaya Masataka Taguri Shigeru Toyoda
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0103, (Released:2023-05-16)
- 参考文献数
- 28
Background: Because the penetration of transvenous lead extraction (TLE) for cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) infection has not been investigated in Japan, we conducted a population-based, retrospective, descriptive study to evaluate regional disparities in the use of TLE for CIED infection and the potential undertreatment of CIED infection using a nationwide insurance claims database.Methods and Results: Patients who underwent CIED implantation or generator exchange and TLE between April 2018 and March 2020 were identified. Moreover, the penetration ratio of TLE for CIED infection in each prefecture was estimated. CIED implantation and TLE were most prevalent in the age categories of 80–89 years (40.3%) and 80–89 years (36.9%), respectively. There was no correlation between the number of CIED implantations and that of TLE (rho=−0.087, 95% confidence interval −0.374 to 0.211, P=0.56). The median penetration ratio was 0.00 (interquartile range 0.00–1.29). Of the 47 prefectures, 6, comprising Okinawa, Miyagi, Okayama, Fukuoka, Tokyo, and Osaka, showed a penetration ratio ≥2.00.Conclusions: Our study data indicated great regional disparities in the penetration of TLE and potential undertreatment of CIED infection in Japan. Additional measures are needed to address these issues.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Omori Yoshiaki Kawase Takuya Mizukami Toru Tanigaki Tetsuo Hirata Munenori Okubo Hiroki Kamiya Akihiro Hirakawa Masanori Kawasaki Takeshi Kondo Takahiko Suzuki Hitoshi Matsuo
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0771, (Released:2023-03-28)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Angiographic fractional flow reserve (angioFFR) is a novel artificial intelligence (AI)-based angiography-derived fractional flow reserve (FFR) application. We investigated the diagnostic accuracy of angioFFR to detect hemodynamically relevant coronary artery disease.Methods and Results: Consecutive patients with 30–90% angiographic stenoses and invasive FFR measurements were included in this prospective, single-center study conducted between November 2018 and February 2020. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed using invasive FFR as the reference standard. In patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, gradients of invasive FFR and angioFFR in the pre-senting segments were compared. We assessed 253 vessels (200 patients). The accuracy of angioFFR was 87.7% (95% confidence interval [CI] 83.1–91.5%), with a sensitivity of 76.8% (95% CI 67.1–84.9%), specificity of 94.3% (95% CI 89.5–97.4%), and area under the curve of 0.90 (95% CI 0.86–0.93%). AngioFFR was well correlated with invasive FFR (r=0.76; 95% CI 0.71–0.81; P<0.001). The agreement was 0.003 (limits of agreement: −0.13, 0.14). The FFR gradients of angioFFR and invasive FFR were comparable (n=51; mean [±SD] 0.22±0.10 vs. 0.22±0.11, respectively; P=0.87).Conclusions: AI-based angioFFR showed good diagnostic accuracy for detecting hemodynamically relevant stenosis using invasive FFR as the reference standard. The gradients of invasive FFR and angioFFR in the pre-stenting segments were comparable.
- 著者
- Norihisa Miyawaki Kenichi Ishizu Akihiro Isotani Miho Nakamura Takashi Morinaga Masaomi Hayashi Shinichi Shirai Nobuhisa Ohno Shinichi Kakumoto Kenji Ando
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0672, (Released:2023-04-07)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
7 0 0 0 OA Pathology of Sapien 3 After Impella-CP Insertion for Acute Coronary Syndrome With Cardiogenic Shock
- 著者
- Yotaro Sekigawa Shigemitsu Tanaka Daiki Suzuki Junichi Miyamoto Norihito Nakamura Sho Torii Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Natsumeda Yohei Ohno Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.5, pp.672, 2023-04-25 (Released:2023-04-25)
- 参考文献数
- 1
7 0 0 0 OA Validity of Diagnostic Algorithms for Cardiovascular Diseases in Japanese Health Insurance Claims
- 著者
- Koshiro Kanaoka Yoshitaka Iwanaga Katsuki Okada Satoshi Terasaki Yuichi Nishioka Michikazu Nakai Daisuke Kamon Tomoya Myojin Tsunenari Soeda Tatsuya Noda Manabu Horii Yasushi Sakata Yoshihiro Miyamoto Yoshihiko Saito Tomoaki Imamura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.4, pp.536-542, 2023-03-24 (Released:2023-03-24)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Background: We aimed to validate a claims-based diagnostic algorithm to identify hospitalized patients with acute major cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) from health insurance claims in Japan.Methods and Results: This retrospective multicenter validation study was conducted at 4 institutes, including Japanese Circulation Society-certified and uncertified hospitals in Japan. Data on patients with CVDs in departmental lists or with International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) codes for CVDs hospitalized between April 2018 and March 2019 were extracted. We examined the sensitivity and positive predictive value of a diagnostic algorithm using ICD-10 codes, medical examinations, and treatments for acute coronary syndrome (ACS), acute heart failure (HF), and acute aortic disease (AAD). We identified 409 patients with ACS (mean age 70.6 years; 24.7% female), 615 patients with acute HF (mean age 77.3 years; 46.2% female), and 122 patients with AAD (mean age 73.4 years; 36.1% female). The respective sensitivity and positive predictive value for the algorithm were 0.86 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.82–0.89) and 0.95 (95% CI 0.92–0.97) for ACS; 0.74 (95% CI 0.70–0.77) and 0.79 (95% CI 0.76–0.83) for acute HF; and 0.86 (95% CI 0.79–0.92) and 0.83 (95% CI 0.76–0.89) for AAD.Conclusions: The validity of the diagnostic algorithm for Japanese claims data was acceptable. Our results serve as a foundation for future studies on CVDs using nationwide administrative data.
7 0 0 0 OA Clinical Risk Factors and Prognostic Impact of Osteoporosis in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure
- 著者
- Satoshi Katano Toshiyuki Yano Takanori Tsukada Hidemichi Kouzu Suguru Honma Takuya Inoue Yuhei Takamura Ryohei Nagaoka Tomoyuki Ishigo Ayako Watanabe Katsuhiko Ohori Masayuki Koyama Nobutaka Nagano Takefumi Fujito Ryo Nishikawa Hiroyuki Takashima Akiyoshi Hashimoto Masaki Katayose Tetsuji Miura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.12, pp.2224-2234, 2020-11-25 (Released:2020-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 5 15
Background:The clinical significance of osteoporosis in chronic heart failure (CHF) remains unclear.Methods and Results:A total of 303 CHF patients (75 years, [interquartile range (IQR) 66–82 years]; 41% female) were retrospectively examined. Bone mineral densities (BMDs) at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total femur were measured by using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and osteoporosis was diagnosed when the BMD at any of the 3 sites was <70% of the Young Adult Mean percentage (%YAM). The prevalence of osteoporosis in CHF patients was 40%. Patients with osteoporosis were older (79 [IQR, 74–86] vs. 72 [IQR, 62–80] years), included a large percentage of females, had slower gait speed and had a lower body mass index. Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that sex, BMI, gait speed, loop diuretics use and no use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) were independently associated with osteoporosis. Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that the rate of death and heart failure hospitalization was higher in patients with osteoporotic BMD at 2 or 3 sites than in patients without osteoporosis (hazard ratio 3.45, P<0.01). In multivariate Cox regression analyses, osteoporotic BMD at 2 or 3 sites was an independent predictor of adverse events after adjustment for prognostic markers.Conclusions:Loop diuretics use and no DOACs use are independently associated with osteoporosis in CHF patients. Osteoporosis is a novel predictor of worse outcome in patients with CHF.
- 著者
- Satoshi Kodera Hiroyuki Morita Hiroshi Nishi Norifumi Takeda Jiro Ando Issei Komuro
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.12, pp.2021-2028, 2022-11-25 (Released:2022-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background: The cost-effectiveness of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) has not been evaluated in Japan, so we analyzed the cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, for CKD stages 3a and 3b.Methods and Results: We used the Markov model for CKD to assess the costs and benefits associated with and without dapagliflozin from a health system perspective. We estimated the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), expressed as per quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). An ICER <5 million Japanese yen (JPY)/QALY was judged to be cost-effective. The effect of dapagliflozin on renal and cardiovascular events was based on published clinical trials. In patients with CKD stage 3a, the ICER of dapagliflozin over standard treatment was 4.03 million JPY/QALY gained. With a cost-effectiveness threshold of 5 million JPY/QALY gained, the cost-effectiveness probability of dapagliflozin over standard treatment was 52.6%. In patients with CKD stage 3b, the ICER of dapagliflozin over standard treatment was 0.12 million JPY/QALY gained. The cost-effectiveness probability of dapagliflozin over standard treatment was 75.2%.Conclusions: The results seemed to show acceptable cost-effectiveness when dapagliflozin was used for CKD stage 3b. On the other hand, cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin for CKD stage 3a was ambiguous, and further validation is needed.
- 著者
- Yuichi Ozaki Hector M. Garcia-Garcia Solomon S. Beyene Alexandre Hideo-Kajita Kayode O. Kuku Paul Kolm Ron Waksman
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.7, pp.1480-1488, 2019-06-25 (Released:2019-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 16 22
Background:Statin therapy has been shown to result in coronary plaque regression, but the relationship between statin use and stabilization of coronary plaque has not been elucidated. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the effect of statin therapy on fibrous cap thickness (FCT) on optical coherence tomography (OCT).Methods and Results:Nine OCT studies (6 randomized controlled trials and 3 observational studies) were enrolled with a total of 341 patients (390 lesions). Arms of the studies were grouped according to statin type and/or dose. Random effects meta-analysis was used to estimate a pooled mean change in FCT from baseline to follow-up. The overall effect mean FCT change was 67.7 µm (95% CI: 51.4–84.1, I2=95.0%, P<0.001). All statin groups had an increase in FCT, but the magnitude of the increase differed according to the statin. Two homogeneous subgroups with I2=0 were identified: mean FCT change was 27.8 µm (for subgroup atorvastatin 5 mg and rosuvastatin), and 61.9 µm (for subgroup atorvastatin 20 mg, fluvastatin 30 mg, and pitavastatin 4 mg). On meta-regression modeling, statin therapy alone explained most of the change in FCT.Conclusions:Statin therapy induced a significant increase in FCT as assessed on OCT, independent of coronary risk factors and other medications.
7 0 0 0 OA Mediastinal Hematoma Associated With Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation
- 著者
- Takayuki Kitai Yuhei Kasai Jungo Kasai Junji Morita Tsutomu Fujita
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0174, (Released:2022-08-11)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Yohei Okada Sho Komukai Tetsuhisa Kitamura Takeyuki Kiguchi Taro Irisawa Tomoki Yamada Kazuhisa Yoshiya Changhwi Park Tetsuro Nishimura Takuya Ishibe Yoshiki Yagi Masafumi Kishimoto Toshiya Inoue Yasuyuki Hayashi Taku Sogabe Takaya Morooka Haruko Sakamoto Keitaro Suzuki Fumiko Nakamura Tasuku Matsuyama Norihiro Nishioka Daisuke Kobayashi Satoshi Matsui Atsushi Hirayama Satoshi Yoshimura Shunsuke Kimata Takeshi Shimazu Shigeru Ohtsuru Taku Iwami
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0675, (Released:2021-11-02)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Background:The hypothesis of this study is that latent class analysis could identify the subphenotypes of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients associated with the outcomes and allow us to explore heterogeneity in the effects of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR).Methods and Results:This study was a retrospective analysis of a multicenter prospective observational study (CRITICAL study) of OHCA patients. It included adult OHCA patients with initial shockable rhythm. Patients from 2012 to 2016 (development dataset) were included in the latent class analysis, and those from 2017 (validation dataset) were included for evaluation. The association between subphenotypes and outcomes was investigated. Further, the heterogeneity of the association between ECPR implementation and outcomes was explored. In the study results, a total of 920 patients were included for latent class analysis. Three subphenotypes (Groups 1, 2, and 3) were identified, mainly characterized by the distribution of partial pressure of O2(PO2), partial pressure of CO2(PCO2) value of blood gas assessment, cardiac rhythm on hospital arrival, and estimated glomerular filtration rate. The 30-day survival outcomes were varied across the groups: 15.7% in Group 1; 30.7% in Group 2; and 85.9% in Group 3. Further, the association between ECPR and 30-day survival outcomes by subphenotype groups in the development dataset was as varied. These results were validated using the validation dataset.Conclusions:The latent class analysis identified 3 subphenotypes with different survival outcomes and potential heterogeneity in the effects of ECPR.
- 著者
- Hidenori Kato Hiroki Watanabe Akira Koike Longmei Wu Kosuke Hayashi Hirotomo Konno Takeshi Machino Isao Nishi Akira Sato Hiroaki Kawamoto Kazutaka Aonuma Yoshiyuki Sankai Masaki Ieda
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.1, pp.60-67, 2021-12-24 (Released:2021-12-24)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 1 5
Background:Aiming to establish an effective tool in new cardiac rehabilitation programs, we investigated the use of a lumbar-type hybrid assistive limb (HAL) in patients with heart failure (HF) who had difficulty in walking at the usual speed of healthy subjects (≈80 m/min).Methods and Results:We randomly assigned 28 HF patients (age, 73.1±13.8 years) to perform a sit-to-stand exercise with or without HAL. The sit-to-stand exercise was repeated as many times as possible as cardiac rehabilitation therapy over a period of 6–10 days. We measured 5 parameters before and after the completion of cardiac rehabilitation: B-type natriuretic peptide, Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), 6-min walking distance (6MWD), 30-s chair-stand test (CS-30), and isometric knee extensor muscle strength. The SPPB and 6MWD were significantly improved, and the CS-30 score was somewhat improved, after the exercise therapy in both the HAL and non-HAL groups. The knee extensor muscle strength improved significantly in the HAL group (0.29±0.11 to 0.35±0.11 kgf/kg, P<0.01), but showed no change in the non-HAL group (0.35±0.11 to 0.35±0.13 kgf/kg, P=0.40).Conclusions:The improved knee extensor muscle strength in the HAL group suggests that the lumbar-type HAL may be an effective tool for cardiac rehabilitation in HF patients with frailty, which is a predictor of poor prognosis in HF.
- 著者
- Ken Kozuma Taishiro Chikamori Jun Hashimoto Junko Honye Takanori Ikeda Sugao Ishiwata Mamoru Kato Hiroshi Kondo Kosuke Matsubara Kazuma Matsumoto Naoya Matsumoto Sadako Motoyama Kotaro Obunai Hajime Sakamoto Kyoko Soejima Shigeru Suzuki Koichiro Abe Hideo Amano Hirofumi Hioki Takashi Iimori Hideki Kawai Hisanori Kosuge Tatsuya Nakama Yasuyuki Suzuki Kazuya Takeda Akiko Ueda Takashi Yamashita Kenzo Hirao Takeshi Kimura Ryozo Nagai Masato Nakamura Wataru Shimizu Nagara Tamaki on behalf of the Japanese Circulation Society Joint Working Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0379, (Released:2022-04-22)
- 参考文献数
- 230
- 被引用文献数
- 8
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Tsutsui Shin-ichi Momomura Yoshihiko Saito Hiroshi Ito Kazuhiro Yamamoto Yasushi Sakata Akshay Suvas Desai Tomomi Ohishi Takayuki Iimori Toshihito Kitamura Weinong Guo on behalf of the PARALLEL-HF Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-20-0854, (Released:2021-03-16)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 37
Background:In the Prospective Comparison of angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) With ACEi to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM-HF) study, treatment with sacubitril/valsartan reduced the primary outcome of cardiovascular (CV) death and heart failure (HF) hospitalization compared with enalapril in patients with chronic HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). A prospective randomized trial was conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan in Japanese HFrEF patients.Methods and Results:In the Prospective comparison of ARNI with ACEi to determine the noveL beneficiaL trEatment vaLue in Japanese Heart Failure patients (PARALLEL-HF) study, 225 Japanese HFrEF patients (New York Heart Association [NYHA] class II–IV, left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] ≤35%) were randomized (1 : 1) to receive sacubitril/valsartan 200 mg bid or enalapril 10 mg bid. Over a median follow up of 33.9 months, no significant between-group difference was observed for the primary composite outcome of CV death and HF hospitalization (HR 1.09; 95% CI 0.65–1.82; P=0.6260). Early and sustained reductions in N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) from baseline were observed with sacubitril/valsartan compared with enalapril (between-group difference: Week 2: 25.7%, P<0.01; Month 6: 18.9%, P=0.01, favoring sacubitril/valsartan). There was no significant difference in the changes in NYHA class and Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) clinical summary score at Week 8 and Month 6. Sacubitril/valsartan was well tolerated with fewer study drug discontinuations due to adverse events, although the sacubitril/valsartan group had a higher proportion of patients with hypotension.Conclusions:In Japanese patients with HFrEF, there was no difference in reduction in the risk of CV death or HF hospitalization between sacubitril/valsartan and enalapril, and sacubitril/valsartan was safe and well tolerated.
- 著者
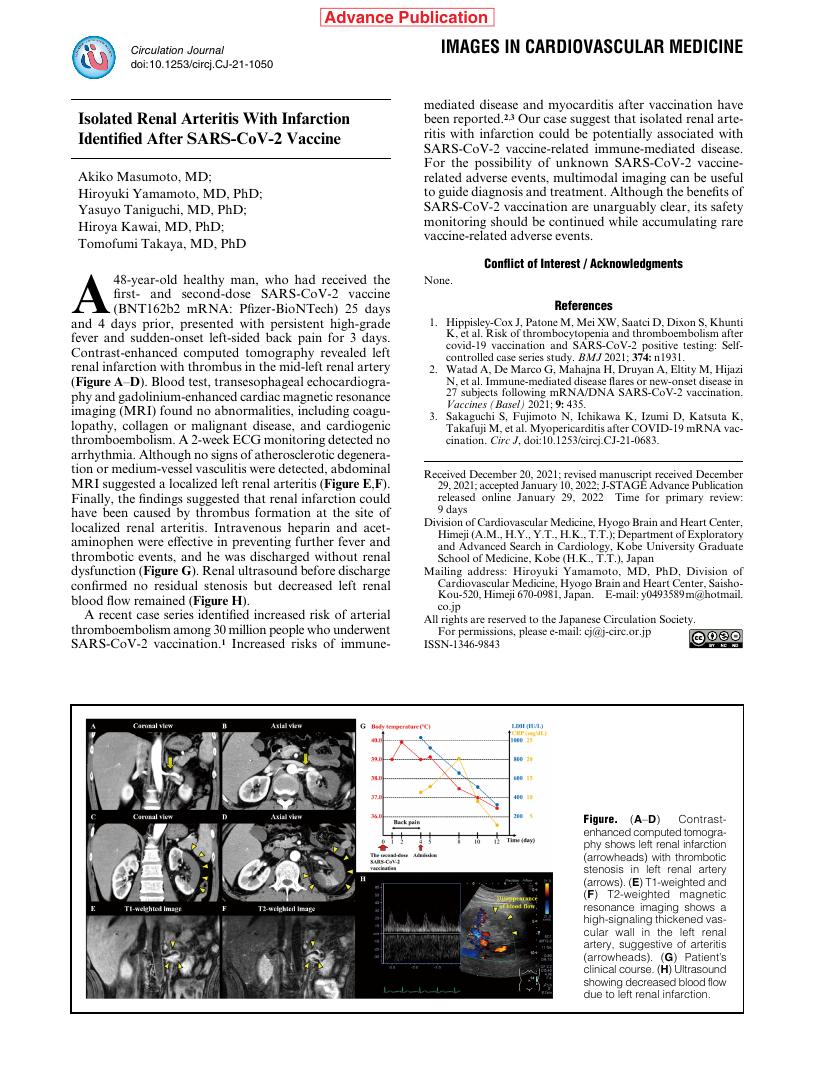
- Akiko Masumoto Hiroyuki Yamamoto Yasuyo Taniguchi Hiroya Kawai Tomofumi Takaya
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-1050, (Released:2022-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 被引用文献数
- 2
- 著者
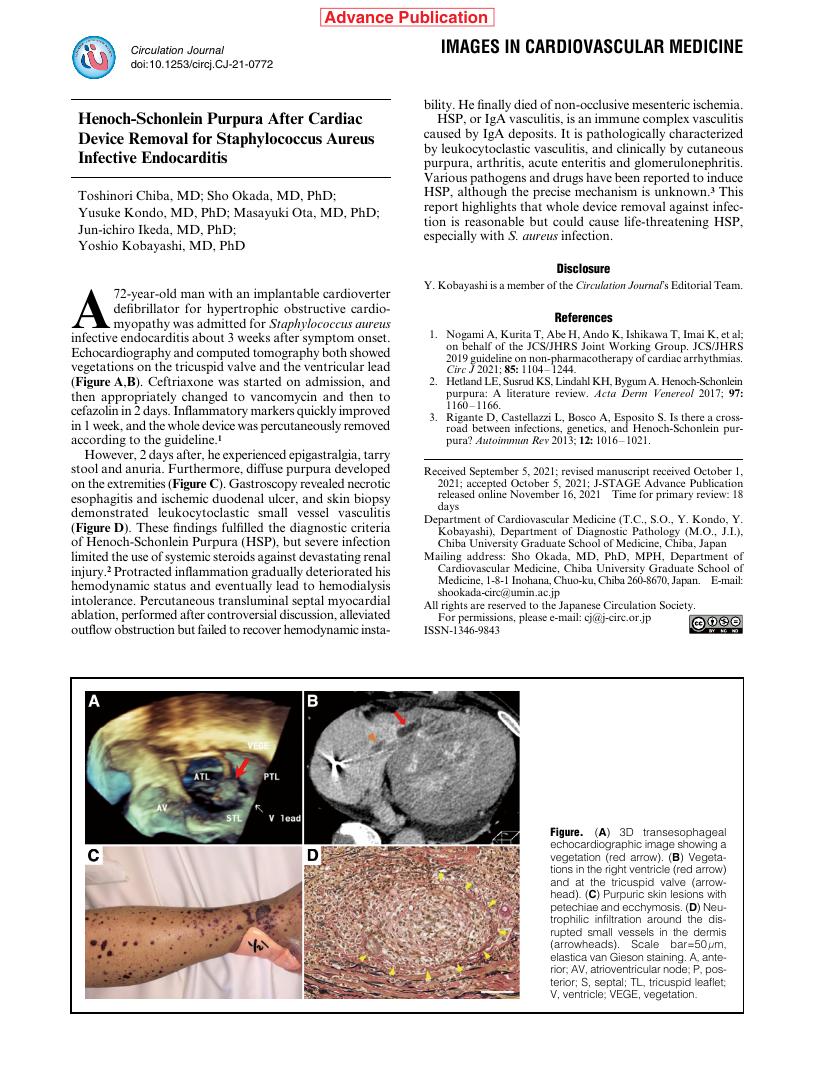
- Toshinori Chiba Sho Okada Yusuke Kondo Masayuki Ota Jun-ichiro Ikeda Yoshio Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0772, (Released:2021-11-16)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Kazuhiro Nakao Teruo Noguchi Chris P Gale
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0662, (Released:2021-08-28)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 著者
- Anthony C. Keech Kazuma Oyama Peter S. Sever Minao Tang Sabina A. Murphy Atsushi Hirayama Chen Lu Leslie Tay Prakash C. Deedwania Chung-Wah Siu Armando Lira Pineda Donghoon Choi Min-Ji Charng John Amerena Wan Azman Wan Ahmad Vijay K. Chopra Terje R. Pedersen Robert P. Giugliano Marc S. Sabatine on behalf of the FOURIER Study Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-20-1051, (Released:2021-05-12)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Background:There are concerns that Asian patients respond differently to some medications. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of evolocumab among Asian vs. other subjects in the FOURIER trial, which randomized stable atherosclerosis patients to receive either evolocumab or placebo.Methods and Results:Effects of adding evolocumab vs. placebo to background statin therapy on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reductions, cardiovascular outcomes, and adverse events were compared among 27,564 participants with atherosclerotic disease, according to self-reported Asian (n=2,723) vs. other (n=24,841) races followed for a median of 2.2 years in the FOURIER trial. The primary endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or coronary revascularization. At randomization, Asians had slightly lower LDL-C (median 89 [IQR 78–104] mg/dL vs. 92 [80–109] mg/dL; P<0.001) and were much less likely to be on a high-intensity statin (33.3% vs. 73.3%; P<0.001). Evolocumab lowered LDL-C more in Asians than in others (66% vs. 58%; P<0.001). The effect of evolocumab on the primary endpoint was similar in Asians (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.61–1.03) and others (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.79–0.93; P interaction=0.55). There was no excess of serious adverse events with evolocumab among Asians over others.Conclusions:Use of evolocumab robustly lowers LDL-C and is equally efficacious in lowering the risk of cardiovascular events and safe in Asians as it is in others.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Omori Hideaki Ota Takuya Mizukami Yoshiaki Kawase Toru Tanigaki Tetsuo Hirata Munenori Okubo Masanori Kawasaki Hitoshi Matsuo
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.85, no.8, pp.1404, 2021-07-21 (Released:2021-07-21)
- 参考文献数
- 2
- 被引用文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Soichi Komaki Masanobu Ishii Kazumasa Kurogi Nobuyasu Yamamoto
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0039, (Released:2021-04-22)
- 参考文献数
- 2
- 被引用文献数
- 1