1 0 0 0 OA 青森県のアカシボ発生地域における雪中の無脊椎動物
- 著者
- 大高 明史 山崎 千恵子 野原 精一 尾瀬アカシボ研究グループ
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.2, pp.107-119, 2008 (Released:2009-09-10)
- 参考文献数
- 23
赤雪の一種であるアカシボ現象が知られている青森県の水田や山間休耕田,および高層湿原で,雪中に出現する無脊椎動物の群集構造や雪中での分布を調べた。雪に出現した動物は,表層や上層でわずかに見られる陸上動物と下層で優占する水生動物から構成されていた。冬期間の継続調査によると,水生動物の密度は雪がざらめ状になる積雪後期に水分含量の多い下層で高まり,特にアカシボ層では900 L-1を超える高密度での出現が観察された。雪中に見られる無脊椎動物群集は,カイアシ類や貧毛類,ユスリカ類やヌカカ類の幼虫が優占し,尾瀬ヶ原で知られている構成と類似していた。これらの動物はいずれも調査地の土壌中でも確認されることから,土壌動物に由来すると推測された。水を多量に含んだざらめ状の雪に出現する無脊椎動物には小型で細長い体型の水生種が多く,海浜や地下水などの間隙性動物との生態的な類似性が指摘される。弘前市の休耕田での継続観察から,融雪期に積雪下層あるいは土壌表面で起こるアカシボの生成に伴って,高密度の水生無脊椎動物群集が形成されることが推測された。
1 0 0 0 OA バイオマニピュレーションが行われた白樺湖における動物プランクトンの群集変動について
- 著者
- 吉田 悠 河 鎭龍 花里 孝幸
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 日本陸水学会 講演要旨集 日本陸水学会第70回大会 大阪大会
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.24, 2005 (Released:2006-09-07)
1 0 0 0 OA ミジンコのヘモグロビンについて
- 著者
- 小林 道頼
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.4, pp.385-394, 1992-10-29 (Released:2009-06-12)
- 参考文献数
- 44
オオミジンコの血リンパ中のHb濃度と生息水の溶存O2量には逆相関の関係が見られる。低O2下でのHb合成は未成熟個体で高い。Hbの多い個体は少ない個体が遊泳できない程の低い酸素下でも長距離を遊泳できる。オオミジンコは02調節形の呼吸を示し,Hbの多い個体は少ない個体よりも低い臨界O2濃度を持っている。Hbの多い個体と少ない個体の生体内Hbが50%O2化するO2圧はそれぞれ15と35torrである。Hbの多い個体の精製HbのO2親和性は少ない個体のものよりも高い。等電点電気泳動法によりオオミジンコHbは少なくとも6種以上の成分に分離される。Hbの多い個体と少ない個体ではHb成分の量比が異なり,Hbの多い個体では,等電点の高い成分が増加している。オオミジンコはO2親和性の異なる多成分系Hbをもつことにより,広範なO2環境に適応することができるものと思われる。
1 0 0 0 OA 有馬流紋岩層群の浅層地下水の水質
- 著者
- 日下 譲 辻 治雄 玉利 祐三 西村 公男 藤原 儀直
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.2, pp.93-99, 1984-04-30 (Released:2009-11-13)
- 参考文献数
- 5
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Chemical species of the shallow groundwaters collected from the Arima rhyolite strata around Sanda and Nishiwaki cities are studied. Since the chemical composition of the igneous effusive rock is reasonably representative of rocks of the continental crust, the water quality is important from the geochemical and environmental viewpoints. The concentrations of 28 chemical species, pH and ER are determined by conventional chemical and neutron activation analyses. By showing log-normal distribution character of the concentrations, the median value schematically obtained in the frequency distribution curve is proposed as most suitable as the chemical composition of groundwaters in the strata. It is also pointed out that the CO2 weathering process is the most dominant phenomenon controlling the water qualities.
1 0 0 0 OA 琵琶湖における太陽紫外線の水中透過性について
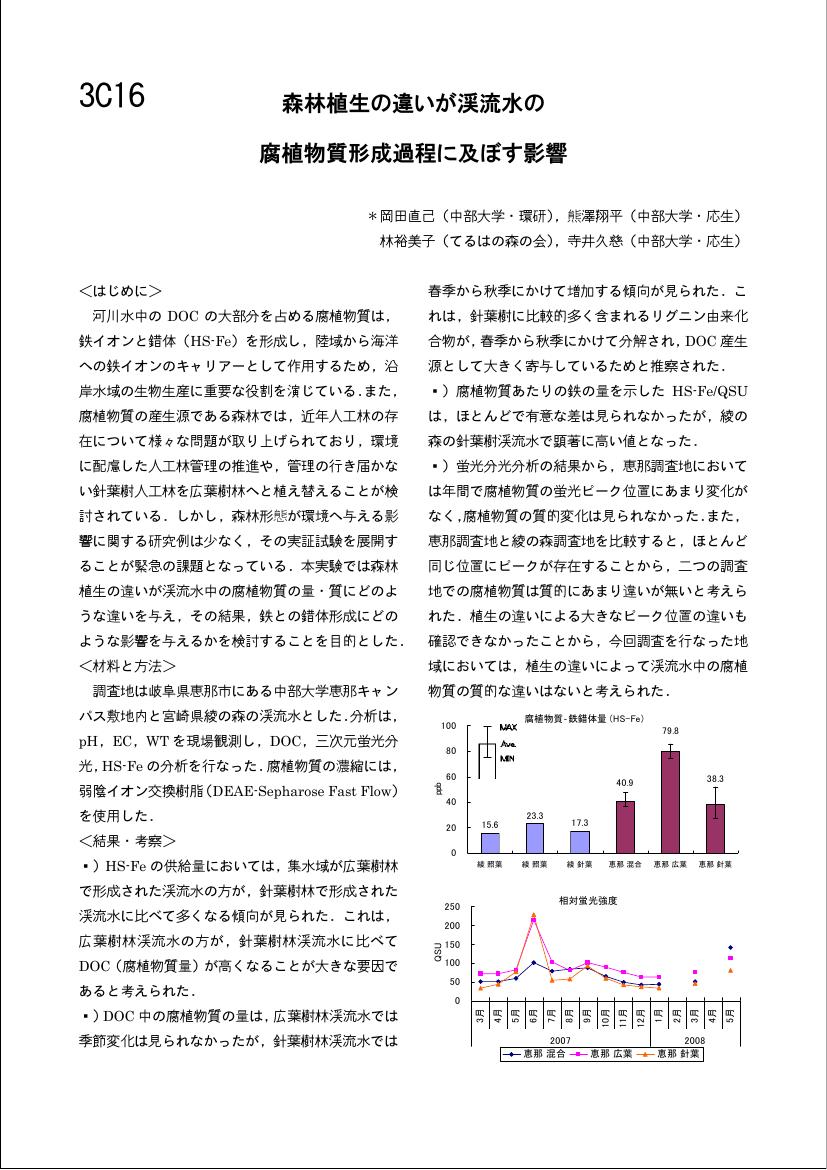
1 0 0 0 OA 森林植生の違いが渓流水の腐植物質形成過程に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 藤谷 俊仁
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.3, pp.185-207, 2006-12-01 (Released:2008-03-21)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
コカゲロウ科の日本産7属について, 雄成虫と幼虫の属への図解表検索を作成した。対象とした属は, ミジカオフタバコカゲロウ属, シリナガコカゲロウ属, フタバコカゲロウ属, コカゲロウ属 (狭義), フトヒゲコカゲロウ属, トビイロコカゲロウ属, ヒゲトガリコカゲロウ属であった。各属の種組成, 各種の特徴, タイプ産地といった分類情報だけではなく, 種の分布域, ハビタットといった生態情報もまとめた。
- 著者
- 松崎 慎一郎 佐竹 潔 田中 敦 上野 隆平 中川 惠 野原 精一
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.76, no.1, pp.25-34, 2014-09-04 (Released:2016-01-31)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
福島第一原子力発電所事故後に,霞ヶ浦(西浦)の沿岸帯に2定点を設けて,湖水の採水ならびに底生動物である巻貝(ヒメタニシ,Sinotaia quadrata histrica)と付着性二枚貝(カワヒバリガイ,Limnoperna fortunei)の採集を経時的に行い,それらの放射性セシウム137(137Cs)濃度(単位質量あたりの放射能;Bq kg-1)を測定した。これらのモニタリングデータから(2011年7月~2014年3月),貝類における137Csの濃度推移,濃縮係数ならびに生態学的半減期を明らかにした。湖水および貝類の137Cs濃度は定点間で差は認められず,経過日数とともに減少していった。両地点でも,カワヒバリガイよりも,ヒメタニシの137Cs濃度のほうが有意に高かった。濃縮係数を算出したところ,ヒメタニシのほうが2倍近く高かった。巻貝と二枚貝は,摂餌方法や餌資源が異なるため,137Csの移行・蓄積の程度が異なる可能性が示唆された。また生態学的半減期は,ヒメタニシで365~578日,カワヒバリガイで267~365日と推定され,過去の実験的研究で報告されている生物学的半減期よりもはるかに長かった。このことから,餌を通じた貝類への137Csの移行が続いていると考えられた。
1 0 0 0 OA 強酸性湖潟沼における堆積有機物起源の炭素安定同位体比解析
- 著者
- 土居 秀幸 菊地 永祐 日野 修次 伊藤 丈 高木 茂人 鹿野 秀一
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 日本陸水学会 講演要旨集 日本陸水学会第68回大会 岡山大会
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.141, 2003 (Released:2004-11-26)
潟沼は平均pH 2.2の強酸性湖である.潟沼において,炭素安定同位体比を用いて堆積有機物起源の解析を行った.また,潟沼はその生物相が単純であることから,堆積有機物起源の詳細な解析が可能である.一般に酸性湖沼は非調和型湖沼であり,堆積有機物の起源は周りから供給される有機物が多い.しかし炭素安定同位体比解析の結果,潟沼の堆積有機物は周りの森林からの有機物由来のものは少なく,その多くは底生珪藻と植物プランクトン(内生産性の有機物)に由来することが分かった.この要因としては,潟沼が流入河川を持たないこと,珪藻と植物プランクトンの生産が大きいことが考えられた.
1 0 0 0 OA 尾瀬ヶ原上田代池溏群の岸辺水生無脊椎動物に与える洪水の影響
- 著者
- 福原 晴夫 木村 直哉 永坂 正夫 野原 精一
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.3, pp.171-188, 2021-09-25 (Released:2022-09-28)
- 参考文献数
- 100
- 被引用文献数
- 1
尾瀬ヶ原は標高約1400 mに位置し,長さ6 km,幅2 km,面積7.6 km2の本州最大の高層湿原である。尾瀬ヶ原では近年洪水の頻度が増し,池溏に氾濫水が流入する状況が起こっている。そこで,尾瀬ヶ原上田代の12池溏において,2019年10月に岸辺水生無脊椎動物のタモ網による時間単位採集を行い,洪水の影響を検討した。最近の洪水(2019年5月20 ~ 21日,累加雨量84 mm)による池溏の濁り状態の目視観察やドロ-ン映像,池溏の標高,魚類の侵入状況から,12池溏を洪水影響小(OFPool),洪水影響大(FFPool)に分けた。調査池溏には27分類群が出現した。OFPoolには25分類群,FFPoolには26分類群が出現し,差はなかった。各分類群の採集個体数の平均はミズダニ類を除いてFFPoolで少なく,総採集個体数(ササラダニ類を除く)とハエ目採集個体数で有意に少なかった。ササラダニ類もFFPoolで少ない傾向を示した。ハエ目の中ではユスリカ科の採集個体数が,特にモンユスリカ亜科の採集個体数がFFPoolで少なく,洪水は本亜科に大きな影響を与えたと推定される。生体量にはハエ目を除いて有意な差は認められなかった。キイロマツモムシ,ケヨソイカ属の一種,セトトビケラ属の一種 はFFPool での出現池溏が少なかった。氾濫水は池溏の岸辺を攪乱し,動物そのものの流失や動物の付着した枯葉や藻類,菌類の流失を引き起こし,岸辺水生無脊椎動物個体数を低下させた可能性がある。また洪水によって池溏に侵入した魚類の捕食圧の増加も個体数の低下を引き起こしている可能性がある。
1 0 0 0 OA 長野県大沼池の青色呈色について
- 著者
- 野崎 隆夫 小林 紀雄
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.4, pp.287-293, 1987-10-30 (Released:2009-11-13)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The life history of the caddisfly, Nothopsyche ruficollis (ULMER), was studied in a small stream on the Miura Peninsula of Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, from October 1984 to September 1986. The species had a univoltine life cycle. Adults were present from late autumn to early winter and oviposited their egg-mass on the bank. The hatching time of eggs varied greatly, even within an egg-mass, and newly-hatched larvae remained within the gelation until early spring. They may get into the water with rain. There were five larval instars. Larval development occurred during the aquatic stages of the life cycle, from the first to the early fifth instars, present from early spring to early summer. Final instar larvae began to move on land in the early summer and aestivated from early summer to autumn and pupated in the late autumn. The wintering within the gelatinous egg-mass and summer aestivation observed in this species seems to be advantageous to avoid the unstable stream conditions of drought or flooding prevalence in summer and drought or freeze in winter. Although the main larval food was diatoms, vascular plant and animal materials were also found to be utilized as food by aquatic stages. No feeding was evident in terrestrial larvae.
1 0 0 0 OA 浅い湖沼における富栄養化研究のこれまでと将来展開
- 著者
- 篠原 隆一郎
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.1, pp.19-31, 2020-02-25 (Released:2021-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 86
富栄養化及び,藍藻類のブルーミングは依然として世界中で重要な問題となっている。近年,Geo-engineeringな手法を用いることで,湖沼保全方法の知見が増え,また,新しい分析手法が開発されたことで,細かいプロセスが明らかになってきた。本総説では最初に富栄養化対策について俯瞰的に議論し細かいプロセス研究の重要性を示したい。その後,無機態・有機態リンの循環について議論する。最後に,筆者自身が行っている今後の研究について議論したい。
1 0 0 0 2007年秋~冬の滋賀県下のボタンウキクサの分布について
- 著者
- 芳賀 裕樹 琵琶湖博物館 フィールドレポーター
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水大会要旨集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.73, pp.101, 2008
1 0 0 0 OA 砥部川水系における土地利用と環境の相互作用
- 著者
- 松濤 一平
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 日本陸水学会 講演要旨集 日本陸水学会第70回大会 大阪大会
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.95, 2005 (Released:2006-09-07)
1 0 0 0 OA 植物プランクトンが付着藻になる;緑藻イカダモのDaphniaに対する新たな生存戦略
- 著者
- 萩原 萌恵 花里 孝幸
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 日本陸水学会 講演要旨集 日本陸水学会第72回大会 水戸大会
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.18, 2007 (Released:2008-03-31)
1 0 0 0 OA 自然水中での鉄の形態変化と藻類鉄摂取機構
- 著者
- 藤井 学 大村 達夫 Trevor Waite
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 日本陸水学会 講演要旨集 日本陸水学会第74回大会 大分大会
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.134, 2009 (Released:2009-11-06)
1 0 0 0 OA 多摩川水系・日野用水におけるオオシロカゲロウ(カゲロウ目・シロイロカゲロウ科)の生活史
- 著者
- 関根 一希 鶴田 大三郎 東城 幸治
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.2, pp.253-260, 2007 (Released:2008-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 4 6
オオシロカゲロウは進化生態学的に興味深い昆虫であるが,比較的大・中規模とされる河川,かつ水深が深い中・下流域に棲息するため,生活史全般に渡る調査研究は困難とされてきた。本研究では,小規模な農業用水路・日野用水(東京都日野市)において本種が高密度で確認されたため,調査に適した棲息地として2005年の一年間,生活史を詳細に追究した。その結果,主たる孵化期間は2月下旬-3月下旬であり,羽化期間は8月30日-9月20日間(ピークは9月3日,4日)であることを確認した。また一方で,一年を通して孵化前卵が認められたが,これは休眠卵に適切な低温処理がなされず,春になっても休眠解除されなかったものであると考えられる。これらの卵は翌年(あるいは,それ以降の年)の春季に休眠が解除される可能性も考えられ,鰓脚類や一部の昆虫類などでみられるようなエッグバンク的機構が備わっている可能性も示唆された。
- 著者
- 植田 真司 長谷川 英尚 久松 俊一
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.1, pp.75-85, 2016
- 被引用文献数
- 4
<p> 青森県六ヶ所村に点在する淡水湖の田面木沼および市柳沼,汽水湖の鷹架沼および尾駮沼における水質の現状と変遷を明らかにすることを目的に,2004年4月~2015年3月の期間,月一回の水質調査を行った。田面木沼,市柳沼および鷹架沼において全窒素(TN),全リン(TP)および化学的酸素要求量(COD)濃度は高く,富栄養化レベルであった。田面木沼および市柳沼においては,毎年8~10月の期間,アオコの発生が観察され,水質汚濁が顕在化していた。しかしながら,11年間を通してみると汚濁の進行は止まっており,ほぼ横ばいに推移していた。また,鷹架沼は,湖盆の真中を縦断する防潮堤を挟んで水質が異なり,防潮堤の西(奥)側の水質が,東(海)側よりも富栄養化が進んでいた。一方,尾駮沼は年間を通してTN,TPおよびCOD濃度は低く,水質は良好であり,中栄養化レベルであった。尾駮沼が水質を良好に保っている要因は海水交換が大きいことが考えられる。いずれの湖沼の水質も長期間の観測を通してほぼ横ばいに推移していたが,40年前の水質と比較して概ね改善方向にあることが認められた。</p>
1 0 0 0 OA 山形県大鳥池 1959年夏季の状態概報
- 著者
- 上野 益三
- 出版者
- 日本陸水学会
- 雑誌
- 陸水学雑誌 (ISSN:00215104)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.4, pp.121-144, 1959-11-30 (Released:2010-01-27)
- 参考文献数
- 26
Lake Ótori-ke, in latitude 38°22' N., lies at an elevation of 963 ± 3 m to the northern side of Mt. Ito-dake, the northernmost peak of the Asahi mountain range in Yamagata Prefecture. lt is noticeable that this deep mountain lake, having the greatest depth of 65 m, was formed behind a landslide dam which happened in the geological past. The present-day lake, which occupies 0.342 km2 in superficies (when 966 m, 0.406 km2), is situated at the bottom of a small drainage basin of granitic rocks. The lake is fed by three short streams of melted water at the southern shore, and the lake water discharges over the top of the dam at its north-eastern corner and runs down as a rapid. Its volume is 1.1 (or 1.23) × 107 m3. It is natural that such a body of water lying in the igneous rock basin and in the subalpine climatic conditions is oligotrophic in nature.The lake appeared, when the writer visited there in the end of July, 1959, to be dark green and turbid, probably due to the heavy rain in the preceding days. Transparencies were smaller than 2 m. The probable shortness of the daily period of insolation due to the situation of the lake, which is surrounded by steep mountains, may cause the decrease of heat income to the lake. The surface water did not exceed 21°C at the end of July. Sharp but unstable thermal stratification developed at the layers below the surface. This seemed to facilitate heat transport into deep water, where temperatures were observed above 4°C. The oxygen dissolved in the surface water was in an amount of 8.46 mg/l, and its diminution in the deep water was rather great. The water showed acid reaction, probably owing to the acidic igneous rocks of the basin ; its pH values were 6.4 in the surface water and gradually became lower toward the bottom, at which the pH was 5.8. The chemical analyses for some major and minor constituents suggest that this lake has rather dilute water, as is discussed in a separate paper. Besides the surface water, there existed slightly turbid water at the layers below 20 m, suggesting the presence of heterogenous water mass, for which the chemical analyses showed the increase of the amounts of organic matter and nitrogenous compounds. Phosphorus was not found throughout the bottom.There were found deposits of soft dark grey ooze on the bottom of the limited area deeper than 60 m, where a considerable amount of fragments of fallen leaves from the surrounding forests of the lake was present. No bottom-inhabiting animals were found, but a considerable number of ephippial eggs occurred on the surface of mud. These eggs, it was determined in hatching experiments, belonged to Daphnia living in the lake. In the bottom ooze there were found 28 species of diatoms, among which Cyclotella Meneghiniana Meneghiniana and C. stelligera were dominant.The plankton is characterized by the occurrence of a few species of animals, among which Conochilus unicornis is the most abundant. The others are crusta-ceans, namely Holopedinm gibberum, Cyclops vicinus, Acanthodiaptomus pacificus and Daphnia ambigua. They were, however, small in quantity, and were concentrated in the upper layers, shallower than 10 m. The primary productivity (phytoplankton), too, was extremely small in quantity, only a small number of Dinobryon cylindricum occurring in the end of July. TheDaphnia found in this lake is peculiar in having a very short shell-spine, and is identical with the races inhabiting the lakes of northeastern Japan (including Hokkaido). It is presumably a peculiar race of thelongispina group, and is identical withDaphnia ambigua Scourfield.