1 0 0 0 剣道難聴の研究
- 著者
- 堀山 健治 田中 豊穂 中川 武夫 林 邦夫 伊保 清次
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.3, pp.175-183, 1988
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This study was planned to to compare the hearing level of Kendo-Players with that of non-Kendo-Players to make clear whether or not long term practice of Kendo causes hearing loss. Pure-tone audiometry by air conduction was applied to 172 Kendo-Players and 76 non-Kendo-Players with an audiometer (Audiometer AA-69, Audiogram Recorder RE-05, Soundproof Room AT-45, Rion, Japan). Among them, the following cases were excluded from the analysis. 1) Cases who have had medication against tuberculosis. 2) Cases with perforation in the tympanic membranes. 3) Cases with occupational experience of more than a year in noise nuisance. 4) Cases with experience of head phone listening for more than one hour a day, twice a week for at least one year. The thresholds of hearing between 149 Kendo-Players (cases, age: 19-76) and 44 non Kendo-Players (controls' age: 20_78) were analysed to compare mean hearing thresholds between the age groups, and to examine covariance adjusted with age. The dose-response relationship was examined by the partial correlation coefficients controlled by age between the thresholds of hearing and the length of Kendo experience (year) or the total experience hours of Kendo (hour). The rusults showed that the hearing loss of Kendo-players was greater than non-Kendo players, especially at the frequency of 4000 and 8000 Hz in the age group of 30-59 years old. It is supposed that long term practice of Kendo may cause hearing loss. Further study, however, will be needed to re-examine the dose-response relactionship with more carefully selected samples for the epidemiological survey in the future.
- 著者
- 里見 悦郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.5, pp.323-336, 1994
The purpose of this study was to make clear the process of establishment of the sport control system in CIS. For this purpose, I had a study on the enterprise for CIS to send the delegation to the 1992 Olympic games. It is possible to point out the special features of the process of the CIS sport control system having been established from 1990 to 1992 as follows. 1. The soviet sport system democratized and approched the western sport system before soviet disappeared at 1991. 2. There was the consensus that they want to keep the tradition of soviet being the winner on Olympic games. this consensus made it possible that CIS could send its delegation to the 1992 Olympic games after soviet disappeared within 3 months. 3. Ex-soviet sport leaders changed the name of sport organization, for example, from Soviet Olympic tommittee to CIS Olympic committee. but, they did not reorganize the inside of ex-soviet organization within 3 months after soviet diappeared. 4. The CIS Olympic delegation was organized by the special instruction of President of Republic of Rossia. 5. The real reorganization of CIS sport system will begin after 1992. These results suggest that the special features for CIS sport system, that the CIS basic organization is the same system of ex-soviet sport organization from 1991 to 1992. Only one financial system of CIS is different from that of ex-soviet. New financial system of CIS is consist of stats financial support, sport lottery which is same as at ex-soviet years and the finacinl support of western sponser enterprise. I may point it out that there were only 3 months before 1992 Olympic games starts,they did only change the name of organization. but, could not reorganize the sport system.so CIS sport system will construct after 1992 Olympic games.
- 著者
- 内藤 貴司 山口 裕嗣 大柿 哲朗
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.103-113, 2016 (Released:2016-06-17)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
The timing at which ice is ingested prior to exercise may be important for optimizing internal pre-cooling effects. However, previous reports have not evaluated the influence of timing of ice ingestion on internal pre-cooling in the heat. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of differences in the timing of ice ingestion on endurance cycling capacity, body temperature and perceptional sensation during heat stress. Seven healthy males [age=26±2 yr, height=1.71±0.04 m, body mass=63.6±2.8 kg, surface area=1.74±0.03 m2, VO2max=49.7±4.4 ml・kg−1・min−1] ingested ice for 30 min before exercise under 3 separate conditions: ice ingestion at 30-(30D), 15-(15D) and 5-(5D) minute intervals. The total volume of ice ingestion was identical during 30D, 15D, 5D and was divided equally by the number of times drunk in each experiment. Subjects performed cycling to exhaustion at 70%VO2max in a hot environment (35℃ room temperature and 30% relative humidity). Rating of thermal sensation was lower in the 5D group at 15 min period during exercise than those under the other conditions (p<.05). Rating of perceived exertion was lower in the 5D group at 20 and 25 min periods during exercise than those under the other conditions (p<.05). There were no significant differences in rectal temperature, mean skin temperature or exhaustion time between the 3 conditions. These results suggest that there are no significant differences in exhaustion time or rectal temperature if the total volume of ice ingestion is identical, although ice ingestion until just before exercise attenuated the perceptual sensation of heat during exercise in a hot environment.
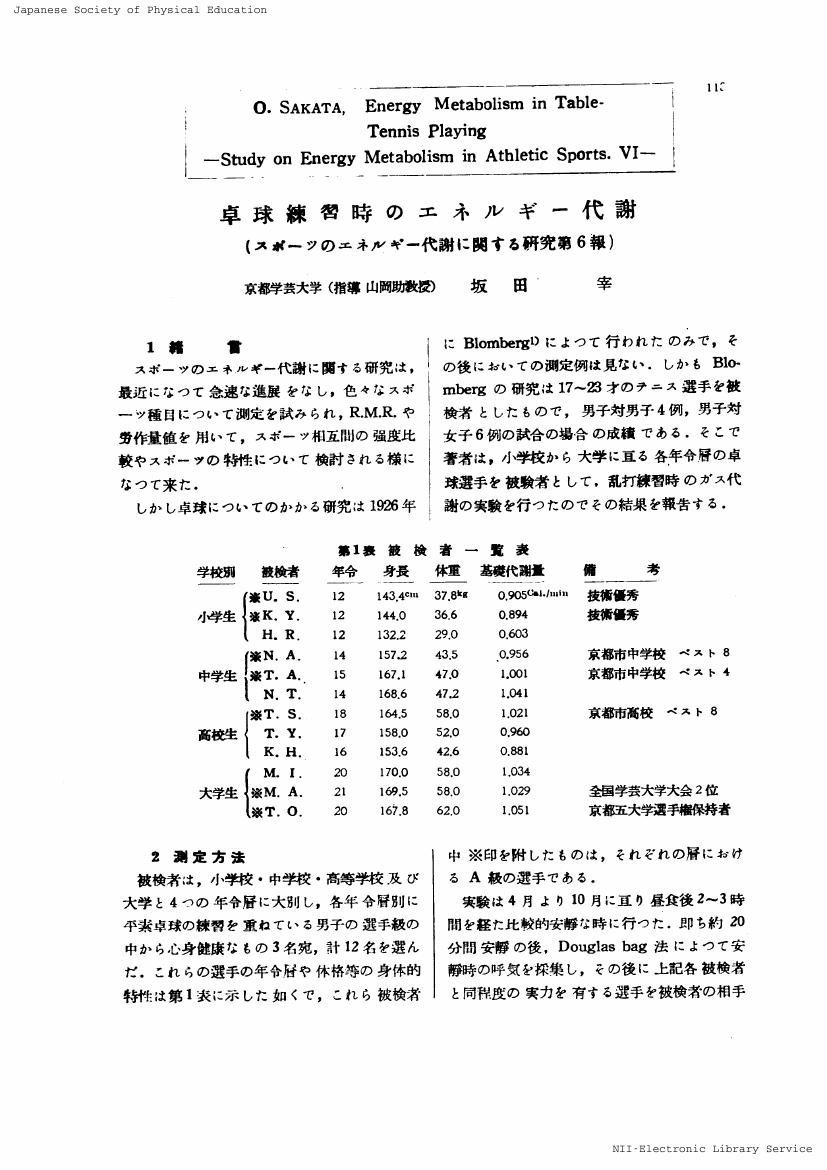
1 0 0 0 OA 卓球練習時のエネルギー代謝 : スポーツのエネルギー代謝に関する研究 第6報
- 著者
- 坂田 宰
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.3, pp.113-116, 1956-10-30 (Released:2016-12-31)
1 0 0 0 OA 近代体育とクーベルタン : 体育学の教育思想史
- 著者
- 清水 重勇
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3, pp.227-239, 2001-05-10 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Present paper aims to draw attention to the potential problem of the concept of body and culture, subsisting from the emergence of modern European physical education theory to the coming of P. de Coubertin's Olympism, in the realm of the French history of pedagogical philosophy, and to represent it as an origin of theoretical problem that our Society has been confronting with. The outline of discussion is as follows: 1. The education in the period of the Ancien regime looked Health or Physical performance as Moral profiles of particular beings. Body is attributed to private-ness. 2. On arrival of the Enlightment, Body, amalgamated with the Performance culture in the Ancien regime education, is conceived as the Physical, and it is the beginning of a peculiar type of theory for educating the Physical. 3. The Physical grasped by new pedagogy becomes not only a blank depriving the Body of its given traditional bases of Performance culture, but also a functional spot of the physics' time axis. 4. Guts Muths' pedagogy grappled with above conceptual problem of compatibility of the Physical as nature with the culture. His way of thinking provides our Society of Physical Education with the prototype. 5. Attempting to build up a practical moral science by rigid method of physical training and by codification of motorics, Amoros' pedagogy suffered from dilemma of "funambulism" which persisted between the highest exploitation of physical functions and the formation of moral conduct. 6. In the modem education theory, the problem of the Performance culture was requested retrospectively to the ancient Greek culture, while there were no alternatives during 19th century. 7. Looking for the deepest entity of the Physical, and deeply influenced by the philosophical trends of the 20th century, the New physical education theories came up to investigate the monistic totality of the non-intellectuals in the Physical, whereas it becomes more and more difficult to apprehend the humanity going over the scientifism and the philosophism. 8. P. de Coubertin's Olympism challenges to restore the Physical to the humanistic culture. He wrote a civilization history of 'sport instinct', on the other hand, he intended to describe psycho-motor representation tied the muscle up the awareness in order to identify proper live time axis of body with overarching historical time axis. This would be considered, however, as aggravation of the theoretical problem of modem education of the Physical and the Culture.
- 著者
- 志村 芽衣 宮澤 隆 矢内 利政
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.2, pp.487-500, 2019-12-16 (Released:2019-12-20)
- 参考文献数
- 16
The purpose of this study was two-fold; to determine the optimum impact condition for maximizing flight distance toward the opposite field and to examine the influence of the bat angles at impact on the batted ball characteristics (speed, rotation, and angle immediately after impact) and the flight characteristics (distance, trajectory, and time). Various impact conditions were defined using 3 factors: the angles of the bat at impact projected to the horizontal and vertical planes, and the vertical inclination angle of the line of impact (the product of the sine of this angle and the radius of the ball determines the under-cut distance). Three-dimensional finite element analysis was used to construct a model of impact between a baseball and a wooden baseball bat and to conduct simulation analysis. The initial flight condition of the batted ball after the impact was determined for each simulated condition, and the flight distance was estimated from the initial flight condition. The results showed that a nearmaximum flight distance of 90-95 m was attained over a wide range of the opposite field when the bat head was not lowered substantially more than the grip-end. However, when the bat head was lowered substantially more than the grip-end, the flight distance attainable with the given impact condition decreased as the vertical bat angle increased, and the range of horizontal bat angle within which a great flight distance was attainable became narrower. The latter results suggest that a batsman needs to acquire a sophisticated technique with a greater precision of ball impact to hit a ball toward a given horizontal angle in the opposite field if the bat swing is characterized as lowering of the bat head to a large extent.
1 0 0 0 OA 運動持続距離の分散が心肺持久性及び血液脂質に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 戎 利光
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.1, pp.37-43, 1985-06-01 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
本研究の目的は,運動持続距離を二等分あるいは三等分と分散して走運動を行った場合に,心肺持久性及び血液脂質に及ぼす身体的効果が,分散しないで一度に全距離を走った場合の効果と異なるか否かを明らかにすることである。53名の健康な男子学生をA群からD群の4群に分類した。A群は全距離を一度に走り,B群は半分の距離を1日2度(朝,夕)に分散して走り,C群は3分1の距離を1日3度(朝,昼,夕)に分散して走った。D群は対照群であり,本研究期間中特別な身体運動をしなかった。D群を除く全被験者は,週に3日間,各個人の最高心拍数の80%を維持して10週間に渡り,屋内のタータントラックを走った。そして, このトレーニング期間前後の最大酸素摂取量,最高心拍数,脂肪百分率(水中体重測定による),1.5マイル走の記録,総トリグリセライド,総コレステロール,高比重リボ蛋白コレステロール,低比重リボ蛋白コレステロール,超低比重リボ蛋白コレステロールを,各群ごどに比較,検討した。その結果,次のような結論を得た。分散した最短走距離が心肺持久性や血液脂質に影響を及ぼすような距離であれば,同一の運動強度及び頻度で同一距離を走る限り,その走距離を二等分あるいは三等分と分散しても総消費エネルギーは同一であり,心肺持久性や血液脂質に及ぼす影響に差はない。本研究は,米国ブリガムヤング大学及び米国デザレットジム財団からの研究交付金を受けた。
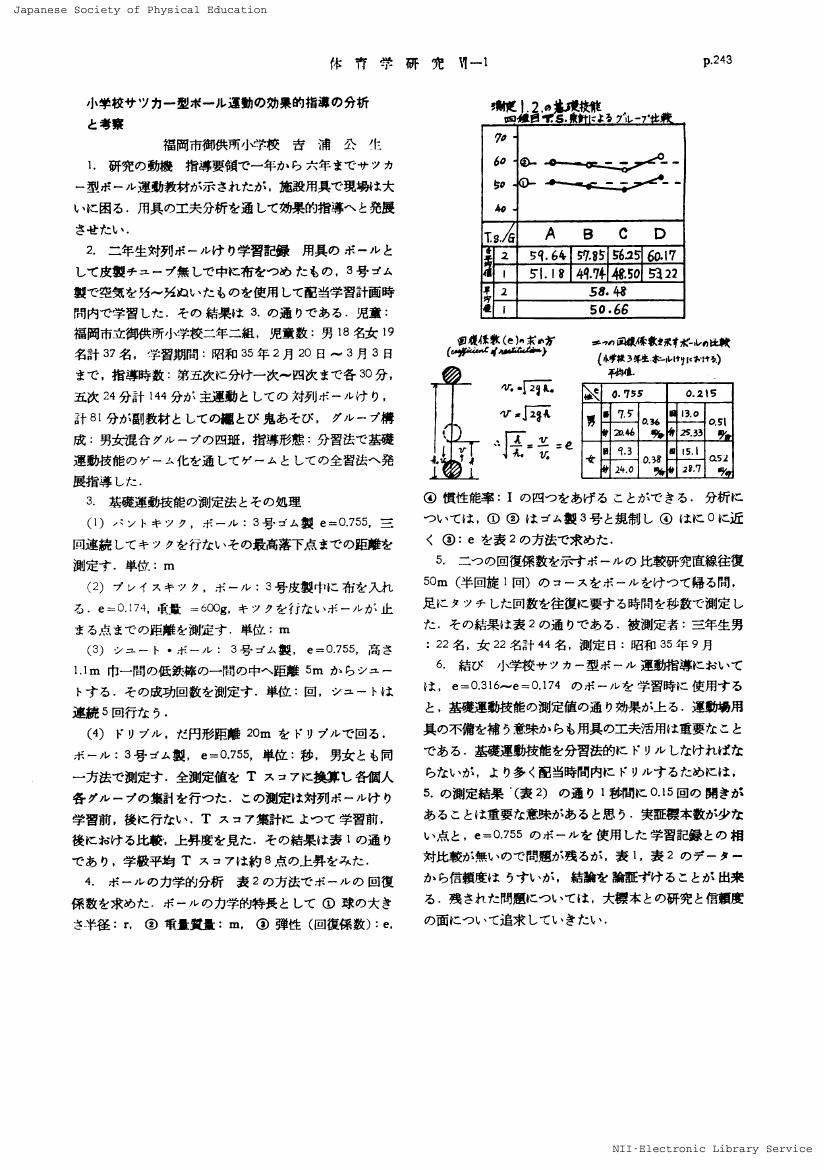
1 0 0 0 OA 小学校サツカー型ボール運動の効果的指導の分析と考察
- 著者
- 吉浦 公生
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, no.1, pp.243, 1961-09-01 (Released:2016-12-31)
- 著者
- 鈴木 秀人
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2021
1 0 0 0 OA 高齢者における体格・体力の加齢に伴う変化及びその性差
- 著者
- 中 比呂志 出村 慎一 松沢 甚三郎
- 出版者
- 日本体育学会 = Japan Society of Physical Eduction, Health and Sports Science
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 = Japanese journal of physical education (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.2, pp.84-96, 1997-07-10
The purpose of this study were to investigate factorial structures of physique and physical fitness, and to determine the change of physique and physical fitness with age and its sex difference in the elderly. Nineteen test items were selected from 5 domains of physique, muscle function, joint function (flexibility), neuromuscular function and lung function, considering the validity, safety and convenience of tests. The subjects were 207 males and 226 females aged 65 to 89 years. Factor analysis was applied to each correlation matrixes consisting of 8 physique variables and 11 physical fitness variables. In physique domain, three extracted factors were interpreted as body fat, body linearity and body bulk. Body bulk and body linearity in both sexes and body fat in females decrease significantly with age. Body linearity was found significantly larger in males than females. Body fat was significantly greater in females. In physical fitness domain, four factors were extracted and interpreted as muscular strength, balance, agility of upper and lower limbs, and flexibility. A significant declining trend with age was found in the above-mentioned physical fitness elements both sexes. Also, significant sex differences in muscular strength, balance, and flexibility were found, and males were superior to females except for flexibility. It was inferred that the influence of aging in muscular strength and balance is greater flexibility and agility of upper and lower limbs in the elderly. Further, the decrease of muscular strength seems to facilitate the decline of balance with age.
1 0 0 0 OA エリートサッカーゴールキーパーにおける異なるシュートパタンに対する事前動作の特性
- 著者
- 松倉 啓太 平嶋 裕輔
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, pp.1049-1067, 2020 (Released:2020-12-24)
- 参考文献数
- 21
The aim of this study was to shed light on preparatory sequences performed by elite goalkeepers for defense against shots in response to variations in the position from where a shot at goal is taken, and in the number of touches ahead of the shot. The samples were extracted from videos of shots in all 64 matches of the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia. First, to analyze the characteristics of shots in elite games, data on shots from different areas and after various numbers of touches were studied. Then, to analyze the preparatory sequences taken by goalkeepers to defend against those shots, the shots were classified into 6 groups based on ‘the presence or absence of a specific prejump’, ‘a change in the distance between the feet during the preparation period’, and ‘whether the goalkeeper was still in a moving position or had completed the move’. The results of this analysis of the characteristics of the elite game made it possible to divide the positions from where shots were taken in 2 types, based on the probability of the shot being on target and the probability that a goal would be scored. In addition, it was shown that when one-touch shots were on target, it was difficult for goalkeepers to defend against them. Next, as an overall trend, the most frequent preparatory sequence performed by goalkeepers was to prepare for a shot with a slight jump in order to widen the distance between the feet after they had finished moving into position. In addition, a breakdown of the preparatory sequences for various numbers of touches ahead of the shot revealed that – for onetouch shots – a proportion of goalkeepers moved into position until immediately before the shot was taken. Overall, from these analyses, it was concluded that elite goalkeepers must engage in different preparatory sequences depending on the circumstances of the shot.
- 著者
- 小野 雄大 友添 秀則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.14043, (Released:2014-09-29)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 6 3
The Young Men's Association (YMA) was an education institute that provided business programmes and further education for young men. It aimed to train both mind and body, and valued sporting activities. However, there has been little knowledge about the state of sporting activities provided by the YMA. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the state of the sporting activities at Fuchu YMA in Tokyo. For this purpose, the study used Fuchu-sport bulletins which specialized in such sporting programmes during the Taisho era and pre-war Showa era. The main findings are summarized as follows. 1) Fuchu-sport was modeled on a specialized magazine, Asahi Sports. The publication of Fuchu-sport was an indication of the high interest in sport during the Taisho era. 2) After the Ministry of Home Affairs and the Ministry of Education announced their first and second instructions, the Tokyo government independently ran conferences aimed at the development of sport and physical education at Tokyo YMA. Accordingly, Tokyo was one step ahead of other areas in Japan in setting up athletic clubs for the YMA. 3) The organization of kyogi-bu was supported mainly by Fuchu YMA, but also funded by the local authority and by Fuchu ordinary and higher elementary school, the latter being also committed to conducting actual sporting activities. 4) University students were recruited as coaches, and thereby the kyogi-bu provided successful programmes that led to an improvement in competitive level. However, this improvement resulted in elimination of some of the members. 5) The remarkable successes of the kyogi-bu and its development in Fuchu were accomplished by collaborating with the local educational institutions. The relationship between the YMA and school athletic clubs was another significant factor in running the sporting programmes. The present study has provided deeper insights into the nature of sporting activities held by the YMA during the Taisho era and pre-war Showa era.
1 0 0 0 OA 準臨床的な一次性運動依存における心理的要因
- 著者
- 西 泰信 岩井 圭司
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.11110, (Released:2012-07-11)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The purpose of this study was to identify psychological factors that contribute to the development of sub-clinical primary exercise dependence among Japanese exercisers. Most studies of exercise dependence follow a top-down, quantitative, hypothesis-verification approach. The present study, in contrast, used a qualitative method, the Grounded Theory Approach. Dialogue data were collected from 14 exercisers who were evaluated for sub-clinical primary exercise dependence in semi-structured interviews and analyzed by classifying them into categories. Through these steps, seven types as psychological factors were identified as leading to sub-clinical primary exercise dependence among Japanese exercisers: dependence, obsessive-compulsiveness, conflict avoidance, maintenance of a positive self-concept, perceieved benefit of exercise, limited stress-coping resource, and typical increase in exercise volume. It was also found that dependence and obsessive-compulsiveness play a crucial and direct role in the development of sub-clinical primary exercise dependence, and that conflict avoidance and maintenance of a positive self-concept can precipitate obsessive-compulsiveness. Finally, a perceived benefit of exercise was shown to be an integral component of dependence.
- 著者
- 満下 健太 村越 真
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19048, (Released:2020-01-10)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 野球の打撃におけるローリングの速さを決定する力学的要因
- 著者
- 谷中 拓哉 近田 彰治 矢内 利政
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.16056, (Released:2017-01-24)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A wide range of topspin rotation of a bat around the long-axis, referred to as “rolling”, has been observed in baseball batting, but the mechanical reasons for the large variability among individual batters has not been examined. The purpose of this study was to investigate the factors determining this variability in rolling velocity among professional baseball players. Twenty-nine professional batters each performed eight “free-batting” trials. An electromagnetic tracking device was used to measure the three-dimensional rotational motion of the bat in each trial. The rolling velocity was 678±376°/s, comprised a negative contribution attributable to the batter's effort of exerting torque (Mechanism 1; −1144±488°/s) and a positive contribution attributable to the gyroscopic effect (Mechanism 2; 1808±339°/s). A significant positive correlation (r=0.67, p<0.05) was found between the rolling velocity and the negative contribution of Mechanism 1. These results indicate that (a) the torque exerted by the batter resists the rolling and that (b) a higher rolling velocity is attained by batters who exert a smaller resistive torque on the bat than those who exert a larger torque. On the other hand, no correlation (r=0.09) was found between the rolling velocity and positive contribution of mechanism 2. These findings suggest that the batter makes an active effort to resist rolling, and that the amount of resistive torque exerted by the batter is the primary reason for the inter-individual difference in rolling velocity attained at the instant of ball impact. As the resistive torque is likely to be exerted by the nobside hand in the form of pronation torque (Ae et al. 2015) and the pronation causes lowering of the bat-head (increasing nutation angle), a reduction of the pronation torque should decrease the resistive torque acting on the bat, helping to attain a high rolling velocity. In fact, we observed a greater deceleration of nutation velocity in the fast-rolling group than in the slowrolling group (p<0.05). To attain the high rolling velocity, therefore, we suggest that batters should aim to build up the nutation velocity of the bat until about 50 ms before ball impact, and then vigorously decelerate it immediately before ball impact.
- 著者
- 大峰 光博
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.629-637, 2016
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The purpose of this study was to analyze problems related to the mechanism whereby students can accept corporal punishment during extracurricular sports activities with reference to the books <i>Escape from Freedom</i> and <i>Man for Himself</i> that were central to Erich Fromm's authority theory. Specifically, the author focused on the concepts of “authoritarian character,” “authoritarian ethics,” and “authoritarian conscience.” Fromm pointed out that anxiety prompted Germany's citizens to give up their freedom in order to obey authoritarian powers such as Hitler and the Nazis.<br> Students taking part in extracurricular sports activities were considered from the viewpoint of Fromm's authority theory. It was revealed that students comply with a leader's authority in order to relieve anxiety, and have positive thoughts about corporal punishment. Furthermore, it was found that such acceptance of corporal punishment succeeded in eliminating conspicuous suffering, but not in removing any underlying conflicts.<br> Fromm pointed that fear of anxiety was relieved by spontaneous activity. To achieve spontaneous activity by students, it was suggested that some form of measure that does not create the type of partnership that occurred between Germany's citizens and Hitler would be desirable for any relationship between the leader of extracurricular sports activities and the students.<br>
1 0 0 0 OA ベンチプレスの筋電図学的研究
- 著者
- 中川 宏 熊本 水頼
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.2, pp.83-89, 1973-10-25 (Released:2017-09-27)
ウェイトリフティングの選手について, ベンチプレスを行なわせたときの筋の作用機序について筋電図学的に検討した. 1) 手関節の姿勢制御を示すような筋の働きは認められなかった. 2) 肘関節はただ単純に伸展を行なっているだけで, 姿勢制御を示す筋の働きは殆んど認められなかった. 3) 筋力に余裕のあるとき, 肘関節伸展は上腕三頭筋外側頭のみで行なわれ, 筋力の劣るときは同筋長頭も参画した. 長頭の収縮がもたらす肩関節伸展の力は, 肩関節屈曲筋群の活動の増強で消却された. 4) 肩関節は水平位内転と屈曲の合成された動きを示す筋放電様相を呈した. 5) 挙上能力の劣るものには, 無駄な, かつまた抑制的と考えられる筋放電も認められた.
- 著者
- 堀井 千代鶴 長田 一臣
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.1, 1959
1 0 0 0 OA 野球の投手の投動作の3次元動作解析
- 著者
- 桜井 伸二 池上 康男 矢部 京之助 岡本 敦 豊島 進太郎
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.2, pp.143-156, 1990-09-01 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 10 6
Many joint actions are involved in the throwing motion of a fastball pitch; therefore, two dimensional (2-D) procedures are insufficient for analyzing the throwing motion. In this study,three dimensional (3-D) high-speed cinematography was used to record fastball pitches of varsity baseball pitchers. Two small reference sticks were fixed on the hands and forearms of the throwing arm of the subjects to detect their movements.The direct linear transformation (DLT) method was used for 3-D space reconstruction from 2-D images filmed by two from 2-D images filmed by two phase-locked cameras (200 frames/s).The throwing arm has seven degrees of freedom of joint motion except in the fingers; three for the shoulder, one for the elbow, one for the radioulnar, and two for the wrist. Following seven joint angle changes corresponding to all these degrees of freedom were obtained throughout the pitching motion. 1) horizontal abduction/horizontal adduction angle at the shoulder joint, 2) abduction/adduction angle at the shoulder joint, 3) internal rotation/external rotation angle at the shoulder joint, 4) flexion/extension angle at the elbow joint, 5) pronation/supination angle at the radio-ulnar joint (forearm), 6) radial flexion/ulnar flexion angle at the wrist joint, 7) palmar flexion/dorsi flexion angle at the wrist joint. The results showed that horizontal adduction and internal rotation of the shoulder,extension of the elbow, pronation of the forearm, and palmar flexion of the wrist were the important joint actions for fastball pitching in baseball. Preliminary to these motions were motions in the opposite direction; e.g., horizontal abduction and external rotation of the shoulder,flexion of the elbow, supination of the forearm, and dorsi flexion of the wrist were detected.These motions in the opposite direction would be useful to extend the range of the motion in each joint angle. The results also appear to be connected to intrinsic muscle propertios, that greater power can be exerted during shortening of the muscle when it is stretched just before the shortening action.
1 0 0 0 OA 野球の投球動作におけるボール速度に対する体幹および投球腕の貢献度に関する3次元的研究
- 著者
- 宮西 智久 藤井 範久 阿江 通良 功力 靖雄 岡田 守彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.1, pp.23-37, 1996-05-10 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 7
We investigated the contribution of the motions in the upper torso and the throwing arm joints to the ball velocity during the baseball throw. The ball velocities caused by the anatomical rotations at the upper torso, shoulder, elbow, wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints were calculated as the vector products between the anatomical angular velocity vectors of joints and the respective relative displacement vectors from the joint centers to the center of ball, by using a mathematical model reported by Sprigings et al. (1994). Horizontal throws of twenty-four male university baseball players were filmed using a three-dimensional DLT method. In order to verify the ball velocities obtained from the anatomical joint rotations from the instant of the stride foot contact to the ball release, the velocity of ball measured directly from video recording was compared with that calculated by the mathematical model. A good agreement was acquired between the velocity of ball measured and that calculated. The velocities obtained from the left-rotation, flexion at the upper torso joint and the horizontal flexion at the shoulder joint contributed to the ball velocity in the early phase where the increase of ball velocity was slow. The velocities obtained from the internal-rotation at the shoulder joint, extension at the elbow joint, palmar-flexion at the wrist joint, and left-rotation/flexion at the upper torso joint contributed in the late phase where the increase of ball velocity was rapid. At the ball release, the contribution of each joint, which is the ratio of the positive ball velocity obtained from the anatomical joint rotations to the summation of individual positive ball velocities was as follows; 34.1% by the internal-rotation at the shoulder, 17.7% by the palmar-flexion at the wrist, 15.2% by the extension at the elbow, and 9.6% by the left-rotation at the upper torso joint.