- 著者
- 小宮 勲 白坂 崇 梅津 芳幸 橘 昌幸 泉 隆
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.2, pp.270-277, 2004
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 12 14
In this study, we investigated the usefulness of the fluorescent glass dosimeter for measuring patient dose. The fluorescent glass dosimeter is constructed of a glass element and its holder. One type has a tin (Sn) filter and the other does not. The characteristics of these two types of fluorescent glass dosimeters were studied in the range of diagnostic X-ray energy. The result was excellent for each characteristic. Directional dependency, however, was recognized in the fluorescent glass dosimeter with tin (Sn) filter. Based on these evaluations, patient skin dose was measured for abdominal interventional radiology and diagnostic digital subtraction angiography using the holder without filter, which is less direction-dependent and eliminates obstructive shadows in radiography and fluoroscopy. The average skin dose of 30 patients for abdominal IVR was 1.17±0.44 Gy (0.51-1.94 Gy), while those for diagnostic DSA examination was 0.54±0.21 Gy (0.15-1.02 Gy). The fluorescent glass dosimeter provides high capability for skin dose measurement. The fluorescent glass dosimeter is also useful for controlling patient dose during IVR procedures.
4 0 0 0 医療用放射性廃棄物の課題とは何か?
- 著者
- 福永 晃太 藤原 康博 圓崎 将大 小味 昌憲 平井 俊範 東 美菜子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2023-1378, (Released:2023-08-07)
- 参考文献数
- 24
【目的】Voxel-based quantification (VBQ) smoothingは,Montreal Neurological Institute標準空間上の定量画像に対する平滑化方法の一つである.VBQ smoothingは,組織境界の定量値の変化を抑制する特徴をもつが,脳の緩和時間マップに適用する際に緩和時間の変化をどの程度抑制できるかは明らかになっていない.本研究の目的は,緩和時間マップに対するVBQ smoothingの有用性を明らかにすることである.【方法】健常者20名を対象に2D multi-dynamic multi-echo sequenceを用いて脳を撮像し,緩和時間(T1値,T2値,プロトン密度)画像を取得した.緩和時間マップのカーネルサイズを1から6 mmまで変化させてVBQ smoothingとGaussian smoothingを適用し,脳組織を対象に平滑化後の緩和時間の変化を評価した.【結果】VBQ smoothingを適用した緩和時間マップは,Gaussian smoothingと比較して平滑化による緩和時間の変化が小さかった.また,カーネルサイズの増加に伴う緩和時間の変化は,Gaussian smoothingと比較して小さかった.そのため,VBQ smoothingは,緩和時間マップに対して平滑化を行う場合,Gaussian smoothingよりも緩和時間の変化を小さくできることが示された.【結語】VBQ smoothingは,平滑化による緩和時間の変化を抑制でき,緩和時間マップに対して有用な平滑化方法である.特に緩和時間が大きく異なる組織が隣接する領域で有用性が高い.
3 0 0 0 OA 表計算ソフトウェアを利用したCT検査における線量管理ツールの開発
- 著者
- 佐藤 顕広 古屋 聖兒
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.2, pp.142-150, 2023 (Released:2023-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 8
【目的】表計算ソフトを用いてCT(computed tomography)検査における照射線量管理ツールを作成し,実用化への可能性を検証する.【方法】2020年4月から2022年4月までの期間において,当院で実施したCT検査2,128人のうち,体重が50–70 kgの患者1,212人を対象にデータを解析した.データは,CT装置から出力される操作卓画面情報を利用した.データの入力は手動で行った.照射線量の評価は,Japan DRLs 2020(National Diagnostic Reference Levels in Japan 2020)を参考に,箱ひげ図や散布図を用いて行った.【結果】Japan DRLs 2020と比較して,当院における照射線量が高すぎたり低すぎたりすることはなかった.また,外れ値として照射線量の検証を行った件数が7例存在したが,そのうち,データの入力ミスが3例であった.したがって,その他4例について外れ値となった原因を追求した.【結語】本ツールを利用することで,CTDIvolとDLPの分析をすることができたと考える.更に,外れ値として原因追求を行った4例については,放射線診療の正当性と最適化の概念を逸脱するものではなかった.
3 0 0 0 OA MRIの安全性(<シリーズ>MR)
- 著者
- 宮地 利明
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.12, pp.1508-1516, 2003-12-20 (Released:2017-06-30)
- 参考文献数
- 68
- 被引用文献数
- 9 9
3 0 0 0 OA 頭部CT撮影における頭部固定具が画質と線量に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 横町 和志 西丸 英治 藤岡 知加子 木口 雅夫 石風呂 実 船間 芳憲 粟井 和夫
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.10, pp.1166-1172, 2014 (Released:2014-10-20)
- 参考文献数
- 13
Purpose: For emergency or pediatric head CT scans, a simplified pillow made of hard sponge instead of a dedicated head holder may be used if it is difficult to immobilize the head. However, the radiation dose when using a simplified head holder may be increased due to radiation absorption by the patient couch if the automatic exposure control (AEC) system is used. In this phantom study, we compared the radiation dose delivered when using a dedicated and a simplified head holder. Materials and Methods: We used a dedicated-type and a pillow-type head holder made of hard sponge (simplified head holder). We placed a 20 cm-diameter cylindrical phantom made of water-equivalent material and an anthropomorphic head phantom in the head holders and then scanned them five times with a 64-detector CT scanner (VCT, GE Healthcare). We performed step-and-shoot and helical scanning with AEC; the noise index was set to 2.8. We measured the radiation dose using fluorescent glass dosimeters in the head phantom and the image noise at five sites in the cylindrical phantom. All values were averaged. Results: With step-and-shoot scans, the mean image noise with the dedicated and the simplified head holder was 3.30 ± 0.05 [SD] and 3.20 ± 0.05, respectively. With helical scans they were 3.00 ± 0.09 and 2.88 ± 0.03, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference (p = 0.02 and 0.04, Student’s t-test). The radiation doses with the dedicated and the simplified head holder were 58.6 and 70.4 mGy, respectively, for step-and-shoot scanning and 41.8 and 49.0 mGy, respectively, for helical scanning. The doses were thus significantly higher with the simplified head holder for both step-and-shoot and helical scanning (p < 0.01 and < 0.01). Conclusion: We recommend the use of a dedicated head holder for head scanning with AEC since the radiation dose was lower than with the simplified head holder.
- 著者
- 齋藤 俊輝 町田 好男 宮本 宏太 一関 雄輝
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.11, pp.1080-1089, 2015 (Released:2015-11-20)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 4 2
As an acceleration technique for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), compressed sensing MRI (CSMRI) was introduced recently to obtain MR images from undersampled k-space data. Images generated using a nonlinear iterative procedure based on sophisticated theory in informatics using data sparsity have complicated characteristics. Therefore, the factors affecting image quality (IQ) in CS-MRI must be elucidated. This article specifically describes the examination of the IQ of clinically important MR angiography (MRA). For MRA, the depictability of thin blood vessels is extremely important, but quantitative evaluation of thin blood vessel depictability is difficult. Therefore, we conducted numerical experiments using a simple numerical phantom model mimicking the cerebral arteries so that the experimental conditions, including the thin vessel positions, can be given. Results show that vessel depictability changed depending on the noise intensity when the wavelet transform was used as the sparsifying transform. Decreased vessel depictability might present difficulties at the clinical signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) level. Therefore, selecting data acquisition and reconstruction conditions carefully in terms of the SNR is crucially important for CS-MRI study.
- 著者
- 池口 裕昭 庄内 孝春 渡部 智仁 縄手 満 矢野 竜太朗
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.76, no.12, pp.1256-1265, 2020 (Released:2020-12-20)
- 参考文献数
- 14
T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) using inversion recovery pulse to suppress cerebrospinal fluid signal needs adequate T1 recovery time after data acquisition, otherwise, the T2-weighted contrast in brain tissue will get lower. Over 10000 ms of repetition time (TR) is recommended for the 1.5 T MR scanner, so it is difficult to shorten the imaging time. We verified whether T2 FLAIR combined with the magnetization transfer contrast (MTC) pulse shows better gray-to-white matter (GM/WM) and lesion-to-normal tissue contrasts even when the TR is shortened compared to the conventional T2 FLAIR. Optimal parameters of the MTC pulse were determined with a self-produced phantom, which modeled on cerebral cortical gray and white matters. GM/WM contrasts of the phantom were measured in T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse while decreasing TR gradually from 10000 ms to 6500 ms. Although GM/WM contrast of the phantom in T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse gradually decreased as the TR got shortened, the T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse of 6500 ms of TR still showed 27% higher contrast than the conventional T2 FLAIR (TR 10000 ms). GM/WM contrast in T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse was improved also in healthy volunteers, but improvement in thalamo-medullary contrast was less than that of cerebral cortico-medullary and putamino-medullary contrasts. It seems to be because thalamus, which is a deep gray matter, shows a higher MTC effect than other gray matters. Thus, it is necessary to note that the tissue contrast might differ between T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse and the conventional T2 FLAIR. Because general lesions with an elongated T2 value show lower MTC effect compared to the normal brain tissue, a clinical case with thalamic lesion showed that the lesion-to-normal tissue contrast improved in T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse of 6500 ms of TR. Although it is necessary to note the difference in contrast between some tissues, T2 FLAIR with the MTC pulse improves GM/WM and lesion-to-normal tissue contrasts even when the TR is shortened compared to the conventional T2 FLAIR, and it enables to shorten the imaging time.
3 0 0 0 OA 血管造影用耐圧チューブの膨張に関する基礎的検討
- 著者
- 川崎 達哉 加藤 英幸 笠原 哲治 田岡 淳一 梅北 英夫 桝田 喜正
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.76, no.3, pp.278-284, 2020 (Released:2020-03-20)
- 参考文献数
- 18
This study was designed to clarify the relation between the pressure resistance of an angiographical tube and the amount of contrast medium injected under a connected microcatheter used for interventional radiology (IVR). We investigated the injection pressure and the expansion rate at the center of the tube during contrast enhancement by setting the power injector to 1200 PSI pressure, with 2.0 ml/s injection speed, 10 ml injection volume, 5.0 s injection time, and 0 s rise time for tubes with different pressure resistance performance (low or high). Then we examined the amount of contrast medium material discharged from the microcatheter. The low-pressure resistant tube (less than 140 PSI) injection pressure exceeded the pressure performance. The expansion rate increased to 49%, presenting a risk of rupture. The injection pressure of the high-pressure resistant tube (less than 1200 PSI) was within the pressure-resistance performance. The expansion rate increased to 38%. However, when the contrast medium discharge amount contributing to the image was measured within the injection time under the condition of 10 ml injection for 5.0 s, the former was 2.3 ml and the latter was 4.2 ml. The entire amount was not discharged during the injection period. It became apparent that it is discharged in drips after some time. Results show that the tube expansion caused retention of the contrast medium inside, which decreases the actual amount of the injected contrast medium. From the results, we infer the possibility of preventing reduction of the injected contrast medium amount attributable to expansion.
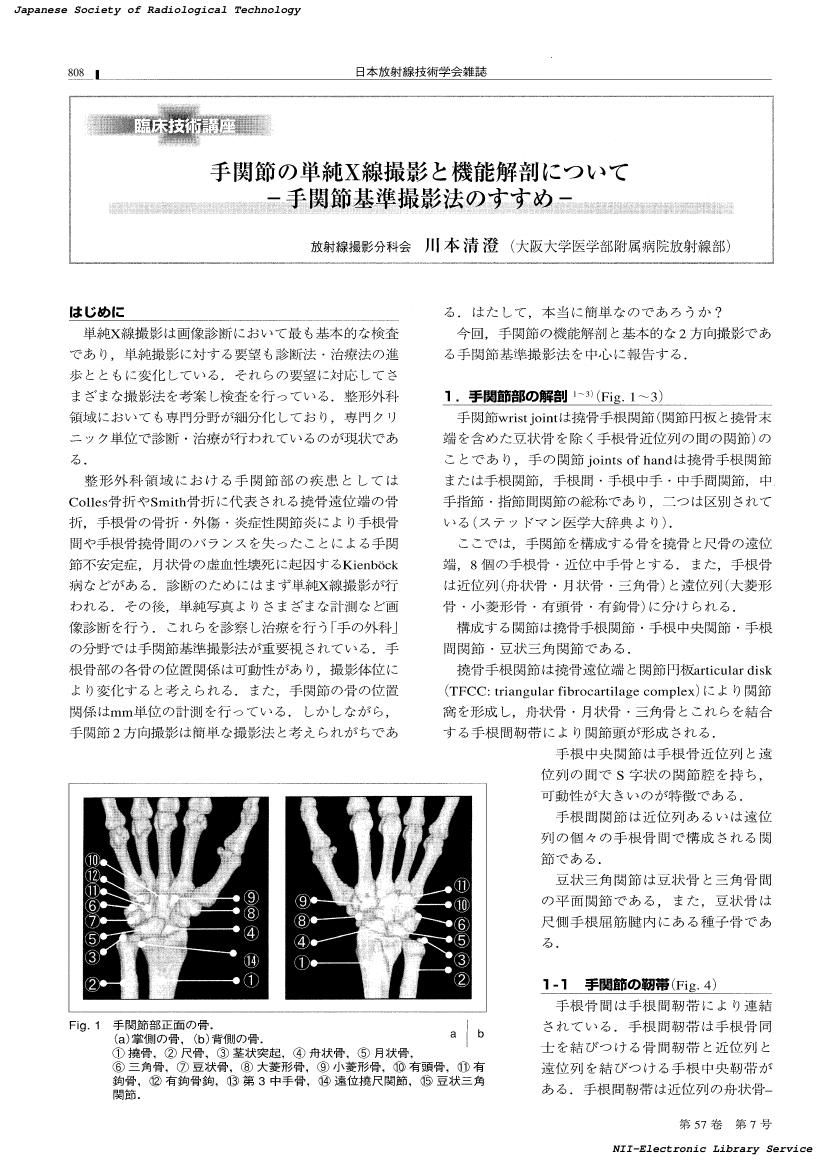
3 0 0 0 OA 手関節の単純X線撮影と機能解剖について : 手関節基準撮影法のすすめ
- 著者
- 川本 清澄
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.7, pp.808-813, 2001-07-20 (Released:2017-06-30)
- 参考文献数
- 8
3 0 0 0 OA 診療放射線技師養成課程における超音波検査に関する教育の特徴:臨床検査技師養成課程との相違
- 著者
- 元日田 和規 田川 まさみ 池田 賢一 福士 政広 亀岡 淳一
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.8, pp.979-985, 2012-08-20 (Released:2012-08-24)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Radiological technologists (RTs) and medical technologists (MTs) are legally allowed to work as sonographers performing medical ultrasound examination. Despite the total number, much fewer RTs work as sonographers than MTs. To explore the reason, we investigated educational programs, universities, and colleges for both specialties. First, we established five categories of sonographers’ competency: 1) Anatomy for imaging diagnosis, 2) Diseases and diagnosis, 3) Imaging, 4) Structure and principle of the equipment, and 5) Evaluation of image quality, using competence reported by the International Society of Radiographers and Radiological Technologists (ISRRT) and diagnostic competency required of sonographers in Japan. Using these categories, we analyzed the content and total instruction time by lectures and seminars based on information written in the syllabi, and explored the differences in education related to sonographers’ competency in both programs. “Anatomy for imaging diagnosis” was taught in 15 RT programs (93.8%), and 6 MT programs (31.6%). “Diseases and diagnosis” was taught in 13 RT programs (86.7%), and 8 MT programs (53.3%). “Imaging” was taught in 14 RT programs (100%), and 13 MT programs (76.5%). “Structure and principle of the equipment” was taught in 12 RT programs (85.7%), and 6 MT programs (31.6%). “Evaluation of image quality” was taught in 11 RT programs (84.6%), and 3 MT programs (15.0%). The average instruction time for RT was longer than for MT programs in all categories. RTs are educated and have a foundation to be sonographers at graduation, and may have the possibility to expand their career in this field.
3 0 0 0 IR 蛍光ガラス線量計を用いたナロービームにおける線量の高度評価に関する研究班報告
- 著者
- 荒木 不次男 守部 伸幸 下之坊 俊明 吉浦 隆雄 池上 徹 石戸谷 達世
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.7, pp.939-947, 2004
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
近年,リニアック装置を用いた頭部の定位放射線照射(stereotactic irradiation : STI,これにはSRSとSRTが含まれる),ガンマナイフ装置による定位手術的照射(stereotactic radiosurgery : SRS),サイバーナイフ装置による定位放射線治療(stereotactic radiotherapy :SRT)が急激な勢いで普及している(現在,サイバーナイフ装置は稼動停止状態である).さらに北米では,サイバーナイフの出現によりSRTは頭部のみならず体幹部にまで普及しはじめている.わが国においても一部の施設では,リニアック装置による動体追跡による高精度なSRTが試みられている.しかしながら,これらの定位放射線照射で用いられる極小照射野であるナロービームに問しては,十分に線量評価が確立されていないのが現状である.特に10mm以下の照射野に関しては,現在フィルムや半導体検出器などが利用されているが,フィルムでは濃度-線量変換の精度の問題,半導体検出器においてもエネルギー依存性や方向依存性などの問題があるため,より精度の高い検出器の開発が求められている.本研究班の目的は,初期の蛍光ガラス線量計に新かな技術的改良を加えて最近開発された蛍光ガラス線量計^<1,2)>を用いて,現在不可欠な放射線治療となってきているナロービームを用いた定位放射線照射の高精度な線量評価を確立することである.蛍光ガラス線量計は熱蛍光線量計(thermoluminescence dosimeter : TLD)に代わる新たな検出器として期待されているが,高エネルギー放射線治療領域の線量評価に対する報告はまだ少ない.本研究班報告書では,1)蛍光ガラス線量計の高線量モードにおける物理特性の評価,2)リニアック,サイバーナイフ,ガンマナイフ装置のナロービームの出力係数の評価について報告する.特に出力係数の評価については,現在一般的に使用されている他の検出器との比較から蛍光ガラス線量計の有用性について明らかにする.
3 0 0 0 救急車の過ち
- 著者
- 樋口 範雄
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.5, pp.655-657, 2008 (Released:2008-05-29)
抄録はありません.
3 0 0 0 OA イメージングプレートの放射能汚染による黒点計数法の開発
- 著者
- 林 裕晃 西原 貞光 小沼 洋治
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.5, pp.545-553, 2012-05-20 (Released:2012-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Due to accidents of the nuclear power plants in Fukushima prefecture, a lot of radioisotopes were diffused into the environment. They adhered onto the surface of the X-ray detector (imaging plate; IP) and many black spots were seen on the medical images. The process to count them is important to evaluate the degree of contamination and/or removal. In this study, we aimed to develop a counting method for black spots. Based on the analysis of the medical images having black spots, we summarized that areas affected by the certain black spots were limited to the eight pixels surrounding the most intensive pixel. The newly developed counting method was applied to these nine pixels (3×3 pixels) and selection rules were based on the following two information: 1. differences between the digital value of the most intensive pixel and those of the surrounding eight pixels, and 2. total summation of the digital values in the nine pixels. The estimated image based on our method showed a good concordance with the original image. Therefore, we summarized that our counting method is a powerful tool for estimating numbers of black spots.
3 0 0 0 費用効用分析とQOL
- 著者
- 小笠原 克彦
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.7, pp.791-795, 2007-07-20 (Released:2007-10-04)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 4 1 1
(抄録はありません)
- 著者
- 輪嶋 隆博
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.11, pp.1404-1409, 2008-11-20 (Released:2008-12-06)
- 参考文献数
- 15
2 0 0 0 OA EOB-MRI検査における肝ドーム下呼吸停止拡散強調画像の有用性
- 著者
- 大谷 昂 金本 雅行 尾崎 公美 谷内田 拓也 松田 祐貴 木戸屋 栄次
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2023-1380, (Released:2023-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 23
【目的】肝臓のmagnetic resonance imaging(MRI)検査において,全肝の呼吸同期併用拡散強調画像(respiratory-triggered-diffusion-weighted imaging: R-DWI)は磁場不均一の影響により肝臓頭側の横隔膜ドーム下の画質低下が問題となる.そこでドーム下に範囲を絞った呼吸停止下DWI(breath-hold-DWI: B-DWI)の追加撮像の有用性を検討した.【方法】3.0 TのMR装置を使用し,2022年7月から8月に当院でethoxybenzyl(EOB)-MRI検査を受けた22例(男性14名,女性8名,平均年齢69.0±11.7歳)を対象とした.R-DWIとB-DWIのドーム下の視認性について放射線科医1名と放射線技師3名で4段階(1~4点)での視覚評価を行った.また,各DWIのapparent diffusion coefficient(ADC)値を比較した.【結果】R-DWIと比較してB-DWIではドーム下の視認性が向上した(2.67±0.71 vs. 3.25±0.43, p<0.05).各DWIのADC値に有意差はみられなかった(p>0.05).【結語】B-DWIはドーム下の視認性に優れ,R-DWIを補完する役割が期待できるため,EOB-MRI検査において追加撮像する有用性は高い.
2 0 0 0 OA ディジタル時代の画質と線量 : 低線量CTと画質
- 著者
- 船間 芳憲
- 出版者
- 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.11, pp.1461-1467, 2011-11-20
低線量で増加する画像ノイズ、X線量低減の有効策である低管電圧CTと逐次近似画像再構成法について概説する。
2 0 0 0 OA DLP-実効線量換算係数の精度評価と問題点の検討
- 著者
- 小林 正尚 大塚 智子 鈴木 昇一
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本放射線技術学会
- 雑誌
- 日本放射線技術学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694305)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.1, pp.19-27, 2013-01-20 (Released:2013-01-25)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 9 10
The purpose of this paper is to reappraise the accuracy of a conversion coefficient (k) reported by International Commission on Radiological Protection Publication 102 Table A.2. The effective doses of the routine head computed tomography (CT), the routine chest CT, the perfusion CT, and the coronary CT were evaluated using the conversion coefficient (adult head: 0.021 mSv·mGy-1·cm-1, adult chest: 0.014 mSv·mGy-1·cm-1). The dose length product (DLP) used the value displayed on the console on each scanning condition. The effective doses were evaluated using a human body type phantom (Alderson Rando phantom) and thermoluminescent dosimeter (TLD) elements for comparison with the converted value. This paper reported that the effective doses evaluated from conversion coefficient became different by 0.3 mSv (17%) compared with measurements, the effective dose computed with the conversion coefficient of the adult chest may be underestimated by 45%, and the bolus-tracking which scans the narrow beams should not use a conversion coefficient.