1 0 0 0 OA 運動熟練者におけるパフォーマンス能力の違いについて:注意の向け先と運動イメージからの検討
- 著者
- 成田 秀美 鈴木 健一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.773-780, 2016 (Released:2016-12-14)
- 参考文献数
- 17
Focusing on the effects of exercise (external focus) is considered more effective for improving motor performance than focusing on one's own physical movements (internal focus). Furthermore, it has been confirmed that imaging the movement being performed is effective for mental training. The purpose of this study was to investigate differences in performance ability among experienced athletes on the basis of their focus orientation and motor imagery of movements, with the aim of using the findings as basic data for sports coaching. The subjects comprised 16 males who had experience playing basketball. Each subject performed 30 free throws. In addition, a questionnaire survey was conducted regarding their focus orientation and motor imagery of movements (movement imagery questionnaire-revised Japanese version). The subjects were divided into a successful group, who achieved above the mean successful free-throw score, and an unsuccessful group, who achieved below the mean score. The results indicated that many subjects in the successful group used external focus, which demonstrated a correlation with the imaging ability of observed movements. These findings suggest that when coaching experienced athletes who are performing poorly, one may consider encouraging them to focus on the effects of each movement and motor imagery of observed movements to improve their performance.
1 0 0 0 OA 「無気力試合」の問題性: 「失敗した試合」に関する論議を参考として
- 著者
- 大峰 光博
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.2, pp.539-546, 2018-12-10 (Released:2018-12-20)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
The purpose of this study was to present a new perspective on the problem of attempting to lose a game on purpose through a consideration of whether doing so threatens the existence of sport. We began by hypothesizing the concept of “failed athletic contests”, which has been discussed in the field of sport philosophy, as jeopardizing the existence of this activity. We then examined the concept of “losing games on purpose” with reference to the “failed athletic contests” theory of Kawatani (2013). We examined 2 broad categories of “losing games on purpose”: one where defeat is clearly the goal, and the other where players deceive referees and spectators by behaving as though they want to win, while in fact actually trying to lose. Kawatani claims that games where an ethos (internal purpose) is not achieved, even though the contest is based on athletes playing according to the rules, constitute “failed athletic contests”. He found that player commitment to winning is necessary as a condition in achieving the ethos of the game, suggesting that “losing games on purpose”in either category constitutes a “failed athletic contest” in that athletes are not committed to victory and the ethos is not established. On the other hand, it was also clarified that there is a dilemma for players in athletic meets when a commitment to winning is called for, but when this is occasionally in conflict with the ethos of individual games. For the second category, it was also revealed that referees and spectators were not aware of the nature of such a defeat when it was concealed. This suggests that the second category of “losing games on purpose” is more problematic than the first.
- 著者
- 林 洋輔
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.14035, (Released:2015-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 56
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
In the present study, an attempt was made to clarify the whole structure and originality of Taiiku-gaku (Science of PE, Health and Sport Sciences), centering on the ‘tree of sciences’ theory of René Descartes (1596-1650). In the study of physical education philosophy, some attempts have been made to reveal the whole structure and originality of Taiiku-gaku. It seems more appropriate to discuss and address this issue by defining certain principles at the outset. For this purpose, it would informative to examine this issue from the philosophical perspective of Descartes’ ‘tree of sciences’ philosophy. In the history of discussion to clarify the whole structure and originality of Taiiku-gaku among researchers, three essential characteristics become evident: (1) Science should be aimed at being practical and useful, (2) it should contribute to our well-being, and (3) it should aid the search for wisdom. Up to now, it appears that Taiiku-gaku as a science has advanced in line with these characteristics. However, Descartes revealed his vision of the purpose of science through the “tree of sciences” in his Principia Philosophiae (Principles of Philosophy). He analogized the whole structure of science (philosophy) to a tree with its roots, trunk, branches and fruit. The present paper therefore utilizes this concept of Descartes to answer the question. In conclusion, the whole structure of Taiiku-gaku could be understood as being analogous to a tree, and the originality of Taiiku-gaku does not depend on humans themselves or human movement as a fundamental research object. The originality of Taiiku-gaku can be analogized with the achievement of Generosity, which is the goal of the “tree of sciences”. Thus, on the basis of output diversity analogous to fruit taken from branches of the tree, the originality can be characterized as a science that tries to achieve the highest performance of human movement imaginable. More enlightened discussion can ensue by reconsidering the concept of taiiku (which is different from Physical Education) and the identity of Taiiku-gaku researchers.
- 著者
- 比留間 浩介 尾縣 貢
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.1101140174, (Released:2011-01-15)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 2 4
The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of physical fitness in baseball pitchers and infielders focusing on variations in power output ability and stretch-shortening cycle (SSC) ability in field tests. Twenty-five male university pitchers and 22 university infielders participated. They performed five kinds of jumping (Standing triple jump (STJ), Standing double leg triple jump (SDTJ), Standing long jump (SLJ), Counter movement jump (CMJ), 5 rebound jumps (RJ)), and five kinds of medicine ball throw (Overhead throw (OT), Back throw (BT), Push of upper limb (Push), Shoulder horizontal adduction (SHA) and Twist of trunk throw (Twist)). Push, SHA and Twist were performed purely concentrically (concentric throw: CT) and with SSC movement (rebound throw: RT). These powers were assessed using the Throw index (Tauchi et al., 2006), and pre-stretch augmentations (Walshe et al., 1996) were calculated. It was found that: 1) OT, BT and SDTJ in pitchers were significantly higher than in infielders, and that there were significant correlations between pitched ball speed and OT, BT, and SDTJ. 2) Push RT-index and Push CT-index in infielders were significant higher than in pitchers, and significant correlations were found between thrown ball speed, batted ball speed and Push RT-index and Push CT-index in infielders. 3) SHA augmentation in infielders was significantly higher than in pitchers, and there was a significant correlation between thrown ball speed and SHA augmentation in infielders. 4) Twist of trunk power did not differ between pitchers and fielders. These results indicate that baseball pitchers and infielders obtain different physical fitness characteristics through the differences in their movement forms and required abilities.
1 0 0 0 OA 柔道の礼法における戦中・戦後史
- 著者
- 中嶋 哲也
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.20155, (Released:2021-07-10)
1 0 0 0 OA 呼吸様式が重心位置と浮心位置に与える影響:水泳における水平姿勢維持への示唆
- 著者
- 丸山 祐丞 近田 彰治 矢内 利政
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.2, pp.641-651, 2012 (Released:2012-12-05)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 4 3
The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that the position of the center of buoyancy (CB) relative to the center of mass (CM) lay more caudally when the abdominal breathing technique is used, as compared with the chest breathing technique. Ten healthy men who practiced the abdominal and chest breathing techniques participated. The position of the CB, CM, and the distance between them (CB-CM distance) were determined as time-series data during inhalation with each breathing technique, and the changes in the positions and distance due to inhalation were compared between the two techniques. The results showed that both the CB and CM translated due to the inhalation and that the amount and direction of the translations differed between the two techniques (p<0.01). The increase in the CB-CM distance was significantly smaller (p<0.01) with abdominal breathing (1.11 cm) than with chest breathing (1.21 cm). For both breathing techniques, the CB was located more cranially to the CM, regardless of the amount of inhalation. These data demonstrate clearly that the position of the CB relative to the CM lies more caudally with the abdominal breathing technique than with chest breathing, thus supporting our hypothesis. These results indicate that breathing technique influences the magnitude of the moment of buoyant force around the CM and the swimmer's ability to float horizontally on the water surface.
1 0 0 0 OA 打点高の異なる野球ティー打撃動作における体幹のキネティクス的分析
- 著者
- 阿江 数通 小池 関也 川村 卓
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.2, pp.635-649, 2015 (Released:2015-12-18)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 8 2
The purpose of this study was to clarify the kinetic features of the trunk under different hitting-point height conditions (high, middle, and low) in baseball tee-batting. Twenty-three collegiate male baseball players (age: 19.8±1.3 yr, height: 1.74±0.04 m, whole-body mass: 74.1±6.2 kg, athletic career: 12.0±2.1 yr) participated. Three-dimensional coordinate data were captured using a VICON-MX system (12 cameras, 250 Hz), and kinetic data for the individual hands were collected using an instrumented bat equipped with 28 strain gauges (1000 Hz). Three kinds of tee-batting heights were set for each participant based on the upper and lower limits of the strike zone according to the baseball rule. The torso was modeled with the rigid upper and lower trunk segments connected by a torso joint with three axes: the ante/retro flexion, right/left lateral flexion, and right/left rotation axes. Kinetic variables, e.g. joint force and torque, mechanical power, and mechanical work, were obtained by inverse dynamic calculation. These data were expressed for a right-handed batter and normalized by the time of the forward swing from the swing start to the ball impact as 0-100%, and the time was divided into down-swing and level-swing phases in order to evaluate the mechanical work. From the last half of down-swing phase until ball impact, the retroflexion torque under the low condition was significantly larger than those under other conditions. The left rotation torque and positive torque power showed particularly large values in the level-swing phase regardless of the hitting-point height. The mechanical energy flow generated by the torso joint torque showed inflow from the lower trunk to the upper trunk, and outflow from the upper trunk to the individual upper arms regardless of the height condition over the forward swing. In addition, there were significant positive correlations between the positive mechanical work done by the joint torque about the right/left rotation axis and the maximum bat-head speed during the level-swing phase under the middle and low conditions. These results indicate that 1) the ante/retro flexion axis torque is needed to maintain the configuration of the upper trunk against the large centrifugal force exerted along the bat around the moment of ball impact, 2) the right/left rotation axis torque contributes to the generation of the large mechanical energy, the transfer of energy to the upper limbs, and the generation of the bat-head speed regardless of the height condition.
- 著者
- 近藤 智靖 高橋 健夫 岡出 美則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.5, pp.533-543, 2005-09-10 (Released:2017-09-27)
Die "Laborschule" als ein Gesamtschulmodell in Bielefeld wurde 1974 gegrundet. Der Reformpadagoge Hartmut von Hentig leitete diese Schule und legte den Schwerpunkt auf eine "Erziehung zur Politik" und eine "Erziehung zur Verantwortung". Um diese Ziele zu erreichen, wurde die Laborschule zu einer "Curriculum-Werkstatt" weiterentwickelt. Weiterhin wurde groβer Wert auf die Idee von "Schule als Erfahrungsraum" und das gemeinsame Lernen von Schulern unterschiedlicher sozialer Herkunft gelegt. Von Hentig kritisierte die uberkommenen Bildungsprivi-legien und forderte eine gemeinsame und allgemeine Bildung fur alle Schuler. Hinter dieser Idee stand die Bildungsreform der 1960er und 70er Jahre in Deutschland. Der ursprungliche, von Reformpadagogen unterstutzte Gedanke dieser Reform war, dass die traditionellen sozialen Schichten sich verandern und alle Burger gleiche Bildungschancen haben sollten. Dieses Konzept hatte auch Einfluss auf den Bereich Sport in der Laborschule. Im Sportunterricht wurde darauf geachtet, dass die Schuler durch korperliche Erfahrung ihren eigenen Korper oder den anderer erfahren und an-nehmen. Um dieses Ziel zu erreichen, wurden nicht nur traditionelle Sportarten, sondern auch an-dere korperliche Aktivitaten in den Unterricht aufgenommen. Dadurch entstanden die Orientierung auf nicht-traditionelle Sportarten und die Korperorientierung im Sportunterricht. In dieser Arbeit geht es um das Verhaltnis von Bildungsreform, Laborschule und dem Bereich Sport in der Laborschule. Es wird analysiert, wie die reformorientierte Idee der Laborschule den Bereich Sport beeinflusste.
- 著者
- 内藤 貴司 山口 裕嗣 大柿 哲朗
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.103-113, 2016 (Released:2016-06-17)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
The timing at which ice is ingested prior to exercise may be important for optimizing internal pre-cooling effects. However, previous reports have not evaluated the influence of timing of ice ingestion on internal pre-cooling in the heat. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of differences in the timing of ice ingestion on endurance cycling capacity, body temperature and perceptional sensation during heat stress. Seven healthy males [age=26±2 yr, height=1.71±0.04 m, body mass=63.6±2.8 kg, surface area=1.74±0.03 m2, VO2max=49.7±4.4 ml・kg−1・min−1] ingested ice for 30 min before exercise under 3 separate conditions: ice ingestion at 30-(30D), 15-(15D) and 5-(5D) minute intervals. The total volume of ice ingestion was identical during 30D, 15D, 5D and was divided equally by the number of times drunk in each experiment. Subjects performed cycling to exhaustion at 70%VO2max in a hot environment (35℃ room temperature and 30% relative humidity). Rating of thermal sensation was lower in the 5D group at 15 min period during exercise than those under the other conditions (p<.05). Rating of perceived exertion was lower in the 5D group at 20 and 25 min periods during exercise than those under the other conditions (p<.05). There were no significant differences in rectal temperature, mean skin temperature or exhaustion time between the 3 conditions. These results suggest that there are no significant differences in exhaustion time or rectal temperature if the total volume of ice ingestion is identical, although ice ingestion until just before exercise attenuated the perceptual sensation of heat during exercise in a hot environment.
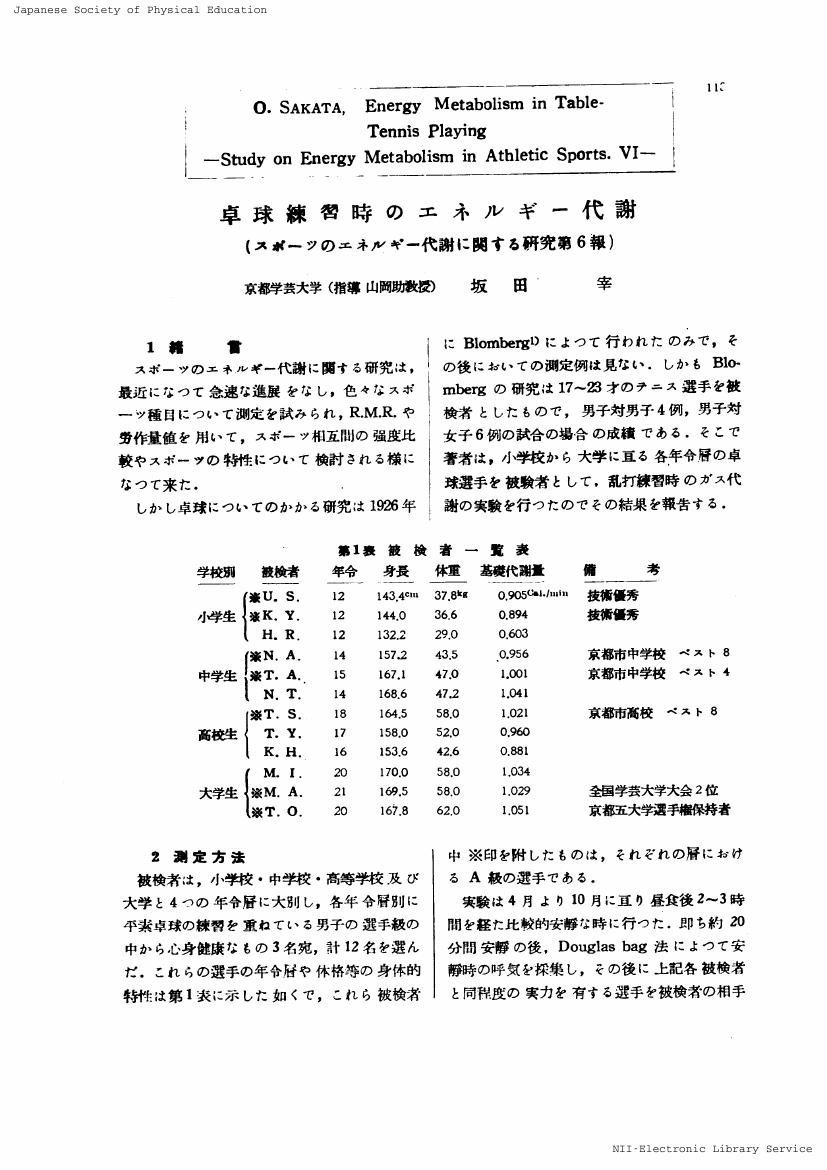
1 0 0 0 OA 卓球練習時のエネルギー代謝 : スポーツのエネルギー代謝に関する研究 第6報
- 著者
- 坂田 宰
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.3, pp.113-116, 1956-10-30 (Released:2016-12-31)
1 0 0 0 OA 近代体育とクーベルタン : 体育学の教育思想史
- 著者
- 清水 重勇
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3, pp.227-239, 2001-05-10 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Present paper aims to draw attention to the potential problem of the concept of body and culture, subsisting from the emergence of modern European physical education theory to the coming of P. de Coubertin's Olympism, in the realm of the French history of pedagogical philosophy, and to represent it as an origin of theoretical problem that our Society has been confronting with. The outline of discussion is as follows: 1. The education in the period of the Ancien regime looked Health or Physical performance as Moral profiles of particular beings. Body is attributed to private-ness. 2. On arrival of the Enlightment, Body, amalgamated with the Performance culture in the Ancien regime education, is conceived as the Physical, and it is the beginning of a peculiar type of theory for educating the Physical. 3. The Physical grasped by new pedagogy becomes not only a blank depriving the Body of its given traditional bases of Performance culture, but also a functional spot of the physics' time axis. 4. Guts Muths' pedagogy grappled with above conceptual problem of compatibility of the Physical as nature with the culture. His way of thinking provides our Society of Physical Education with the prototype. 5. Attempting to build up a practical moral science by rigid method of physical training and by codification of motorics, Amoros' pedagogy suffered from dilemma of "funambulism" which persisted between the highest exploitation of physical functions and the formation of moral conduct. 6. In the modem education theory, the problem of the Performance culture was requested retrospectively to the ancient Greek culture, while there were no alternatives during 19th century. 7. Looking for the deepest entity of the Physical, and deeply influenced by the philosophical trends of the 20th century, the New physical education theories came up to investigate the monistic totality of the non-intellectuals in the Physical, whereas it becomes more and more difficult to apprehend the humanity going over the scientifism and the philosophism. 8. P. de Coubertin's Olympism challenges to restore the Physical to the humanistic culture. He wrote a civilization history of 'sport instinct', on the other hand, he intended to describe psycho-motor representation tied the muscle up the awareness in order to identify proper live time axis of body with overarching historical time axis. This would be considered, however, as aggravation of the theoretical problem of modem education of the Physical and the Culture.
- 著者
- 志村 芽衣 宮澤 隆 矢内 利政
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.2, pp.487-500, 2019-12-16 (Released:2019-12-20)
- 参考文献数
- 16
The purpose of this study was two-fold; to determine the optimum impact condition for maximizing flight distance toward the opposite field and to examine the influence of the bat angles at impact on the batted ball characteristics (speed, rotation, and angle immediately after impact) and the flight characteristics (distance, trajectory, and time). Various impact conditions were defined using 3 factors: the angles of the bat at impact projected to the horizontal and vertical planes, and the vertical inclination angle of the line of impact (the product of the sine of this angle and the radius of the ball determines the under-cut distance). Three-dimensional finite element analysis was used to construct a model of impact between a baseball and a wooden baseball bat and to conduct simulation analysis. The initial flight condition of the batted ball after the impact was determined for each simulated condition, and the flight distance was estimated from the initial flight condition. The results showed that a nearmaximum flight distance of 90-95 m was attained over a wide range of the opposite field when the bat head was not lowered substantially more than the grip-end. However, when the bat head was lowered substantially more than the grip-end, the flight distance attainable with the given impact condition decreased as the vertical bat angle increased, and the range of horizontal bat angle within which a great flight distance was attainable became narrower. The latter results suggest that a batsman needs to acquire a sophisticated technique with a greater precision of ball impact to hit a ball toward a given horizontal angle in the opposite field if the bat swing is characterized as lowering of the bat head to a large extent.
1 0 0 0 OA 運動持続距離の分散が心肺持久性及び血液脂質に及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 戎 利光
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.1, pp.37-43, 1985-06-01 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
本研究の目的は,運動持続距離を二等分あるいは三等分と分散して走運動を行った場合に,心肺持久性及び血液脂質に及ぼす身体的効果が,分散しないで一度に全距離を走った場合の効果と異なるか否かを明らかにすることである。53名の健康な男子学生をA群からD群の4群に分類した。A群は全距離を一度に走り,B群は半分の距離を1日2度(朝,夕)に分散して走り,C群は3分1の距離を1日3度(朝,昼,夕)に分散して走った。D群は対照群であり,本研究期間中特別な身体運動をしなかった。D群を除く全被験者は,週に3日間,各個人の最高心拍数の80%を維持して10週間に渡り,屋内のタータントラックを走った。そして, このトレーニング期間前後の最大酸素摂取量,最高心拍数,脂肪百分率(水中体重測定による),1.5マイル走の記録,総トリグリセライド,総コレステロール,高比重リボ蛋白コレステロール,低比重リボ蛋白コレステロール,超低比重リボ蛋白コレステロールを,各群ごどに比較,検討した。その結果,次のような結論を得た。分散した最短走距離が心肺持久性や血液脂質に影響を及ぼすような距離であれば,同一の運動強度及び頻度で同一距離を走る限り,その走距離を二等分あるいは三等分と分散しても総消費エネルギーは同一であり,心肺持久性や血液脂質に及ぼす影響に差はない。本研究は,米国ブリガムヤング大学及び米国デザレットジム財団からの研究交付金を受けた。
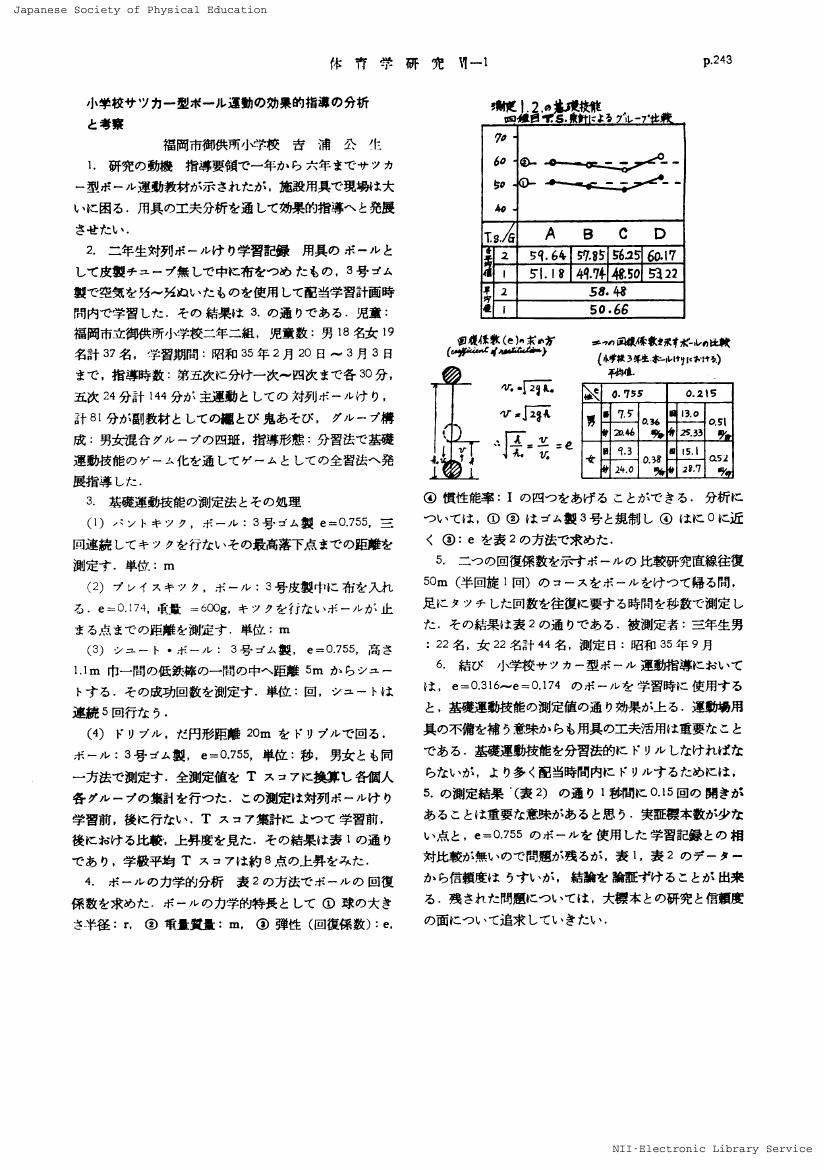
1 0 0 0 OA 小学校サツカー型ボール運動の効果的指導の分析と考察
- 著者
- 吉浦 公生
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, no.1, pp.243, 1961-09-01 (Released:2016-12-31)
- 著者
- 鈴木 秀人
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2021
1 0 0 0 OA エリートサッカーゴールキーパーにおける異なるシュートパタンに対する事前動作の特性
- 著者
- 松倉 啓太 平嶋 裕輔
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, pp.1049-1067, 2020 (Released:2020-12-24)
- 参考文献数
- 21
The aim of this study was to shed light on preparatory sequences performed by elite goalkeepers for defense against shots in response to variations in the position from where a shot at goal is taken, and in the number of touches ahead of the shot. The samples were extracted from videos of shots in all 64 matches of the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia. First, to analyze the characteristics of shots in elite games, data on shots from different areas and after various numbers of touches were studied. Then, to analyze the preparatory sequences taken by goalkeepers to defend against those shots, the shots were classified into 6 groups based on ‘the presence or absence of a specific prejump’, ‘a change in the distance between the feet during the preparation period’, and ‘whether the goalkeeper was still in a moving position or had completed the move’. The results of this analysis of the characteristics of the elite game made it possible to divide the positions from where shots were taken in 2 types, based on the probability of the shot being on target and the probability that a goal would be scored. In addition, it was shown that when one-touch shots were on target, it was difficult for goalkeepers to defend against them. Next, as an overall trend, the most frequent preparatory sequence performed by goalkeepers was to prepare for a shot with a slight jump in order to widen the distance between the feet after they had finished moving into position. In addition, a breakdown of the preparatory sequences for various numbers of touches ahead of the shot revealed that – for onetouch shots – a proportion of goalkeepers moved into position until immediately before the shot was taken. Overall, from these analyses, it was concluded that elite goalkeepers must engage in different preparatory sequences depending on the circumstances of the shot.
- 著者
- 小野 雄大 友添 秀則
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.14043, (Released:2014-09-29)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 6 3
The Young Men's Association (YMA) was an education institute that provided business programmes and further education for young men. It aimed to train both mind and body, and valued sporting activities. However, there has been little knowledge about the state of sporting activities provided by the YMA. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the state of the sporting activities at Fuchu YMA in Tokyo. For this purpose, the study used Fuchu-sport bulletins which specialized in such sporting programmes during the Taisho era and pre-war Showa era. The main findings are summarized as follows. 1) Fuchu-sport was modeled on a specialized magazine, Asahi Sports. The publication of Fuchu-sport was an indication of the high interest in sport during the Taisho era. 2) After the Ministry of Home Affairs and the Ministry of Education announced their first and second instructions, the Tokyo government independently ran conferences aimed at the development of sport and physical education at Tokyo YMA. Accordingly, Tokyo was one step ahead of other areas in Japan in setting up athletic clubs for the YMA. 3) The organization of kyogi-bu was supported mainly by Fuchu YMA, but also funded by the local authority and by Fuchu ordinary and higher elementary school, the latter being also committed to conducting actual sporting activities. 4) University students were recruited as coaches, and thereby the kyogi-bu provided successful programmes that led to an improvement in competitive level. However, this improvement resulted in elimination of some of the members. 5) The remarkable successes of the kyogi-bu and its development in Fuchu were accomplished by collaborating with the local educational institutions. The relationship between the YMA and school athletic clubs was another significant factor in running the sporting programmes. The present study has provided deeper insights into the nature of sporting activities held by the YMA during the Taisho era and pre-war Showa era.
1 0 0 0 OA 準臨床的な一次性運動依存における心理的要因
- 著者
- 西 泰信 岩井 圭司
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.11110, (Released:2012-07-11)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The purpose of this study was to identify psychological factors that contribute to the development of sub-clinical primary exercise dependence among Japanese exercisers. Most studies of exercise dependence follow a top-down, quantitative, hypothesis-verification approach. The present study, in contrast, used a qualitative method, the Grounded Theory Approach. Dialogue data were collected from 14 exercisers who were evaluated for sub-clinical primary exercise dependence in semi-structured interviews and analyzed by classifying them into categories. Through these steps, seven types as psychological factors were identified as leading to sub-clinical primary exercise dependence among Japanese exercisers: dependence, obsessive-compulsiveness, conflict avoidance, maintenance of a positive self-concept, perceieved benefit of exercise, limited stress-coping resource, and typical increase in exercise volume. It was also found that dependence and obsessive-compulsiveness play a crucial and direct role in the development of sub-clinical primary exercise dependence, and that conflict avoidance and maintenance of a positive self-concept can precipitate obsessive-compulsiveness. Finally, a perceived benefit of exercise was shown to be an integral component of dependence.
- 著者
- 満下 健太 村越 真
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19048, (Released:2020-01-10)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 1940-1944 年の占領期パリにおける柔道の確立: フランス柔術クラブの活動を中心に
- 著者
- 星野 映
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育・スポーツ・健康学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.18055, (Released:2019-05-10)
- 参考文献数
- 67
From 1940 to 1944, Paris was occupied by the German army. The “Vichy” government began to reform sports activities for French citizens, and under the new Vichy policy, many sports saw an expansion of popularity. The expansion of judo in France during this period was particularly dramatic. This article examines how judo was practiced in German-occupied Paris, and how it acquired the status of a sport in France, with reference to the activities of the Jiu-Jitsu Club de France and its historical context in Paris at that time. In occupied Paris, the Jiu-Jitsu Club and its judoka, especially Paul Bonét-Maury, president of the club, and Mikinosuke Kawaishi, who provided technical guidance, promoted judo as a sport. In the first half of the Occupation, the club held low-key public demonstrations. Also, practitioners in clubs were trained on the basis of teaching methods devised by Kawaishi, which included aspects such as the color belt system, and the establishment of expensive membership fees despite the Occupation situation. As a result, many intellectual professionals and industrial capitalists with economic resources played a principal role as judoka. Furthermore, by encouraging students to open new clubs, the number of judoka practicing Kawaishi judo increased. These factors remained characteristic of French judo after the Second World War. In the latter half of the Occupation Period, the Jiu-Jitsu Club de France joined the French Wrestling Federation, so that judo became better known publicly, and in late May 1943, the First French Judo Championship was held. The Championship was held continuously in subsequent years, and received recognition of being “worthy to be aligned with other sports”. The German army was not directly involved with judo in Paris, but the fact that the Jiu-Jitsu Club de France expanded its activities while adapting to the circumstances of the Occupation encouraged the official recognition of judo in Paris.