- 著者
- 大高 恵莉 大高 洋平 森田 光生 横山 明正 近藤 隆春 里宇 明元
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- The Japanese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine (ISSN:18813526)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.51, no.8-9, pp.565-573, 2014 (Released:2014-09-06)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1 5
目的:システム理論に基づくバランス機能評価,Balance Evaluation Systems Test(BESTest)の日本語版を作成し,その妥当性を検証した.方法:翻訳と逆翻訳を経て日本語版BESTestを作成した.バランス障害群20 名及び健常群5 名(平均年齢71.2±13 歳,66.0±1.2 歳)に日本語版BESTest,Berg Balance Scale(BBS),国際版転倒関連自己効力感尺度(FES-I),Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale(ABC Scale)を実施し,Spearmanの順位相関係数を求めた.またBBSと日本語版BESTestによるバランス障害群と健常群との判別能をROC解析により比較した.結果:日本語版BESTestはBBS(r=0.84),FES-I(r=-0.61),ABC Scale(r=0.63)と有意な相関を認めた(p<0.01).BBS及び日本語版BESTestのROC曲線下面積(AUC)は0.75,0.94(p<0.05)であり有意差を認めた.結論:日本語版BESTestは既存の評価法との妥当性を示し,BBSよりも軽度のバランス障害の検出に優れると考えられた.
8 0 0 0 OA 高齢者の転倒予防の現状と課題
- 著者
- 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 日本転倒予防学会
- 雑誌
- 日本転倒予防学会誌 (ISSN:21885702)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.3, pp.11-20, 2015-03-10 (Released:2015-07-07)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 13
寿命の延伸とともに,転倒予防はその重要性を増している。高齢者の3人に1人は1年間に一度以上の転倒を経験するとされ,転倒による不慮の事故は,窒息に続き第2位であり交通事故を上回っている。また転倒は,大腿骨近位部骨折をはじめとした高齢者の骨折の主原因であり,要介護の主要な原因の1つでもある。転倒のリスク因子には,本人の特性に関連する内因性リスクと環境などの外因性リスクがある。内因性リスクとしては,バランス障害,筋力低下,視力障害,薬剤などさまざまなものが知られている。転倒予防に最も有効な介入は運動である。運動はグループでも,在宅で個別に指導を行う場合でも有効であり,バランス訓練の要素など複数の訓練要素が含まれているものに効果がある。その他,家屋評価や改修,精神作動薬漸減,頸動脈洞過敏症に対するペースメーカー挿入,初回の白内障手術,家庭医に対する内服処方の指導,包括的なリスク評価に基づいたリスクの修正,などのアプローチで転倒予防効果が報告されている。また,低ビタミンD血症に対するビタミンD補充による転倒予防効果も知られているが,さらなる検証が必要である。今後,エビデンスに基づき実現可能性,継続可能性の高いプログラムを地域の中で実践していくことが望まれる。
4 0 0 0 OA 延髄外側梗塞患者における自覚的視性垂直位と静止立位バランスおよび歩行非対称性の関連
- 著者
- 荒井 一樹 松浦 大輔 杉田 翔 大須 理英子 近藤 国嗣 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本理学療法学会連合
- 雑誌
- 理学療法学 (ISSN:02893770)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.11245, (Released:2017-07-19)
- 参考文献数
- 17
【目的】延髄外側梗塞患者において自覚的視性垂直位(以下,SVV)と静止立位バランス,歩行非対称性の関係を検討する。【方法】Body lateropulsion(BL)を呈する延髄外側梗塞患者9 名において,SVV 値と立位重心動揺計の総軌跡長,矩形面積,足圧中心左右偏位および加速度計より算出した歩行非対称性との関係をSpearman の相関係数を用いて検討した。【結果】SVV 値は平均7.4(SD:9.5)度であった。SVV 値と開眼足圧中心偏位とは相関しなかったが,閉眼足圧中心偏位と相関を認めた(r = 0.75, P < 0.05)。また,SVV 値の絶対値は歩行非対称性と有意な相関を認めた(r = –0.78, P < 0.05)。【結語】BL を呈する延髄外側梗塞患者において,SVV 偏位は閉眼の静止立位バランスと歩行非対称性と関連した。その因果関係については今後の検証が必要である。
- 著者
- 松永 玄 山口 智史 鈴木 研 近藤 国嗣 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 日本理学療法士学会
- 雑誌
- 理学療法学 (ISSN:02893770)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.11163, (Released:2016-06-04)
- 参考文献数
- 40
【目的】通所リハビリテーションを2 年間利用した脳卒中者の歩行能力と下肢筋力の変化を検討する。【方法】脳卒中者126 名(平均年齢64 歳)の利用開始時,利用後3,6,12,24 ヵ月の歩行能力と下肢筋力を,開始時の歩行速度によりHousehold 群(0.4 m/s 未満),Limited 群(0.4 m/s ~0.8 m/s),Full群(0.8 m/s 以上)に分類した。【結果】Household 群の歩行速度は,開始時と比較し,6 ヵ月以降で有意に向上し,麻痺側筋力は利用後12,24 ヵ月で有意な増加を認めた。Limited 群の歩行速度は,6 ヵ月以降で有意に向上し,麻痺側筋力は24 ヵ月で有意な増加を認めた。Full 群は有意な変化を認めなかった。【結語】2 年間の通所リハビリテーション利用により,生活期の脳卒中者においても歩行速度と下肢筋力は改善・維持することが示され,その傾向は開始時の歩行能力が低い群で特に得られることが示唆された。
4 0 0 0 OA 千葉県の理学療法士における診療ガイドラインの利用および重要性の認識に関連する因子
- 著者
- 藤本 修平 大高 洋平 高杉 潤 小向 佳奈子 中山 健夫
- 出版者
- 日本理学療法士学会
- 雑誌
- 理学療法学 (ISSN:02893770)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.11351, (Released:2017-11-10)
- 参考文献数
- 27
【目的】理学療法士(以下,PT)の診療ガイドラインの利用,重要度の認識とエビデンスに基づいた実践(以下,EBP)への態度,知識,行動との関連性を明らかにすることとした。【方法】対象は千葉県のPT1,000 名としEBP や診療ガイドラインの利用,重要性の認識の項目を含む無記名自記式質問紙を用いた郵送調査を行った。統計解析は診療ガイドラインの利用,重要性の認識に関連するEBP の関連項目を明らかにするために多重ロジスティック回帰分析を行った。【結果】診療ガイドラインの利用,診療ガイドラインの重要性の認識と関連が強いものは「EBP に関する必要な知識や技術を学びたいと思いますか」(OR = 10.32, 95%CI: 1.82–197.16) であった。【結論】千葉県のPT において診療ガイドラインの利用は十分ではなく診療ガイドラインの利用や重要性の認識に関連する要因は,EBP の必要性の認識とEBP を行ううえで必要な行動であった。
4 0 0 0 OA エビデンスからみた転倒予防プログラムの効果
- 著者
- 大高 洋平 里宇 明元 宇沢 充圭 千野 直一
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.6, pp.374-388, 2003-06-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 72
- 被引用文献数
- 9 8
Fall prevention is one of the major issues in health care in our aging society. The aim of this review is to provide useful information for researchers and practitioners who plan to start fall prevention programs for elderly persons with various risk levels and in different settings. Fifty-three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and several meta-analyses retrieved with extensive literature search formed the basis for this review. Available evidence suggests that several preventive strategies have been proven beneficial in fall prevention. For the community-dwelling elderly, two RCTs and one meta-analysis demonstrated that an individually tailored home exercise program provided by nurses or physical therapists could reduce the rate of falls and injuries. One RCT suggested that Tai Chi Chuan might have a high potential to reduce falls. Two large RCTs indicated that programs including group exercise classes could also reduce the number of fallers. For people with known risk factors living in the community, three RCTs showed that home visits to address multiple risk factor modification were an effective way to reduce falls. One RCT with a relatively small sample showed that psychotropic withdrawal reduced falls in elderly persons taking psychotropic medication. A subgroup analysis of one RCT showed that home hazard reduction at hospital discharge reduced subsequent falls in patients with a past history of falls. However, more evidence is needed to prove its effectiveness, because this effect was also observed outside of homes. Dual chamber pacemaker for elderly persons with hypersensitive carotid sinus, who were detected when investigated for undiagnosed falls, markedly reduced subsequent falls with or without syncope. In institutional settings, two RCTs showed that comprehensive risk assessment and modification reduced the rate of falls and fractures or the number of recurrent fallers. Three RCTs performed in hospital settings failed to show any effectiveness. However, a meta-analysis of 3 controlled trials and 7 cohort studies with a historical control suggested that fall prevention program in hospitals could be promising. There are some methodological problems in fall prevention research such as the definition, measures, and monitoring method of falls, inadequate sample size and a short follow-up period. In the future, we need research based on strong and comprehensive methodological designs.
4 0 0 0 OA エビデンスからみた転倒予防プログラムの効果 : 1. 狭義の転倒予防
- 著者
- 大高 洋平 里宇 明元 宇沢 充圭 千野 直一
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.6, pp.374-388, 2003-06-18
- 被引用文献数
- 11
Fall prevention is one of the major issues in health care in our aging society. The aim of this review is to provide useful information for researchers and practitioners who plan to start fall prevention programs for elderly persons with various risk levels and in different settings. Fifty-three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and several metaanalyses retrieved with extensive literature search formed the basis for this review. Available evidence suggests that several preventive strategies have been proven beneficial in fall prevention. For the community-dwelling elderly, two RCTs and one meta-analysis demonstrated that an individually tailored home exercise program provided by nurses or physical therapists could reduce the rate of falls and injuries. One RCT suggested that Tai Chi Chuan might have a high potential to reduce falls. Two large RCTs indicated that programs including group exercise classes could also reduce the number of fallers. For people with known risk factors living in the community, three RCTs showed that home visits to address multiple risk factor modification were an effective way to reduce falls. One RCT with a relatively small sample showed that psychotropic withdrawal redeced falls in elderly persons taking psyshotropic medication. A subgroup analysis of one RCT showed that home hazard reduction at hospital discharge reduced subsequent falls in patients with a past history of falls. However, more evidence is needed to prove its effectiveness, because this effect was also observed outoside of homes. Dual chamber pacemaker for elderly persons with hypersensitive carotid sinus, who were detected when investigated for undiagnosed falls, markedly redeced subsequent falls with or without syncope. In institutional settings, two RCTs showed that comprehensive risk assessment and modification redeced the rate of falls and fractures or the number of recurrent fallers. Three RCTs performed in hospital settings failed to show any effectiveness. However, a meta-analysis of 3 controlled trials and 7 cohort studies with a historical control suggested that fall prevention program in hospitals could be promising. There are some methodological problems in fall prevention research such as the definition, measures, and monitoring method of falls, inadequate sample size and a short follow-up period. In the future, we need research based on strong and comprehensive methodological designs.
- 著者
- 大高 洋平 里宇 明元 宇沢 充圭 千野 直一
- 出版者
- 社団法人日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 : 日本リハビリテーション医学会誌 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.6, pp.389-397, 2003-06-18
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The cecond part of the review discusses some inportant issues associated with fall prevention and future perspectives on fall related research. Currently, many kinds of interventions ore availavle for the treatment of patients suffering from osteoporosis, i.e. nutritional supports, medications acting on bone metabolism and exercise. However, a series of meta-analyses showed that only alendronate and risedronate have been proven to prevent non-vertebral tractures in persons with osteoporosis. Anaerobic and weight bearing exercises are known to have a positive effect on the bone mineral density of the spine. There is, however, no reliable data for fracture prevention with exercise alone. Also, the synergistic effect of a combination of these interventions has noto been clearly proven. Although there is evidence that the use of hip protectors in institutional settings reduces the rate of hip fractures, this approach faces the problem of patient acceptance and compliance. Psychosocial problems related to falls such as fear of falling, post-fall syndrone and cost-effectiveness of the prevention programs are becoming increasingly important in elderly health care, but little evidence of such has been reported in the literature. In future perspectives on fall relared research, a theory-based approach for fall prevention needs to be included to explore more effective interventions. We must also consider the double-edged effects of interventions that may increase certain fall risk factors while reducing another. Especially, the relation between activities and incidence of falls is important to consider, because increased activity itself may increase the change of falls. When applying exercise or rehabilitative approaches, the interaction between falls, activity levels, frailty, and injury must be studied much more carefully. In addition, one has to always think about what is the true aim of a program, because the aim of fall prevention goes beyond preventing falls. Although some research has so far been conducted in Europe and the U.S.A. by researchers and practitioners in various fields, the quantity and quality of fall prevention research are still lacking and the available data is therefore insufficient to suggest appropriate decision-making in clinical practice. Especially in Japan, there have been only a few RCTs to determine the effectiveness of fall prevention programs. Because there are many differences in the characteristics of our native population and health care systems vs those of Europe and the U.S.A., it is a critical issue for us to establishi fall prevention programs suited to Japanese population and health care system.
要旨 【目的】リハビリテーション分野において,経験に基づく臨床思考はよく用いられる.しかし,臨床思考が経験によってどのように変化するかについての検討はない.本研究では,装具を選定する際の理学療法士の臨床思考を明らかにし,経験年数による相違について検討した.【対象と方法】質的調査と量的調査を混合して行うミクストメソッドを用いた.まず,構造化面接により,装具選定の際にどのような視点や評価指標を参考にしているかについて,理学療法士22名を対象に調査した.その結果より,主要な視点と用いる評価についての質問紙を作成した.次に,作成した質問紙を用いて量的調査を理学療法士40名に実施した.解析は,視点ごとに選択している評価の割合を集計し,経験年数による相違を検討した.また,視点と評価の関連を視覚的に検討するため,コレスポンデンス分析を実施した.【結果】質的調査から,視点として装具の必要性,角度設定など6項目が,評価として可動域,筋緊張など14項目が抽出された.量的調査の結果,装具の必要性における予後の評価や,角度設定における麻痺側の支持性の評価について,経験年数によって相違があった.コレスポンデンス分析の結果,経験年数4年目以上のほうが3年目以下よりも,評価と視点が集約する項目が明確であった.【結語】理学療法士は多様な視点や評価から装具を選定しており,それらは経験年数によって相違があることが示唆された.
3 0 0 0 OA 学会誌リニューアルと英文誌創刊について
- 著者
- 水間 正澄 道免 和久 渡邉 修 佐々木 信幸 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- The Japanese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine (ISSN:18813526)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.12, pp.743-750, 2015 (Released:2015-12-17)
3 0 0 0 OA エビデンスからみた転倒予防プログラムの効果
- 著者
- 大高 洋平 里宇 明元 宇沢 充圭 千野 直一
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:0034351X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.6, pp.389-397, 2003-06-18 (Released:2009-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 2 3
The second part of the review discusses some important issues associated with fall prevention and future perspectives on fall related research. Currently, many kinds of interventions are available for the treatment of patients suffering from osteoporosis, i. e. nutritional supports, medications acting on bone metabolism and exercise. However, a series of meta-analyses showed that only alendronate and risedronate have been proven to prevent non-vertebral fractures in persons with osteoporosis. Anaerobic and weight bearing exercises are known to have a positive effect on the bone mineral density of the spine. There is, however, no reliable data for fracture prevention with exercise alone. Also, the synergistic effect of a combination of these interventions has not been clearly proven. Although there is evidence that the use of hip protectors in institutional settings reduces the rate of hip fractures, this approach faces the problem of patient acceptance and compliance. Psychosocial problems related to falls such as fear of falling, post-fall syndrome and cost-effectiveness of the prevention programs are becoming increasingly important in elderly health care, but little evidence of such has been reported in the literature. In future perspectives on fall relared research, a theory-based approach for fall prevention needs to be included to explore more effective interventions. We must also consider the double-edged effects of interventions that may increase certain fall risk factors while reducing another. Especially, the relation between activities and incidence of falls is important to consider, because increased activity itself may increase the chance of falls. When applying exercise or rehabilitative approaches, the interaction between falls, activity levels, frailty, and injury must be studied much more carefully. In addition, one has to always think about what is the true aim of a program, because the aim of fall prevention goes beyond preventing falls. Although some research has so far been conducted in Europe and the U. S. A. by researchers and practitioners in various fields, the quantity and quality of fall prevention research are still lacking and the available data is therefore insufficient to suggest appropriate decision-making in clinical practice. Especially in Japan, there have been only a few RCTs to determine the effectiveness of fall prevention programs. Because there are many differences in the characteristics of our native population and health care systems vs those of Europe and the U. S. A., it is a critical issue for us to establish fall prevention programs suited to Japanese population and health care system.
2 0 0 0 急性期重度嚥下障害患者に対する完全側臥位導入による帰結の変化
- 著者
- 長尾 恭史 小林 靖 大高 洋平 齊藤 輝海 大林 修文 大隅 縁里子 水谷 佳子 伊藤 洋平 田積 匡平 西嶋 久美子 森 俊明
- 出版者
- 医学書院
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.567-572, 2020-06-10
要旨 【背景】入院の原疾患が脳卒中以外による急性期重度摂食嚥下障害患者に対する,完全側臥位の導入による帰結の変化について検証した.【対象】入院前Eating Status Scale(ESS)4以上であったが,入院後Dysphagia Severity scale(DSS)2以下の嚥下障害を認め嚥下内視鏡を実施した,原疾患が脳卒中以外の58名.【方法】評価姿勢として,完全側臥位を選択肢の1つとして導入した2016年4〜9月の37名(男性28名,平均年齢81.3±12.9歳)を側臥位導入群,導入前の2015年4〜9月の21名(男性15名,平均年齢79.8±10.9歳)を未導入群とし,両群間で帰結を比較した.【結果】退院時ESS 3以上の患者は側臥位導入群18名(48.6%),未導入群は4名(19.0%)であった(p=0.026).院内肺炎合併数は側臥位導入群6名(16.2%),未導入群8名(38.1%)であった(p=0.061).また,側臥位導入群は退院時ESS 3以上に関連する独立した因子であった(オッズ比6.62,95%信頼区間1.24〜35.25,p=0.027).【結語】完全側臥位は急性期摂食嚥下障害の治療戦略として効果的である可能性が示唆された.
2 0 0 0 OA 誤嚥性肺炎患者における早期経口摂取の検討
- 著者
- 長尾 恭史 小林 靖 大高 洋平 篠田 純治 小澤 竜三 水谷 佳子 田積 匡平 西嶋 久美子 長尾 徹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本静脈経腸栄養学会
- 雑誌
- 日本静脈経腸栄養学会雑誌 (ISSN:21890161)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.5, pp.1133-1138, 2018 (Released:2018-12-20)
- 参考文献数
- 27
【目的】誤嚥性肺炎患者に対して多職種協働での包括的摂食嚥下訓練を入院初期から行い食事開始早期化の効果を検証した。【対象および方法】誤嚥性肺炎にて入院後、嚥下訓練処方の時点で絶食であった65歳以上の患者139名を対象とした。2013年9月から翌年2月までの早期介入を行った87名(86.5歳±7.0歳)を早期群、2012年9月から翌年2月までの52名(85.6歳±7.2歳)を対照群とし、両群間で帰結を比較した。【結果】入院より食事開始までの日数(早期群3日/対照群5日・中央値)、抗菌薬継続日数(8日/11日・中央値)、院内肺炎再発率(6.9%/19.2%)は早期群が有意に少なかった。また、入院より食事開始までの日数は、抗菌薬の使用短縮に関連する独立した関連因子であった(オッズ比0.96、95%信頼区間0.94-0.99、P=0.012)。【結論】誤嚥性肺炎患者に対する入院早期の食事開始は治療期間を短縮し、さらには院内肺炎を軽減する可能性が示唆された。
1 0 0 0 OA 脳卒中患者のリハビリテーションへのモチベーションに関するシステマティックレビュー
- 著者
- 吉田 太樹 伊藤 大将 渡邉 翔太 大須 理英子 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本作業療法士協会
- 雑誌
- 作業療法 (ISSN:02894920)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.468-477, 2020-08-15 (Released:2020-08-15)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 2
要旨:脳卒中患者におけるリハビリテーション(以下,リハ)のモチベーションに関する知見をシステマティックレビューを用いて整理した.PubMed,CENTRAL,医中誌Webのデータベースから1,930文献が検索され,適格基準・除外基準を満たした13論文が抽出された.脳卒中患者のモチベーション評価には,リハのモチベーションに特化していない尺度や医療者による観察評価が用いられていた.モチベーションとリハの相互作用については,モチベーションに影響を与える要因,モチベーションが機能や活動に及ぼす影響について報告されていたが,報告の質・量共に不十分であった.今後は脳卒中患者のリハに対するモチベーションの概念形成や評価尺度開発が必要である.
1 0 0 0 OA リハビリテーション医療における転倒予防
- 著者
- 北村 新 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- The Japanese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine (ISSN:18813526)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.3, pp.269-274, 2021-03-18 (Released:2021-07-03)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1
リハビリテーション医療の過程では,活動量の増大と安全は常にトレードオフの関係にあり,いかに転倒を予防しながら患者の活動性を高めるかは重要な課題である.医療機関において,双方のバランスを保ちながら患者を支援していくうえでは,センサーやアセスメントツールを用いて未然に転倒や外傷を防ぐ「ブレーキ」の視点と,患者個人に起因する内因性リスクを調整しながら病棟単位で積極的に活動を促していく「アクセル」の視点が求められる.一方で,従来の医療安全対策の効果に関するエビデンスは少なく,機会費用を見直す必要があることも指摘されている.今後は,最新の科学技術を導入することで,より効率的な転倒予防の実現が期待される.
1 0 0 0 OA 臨床における定性的歩行分析
- 著者
- 谷川 広樹 土山 和大 山田 純也 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- The Japanese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine (ISSN:18813526)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.2, pp.135-142, 2021-02-18 (Released:2021-04-14)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 3
観察による歩行分析は全体像が捉えやすくパターン認識に優れ,簡便で低コストである.また即時性に優れ,場所や条件を選ばない評価が可能である.観察による関節角度判定や時間因子判定は正確性に欠けるが,異常歩行パターンを同定・分類し,重症度の相対評価としては有用である.定性的評価と定期的な定量的歩行分析を併用することで,臨床に役立つ歩行分析ができると考える.精度の高い定性的歩行分析をするためには,正常歩行を理解し,ビデオカメラを活用するなどの工夫をするとともに,観察による歩行分析結果と定量的な歩行分析結果を照合させる,歩行障害の典型例の動画を観察することが有効な方法である.
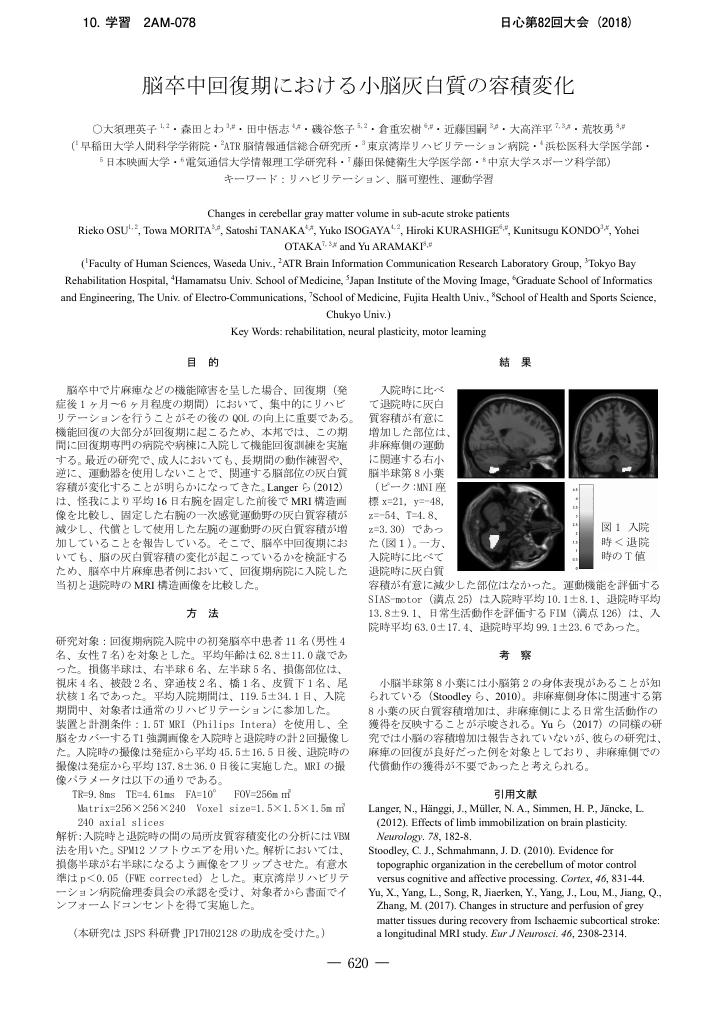
1 0 0 0 OA 脳卒中回復期における小脳灰白質の容積変化
- 著者
- 大須 理英子 森田 とわ 田中 悟志 磯谷 悠子 倉重 宏樹 近藤 国嗣 大高 洋平 荒牧 勇
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本心理学会
- 雑誌
- 日本心理学会大会発表論文集 日本心理学会第82回大会 (ISSN:24337609)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2AM-078, 2018-09-25 (Released:2019-07-19)
1 0 0 0 地域在住高齢者の転倒予防
- 著者
- 大高 洋平
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本リハビリテーション医学会
- 雑誌
- リハビリテーション医学 (ISSN:18813526)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.11, pp.910-914, 2018
<p>高齢者の転倒予防について,系統的レビューでは,運動や転倒リスクの評価と修正などの介入に転倒減少効果があるとされる.しかし,これらは厳しく統制された条件や対象者の選択過程を経て得られた知見であり,実際に地域社会の中で転倒予防プログラムを実施するにあたっては,実現可能性と受け入れ状況が長期間にわたり確認される必要がある.群馬県館林市の高齢者サロンにおいて実施した転倒予防の活動の検証により,転倒リスク評価と個別のフィードバック,転倒予防講義を含むプログラムは,地域社会構造の中で実施することで転倒を減少させ,長期的な地域の受け入れがよく,適切なプログラムであることが示唆された.</p>
要旨:〔目的〕Balance Evaluation Systems Test(BESTest)を用いて地域在住中高年者のバランス機能を評価し,加齢による変化,転倒歴との関連について,検討を行った.〔対象〕市民祭りの健康ブースに参加した地域健常中高年者183名(平均67.1±6.1歳)を解析対象とした.〔方法〕中年群,前期高齢者群,後期高齢者群の3群間および転倒歴を有する群と有さない群の2群間において,総得点率およびセクションごとの得点率を比較した.〔結果〕全得点率では,中年群と前期または後期高齢者群それぞれの間において有意差が認められた.また,セクションごとの解析では,セクションⅢ(姿勢変化-予測的姿勢制御)とセクションⅥ(歩行安定性)においてどの年代間においても有意差が認められた.転倒歴の有無では総得点において群間に有意差が認められ,セクションごとの比較ではセクションⅢにおいて有意差が認められた.〔結語〕地域在住中高年者に対しBESTestを行い,加齢および転倒歴と関連するバランス要素を明らかにした.その結果,加齢および転倒,双方に関連するバランス要素として,予測的姿勢制御が抽出された.
1 0 0 0 OA 経頭蓋直流電気刺激による聴覚言語性短期記憶の増強作用
- 著者
- 數田 俊成 武田 湖太郎 田中 悟志 小田柿 誠二 大須 理英子 大高 洋平 近藤 国嗣 里宇 明元
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本臨床神経生理学会
- 雑誌
- 臨床神経生理学 (ISSN:13457101)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.1, pp.18-22, 2013-02-01 (Released:2015-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 16
経頭蓋直流電気刺激 (transcranial direct current stimulation: tDCS) は頭蓋上に配置した電極から微弱な電流を与える刺激法で, 脳機能を促進あるいは抑制すると言われている。本研究は15単語の記銘・再生を繰り返すRey’s Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) を用い, tDCSが聴覚言語性記憶に及ぼす影響について検証した。健常者12名 (21–32歳) を対象とし, RAVLTの記銘2回目からtDCSを用いて左頭頂葉下部, 後部側頭葉を刺激した (刺激強度: 2 mA) 。陽極刺激条件では10分間, 偽刺激条件では15秒間刺激を与えた。RAVLTの2回目再生数は, 陽極刺激条件が偽刺激条件より有意に多かった。健常者においてtDCS陽極刺激により聴覚言語性記憶の有意な増強が認められた。tDCSは記憶機能賦活に役立つ可能性がある。